Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
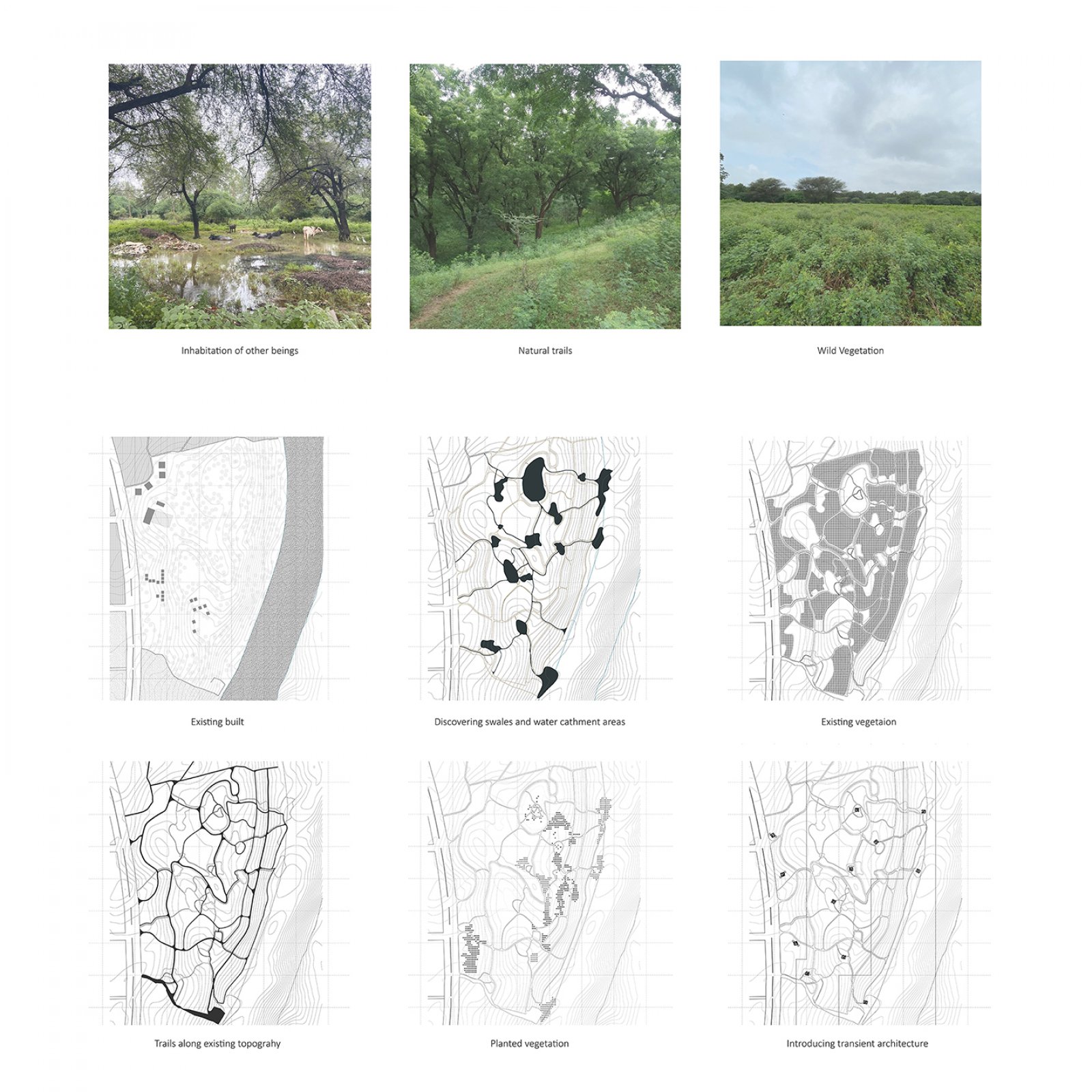
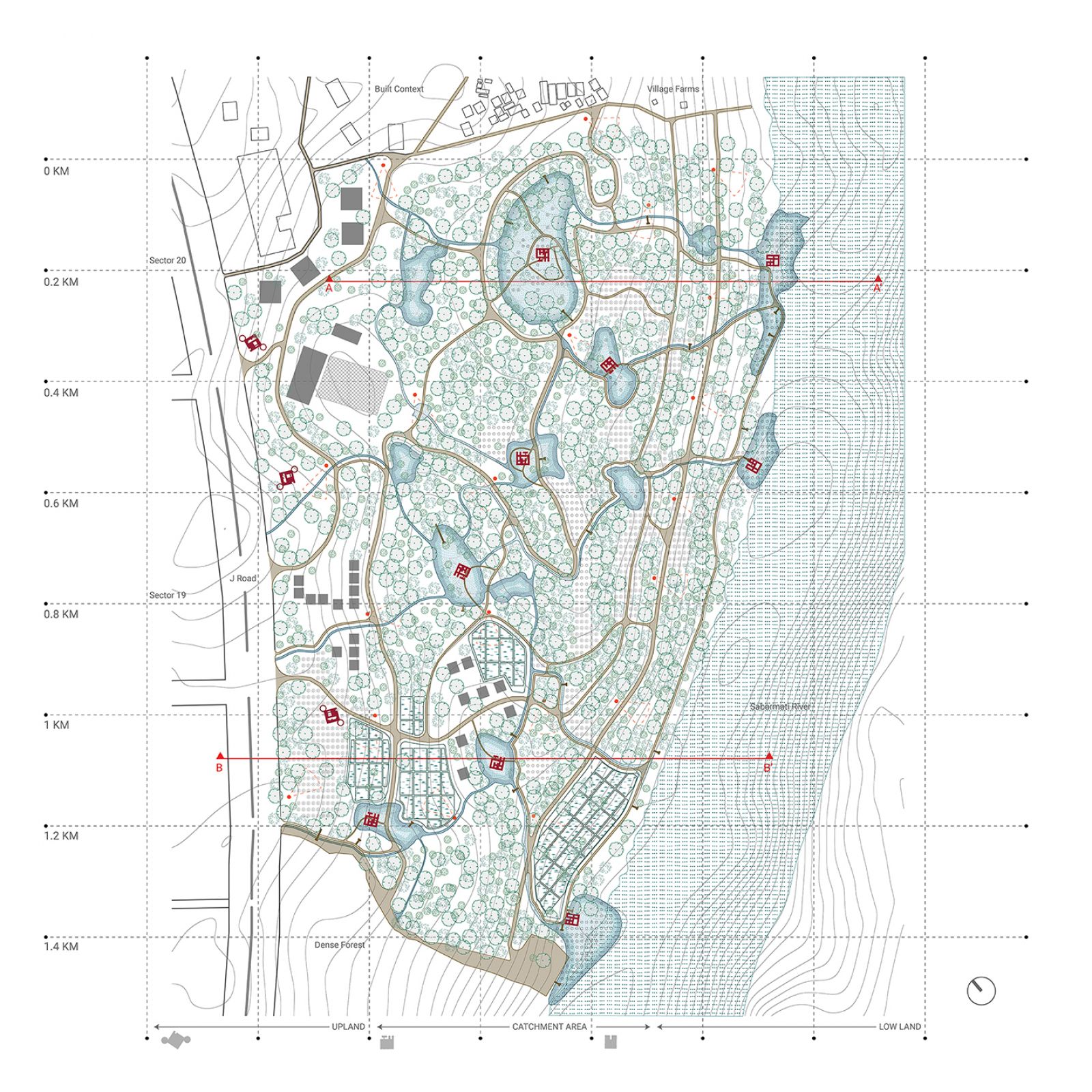
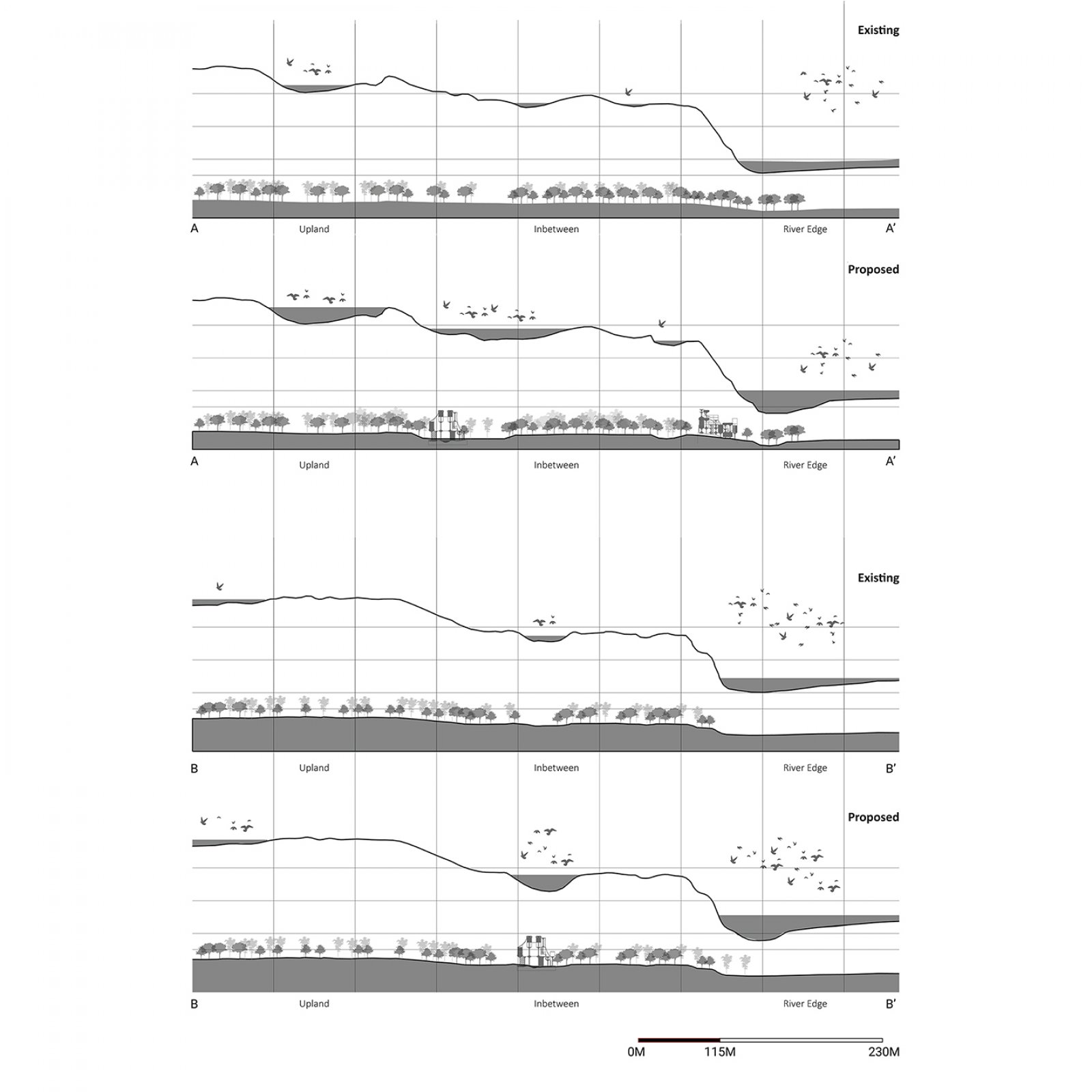
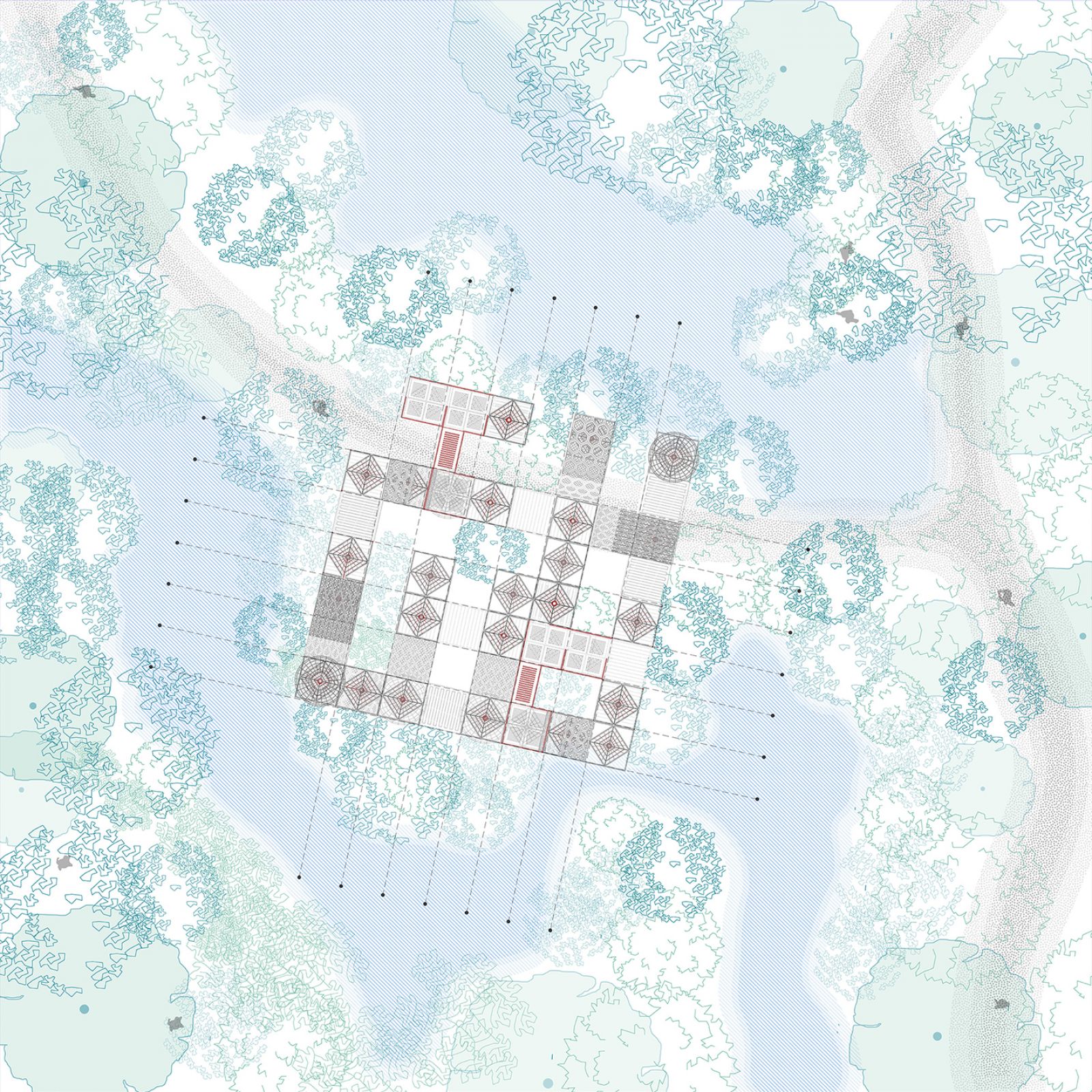
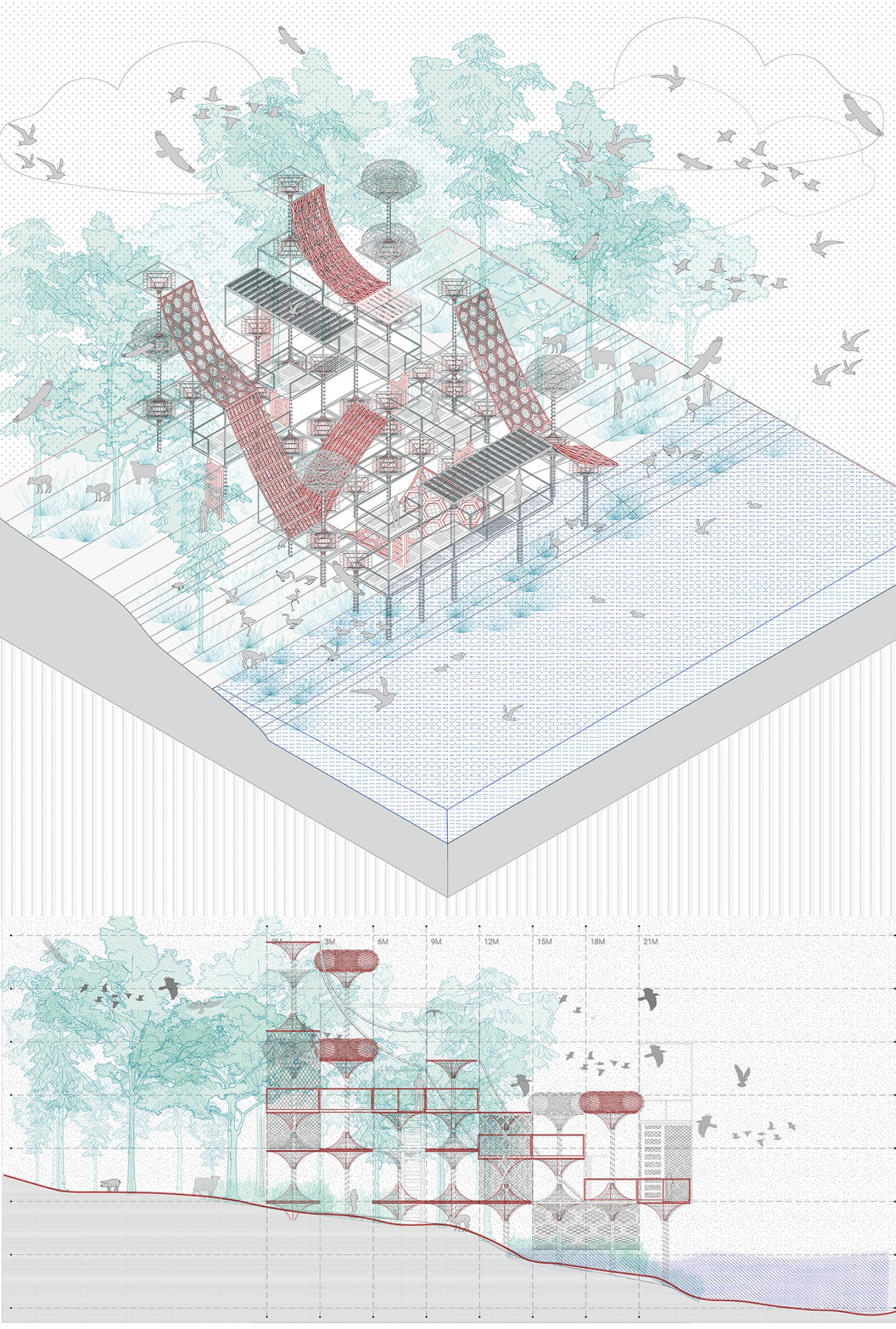
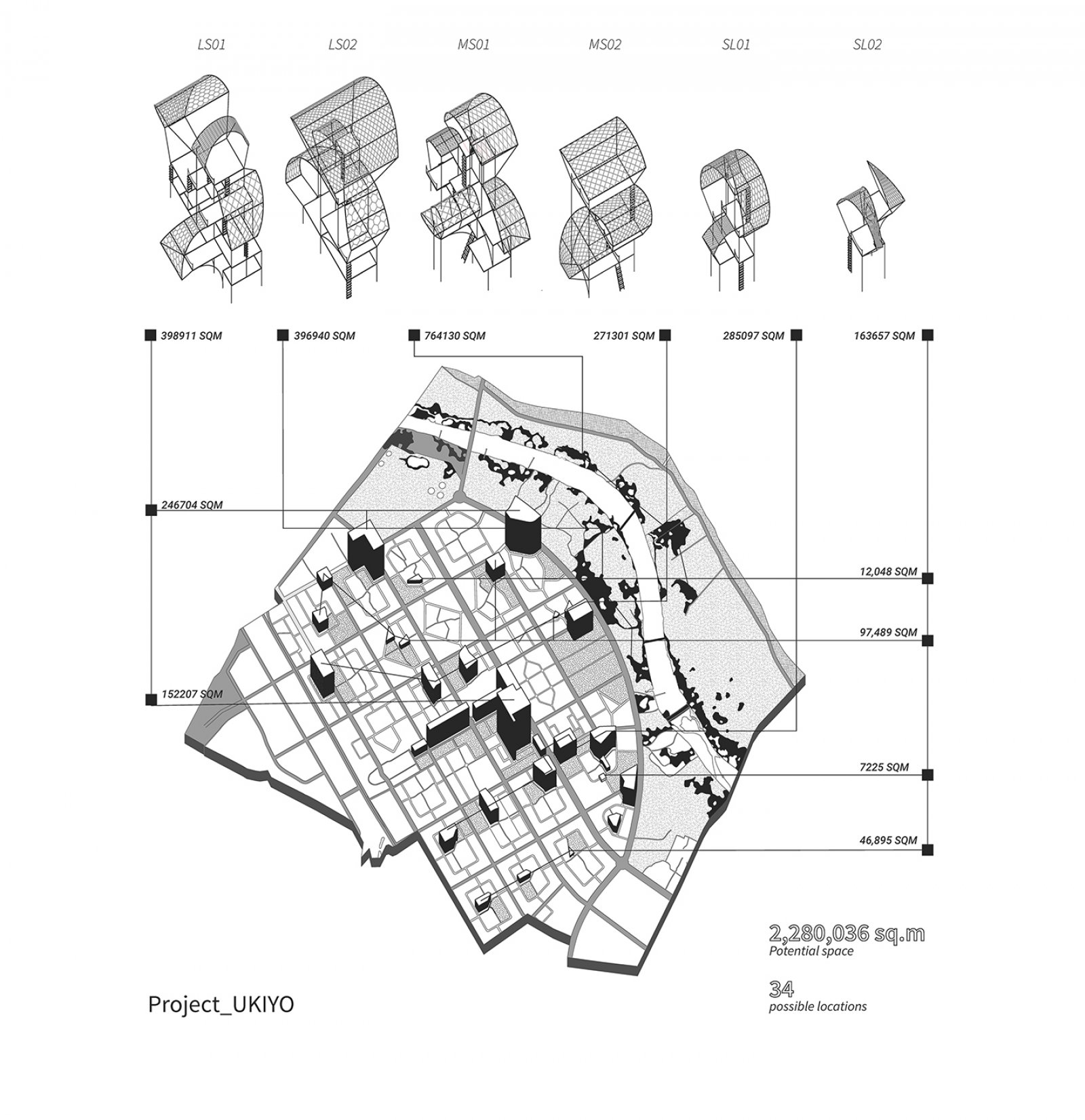
The project questions the anthropocentric development and the dominance of human activity in taking over nature. The stretch of river edge in Gandhinagar is still left unexplored offering a matrix of plantation, villages, and wilderness patch which should not only be preserved but also enhanced to support biodiversity. This is also a great amenity for the residents to come and explore. The idea here is to create 'Ukiyo' or almost transient, unobtrusive architecture interventions that will allow minimal human exploration in sensitive micro ecosystem that is taken over by nature with time.
View Additional Work