Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
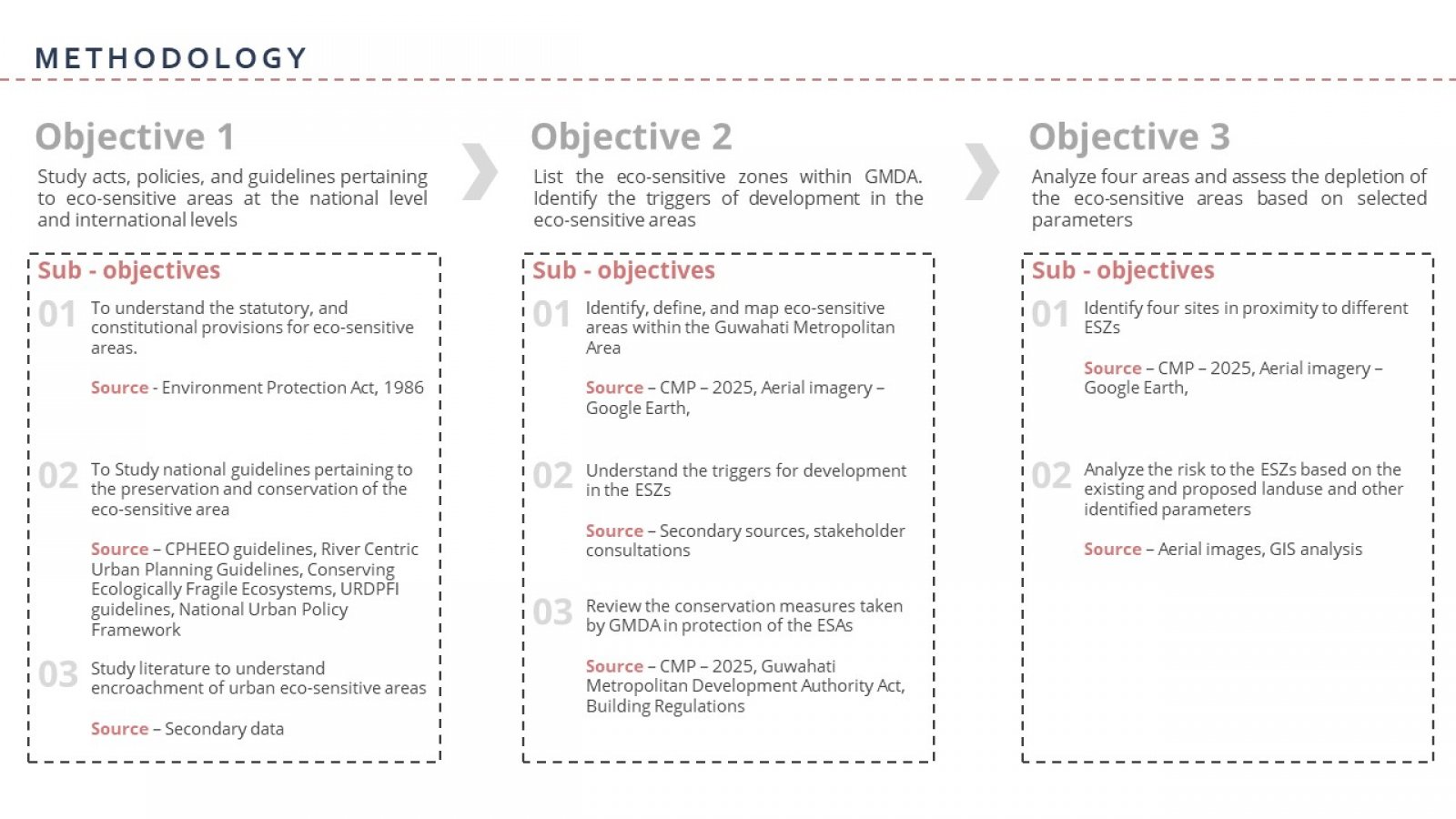
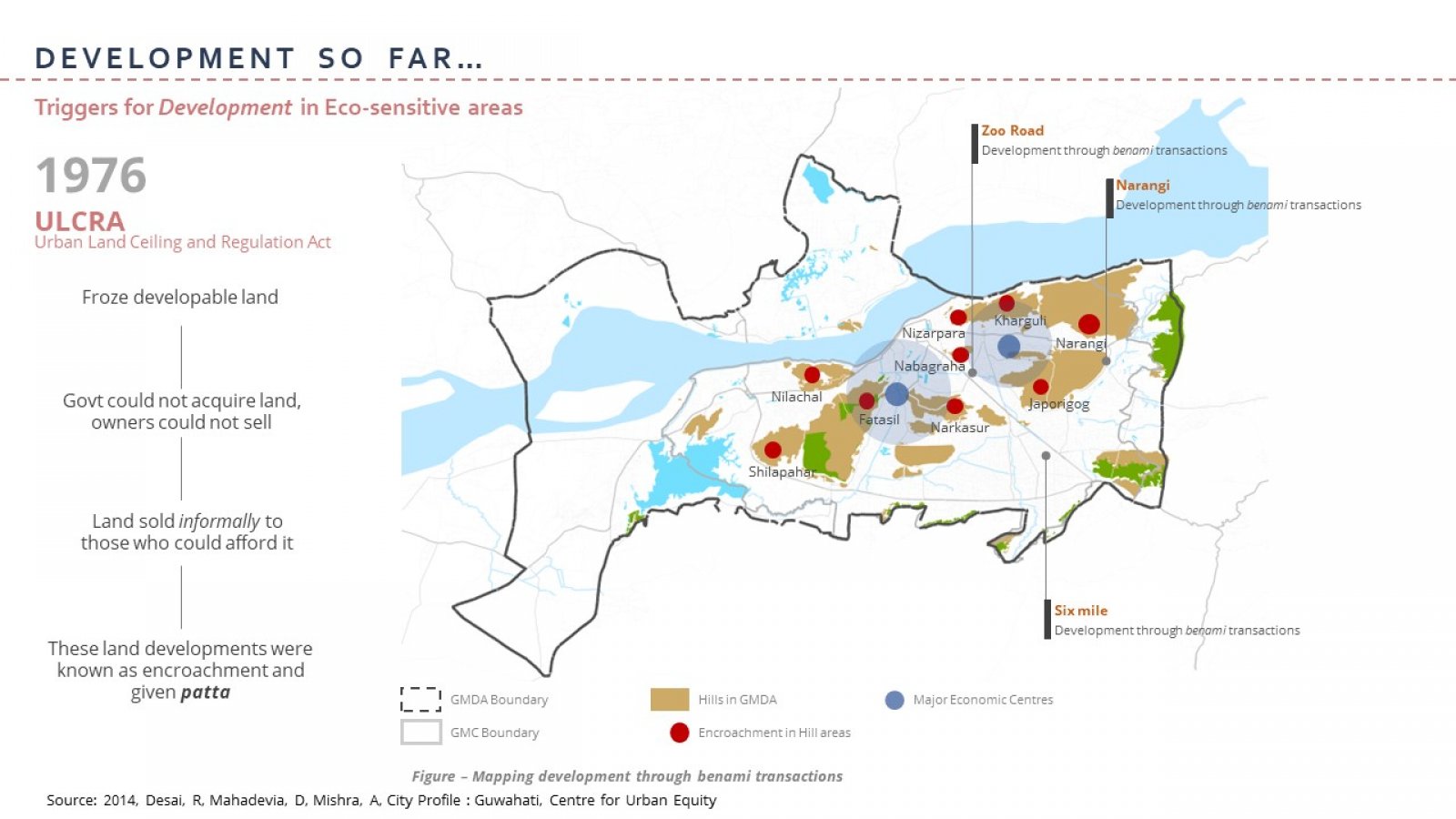
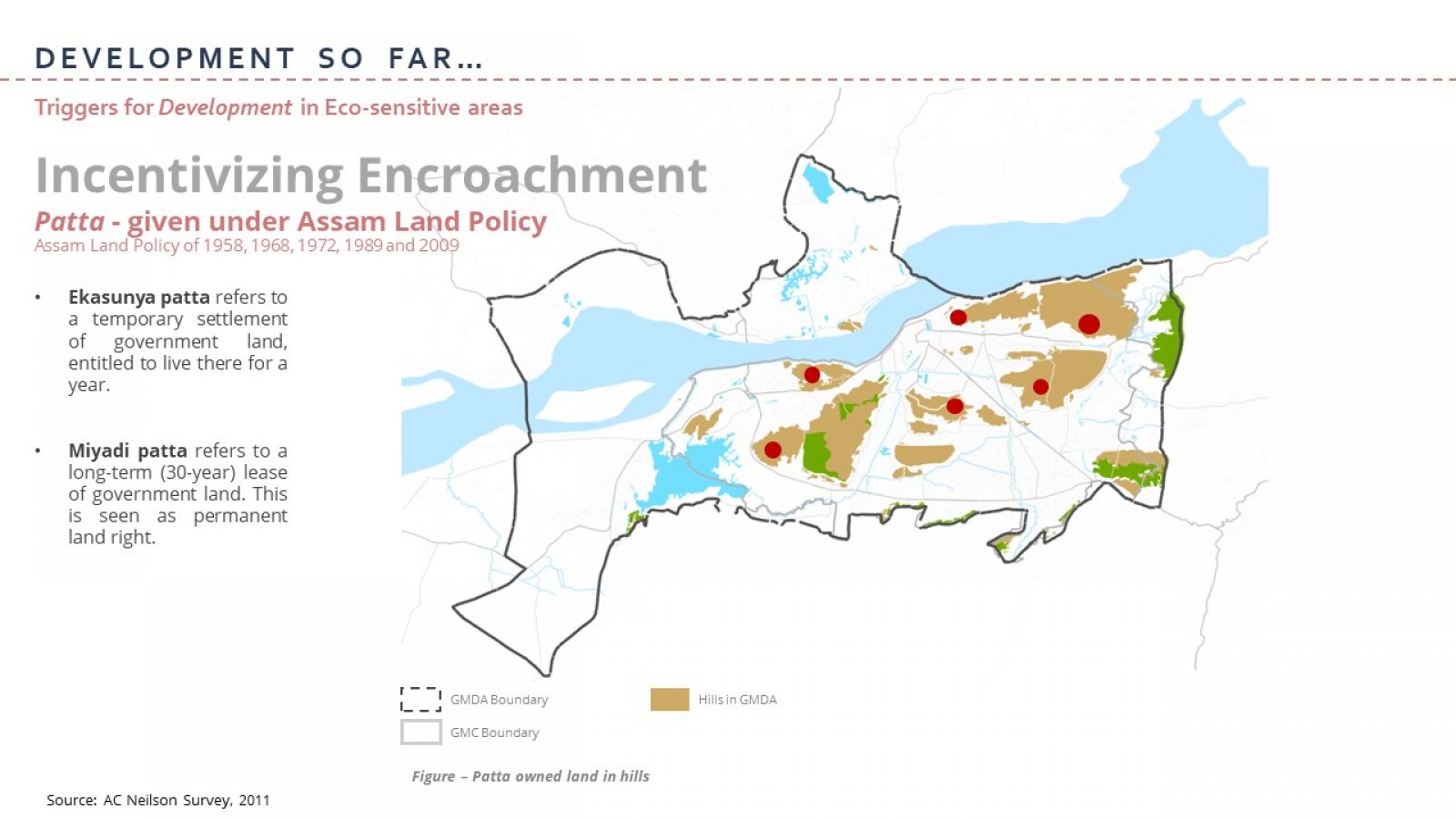
The 21st century is often referred to as the century of cities, highlighting the interdependence between urban areas and ecological concerns. The pressing need to reconcile the pace of urbanization with ecological considerations has emerged as a critical concern in recent times, aligning with SDG 11 goal of creating sustainable cities and communities. As Guwahati takes the lead in driving development in the North-Eastern region of India and enhancing trade and connectivity with ASEAN countries, in line with the Act East Policy, there is an urgent need to examine the city's ecological concerns due to its distinctive geographical location. The lassie-faire trend of urbanization coupled with unsustainable land use practices have already worsened the condition of the city, with flash floods and landslides becoming a regular occurrence, negatively impacting the economy as well as the livelihood of the urban dwellers. The study aims to re-look at Guwahati's planning and development control regulations by examining urban development in and around ecologically sensitive areas within the jurisdiction of the Guwahati Metropolitan Development Authority. The primary objective is to conduct a thorough literature review of the existing national and international laws, regulations, and standards concerning eco-sensitive areas. This review will facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the framework surrounding eco-sensitive areas and establish similarities between the challenges faced in Guwahati and those experienced globally. The second objective is to identify, list and map eco-sensitive areas in GMDA and understand the triggers for development around these areas. The third objective is to analyze these four specific cases in detail to comprehend the factors responsible for the development and depletion of these eco-sensitive areas. This analysis will provide a more detailed understanding of the ecological, social, and economic factors influencing development in these zones. The case studies conducted during the research identified the lack of monitoring and implementation of policies and regulations as one of the primary factors responsible for the degradation of these areas. Another significant factor is the lack of public awareness leading to the encroachment of ESAs, resulting in eviction drives by the urban authorities. The findings suggest that effective monitoring and implementation of regulations, public awareness campaigns, preparation of eco-sensitive plans and policies, capacity building of ULBs and other sustainable development practices are crucial for conserving eco-sensitive areas in Guwahati.


-min.jpg)