Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
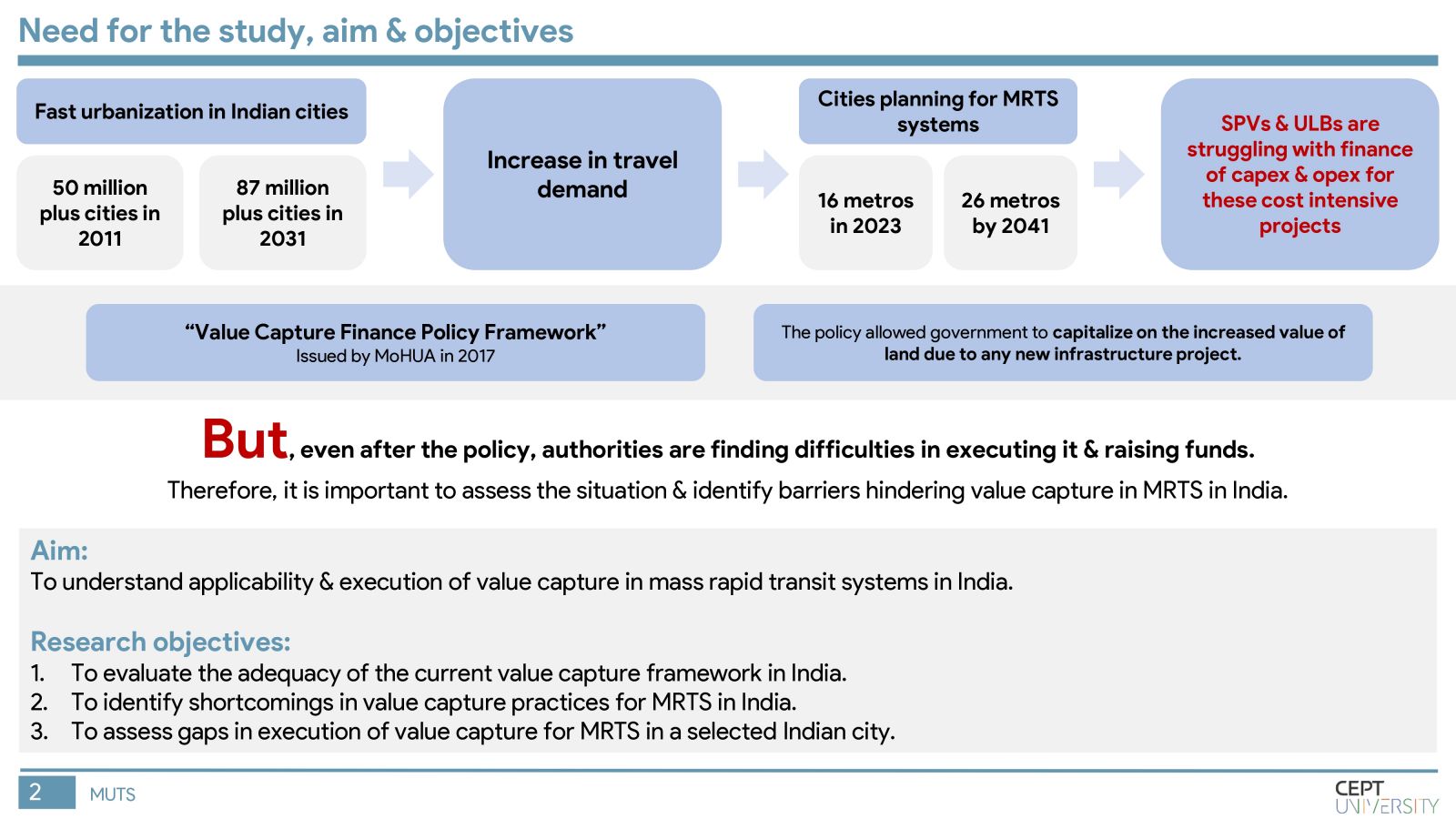
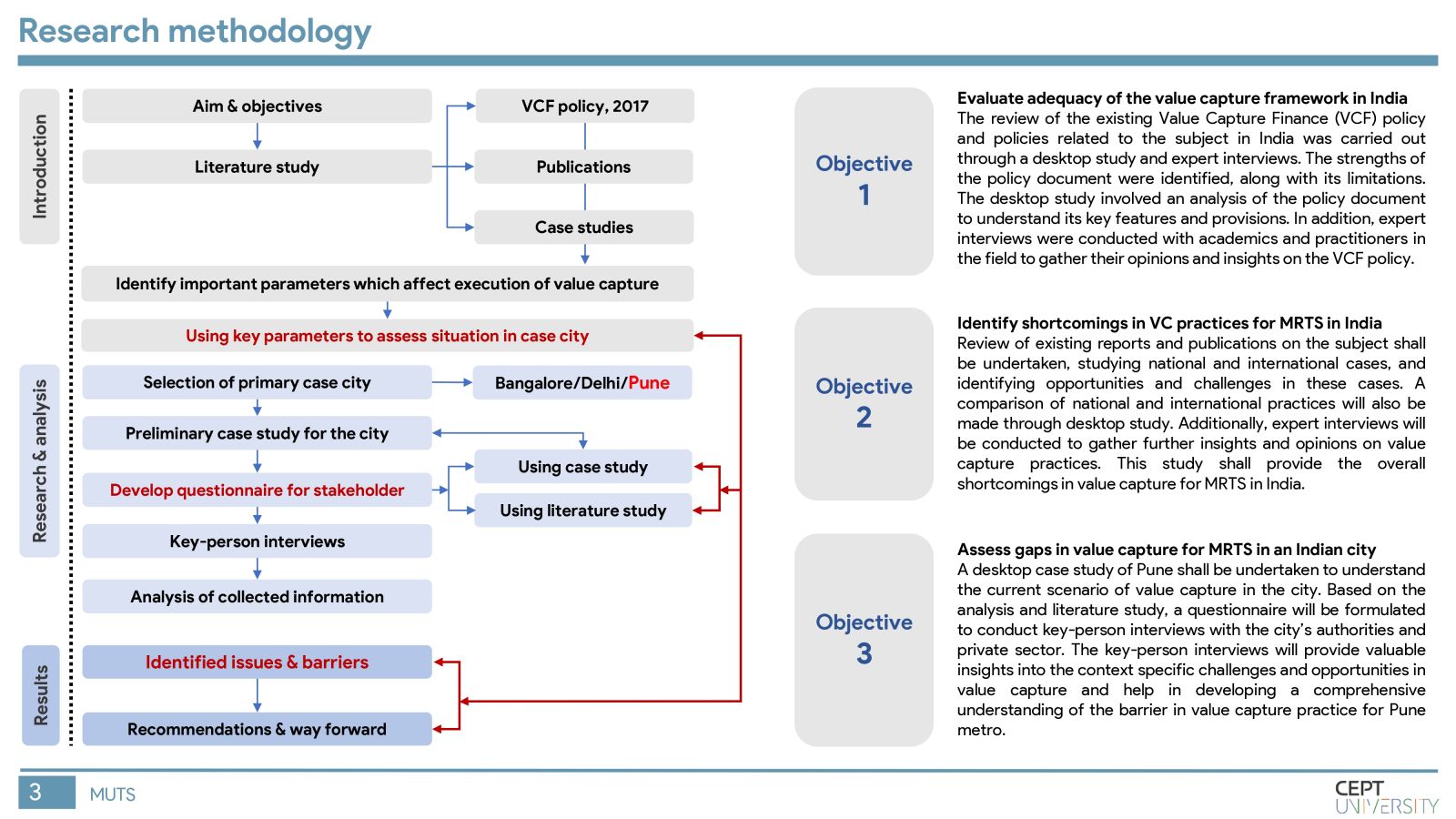
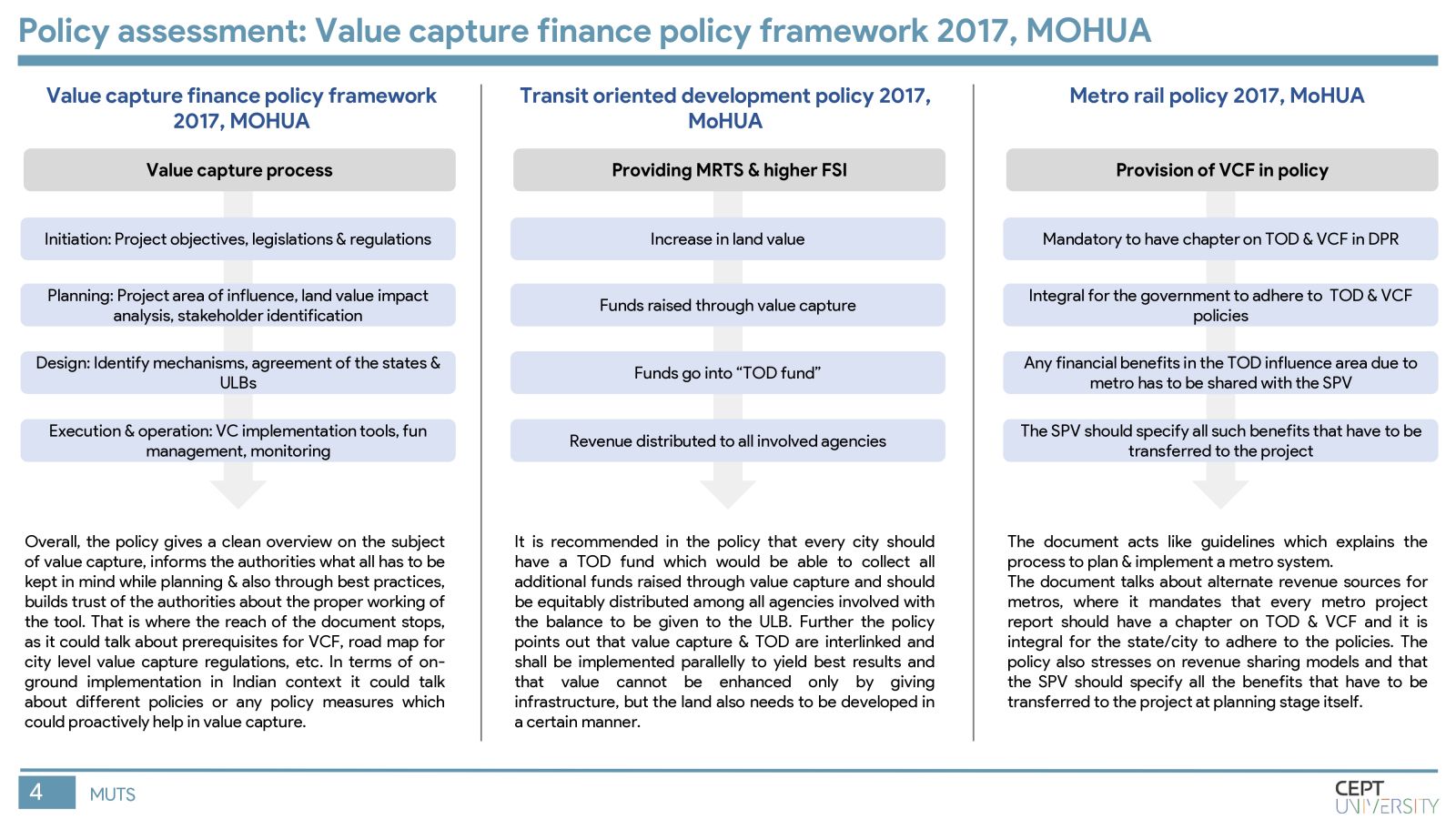
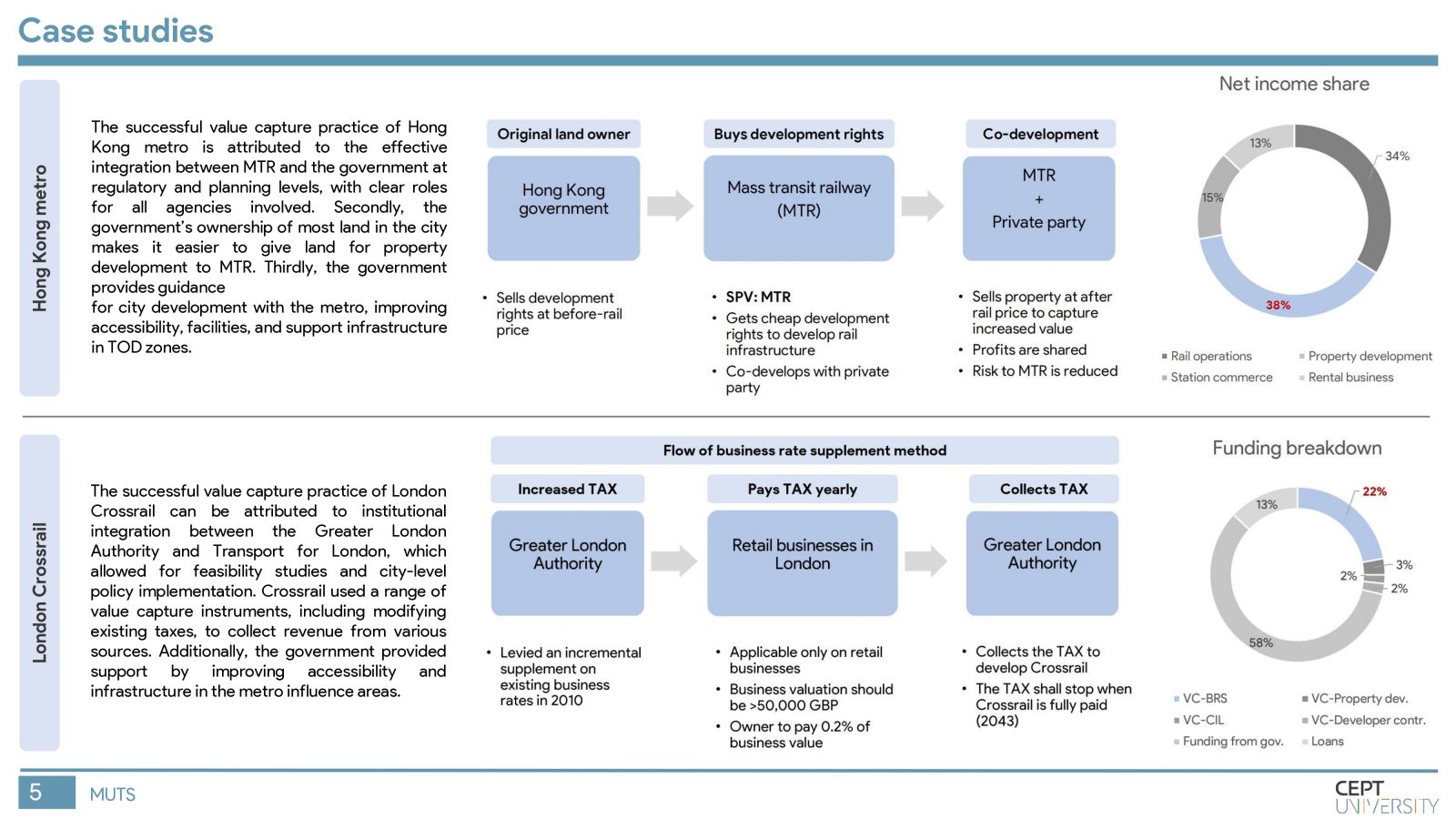
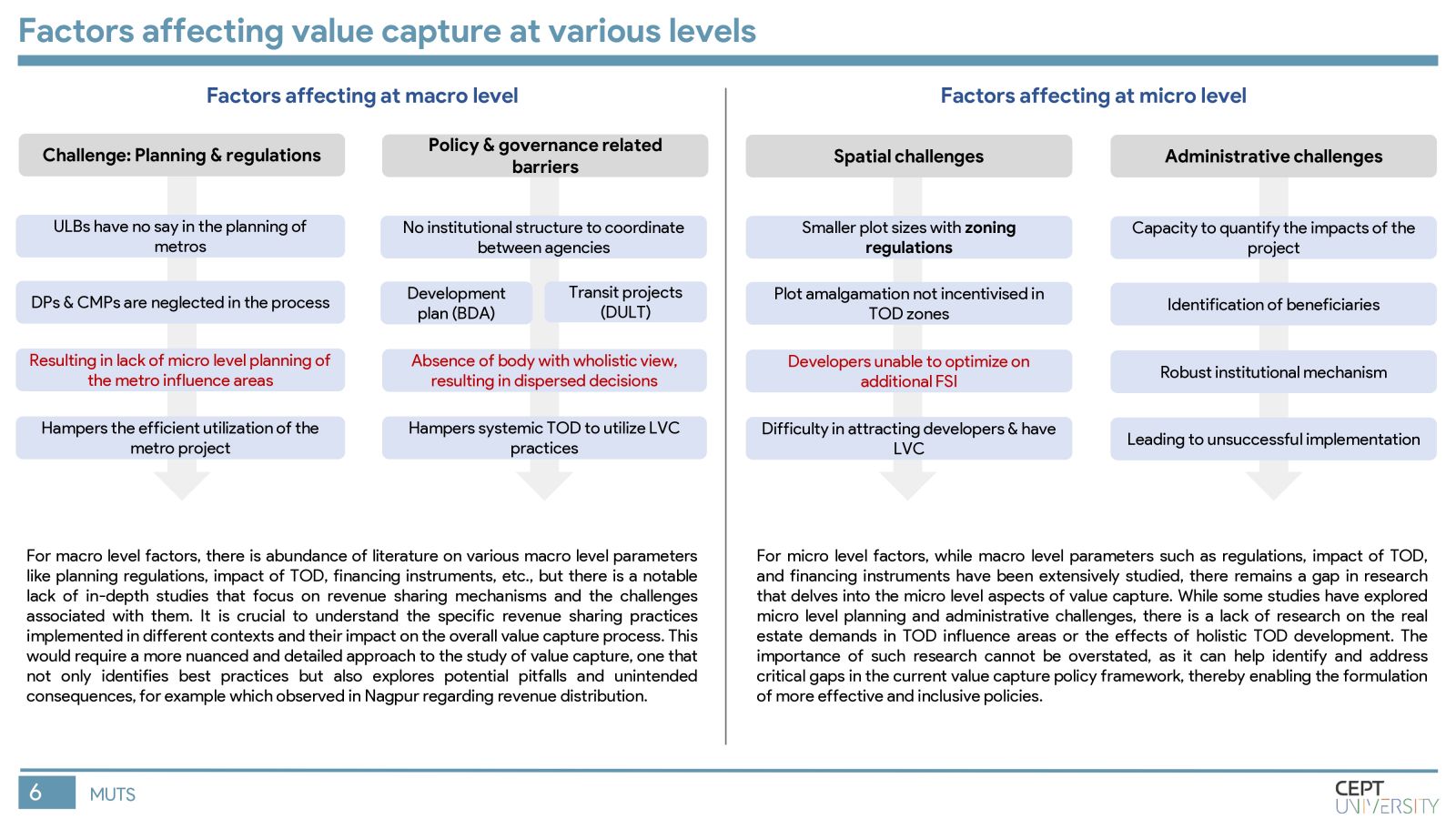
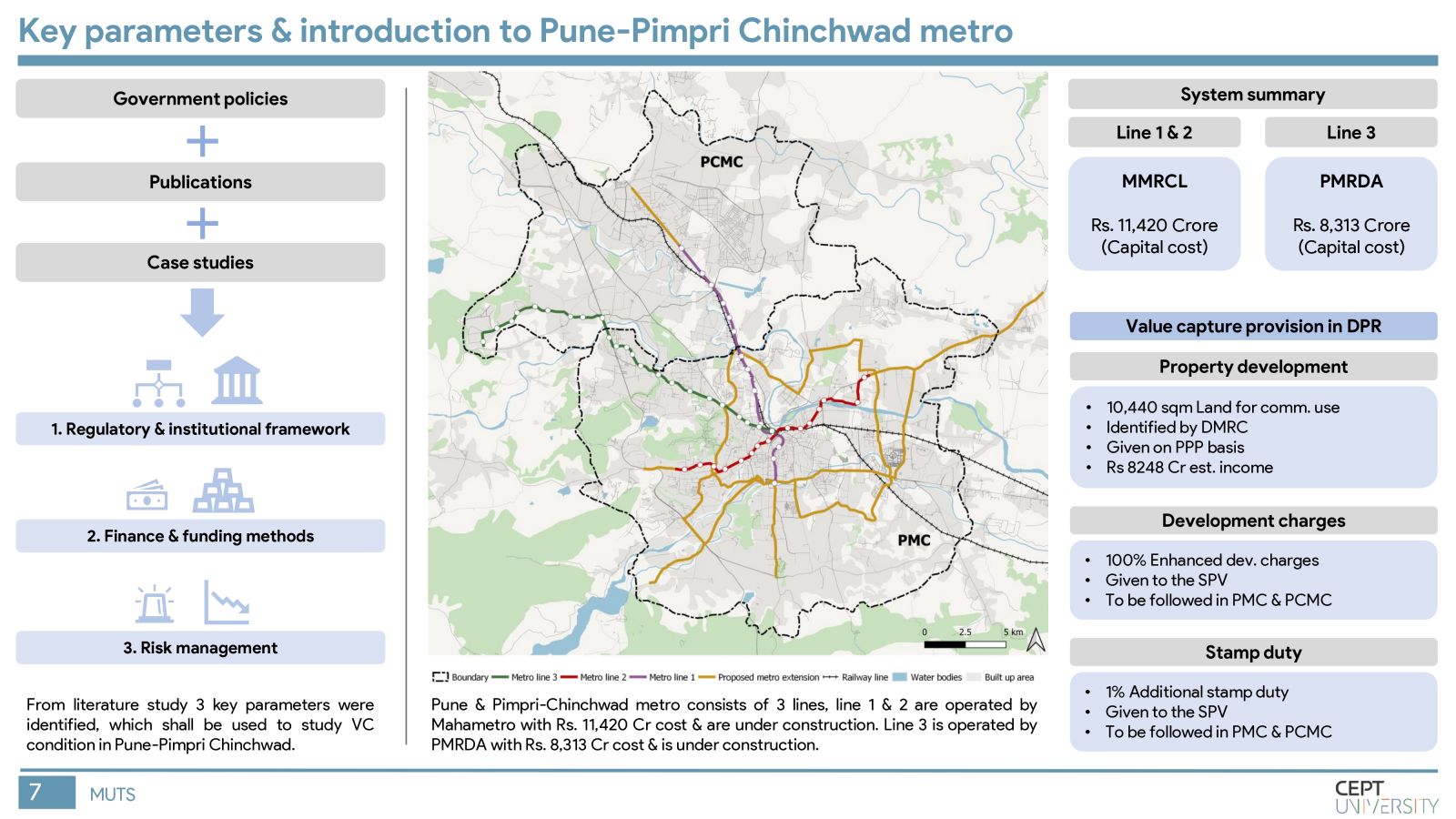
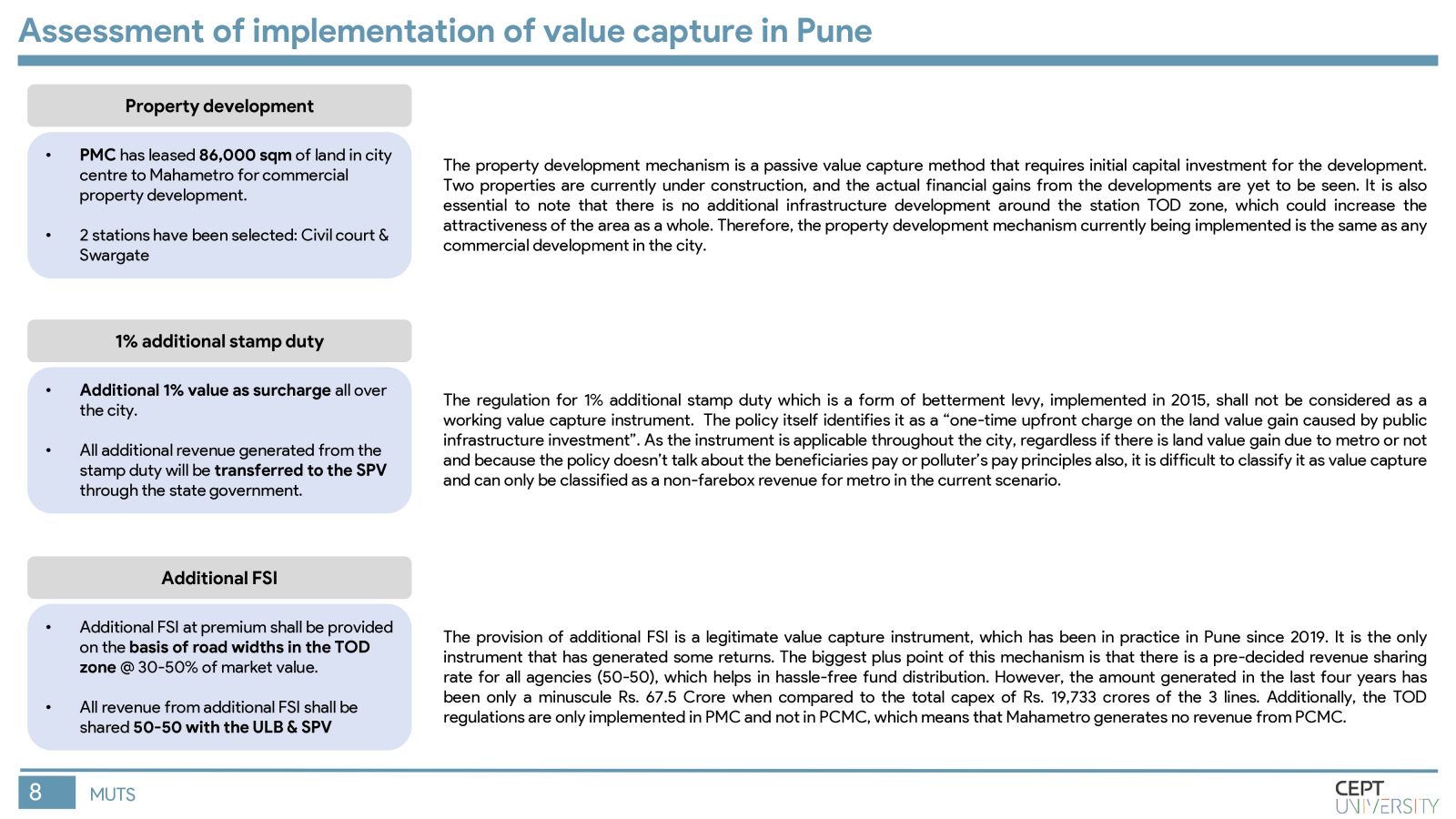
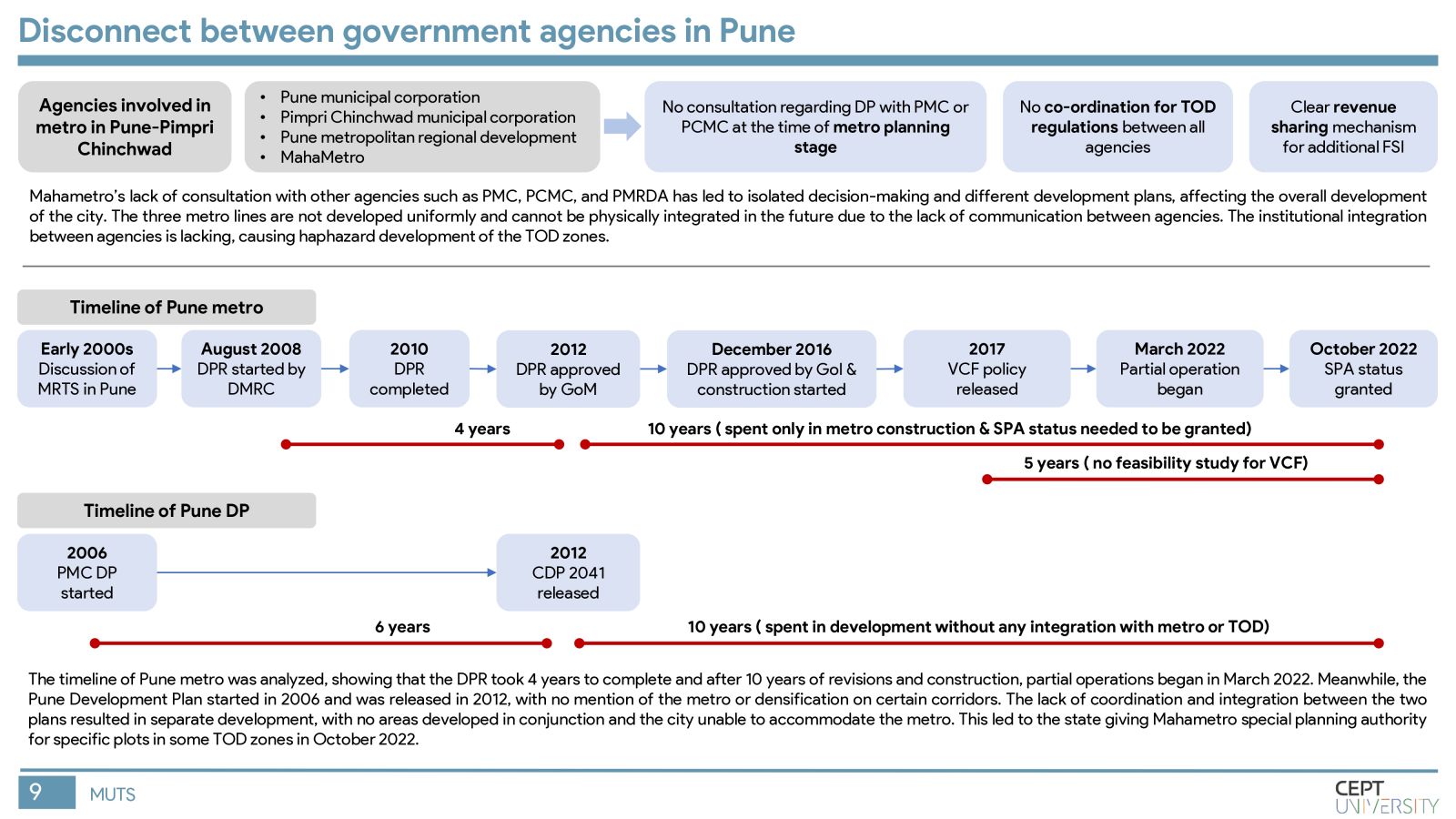
Indian cities need mass rapid transit systems which are capital intensive and require value capture financing. The Value Capture Financing Framework was introduced by MoHUA in 2017, but governments still face difficulties in its implementation. This study identifies key barriers to value capture in MRTS in India by evaluating the current framework, identifying shortcomings in value capture practices, and assessing gaps in execution in Pune city. Inefficient implementation of TOD regulations, lack of coordination among authorities, and unclear revenue-sharing mechanisms are major barriers. The methodology will be replicated in other cities to improve the situation.