Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
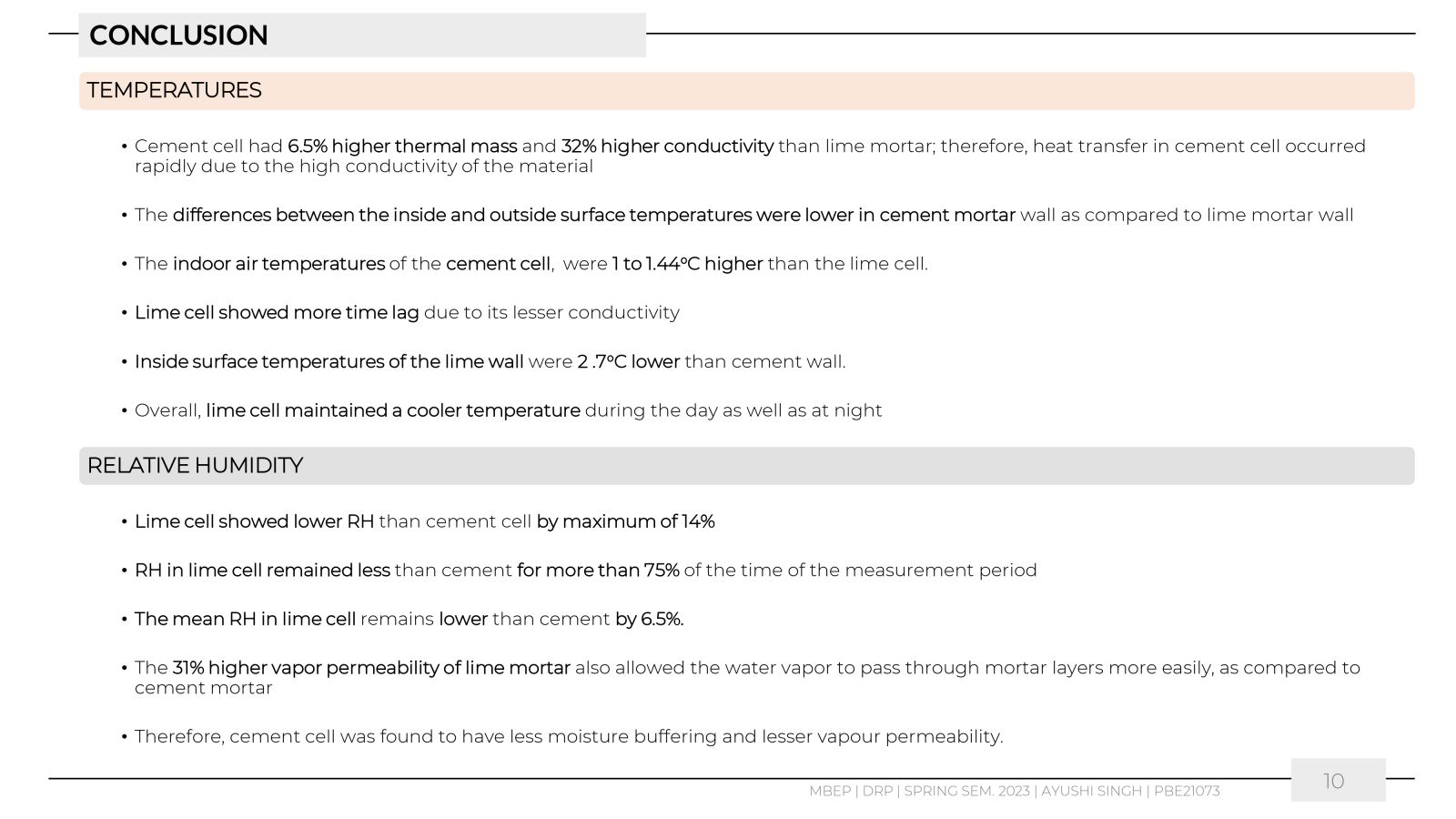
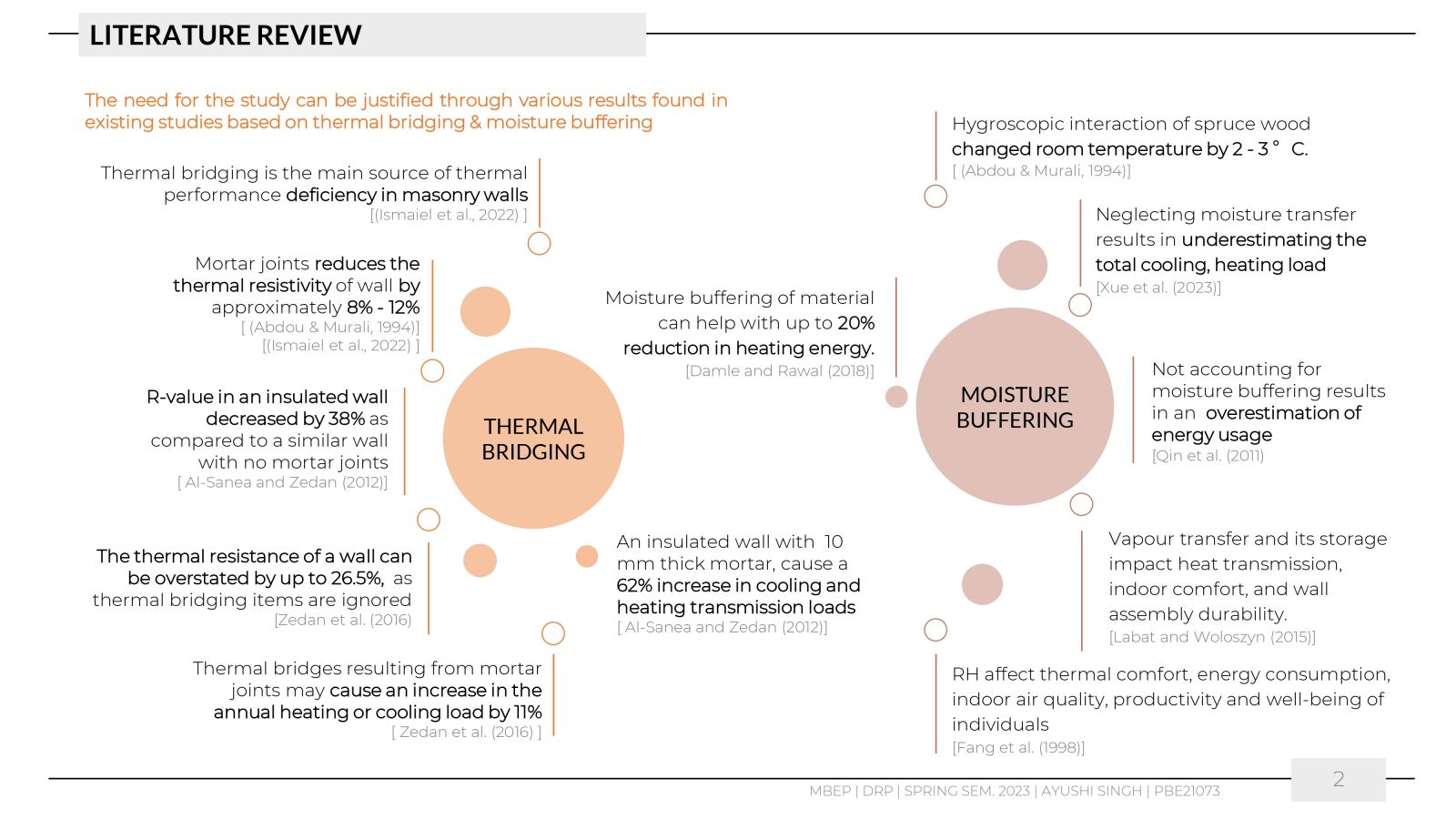
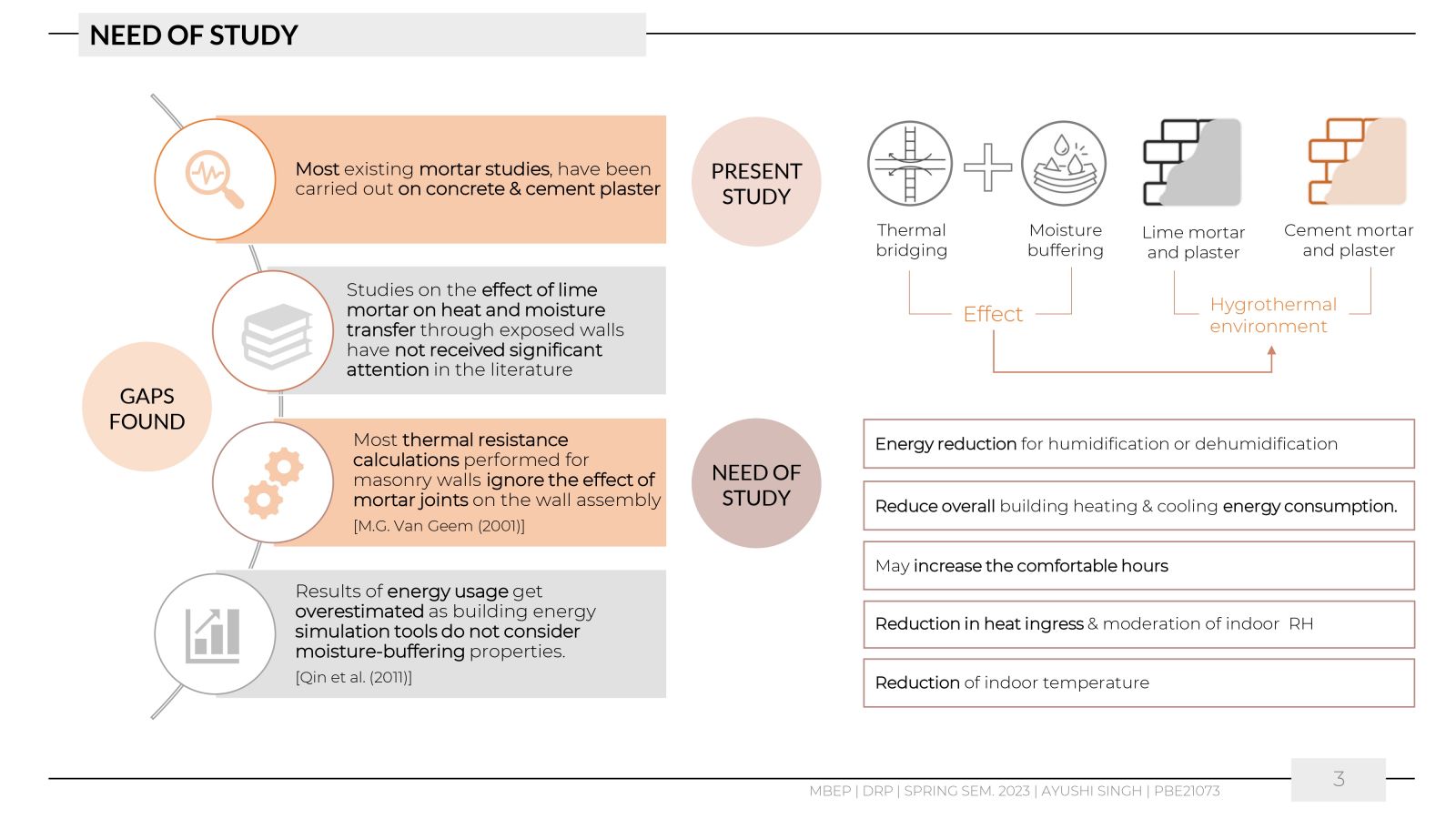
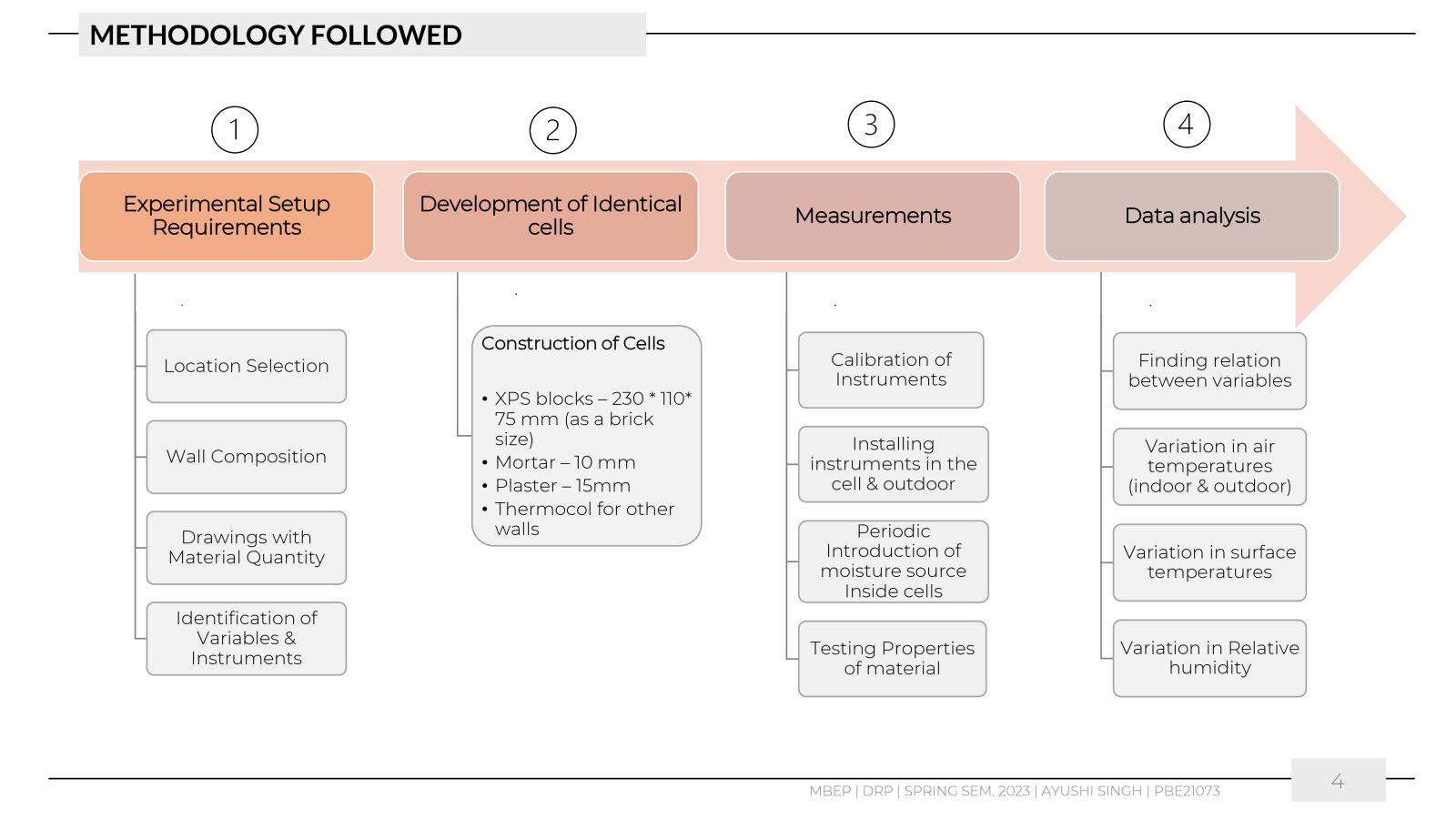
This work aimed to understand the behaviour of the materials like lime and cement in changing weather conditions by comparing the hygrothermal environment of spaces built with mortar and plaster layers of lime and cement. The research aimed to examine and quantify the heat and moisture transfer through two walls of a 1m2 area facing south. One wall was constructed with lime mortar, and the other with cement mortar and XPS (Extruded Polystyrene) blocks, coated with an inner layer of plaster of the same materials. Other test cell walls were made up of EPS (Expanded Polystyrene), thus limiting the heat and moisture transfer only through mortar layers. The study monitored the temperatures, relative humidity, and surface temperatures inside the two identical test cells of 1 m3 volume each. The study helped to understand the heat ingress due to the difference in conductivity of these two materials and the impact of thermal mass on the hygrothermal environment of the cells.
.jpg)
.jpg)