Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
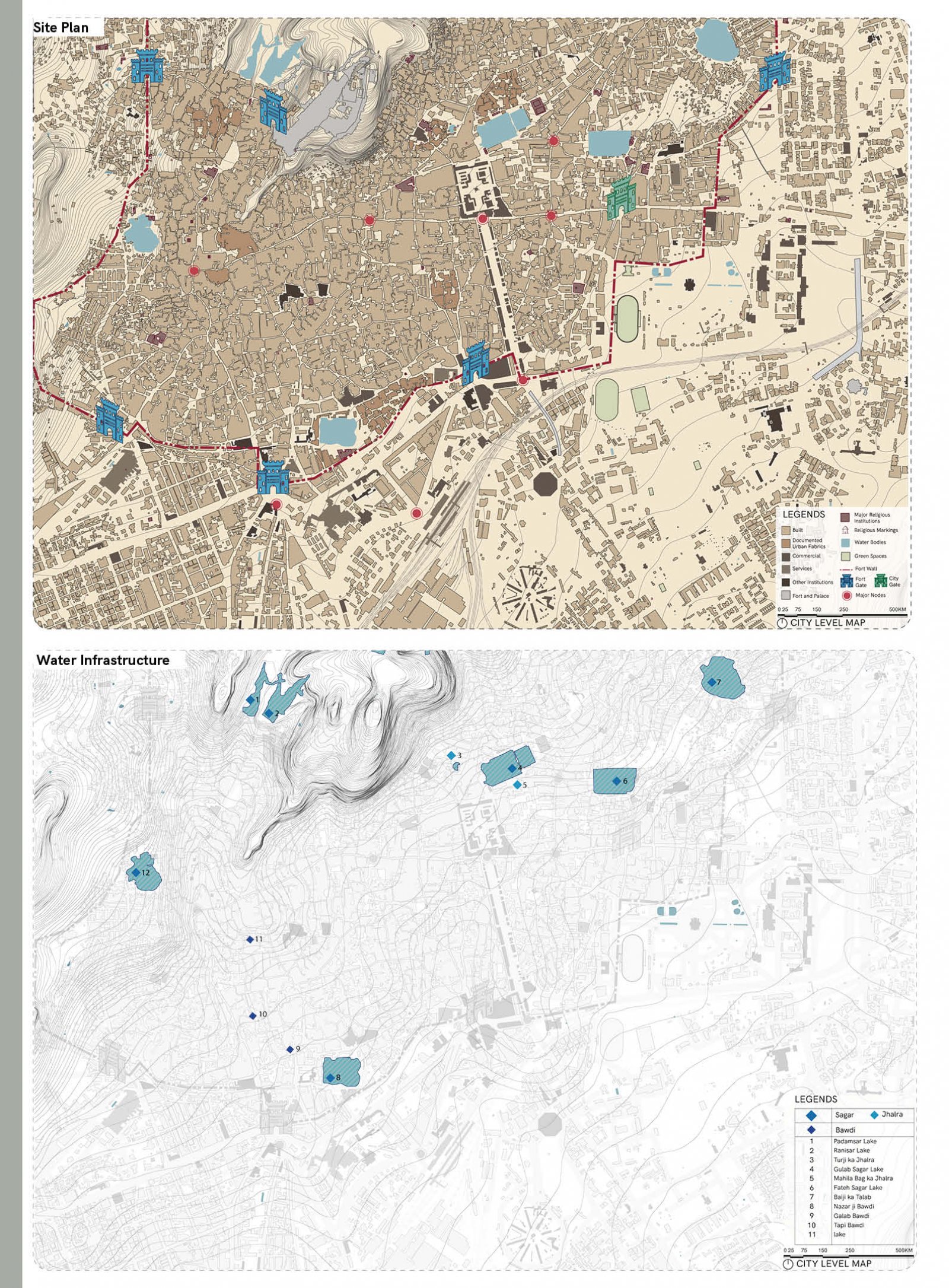
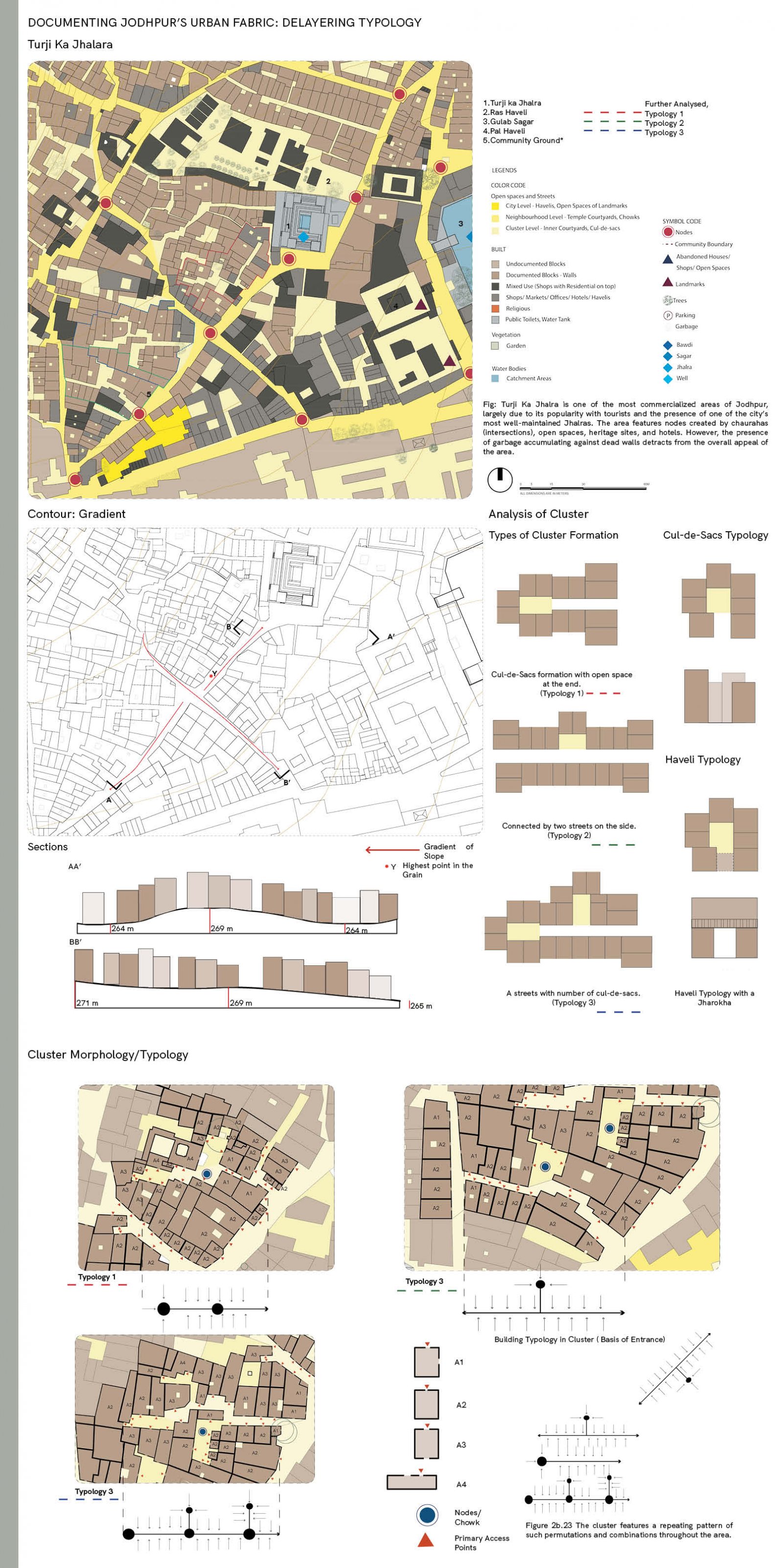
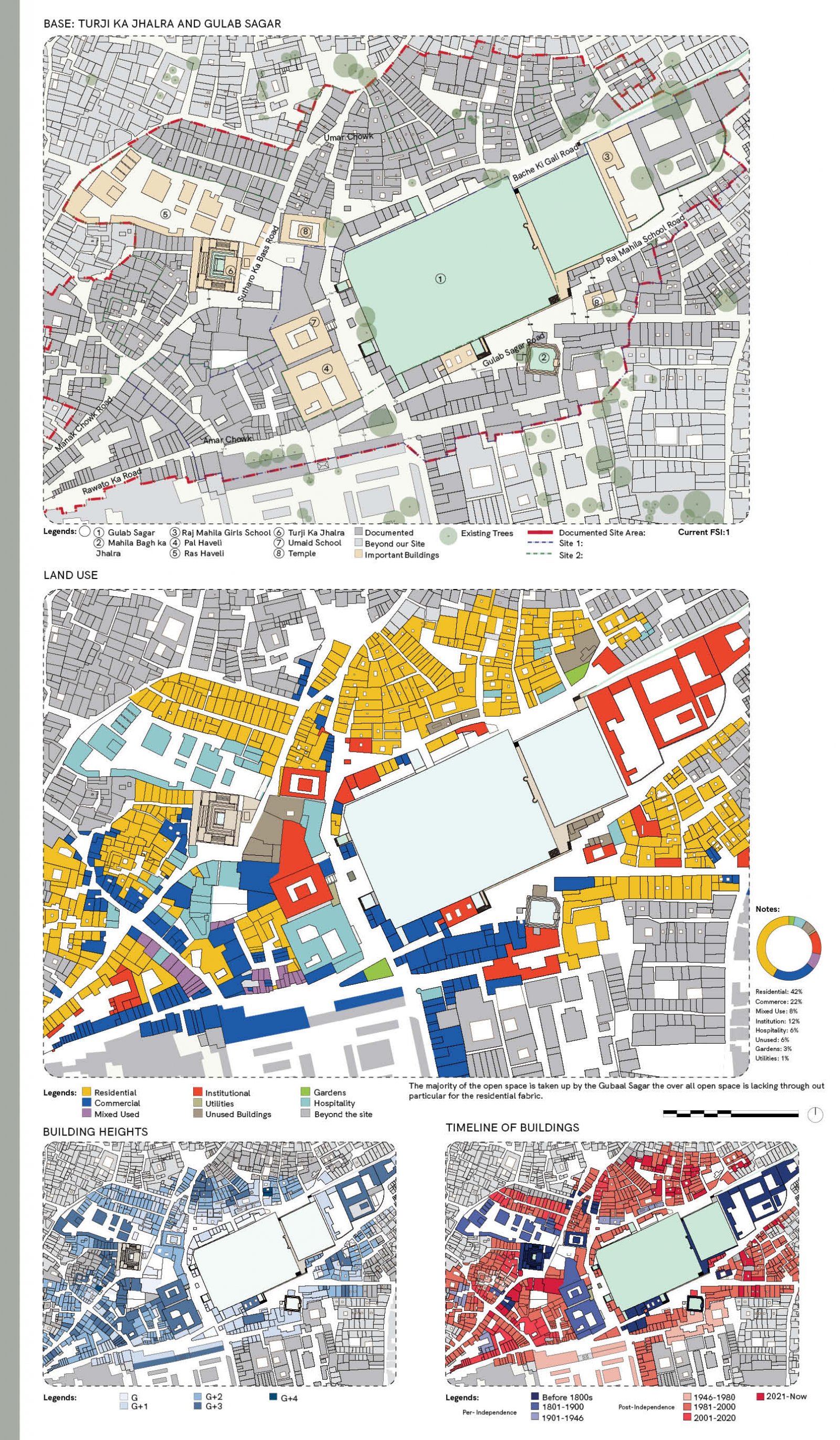
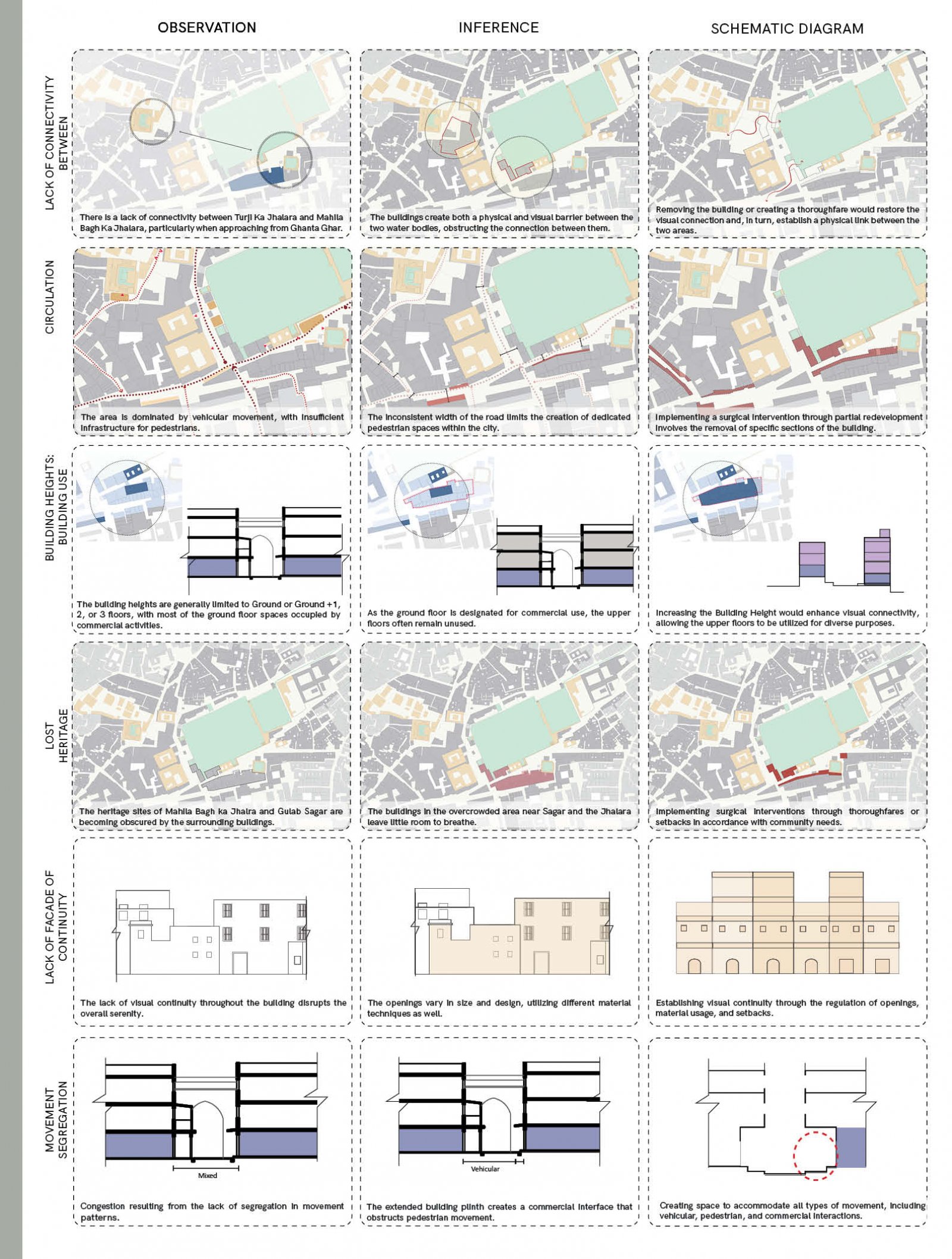
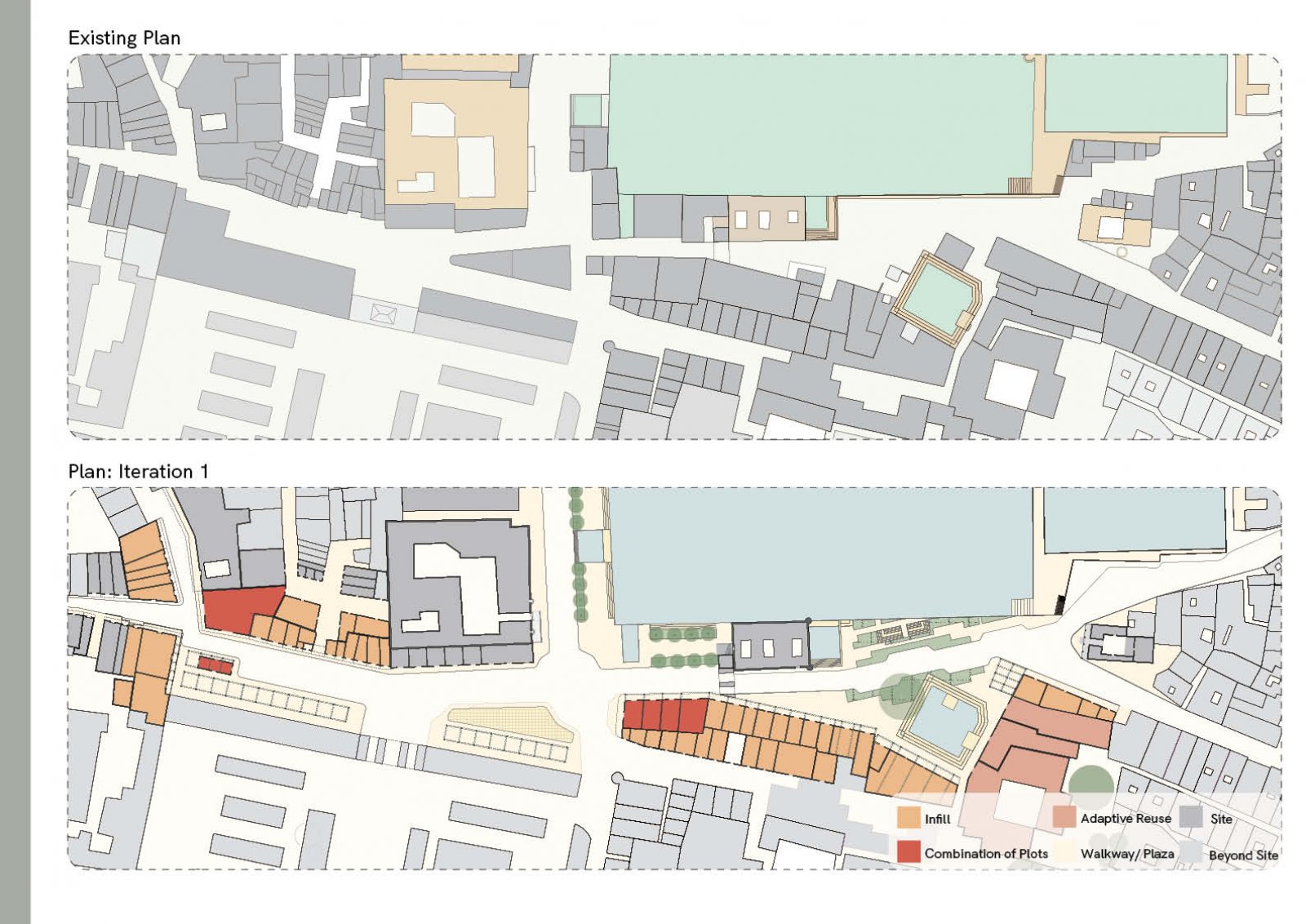
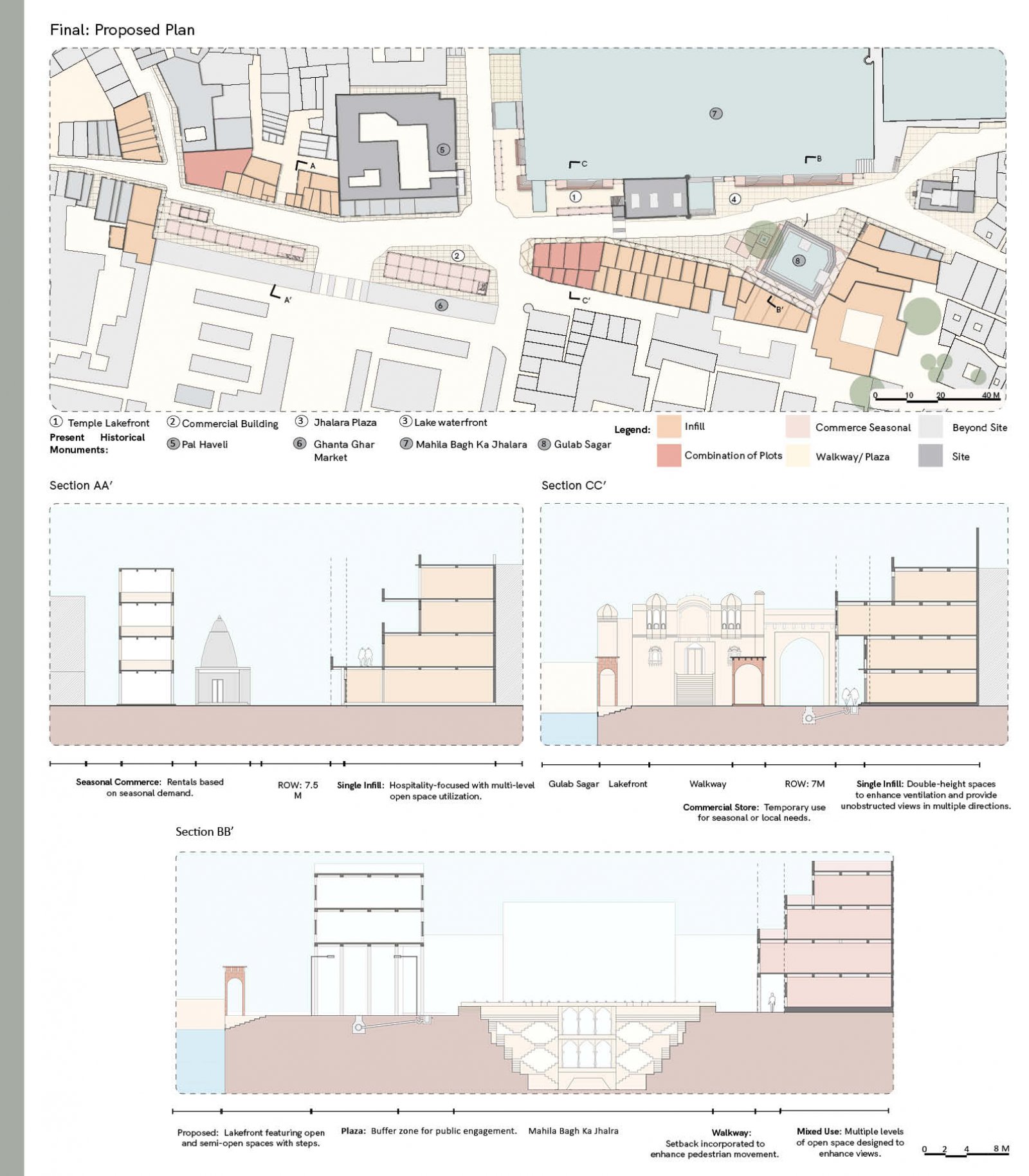
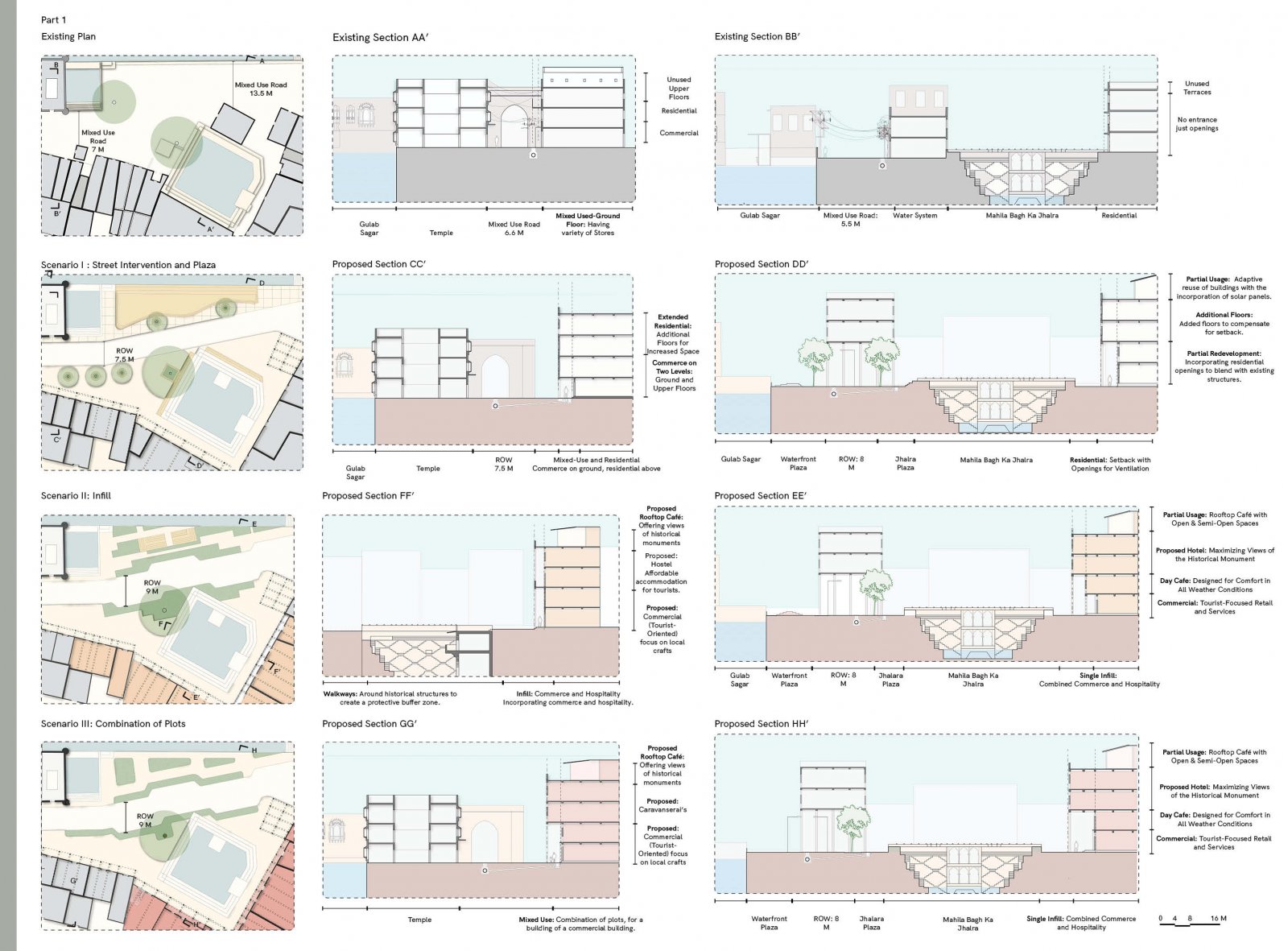
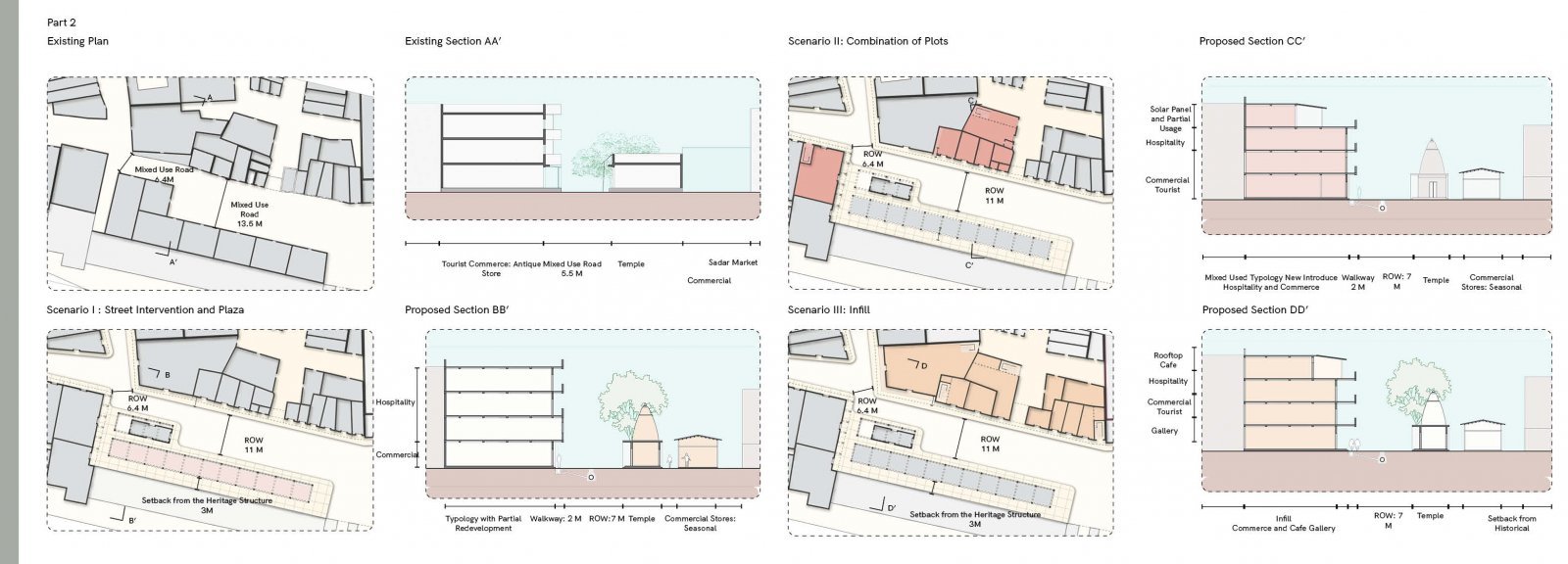
The proposed design aims to revitalize the Gulab Sagar area in Jodhpur, enhancing its economic, cultural, and architectural significance while addressing key urban challenges. Positioned near iconic landmarks like Mahila Bagh ka Jhalra and Mehrangarh Fort, this site has the potential to transform into a vibrant hub that balances Jodhpur’s heritage with contemporary urban needs. Key interventions include increasing building heights to maximize the Floor Space Index (FSI), encouraging developments like rooftop cafes and boutique hotels. This vertical expansion will not only offer panoramic views of historic monuments but also enhance tourism and boost local economic activities. Setbacks will be introduced to create pedestrian-friendly zones, ensuring better integration between built structures and open spaces. The design tackles drainage issues by integrating sustainable water management systems, addressing seasonal inefficiencies, and ensuring the area's functionality throughout the year. Existing encroachments will be reimagined as active public spaces, incorporating vending zones and shaded seating areas to promote interaction while catering to both locals and tourists. In line with Jodhpur’s architectural legacy, the proposal will ensure that fenestration and building forms align with traditional design principles, preserving the city’s unique identity. Commercial areas will prioritize inclusivity by supporting local artisans and businesses, preserving the cultural essence of the region. The aim of this brief is to create a cohesive urban strategy that respects Jodhpur's historic fabric while infusing modern utility. The proposal envisions a global destination that enriches the experience for visitors and elevates the quality of life for the city's residents.
View Additional Work