Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
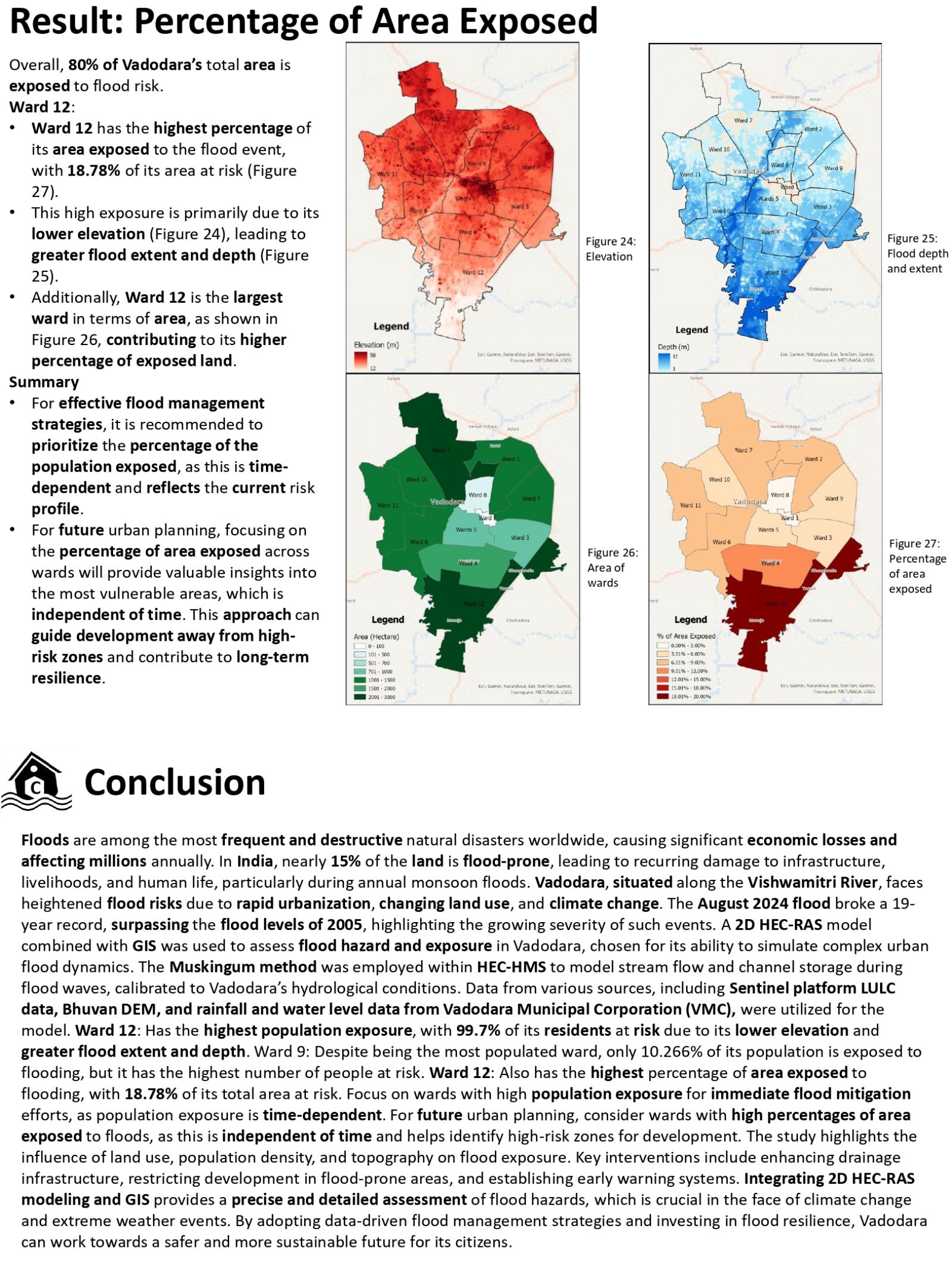
Floods are among the most devastating natural disasters, causing significant economic losses and affecting millions annually. Vadodara, located along the Vishwamitri River, faces heightened flood risks due to urbanization and climate change. The August 2024 flood, surpassing a 19-year record, highlighted the city’s vulnerability. This study uses advanced modeling techniques, including 2D HEC-RAS and GIS, to assess flood hazards and exposure. Hazard maps were created using LULC data and a 10-meter DEM, with rainfall and water level data from the 2024 flood. Overall results show that 80% of Vadodara’s area is inundated and 76% of population exposed, in this Ward 12 experiences the highest area exposure, while Ward 9 has the most residents at risk due to high population. The findings emphasize the need for targeted flood mitigation measures and sustainable urban planning to reduce future flood impacts.
View Additional Work