Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
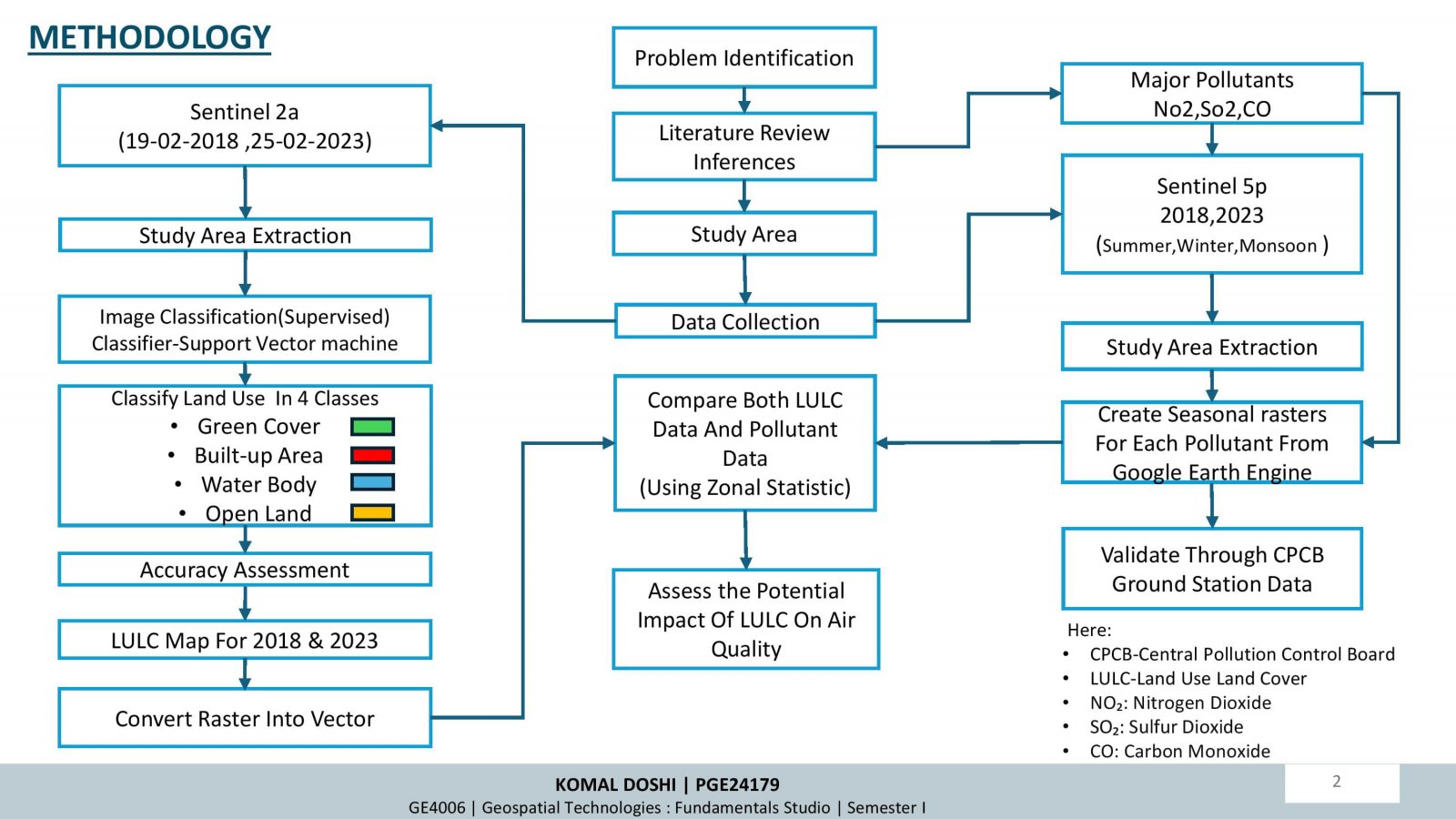
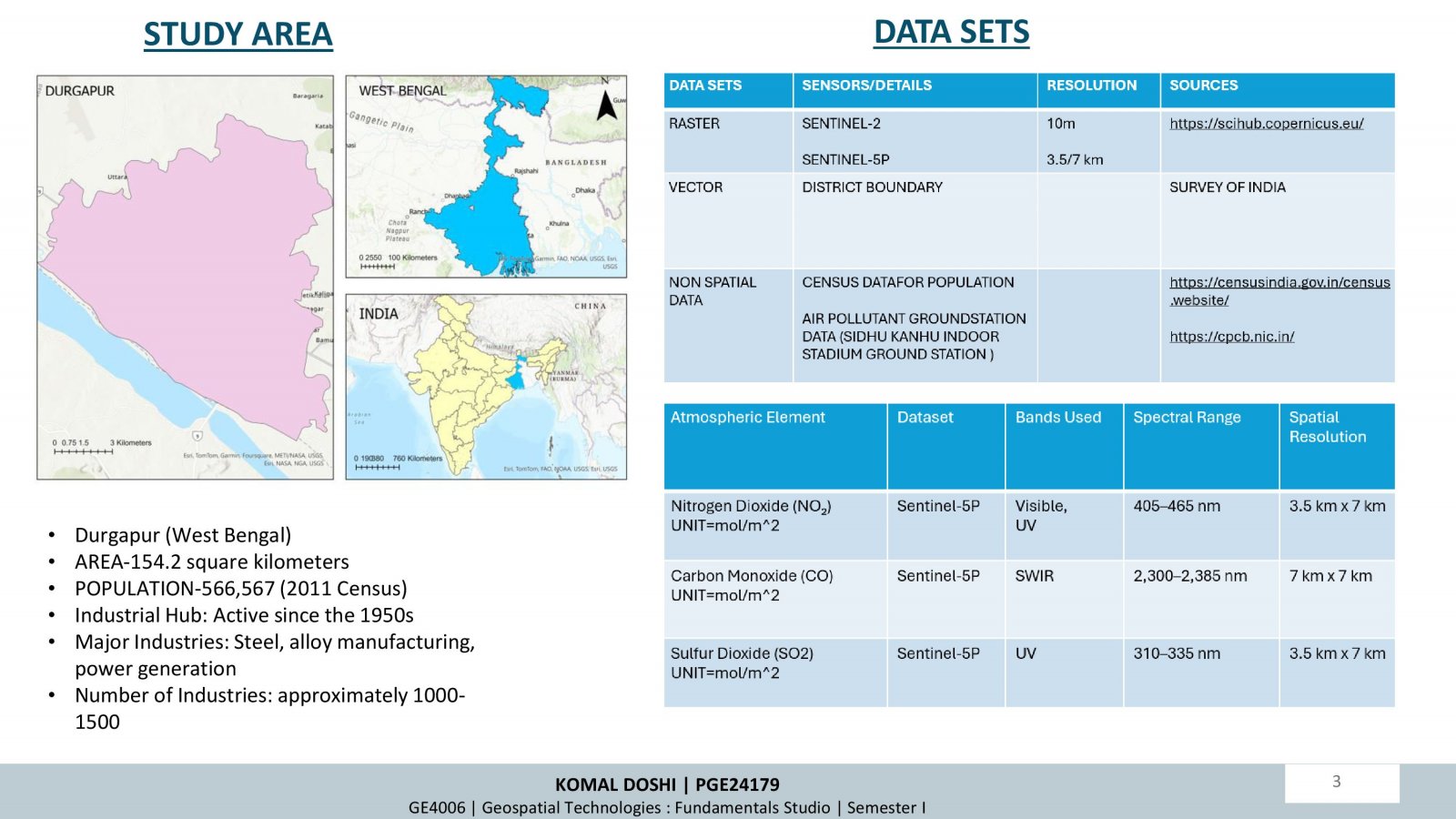
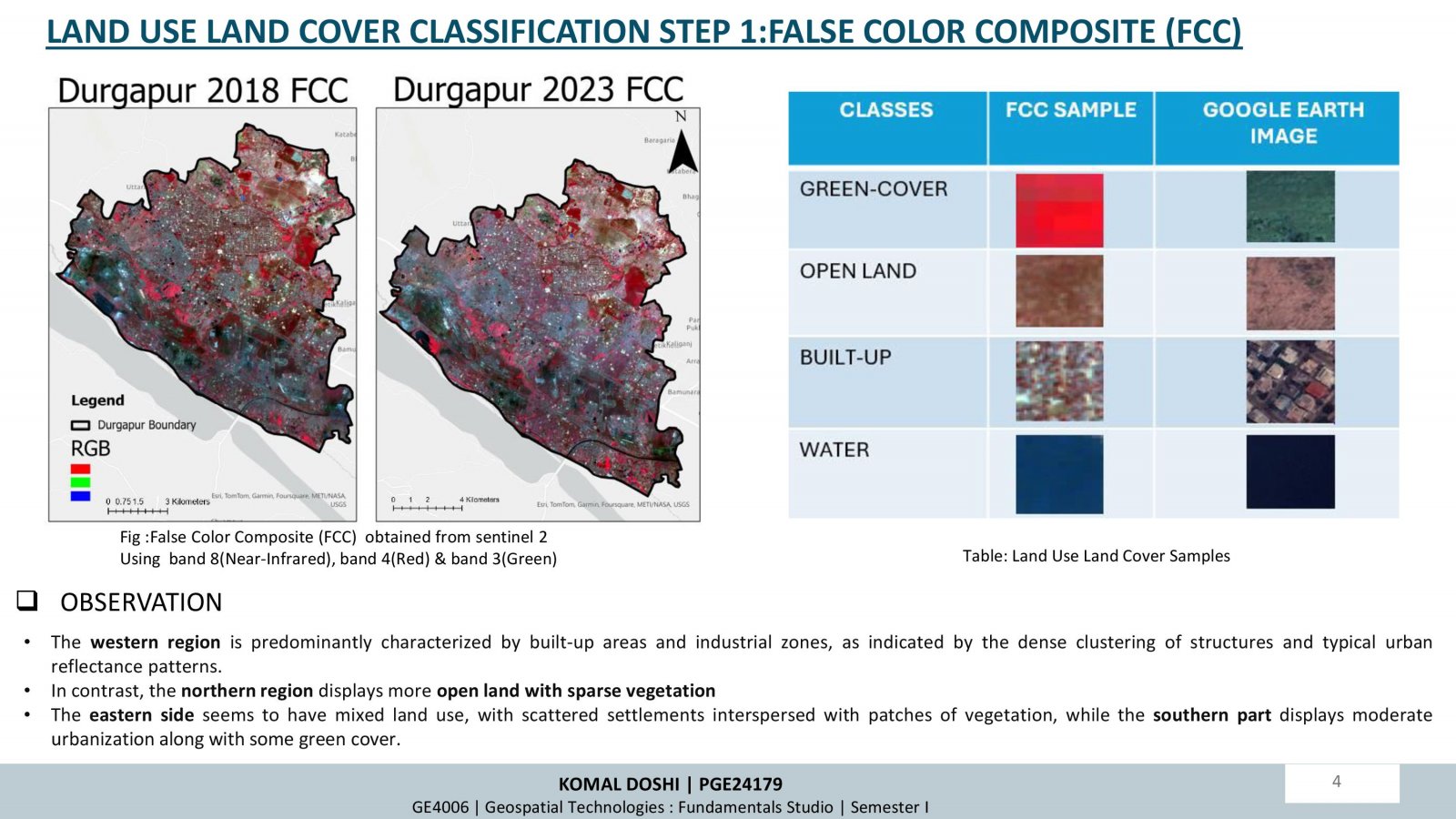
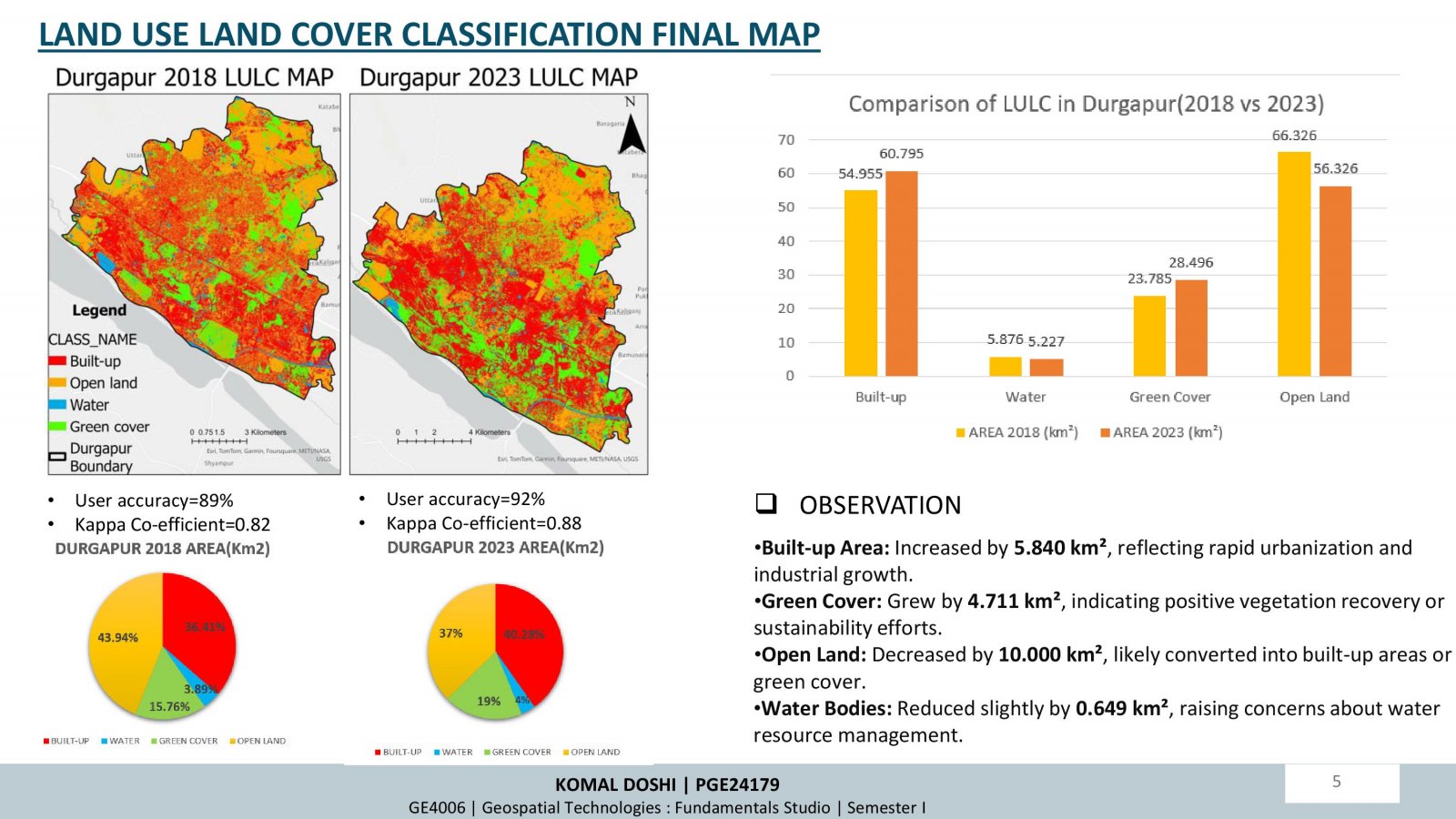
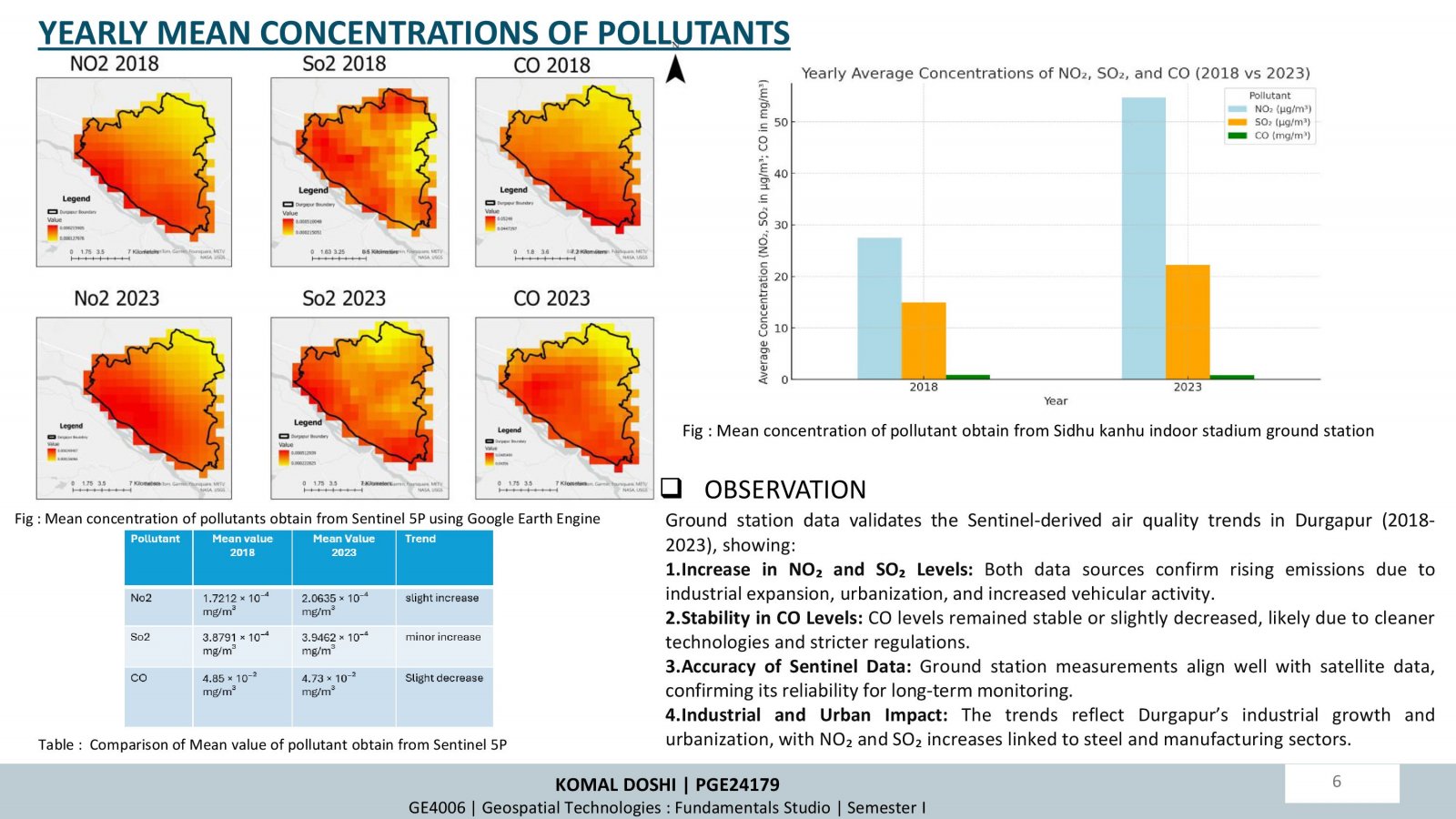
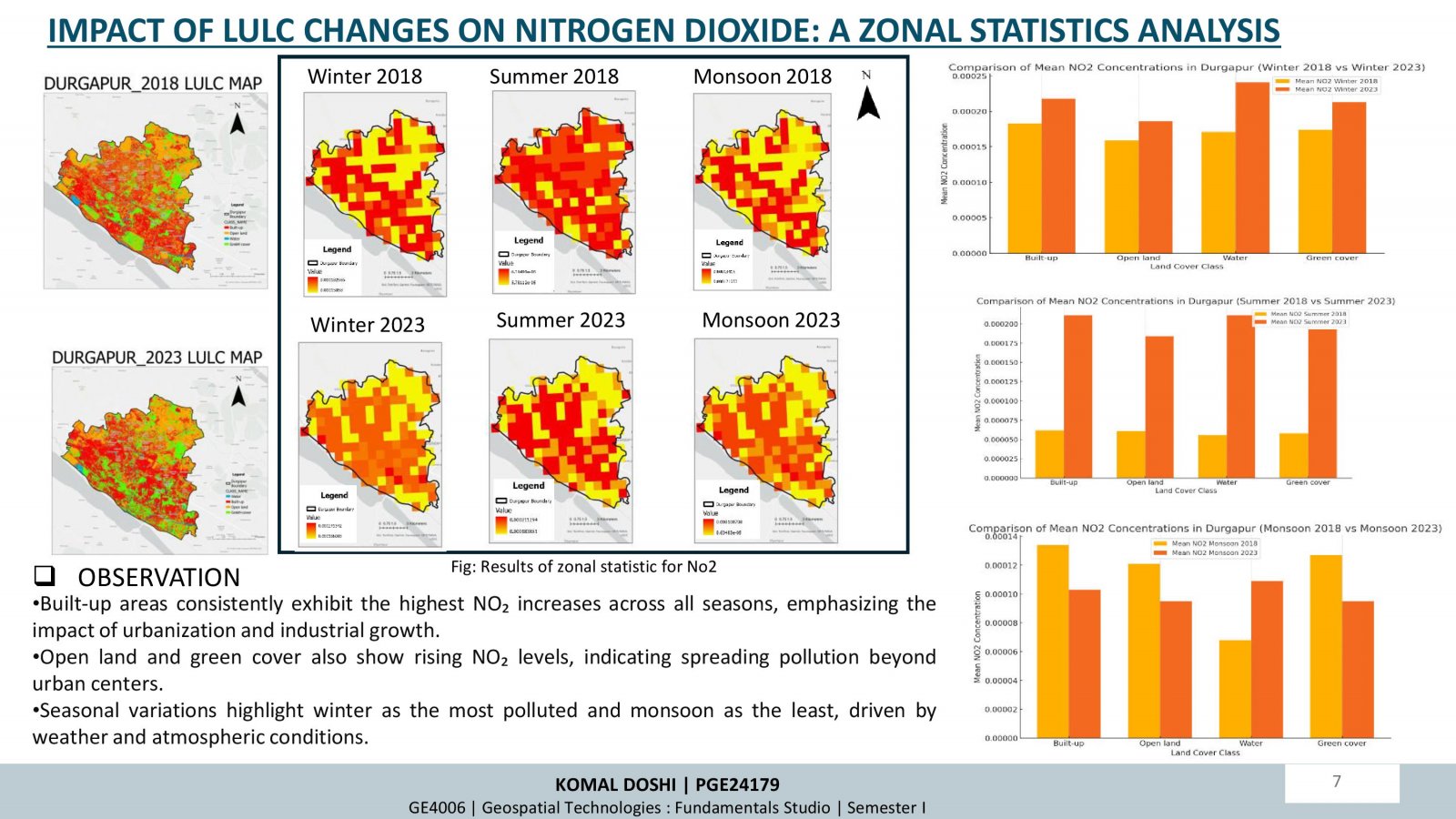
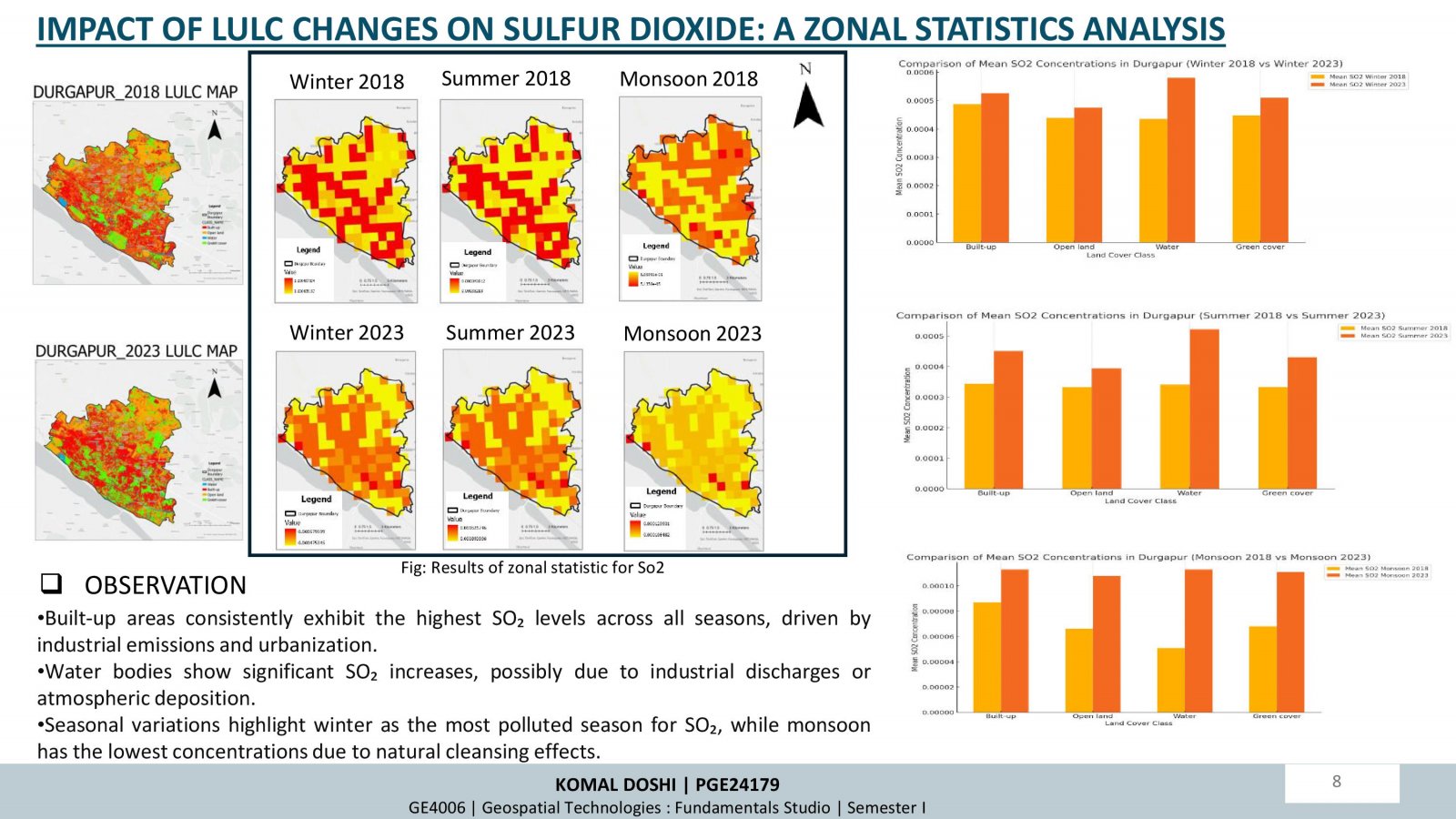
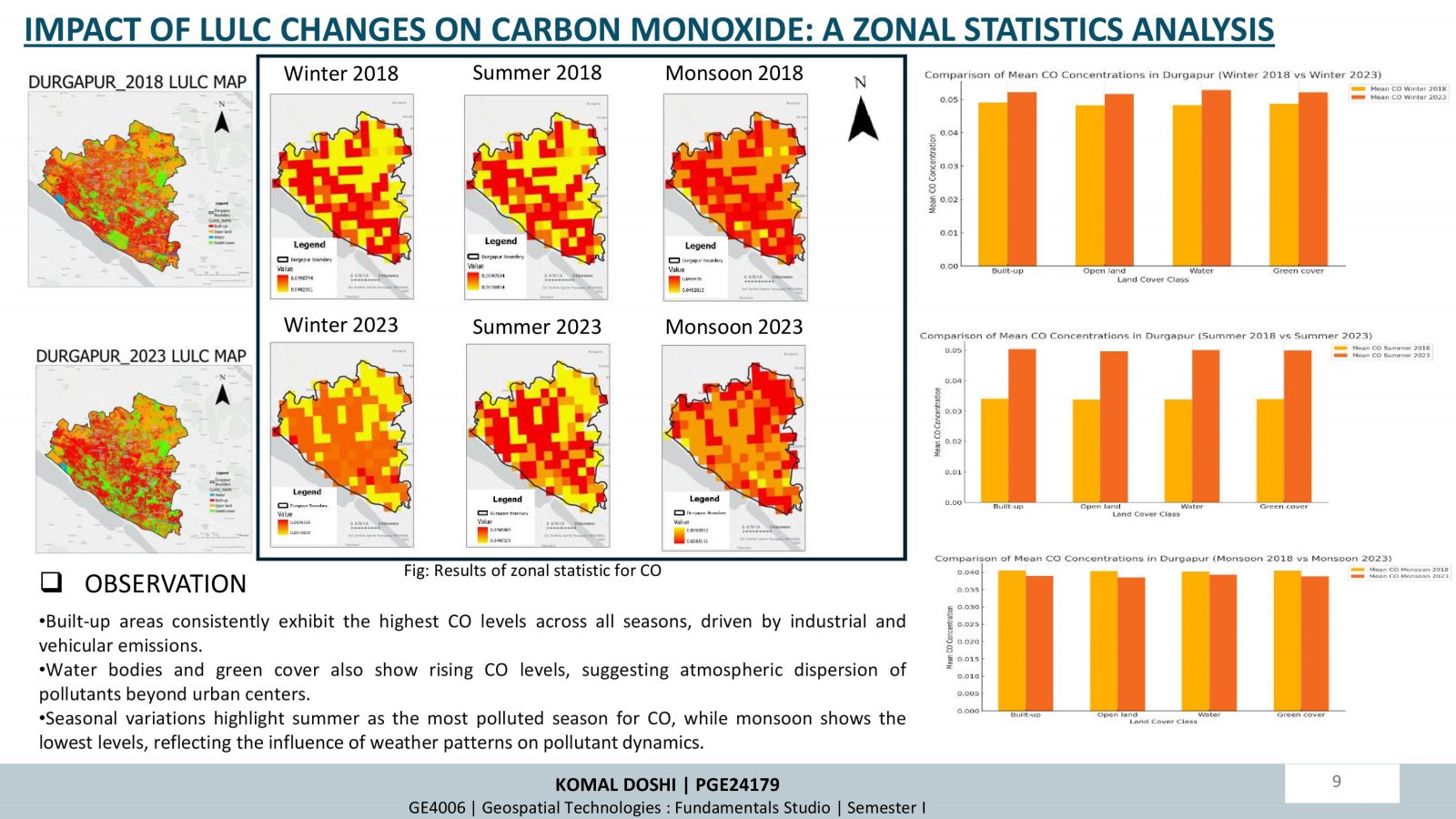
This project examines how changes in land use and land cover (LULC) over time influence air quality, focusing on Durgapur, India. Using satellite data (Sentinel-5P and Sentinel-2A) and supervised classification techniques, the study analyzed LULC changes and their correlation with air pollutants (NO2, SO2, CO) between 2018 and 2023. Key findings highlight increased urbanization and industrialization, leading to higher pollutant levels, especially in built-up areas. Seasonal trends showed winter as the most polluted period. While afforestation efforts improved green cover, pollution impacts persist. The research underscores the importance of sustainable planning and environmental policies to mitigate urbanization effects.