Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
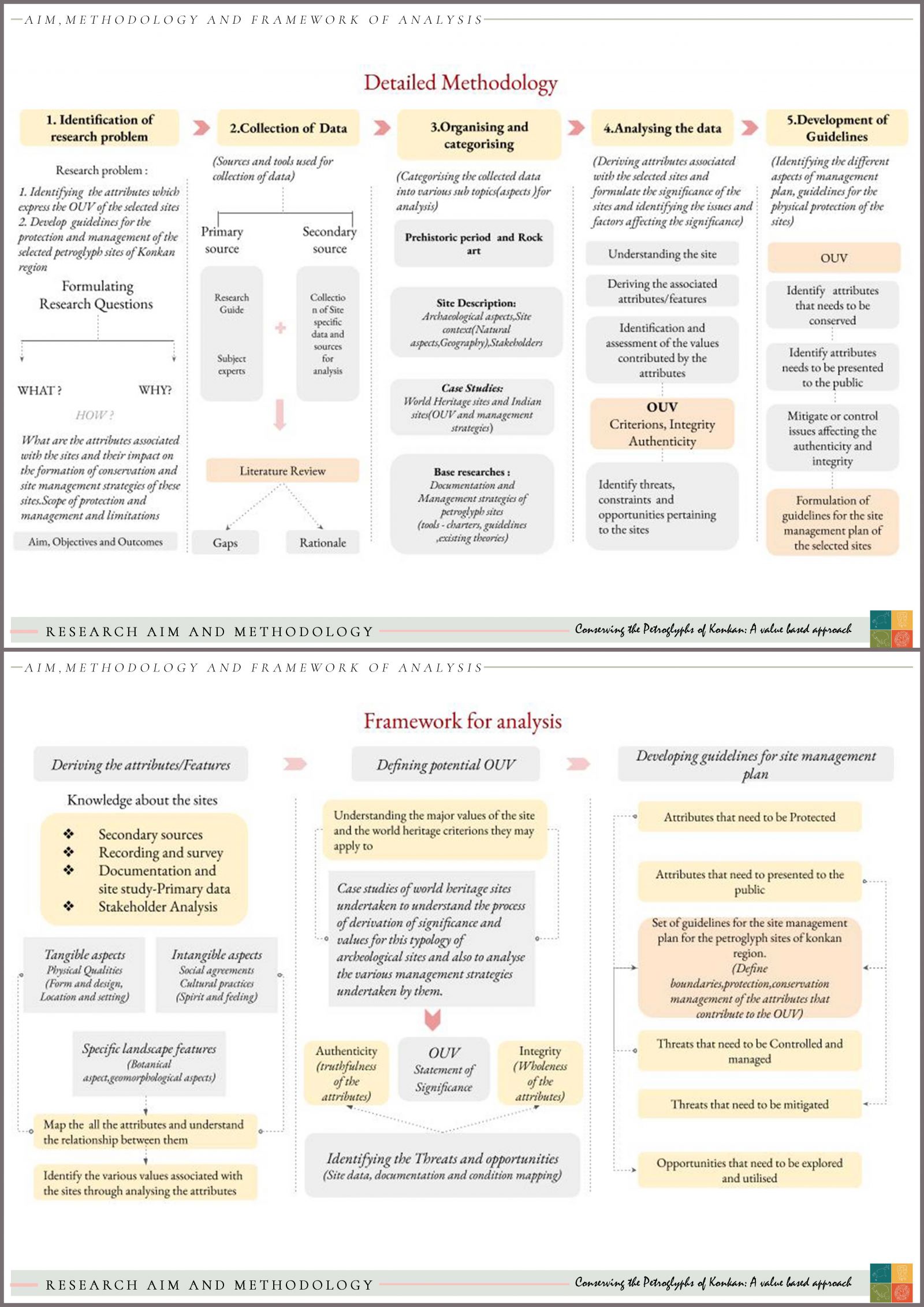
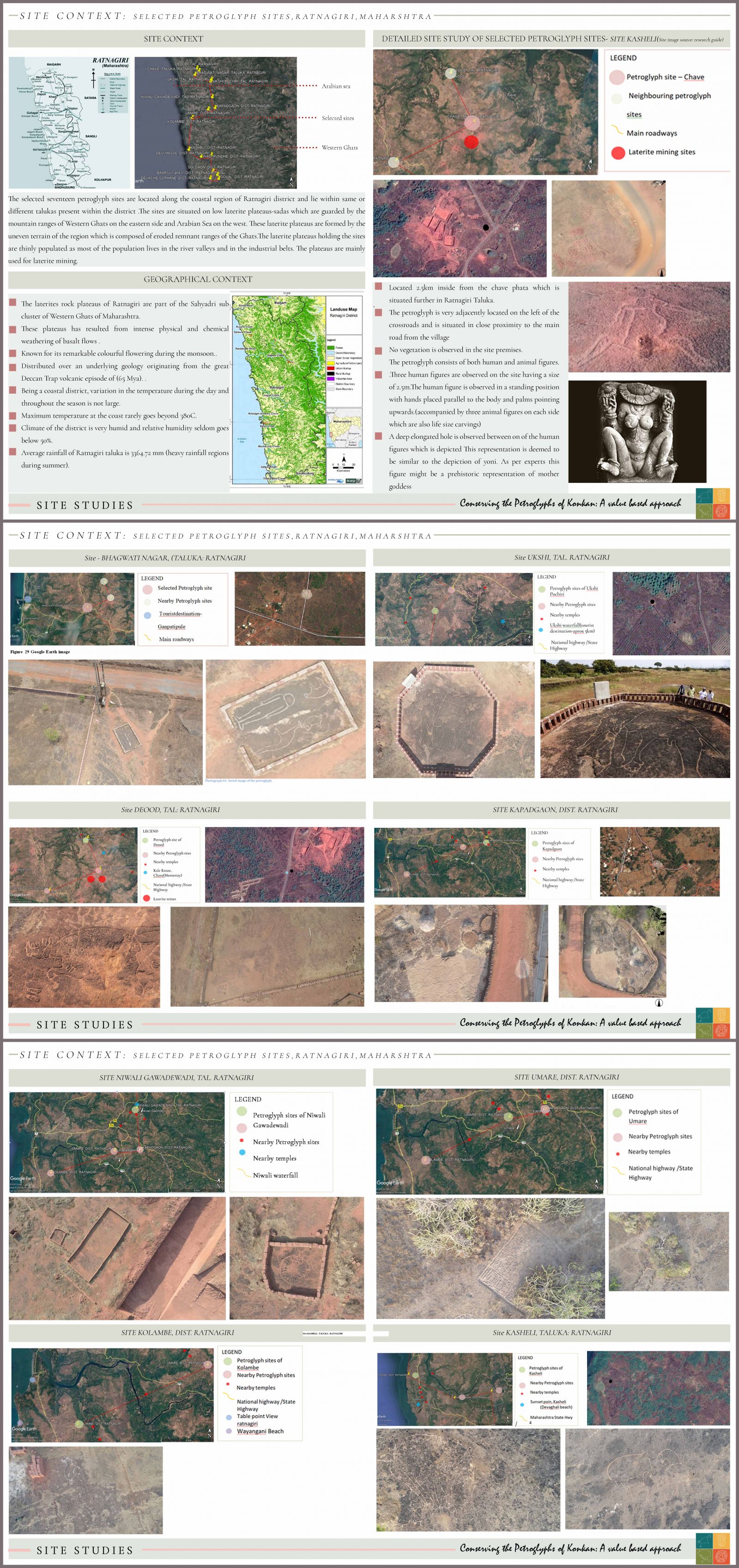
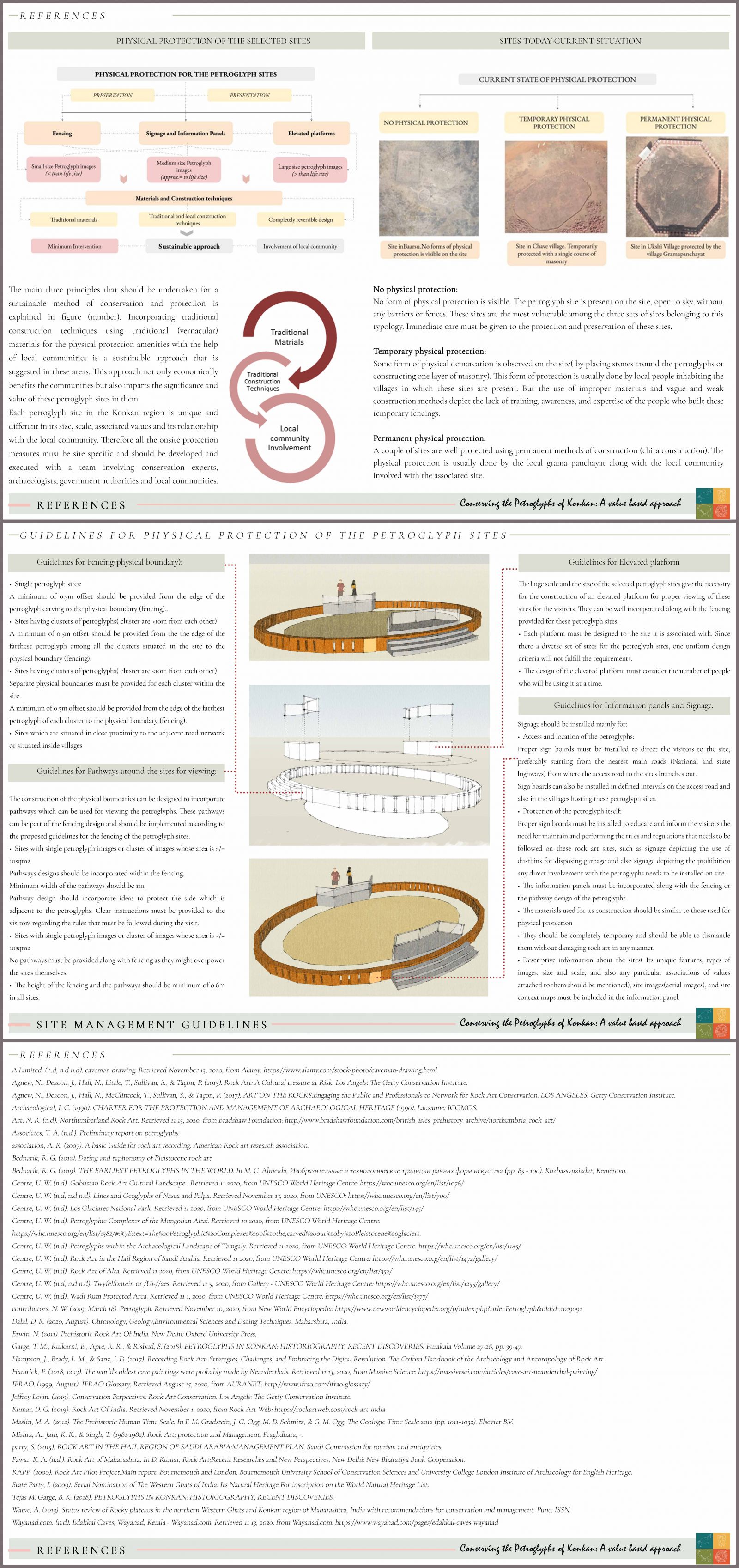
The recent discovery of petroglyphs sites in the district of Ratnagiri in Maharashtra has not only become one of the first known evidences of the presence of human civilization in the upper Paleolithic time period (around 10,000 years ago)in Maharashtra but also contain records ,that might decipher details about the cultural and spiritual orientation of their creators. Yet these rock carvings currently lie in a vulnerable stage severely threatened by the man made and natural impacts affecting the sites both directly and indirectly. This leads to the necessity to conserve and physically protect these sites from further damage. Therefore the aim of the research was to derive and further justify the significance of these petroglyph sites, identify the threats, constrains and opportunities associated with them and further formulate guidelines for the conservation and preservation of these rock art sites A pilot study of 17 petroglyph sites in the district of Ratnagiri was conducted which helped in developing the significance of the sites with diverse set of attributes and associated values.. The guidelines for physical protection and documentation of the selected sites were formulated from the above inferences and analysis. They remain two of the six identified aspects of management plan for the petroglyph sites. A detailed formulation of guidelines and further polices of all these six aspects will eventually produce an efficient manage plan for these rock art sites. The research has been guided by Tejaswini Aphale(Principle conservation architect and archaeologist-Tejaswini Aphale Associates).To view a five minute elevator pitch of this thesis' research idea(s), please click on the link displayed.
View Additional Work