Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
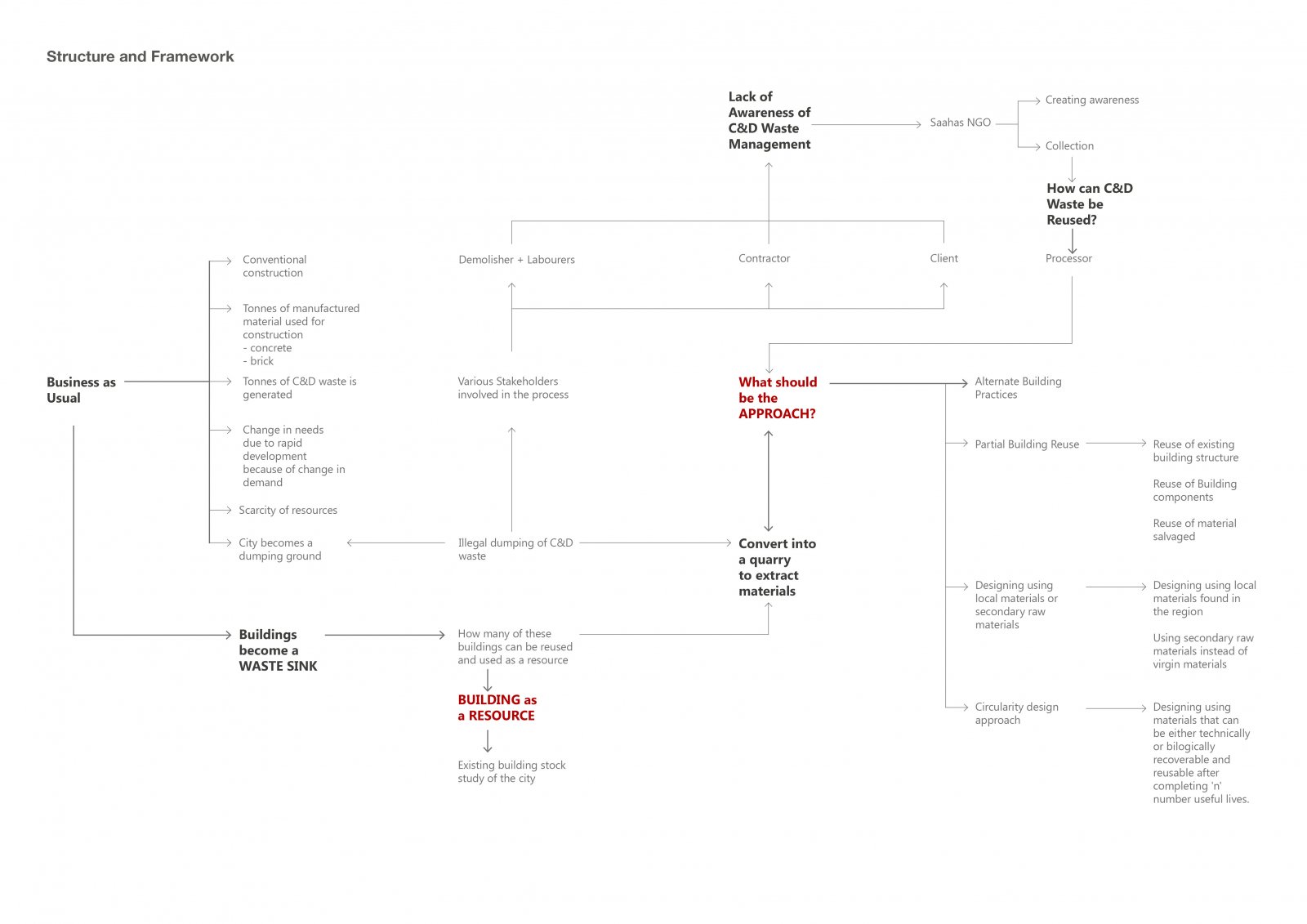
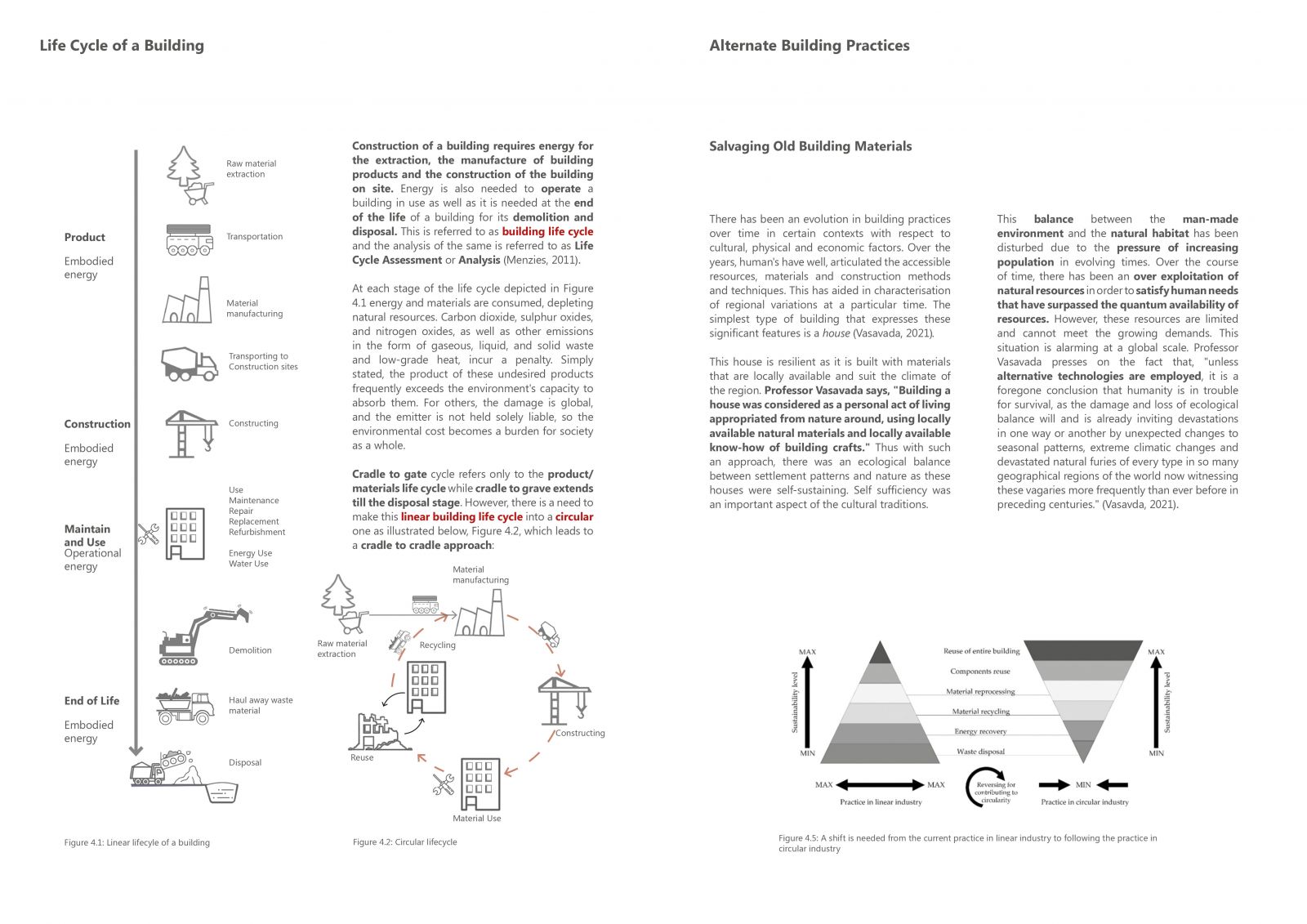
Initiated from ecological concerns with respect to depletion of natural resources due to immeasurable consumption and tonnes of waste being generated by the building construction industry, the research aims to look at ways to reduce the ecological footprint of a building. In evolving times, rapid urbanisation, increasing population growth and changing demands our buildings get older faster before they are due demolition. This results in generation of considerable amount of CDW (construction demolition waste) which is often dumped without actually being useless. This way a potential resource goes waste without serving its purpose to the fullest. Thus the research explores the lifecycle of a building and its materials along with studying the impact and footprint of buildings and their materials. Moreover, remodelling and reuse of C&D Waste is highlighted upon.
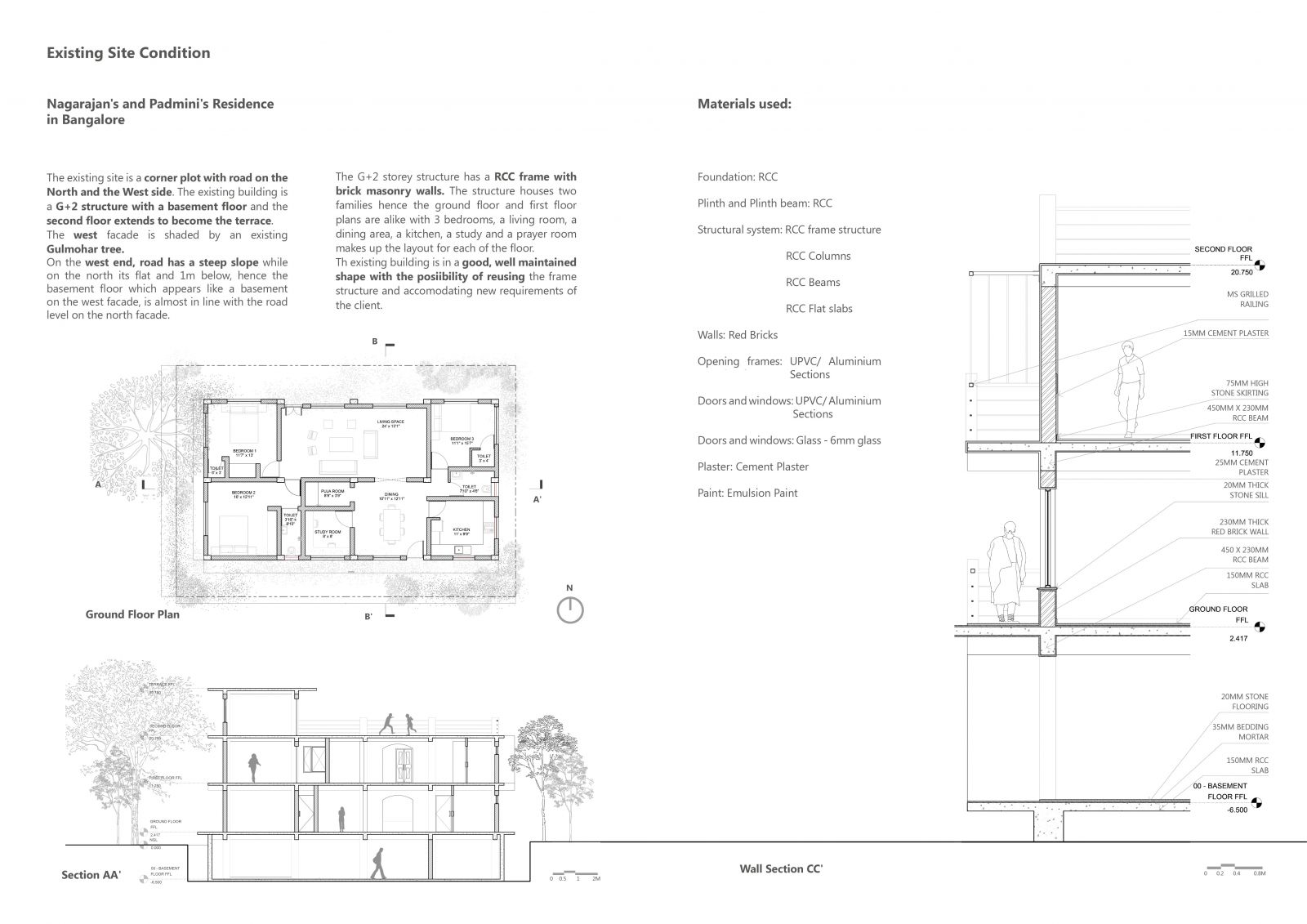
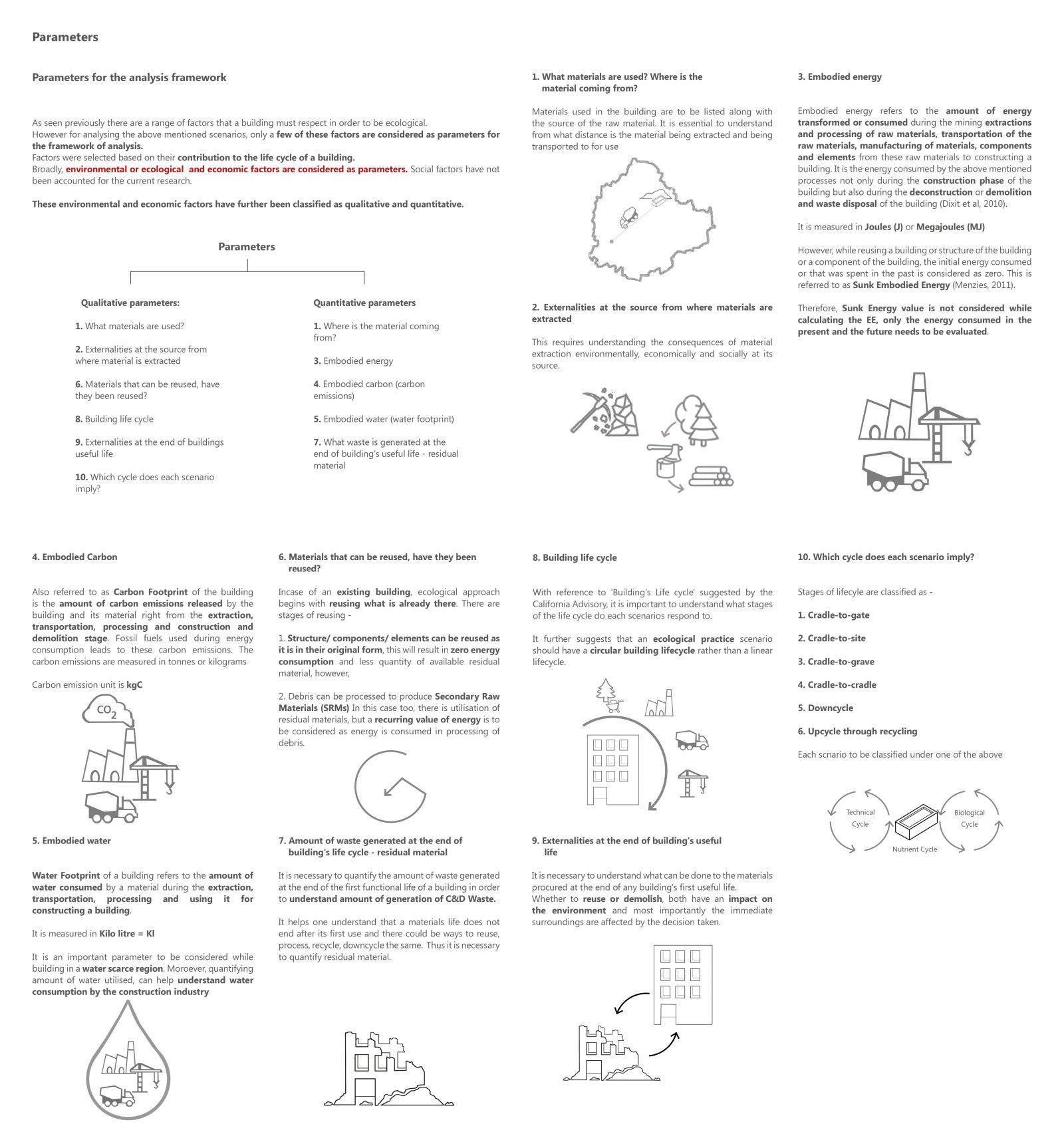
Furthermore, the concept of whether to reuse or rebuild is questioned by developing and analysing a framework to access various scenarios of building ecologically. Framework includes factors that affect a building. Through a comprehensive and comparative analysis of 3 ecological scenarios of constructing against the "Business as Usual" scenario the research aims to address the use of old buildings as a resource for the new ones. Therefore, this alternative approach (3 scenarios of building ecologically) to salvageability will help us restore the ecological balance which as been threatened by our contemporary practices of use and throw.