Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
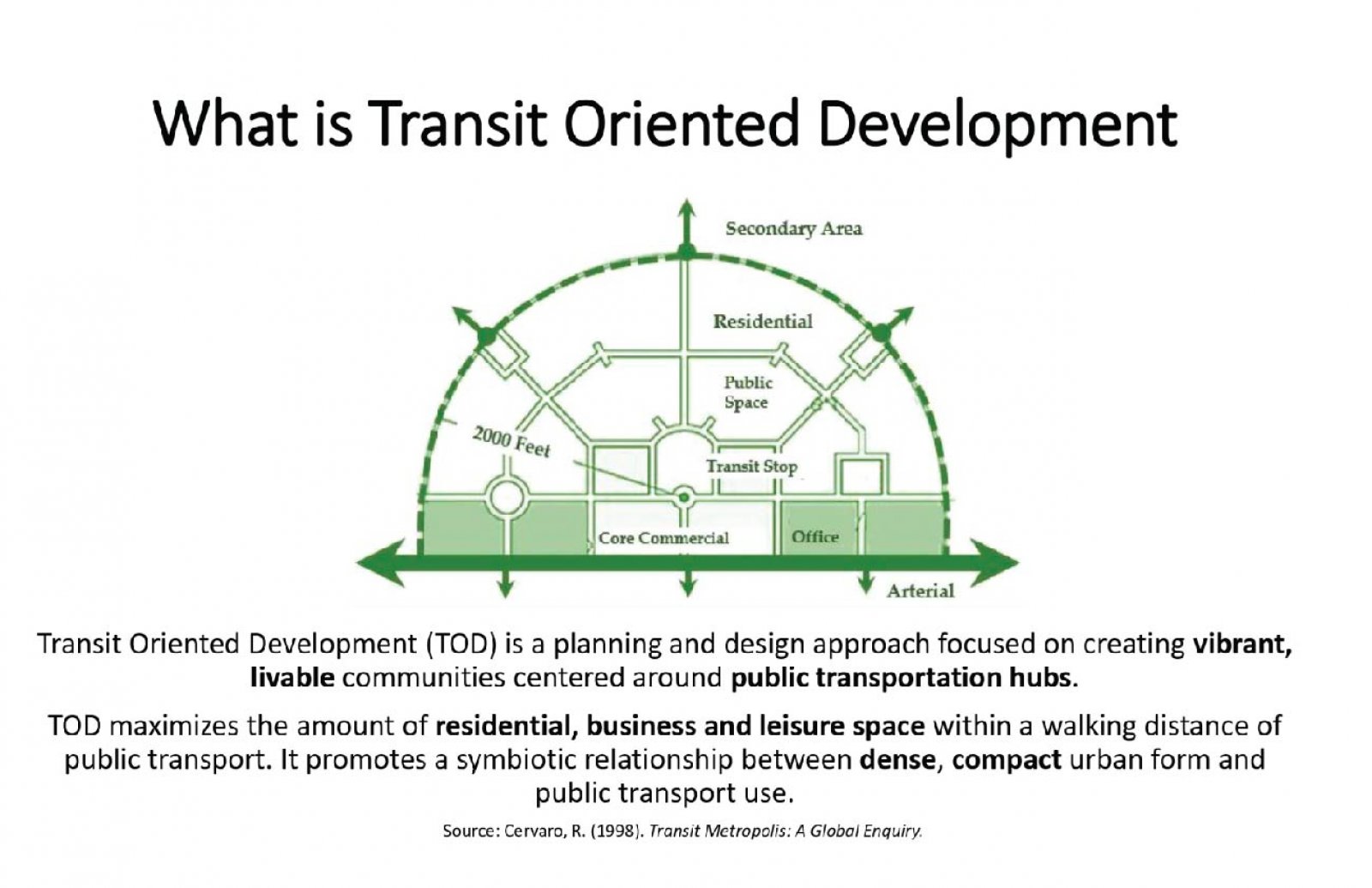
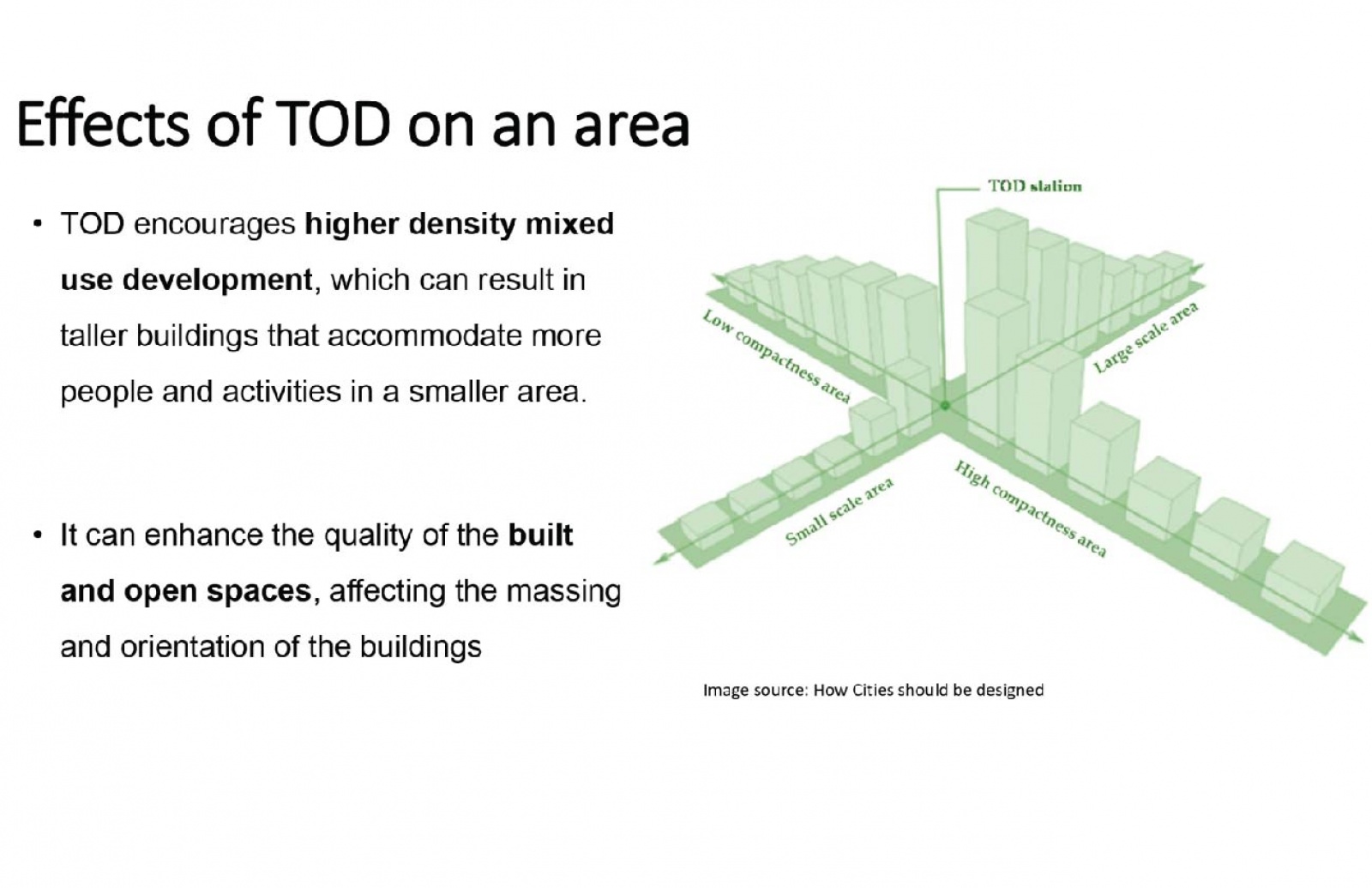
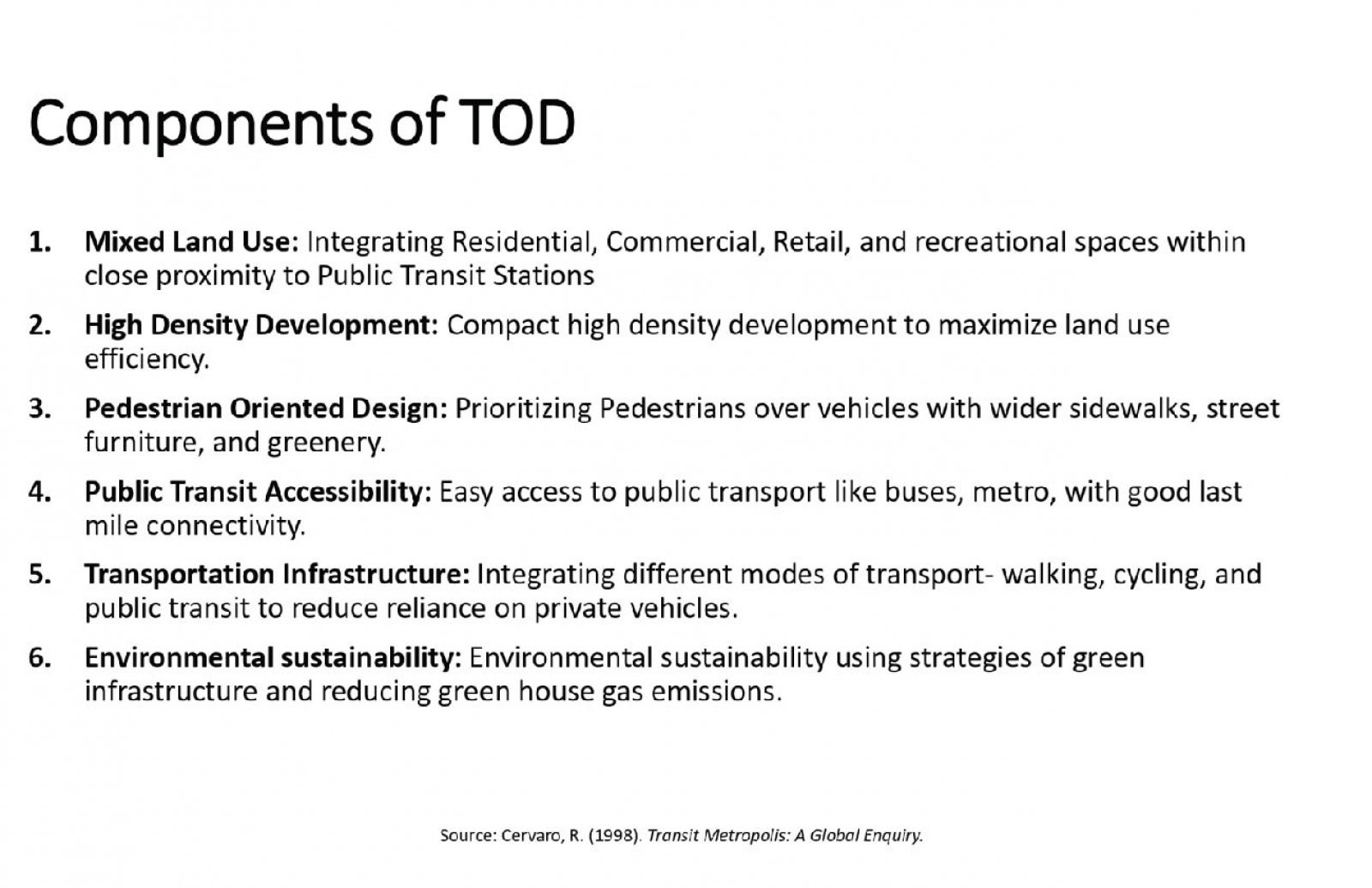
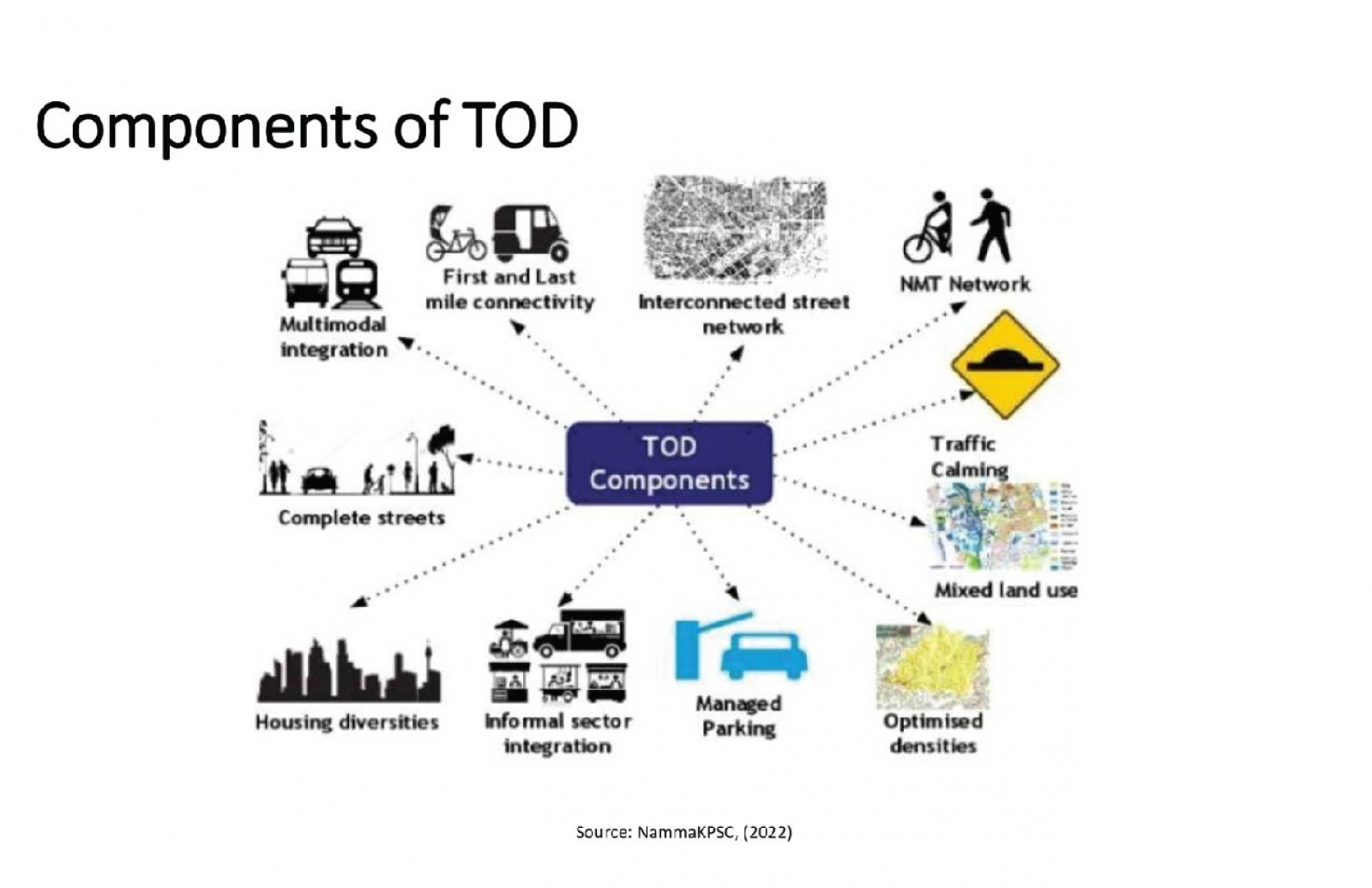
Transit Oriented Development (TOD) addresses challenges like urban sprawl and vehicle dependency. This research evaluates TOD implementation in Delhi and Gurgaon, focusing on their early adoption of TOD principles. Utilizing the 6D’s framework—Density, Diversity, Design, Destination, Distance to Transit, and Demand Management—it assesses both sites. By analyzing these parameters, the study identifies gaps impacting TOD effectiveness. Stakeholder interviews offer insights into challenges such as infrastructure deficits, land use complexities, economic disparities, and funding limitations. Moreover, it underscores how economic and social inequalities influence TOD outcomes, advocating for equitable development strategies. Ultimately, the research aims to deepen understanding of TOD complexities and suggests solutions to advance towards more equitable urban landscapes. By addressing identified gaps, cities can enhance transportation systems, integrate land use, and improve residents' quality of life. These findings are pertinent not only for Delhi and Gurgaon but also for broader urban development strategies, aiding in the creation of more liveable and resilient cities worldwide.