Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
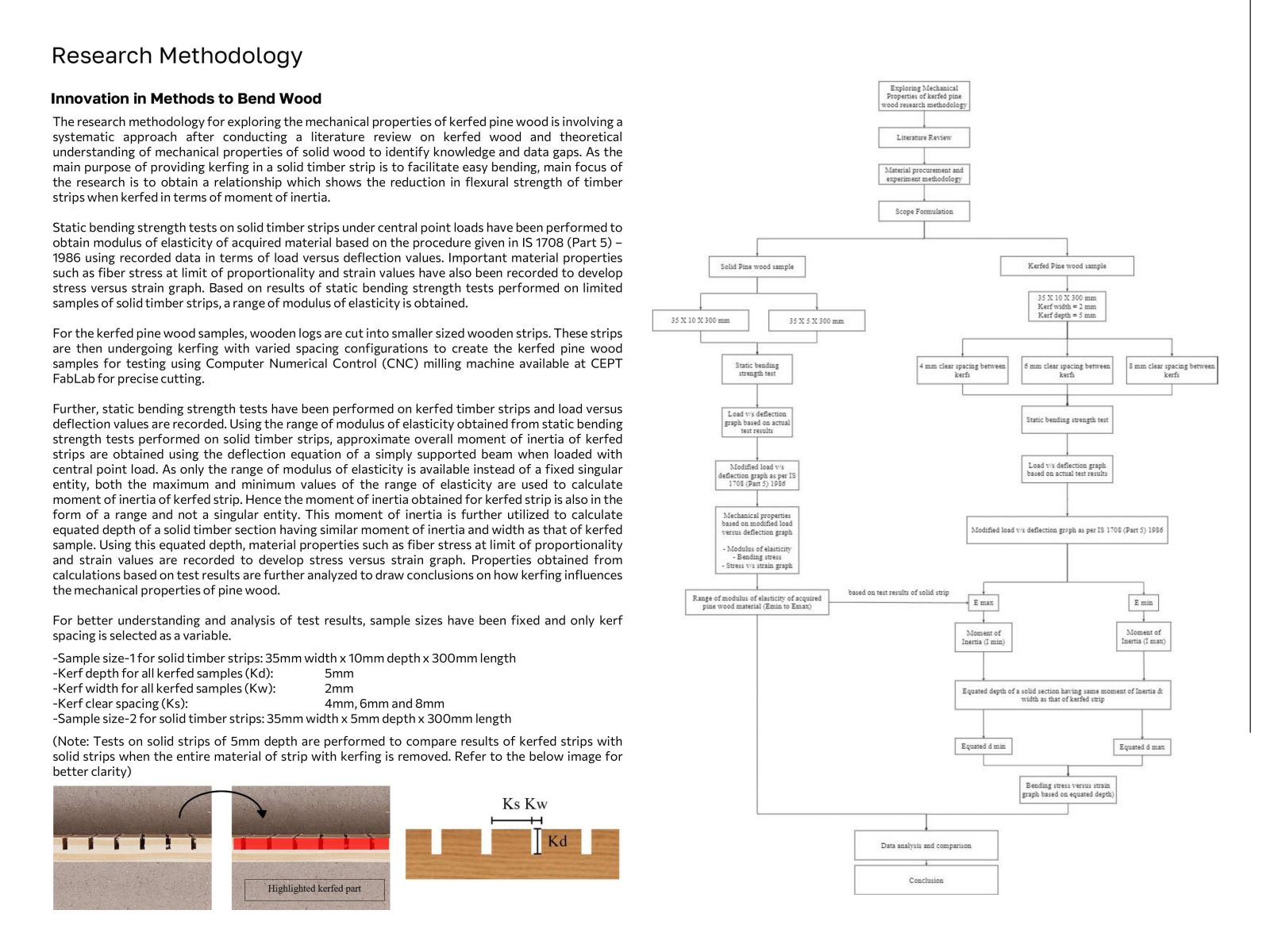
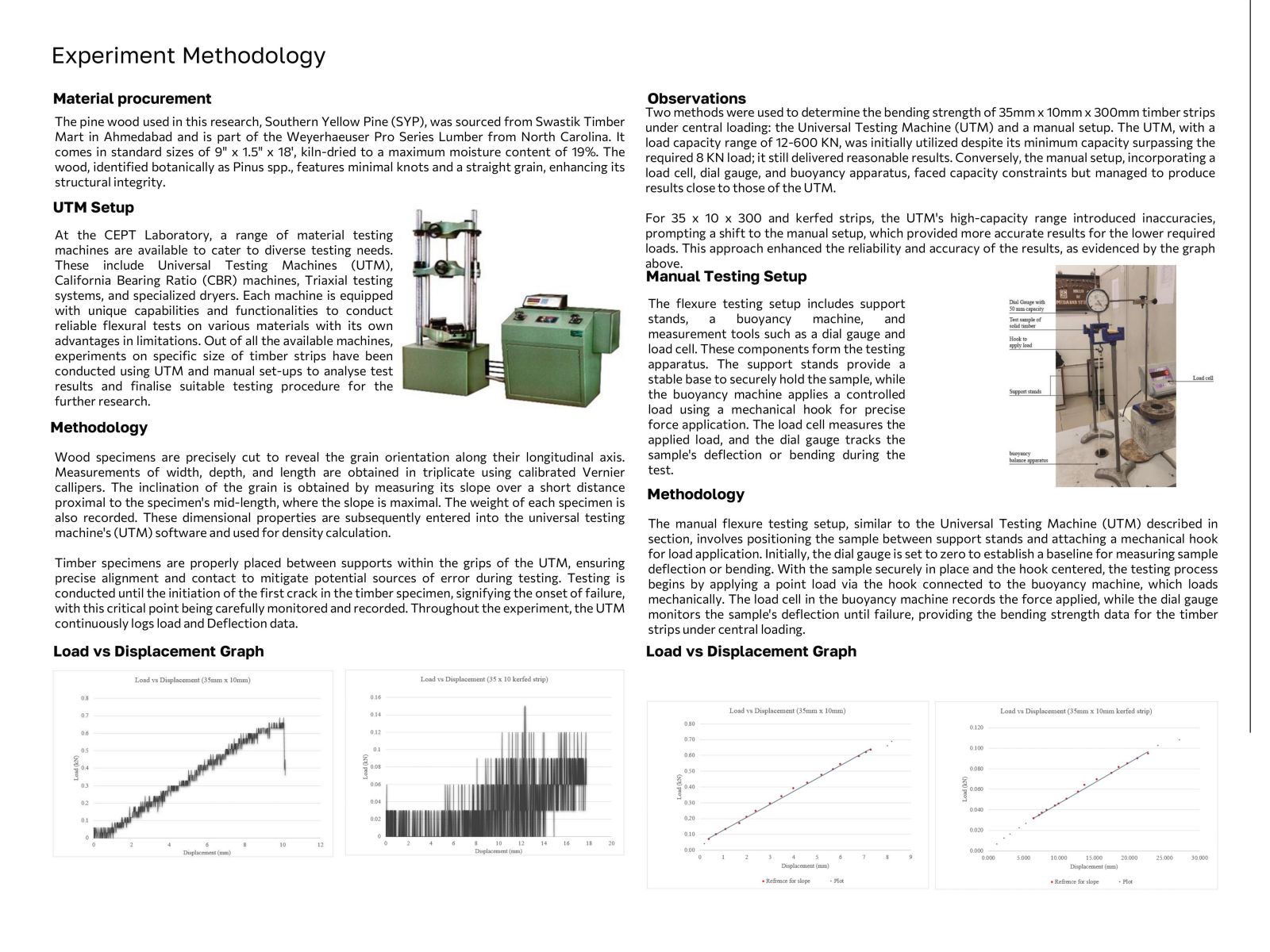
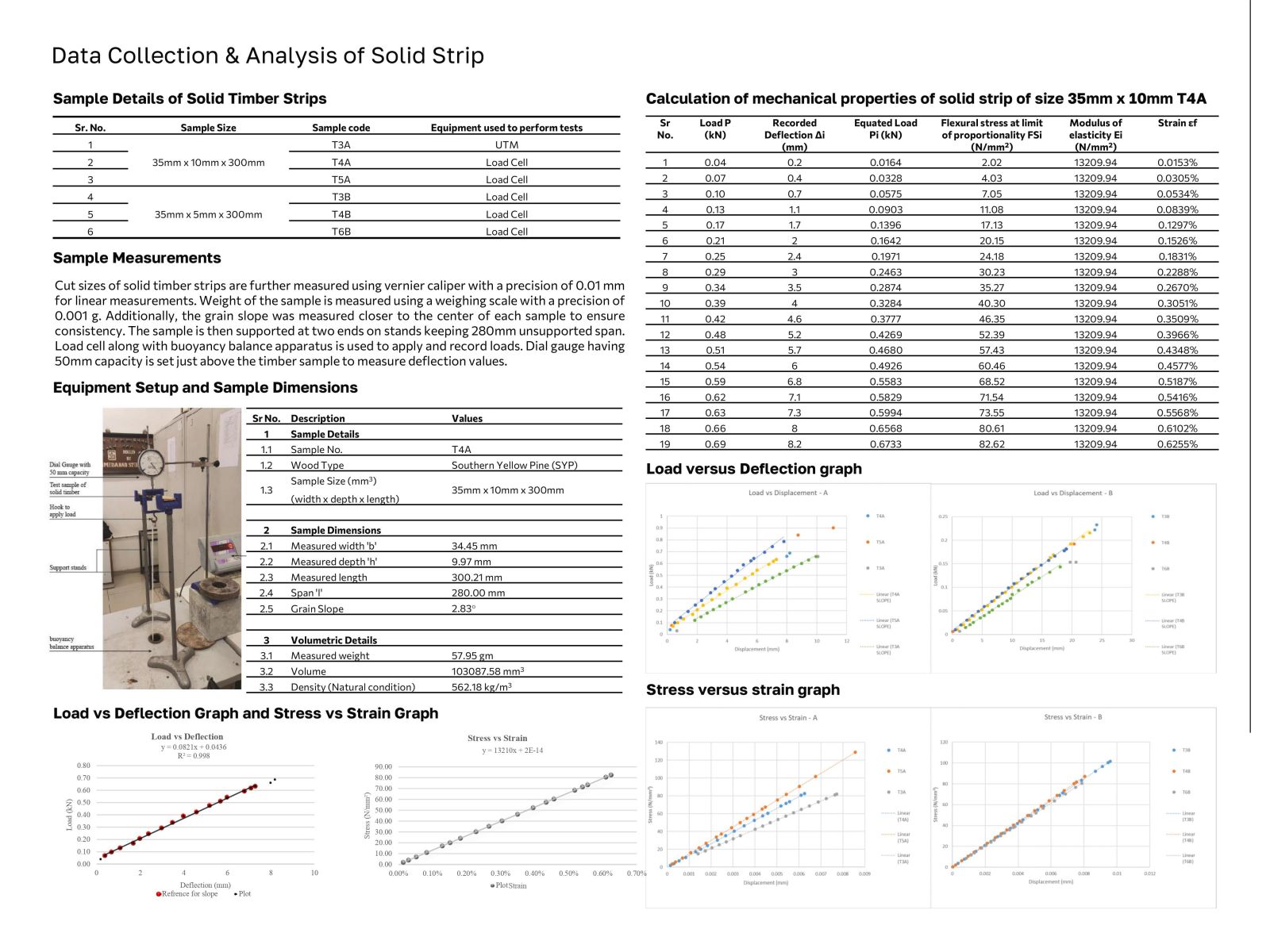
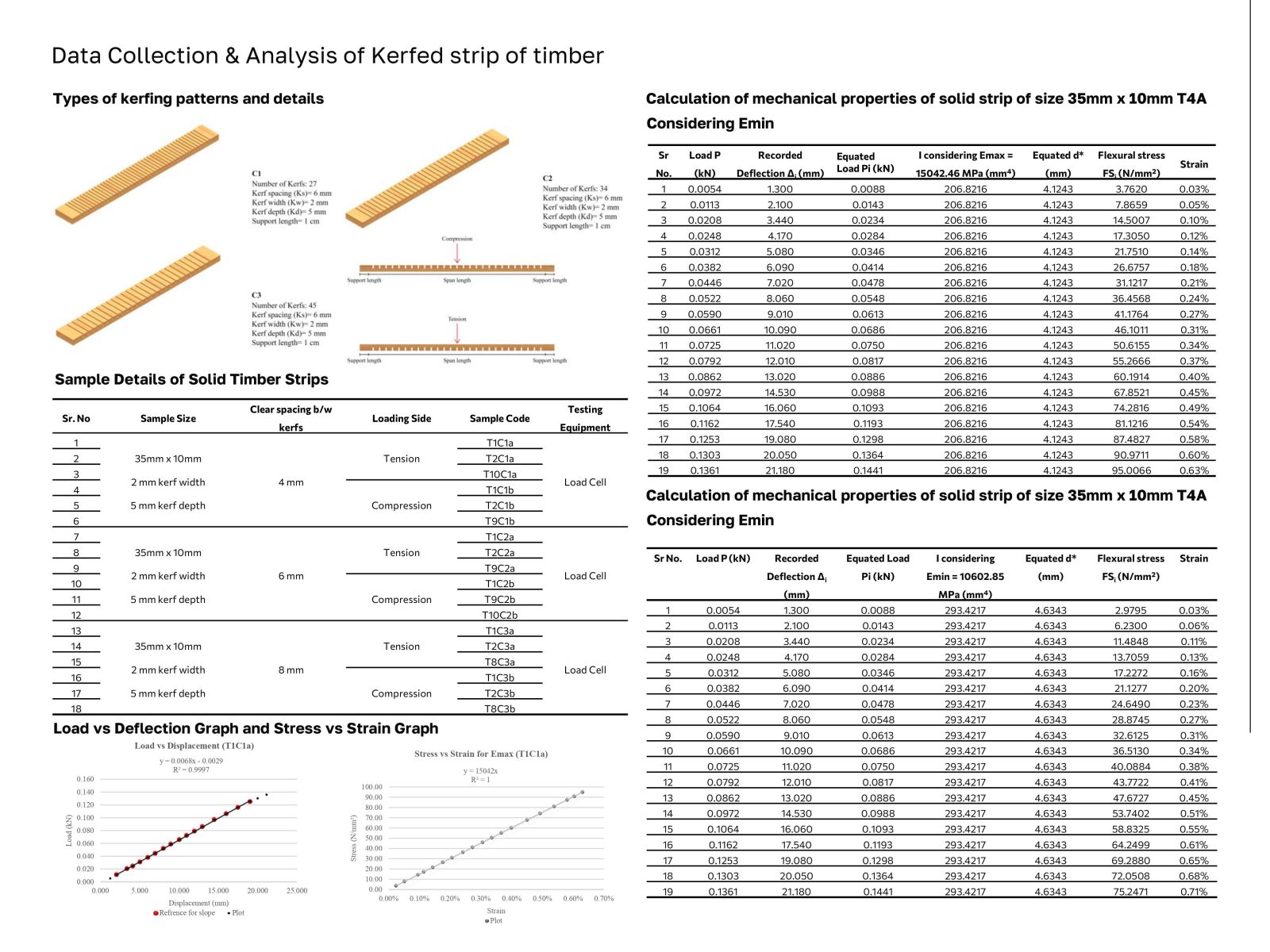
Wood has been a mainstay in construction due to its versatility and sustainability, although its anisotropic nature poses challenges for structural design beyond basic shapes. Innovations such as steam bending and laminating have made it feasible to use wood in curved structures by modifying its directional strength. Techniques like kerfing, which involves cutting slots across the wood grain to increase flexibility, have emerged to address these challenges despite reducing strength and stiffness. This research aims to explore the impact of kerfing on wood's mechanical properties by conducting extensive experiments on pine wood samples, following IS 1708 standards. The study will compare different kerf patterns and their effects on wood behavior under various loading conditions and orientations to provide data and guidelines for kerfing's structural application in curved timber designs.
View Additional Work