Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
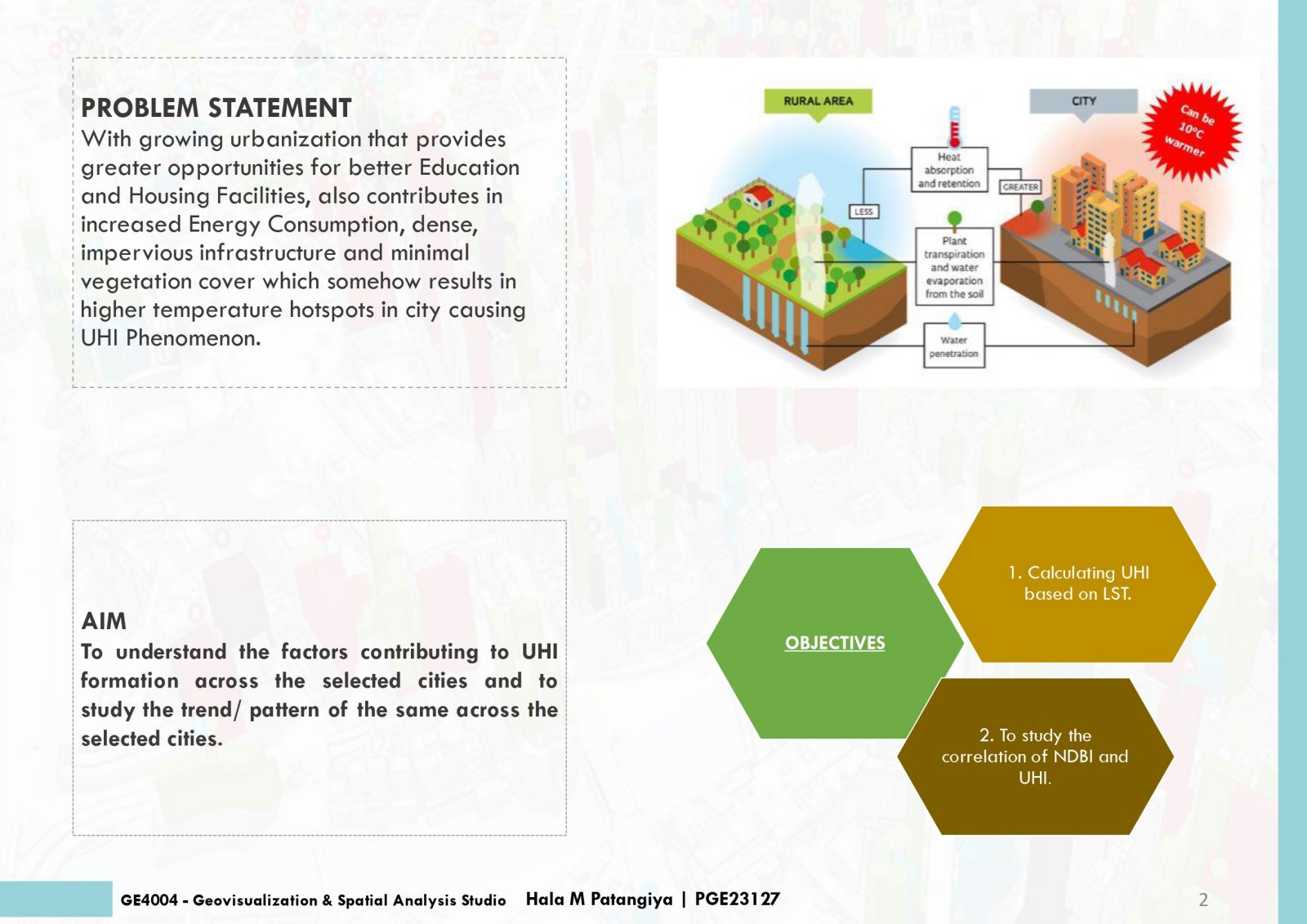
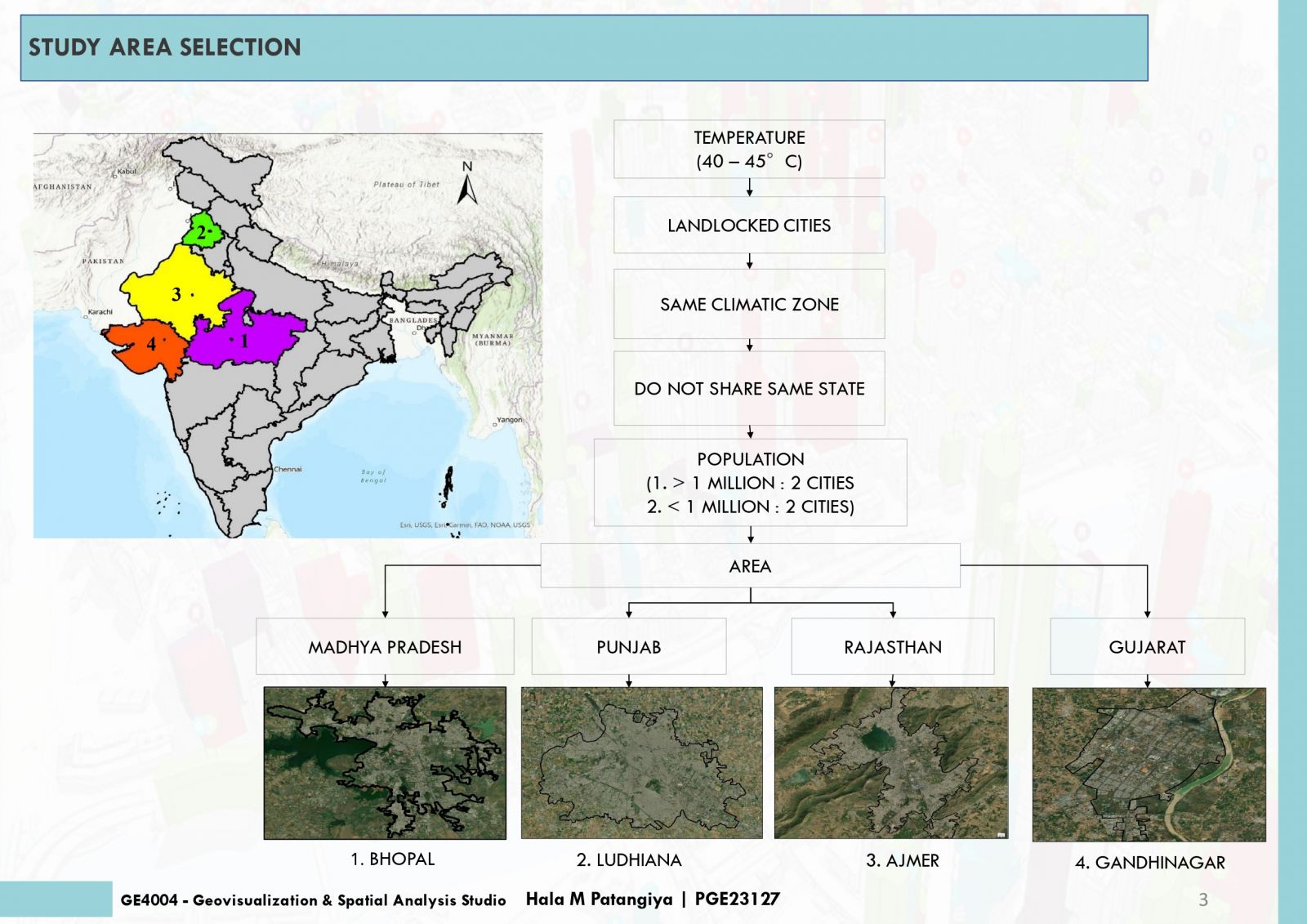
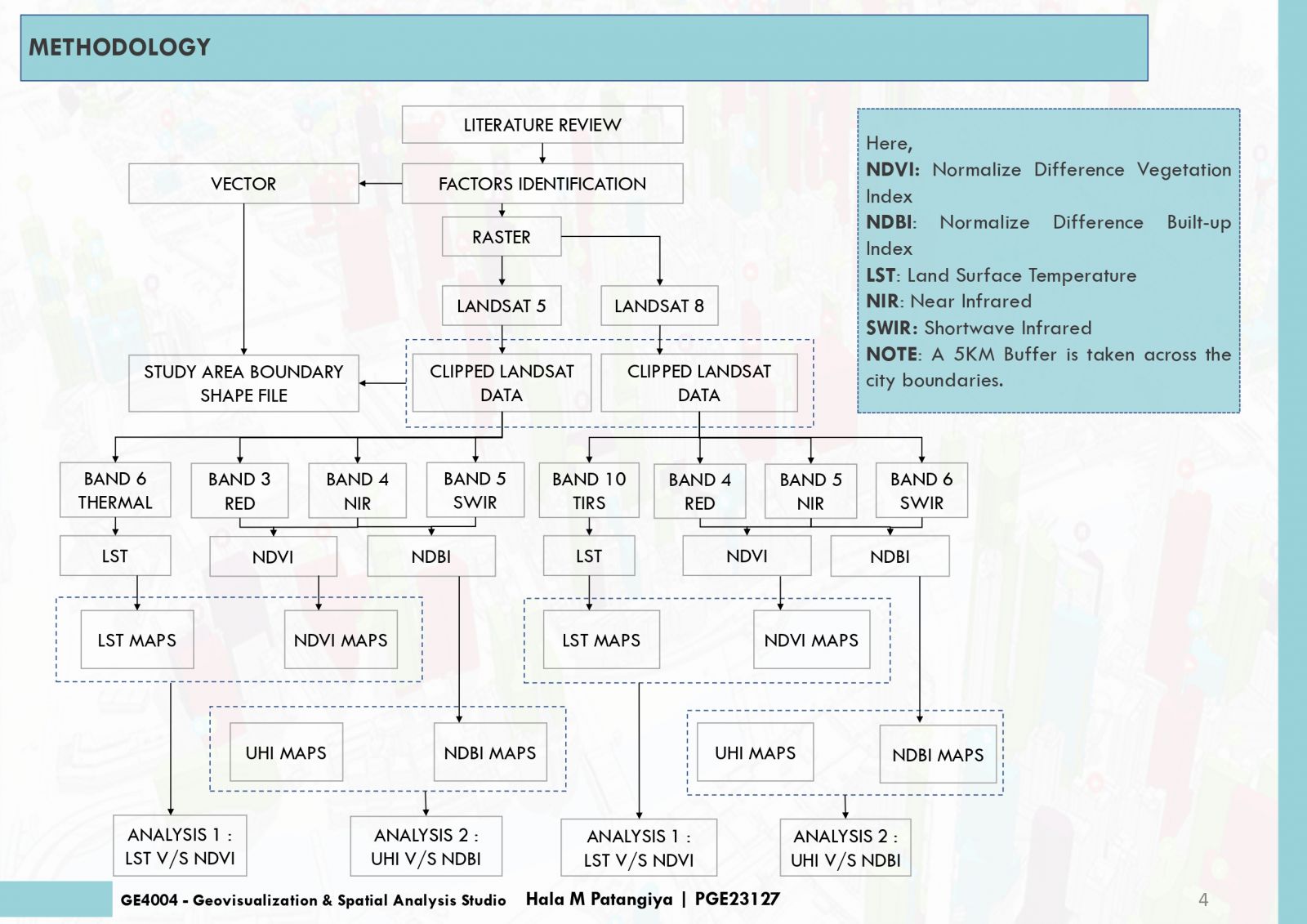
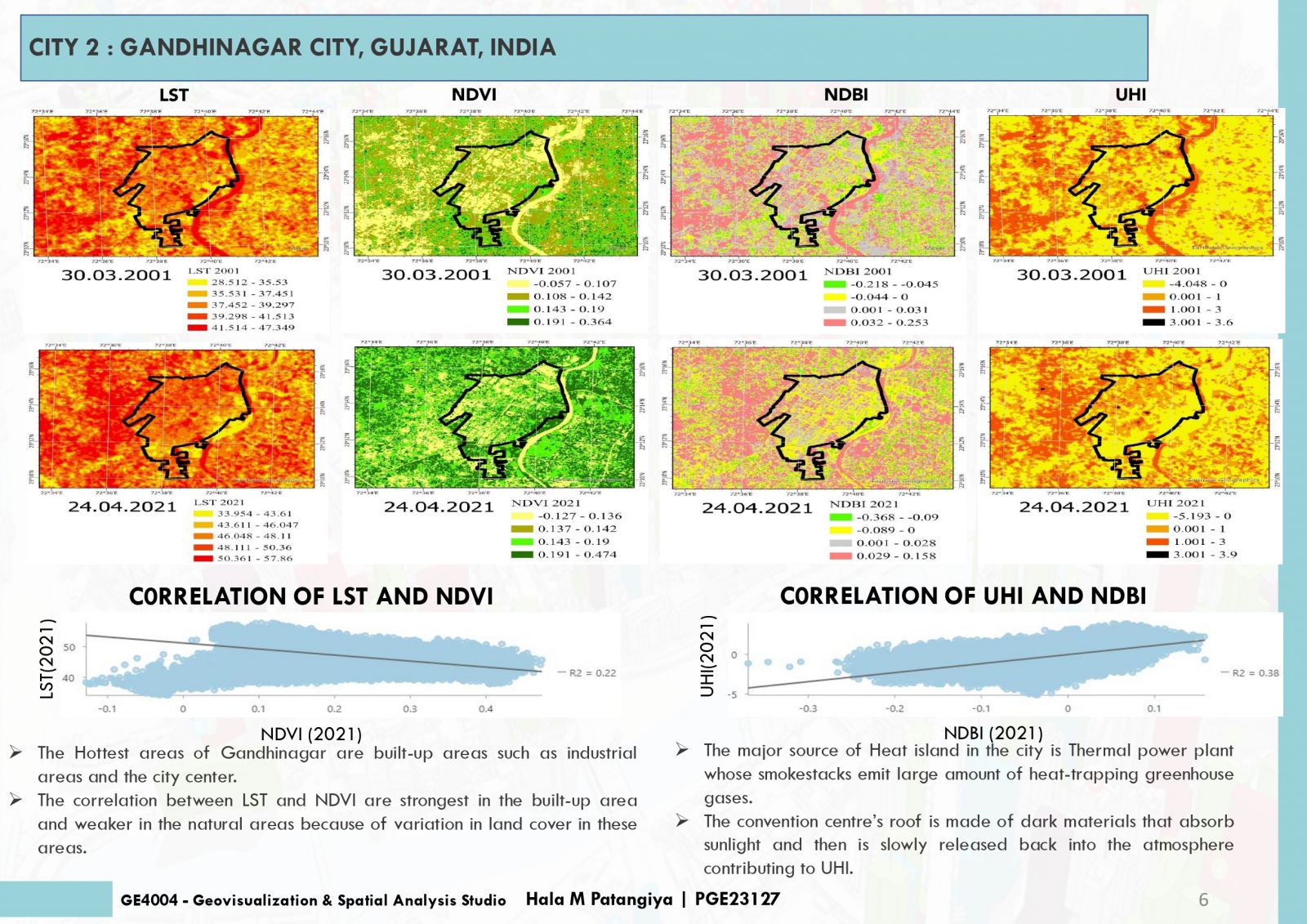
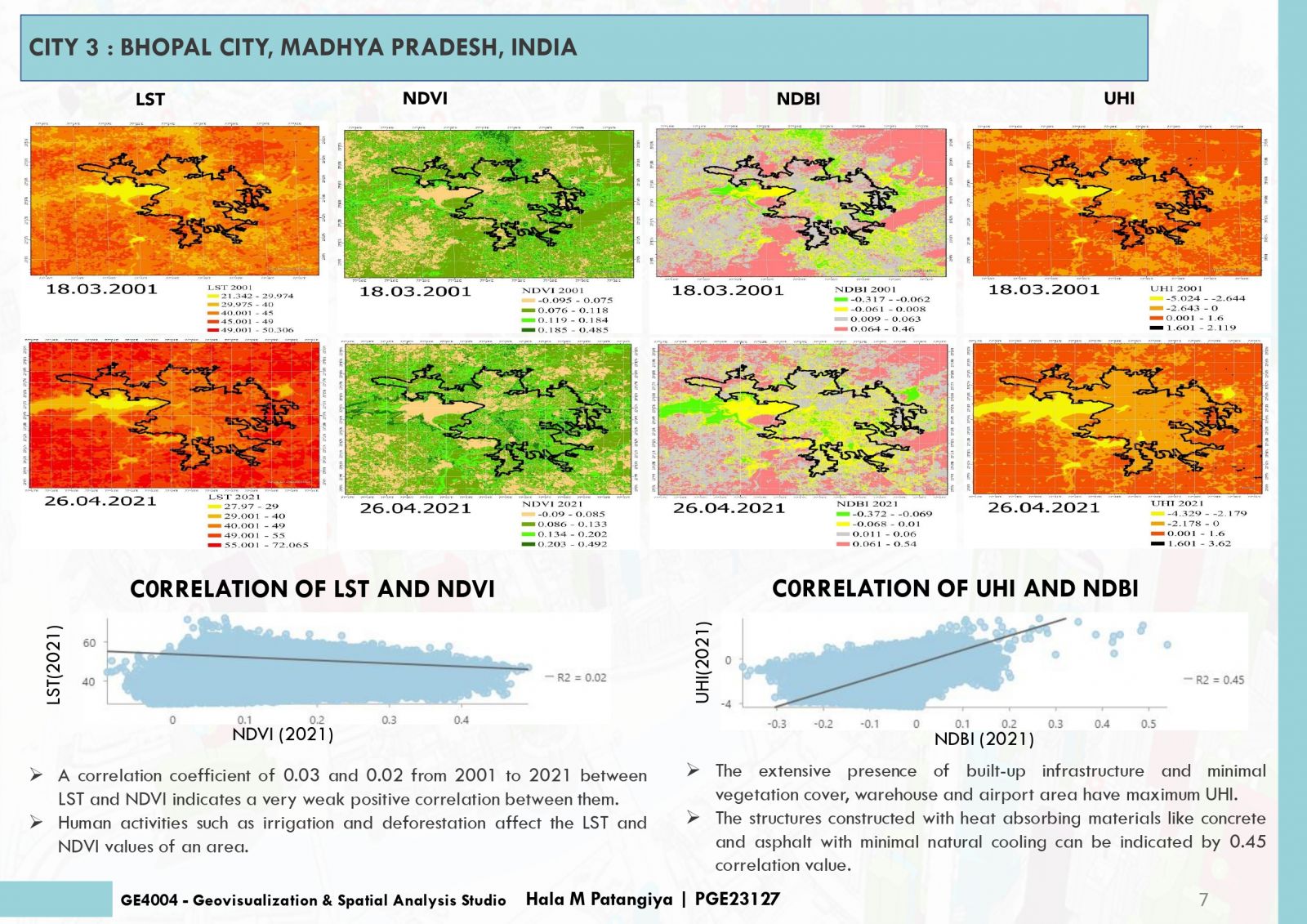
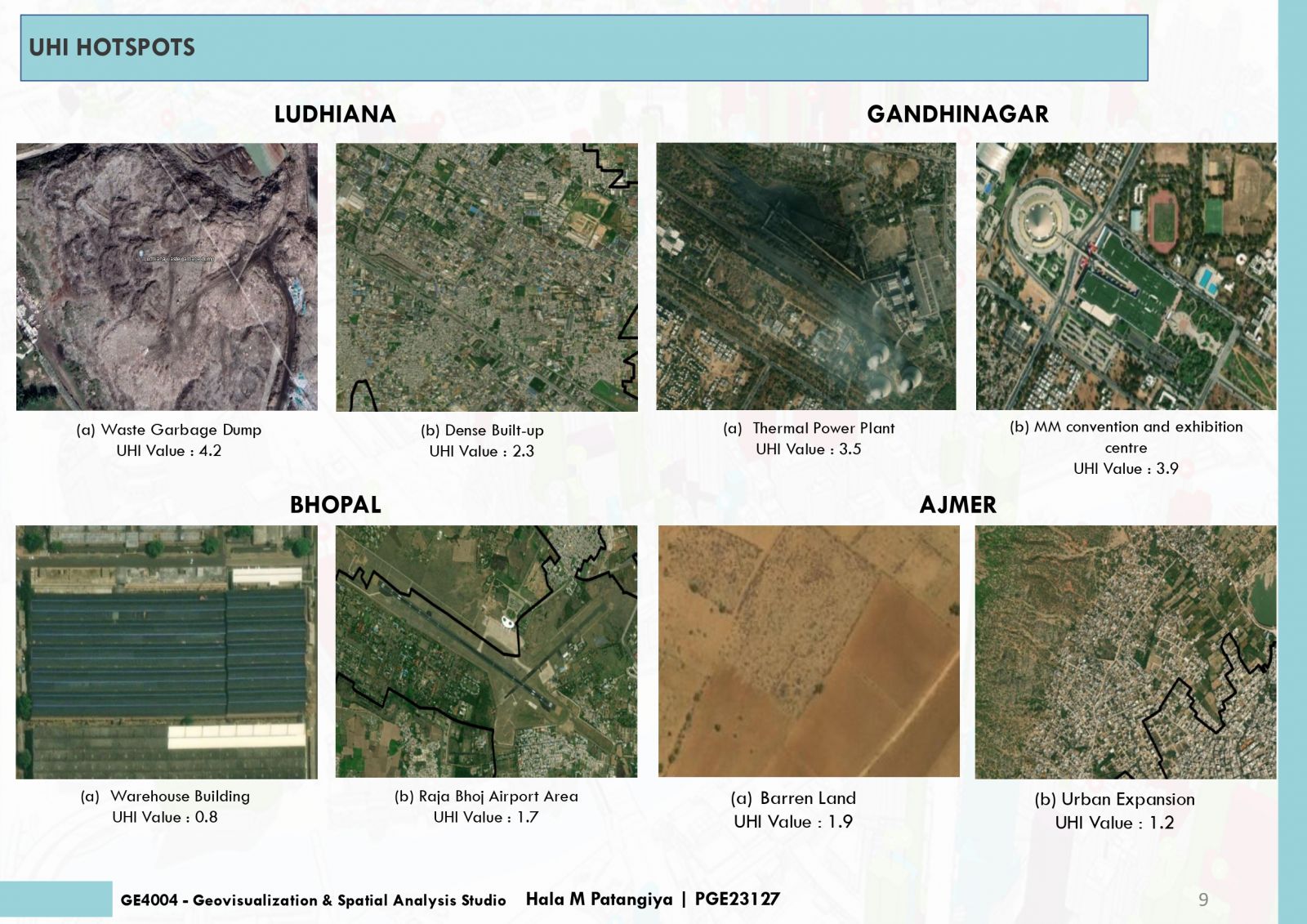
This project endeavors to analyze Land Surface Temperature (LST), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), and Normalized Difference Built-Up Index (NDBI) in urban areas to pinpoint Urban Heat Island (UHI) hotspots. Elevated LST signifies heat retention, while NDVI quantifies green coverage, and NDBI evaluates built-up zones. Correlations between LST, NDVI, NDBI and UHI unveil urban heat patterns. Cities with low NDVI and high NDBI often exhibit intensified UHI effects. Detecting UHI hotspots contributes to sustainable urban planning for climate resilience. The amalgamation of satellite imagery and remote sensing data streamlines comprehensive analyses, empowering informed decisions for UHI impact mitigation and improved urban livability.