Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
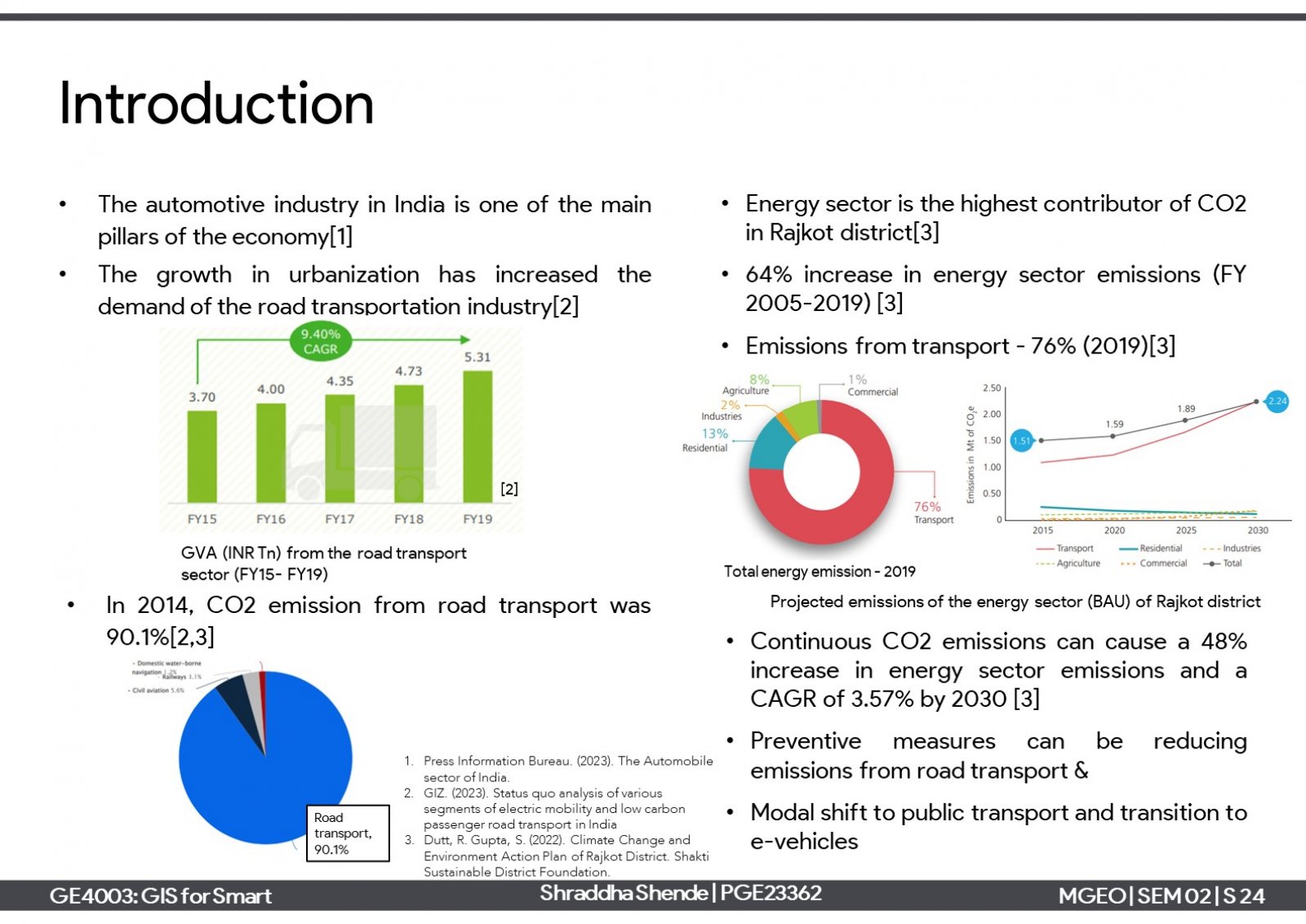
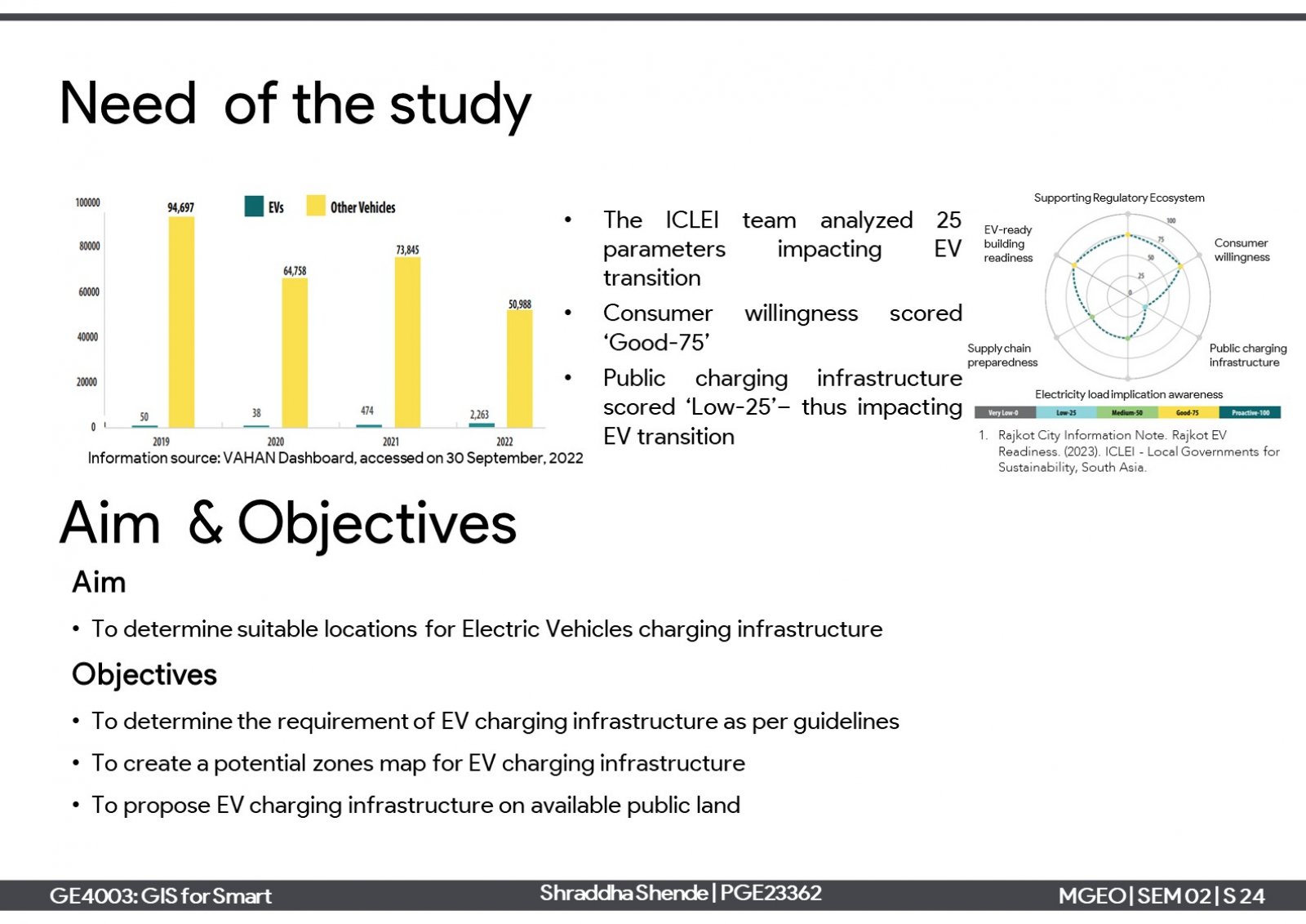
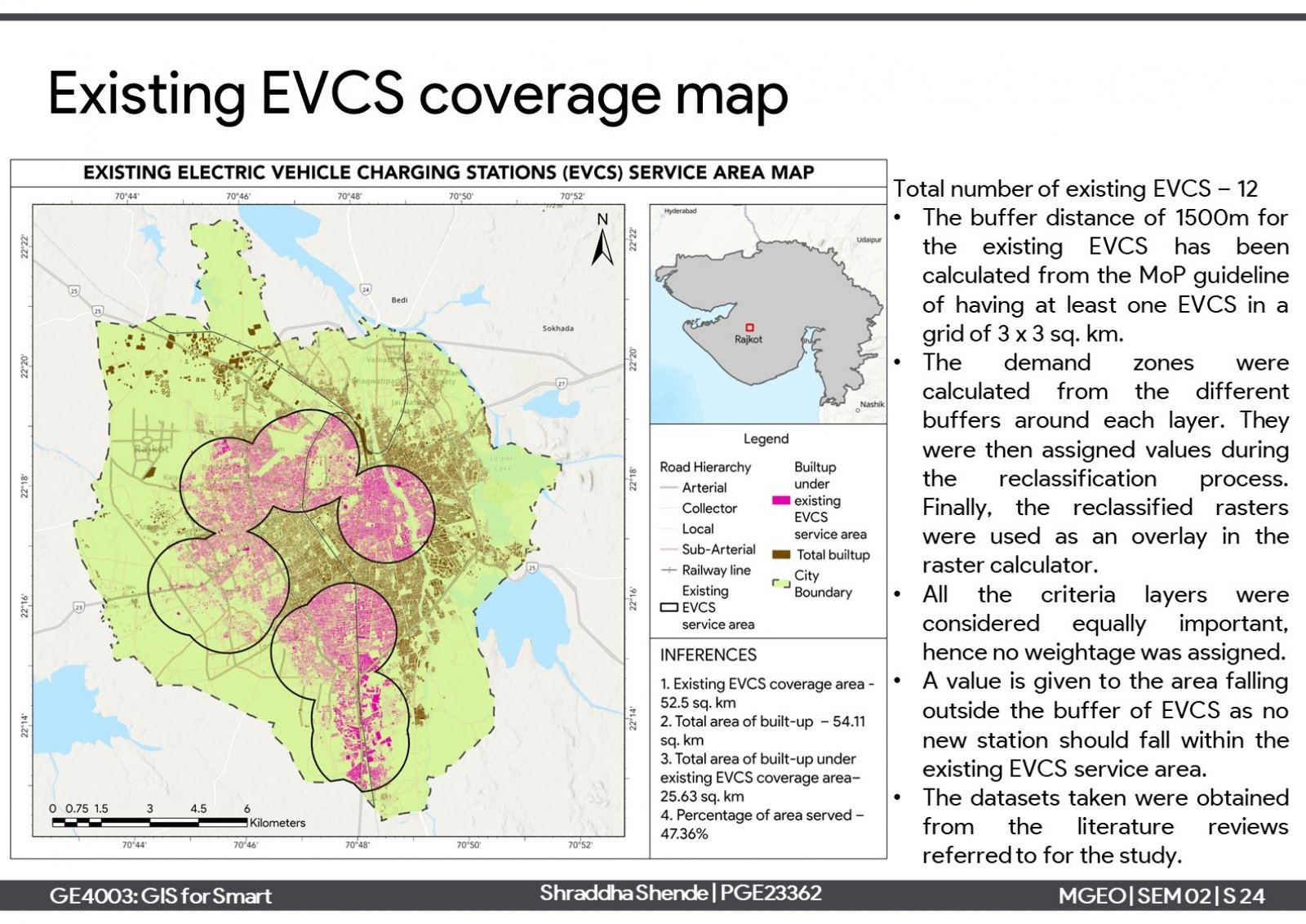
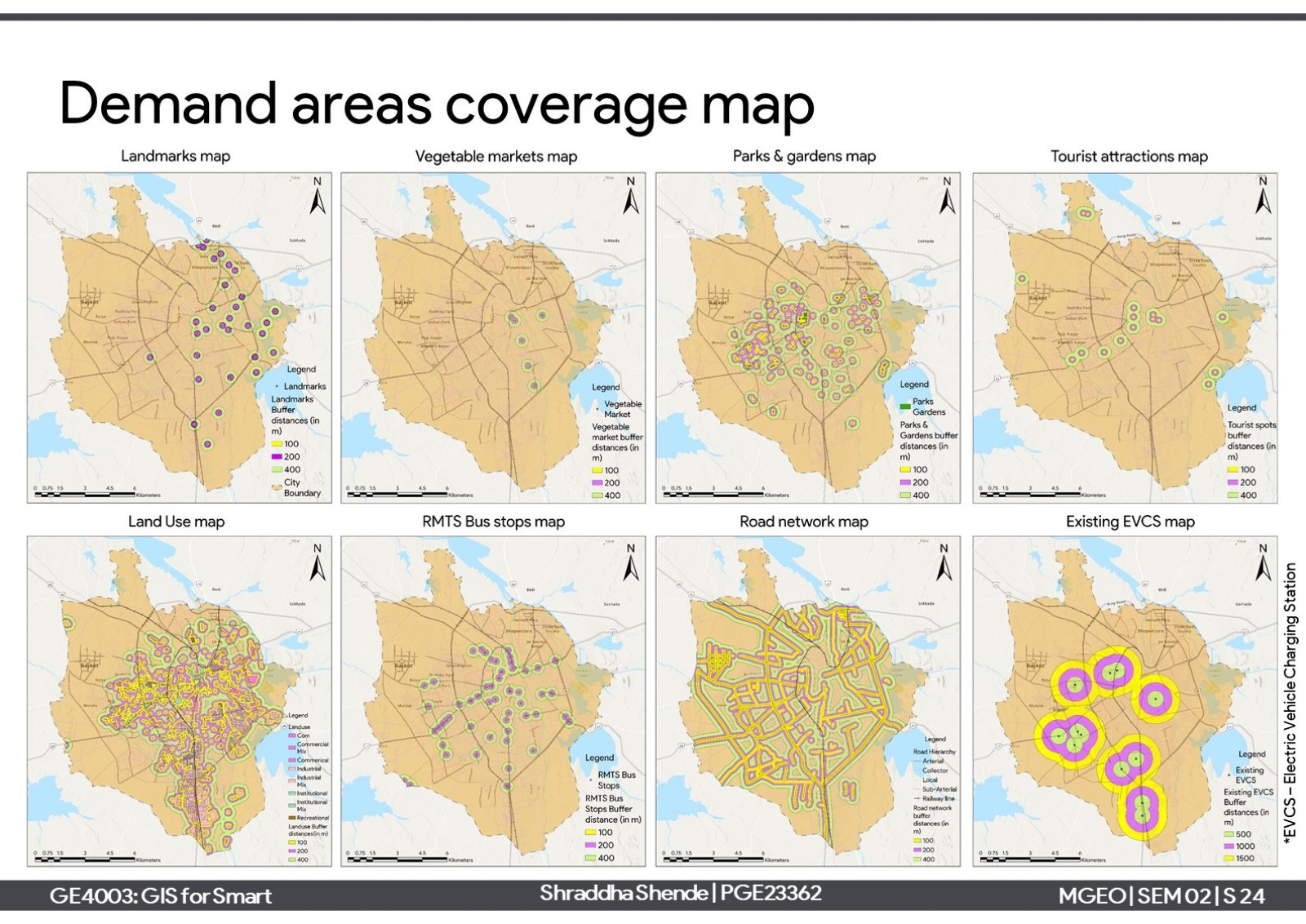
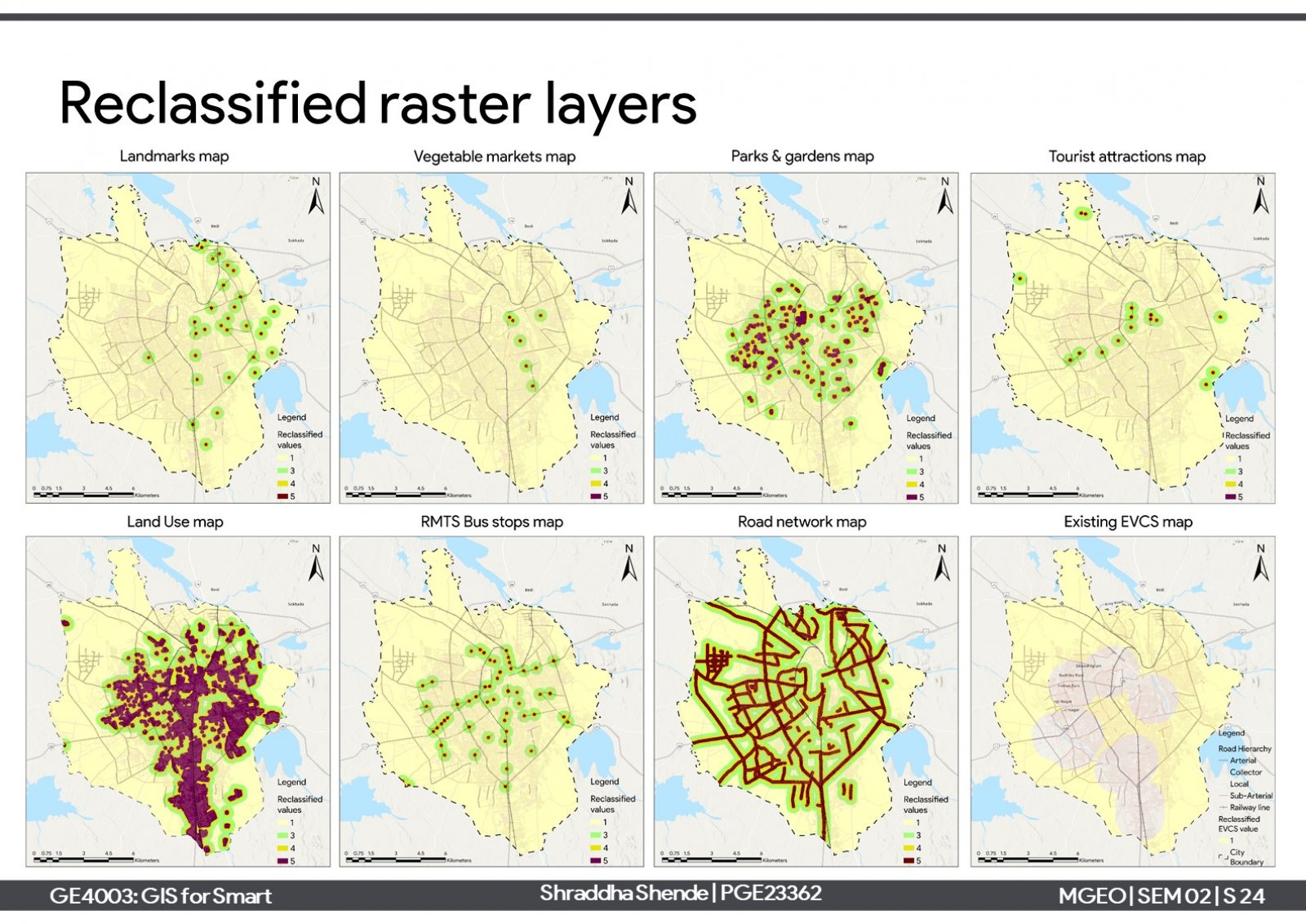
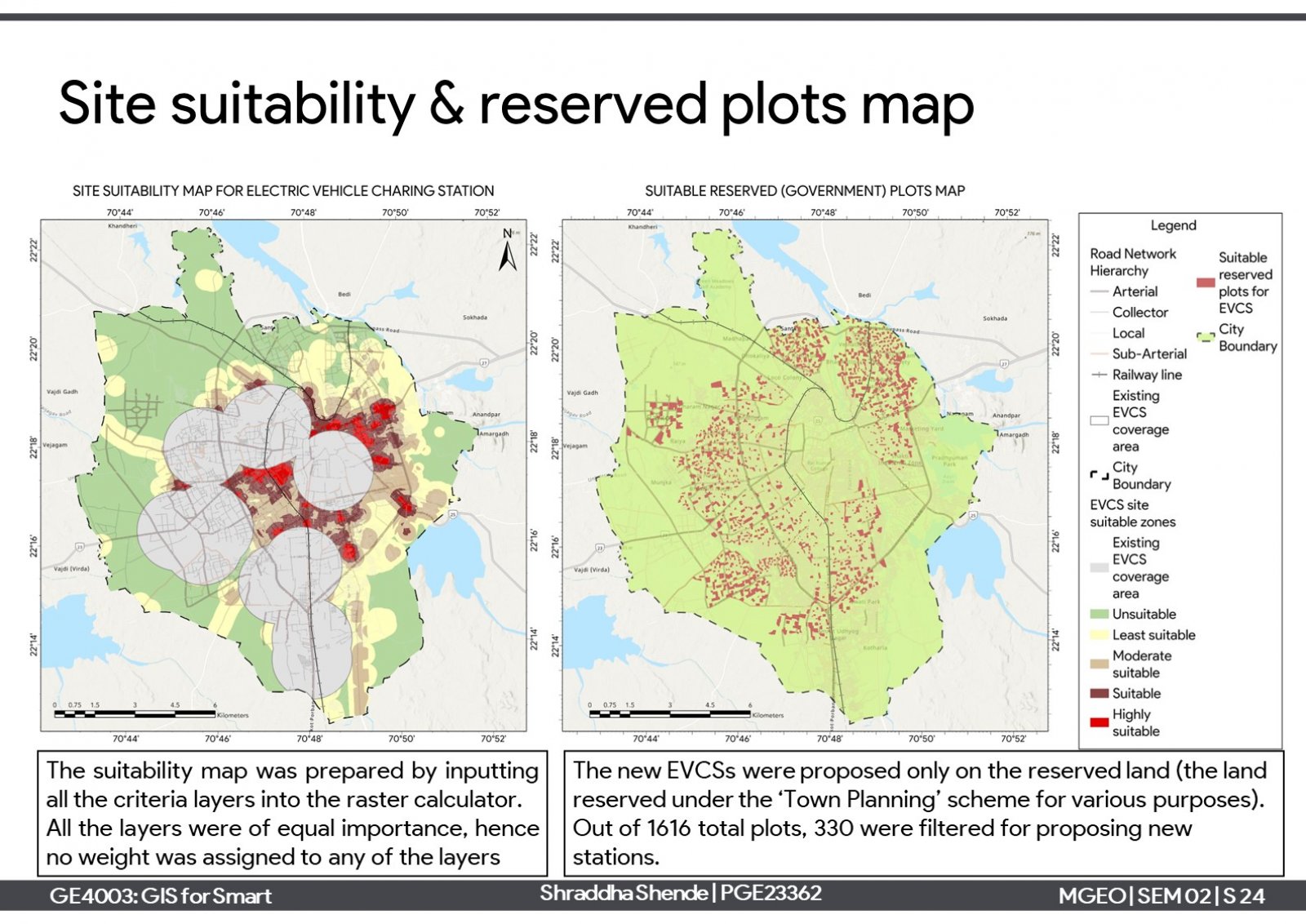
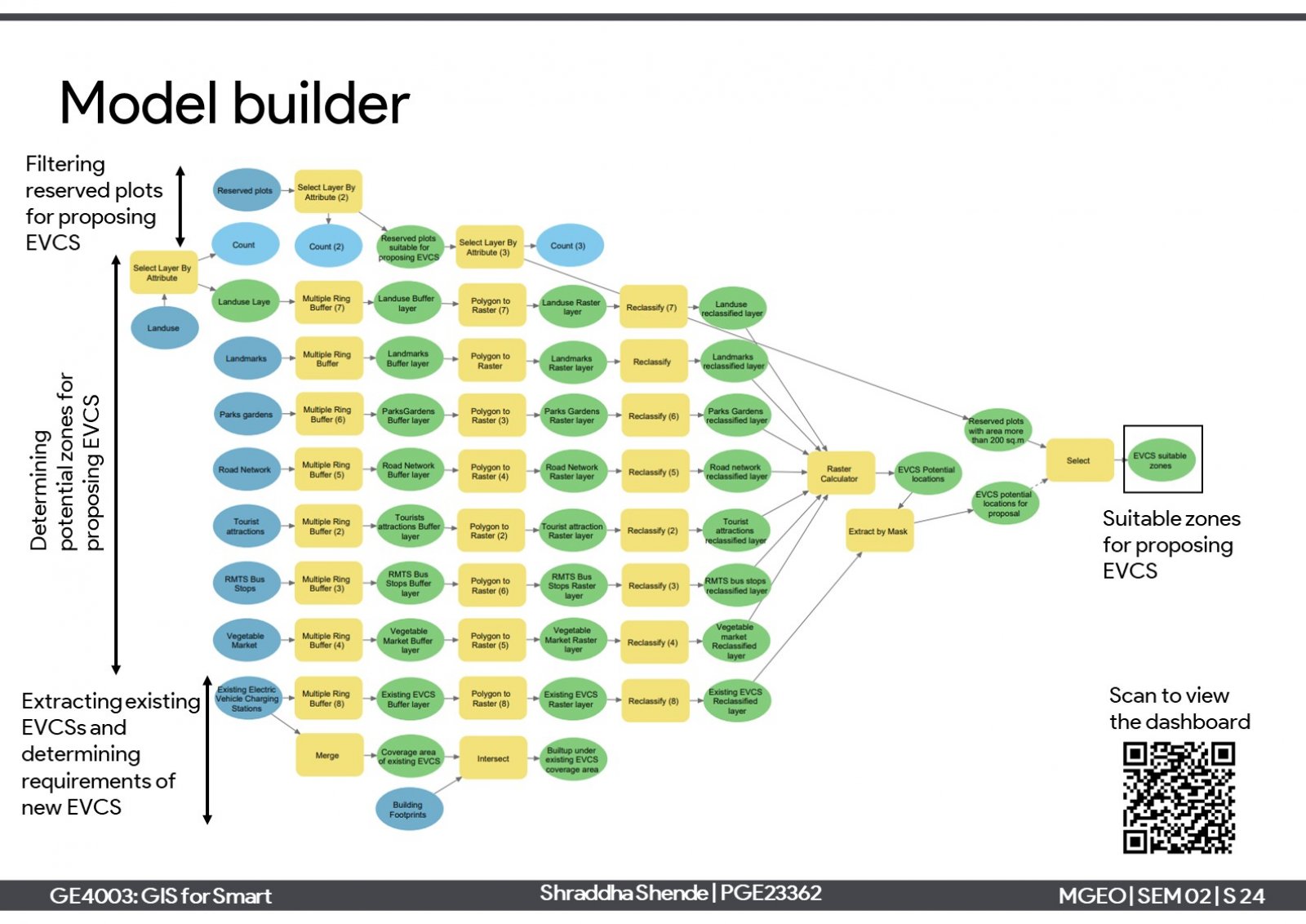
One of the elements of smart cities is the 'sustainable environment' which aims to reduce harmful emissions and produce clean air. One approach is a modal shift towards electric vehicles and support charging infrastructure needs. The project is about proposing electric vehicle charging stations (EVCS) infrastructure in Rajkot city. Considering the current scenario of the city, it has 12 private EVCSs which serve around 47% of the total built-up of the city. Further, 6 new EVCSs have been proposed for the unserved areas in suitable locations on reserved plots. Proposing them can serve around 83% of the total built-up area.
View Additional Work