Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
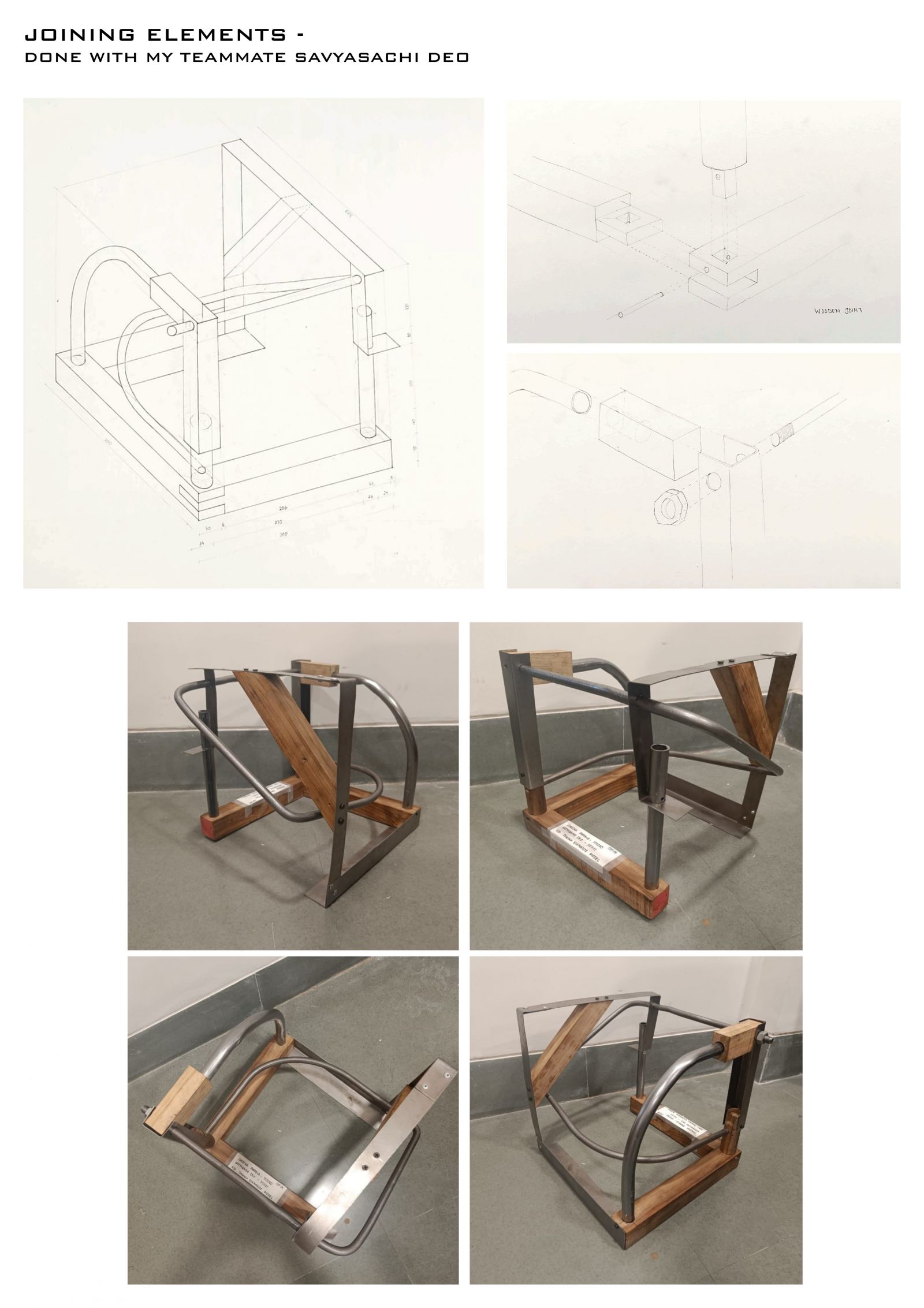
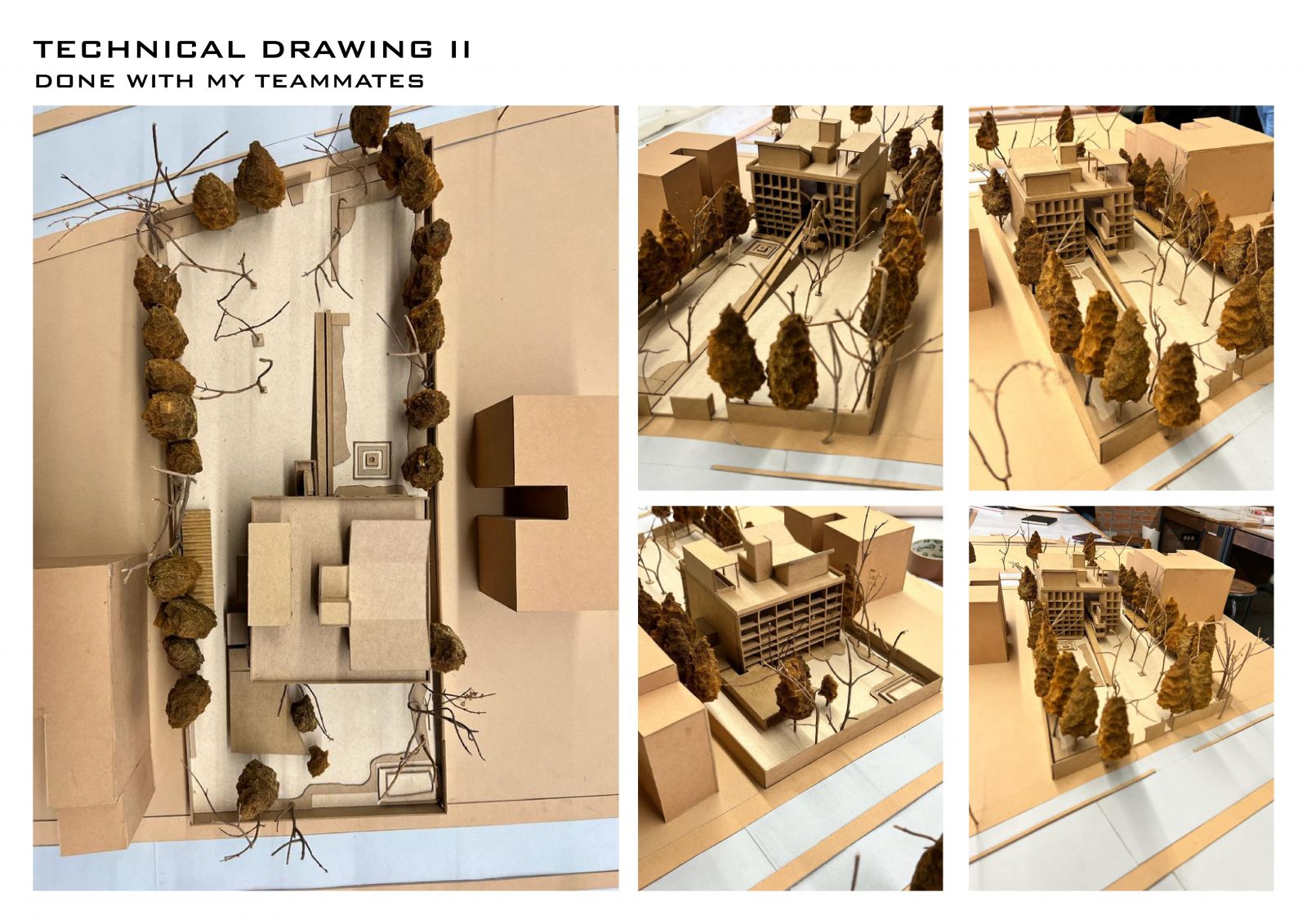
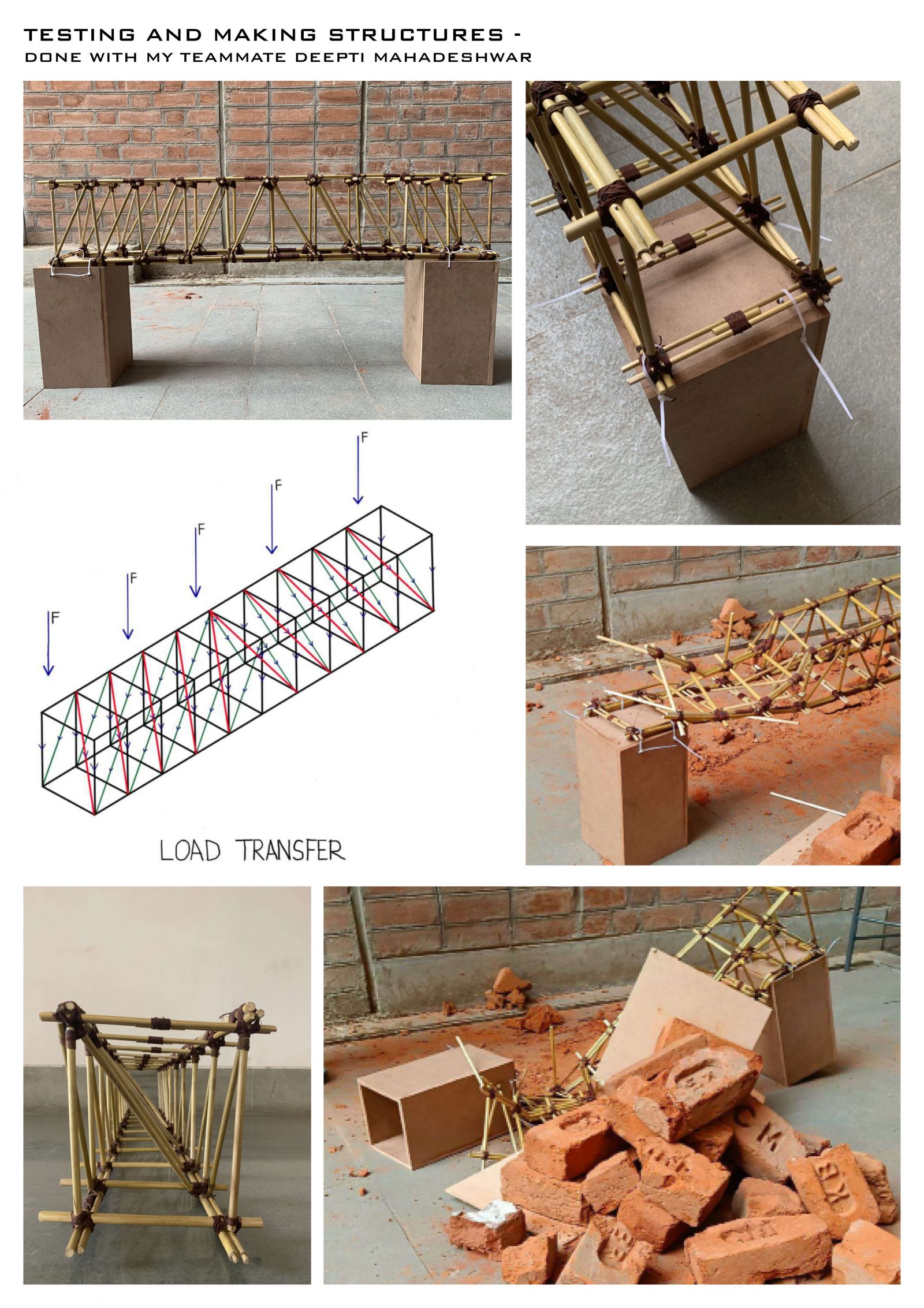
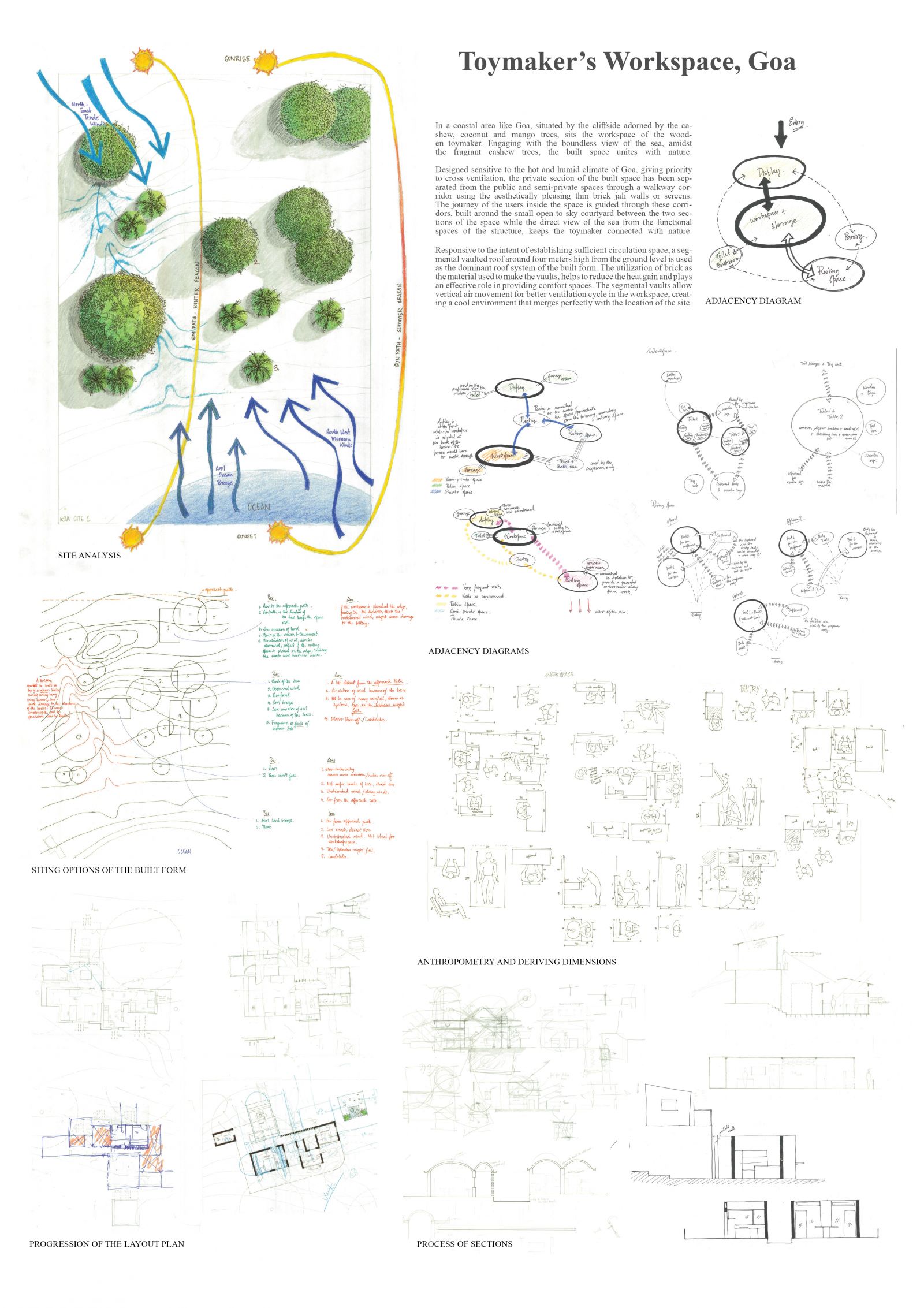
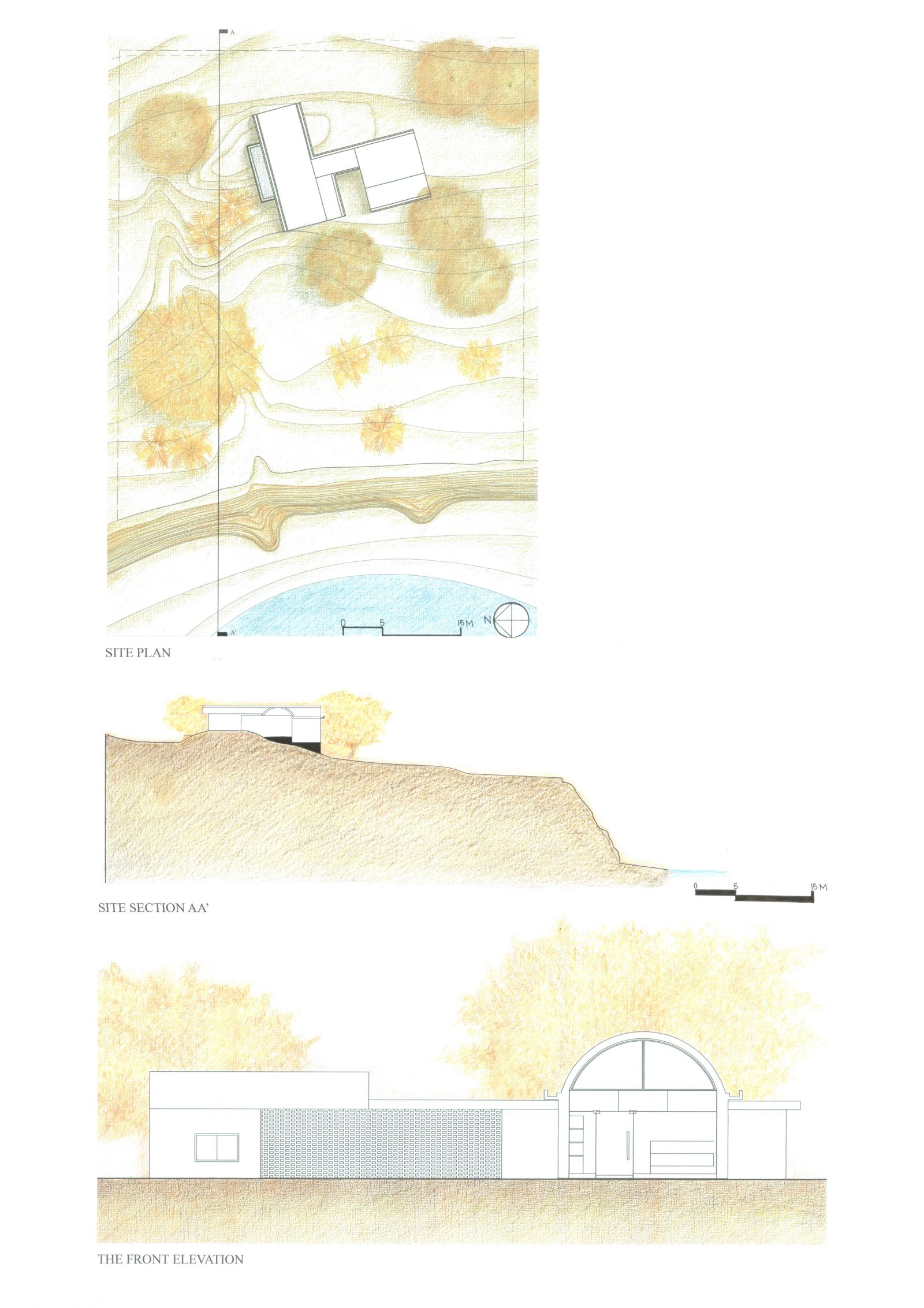
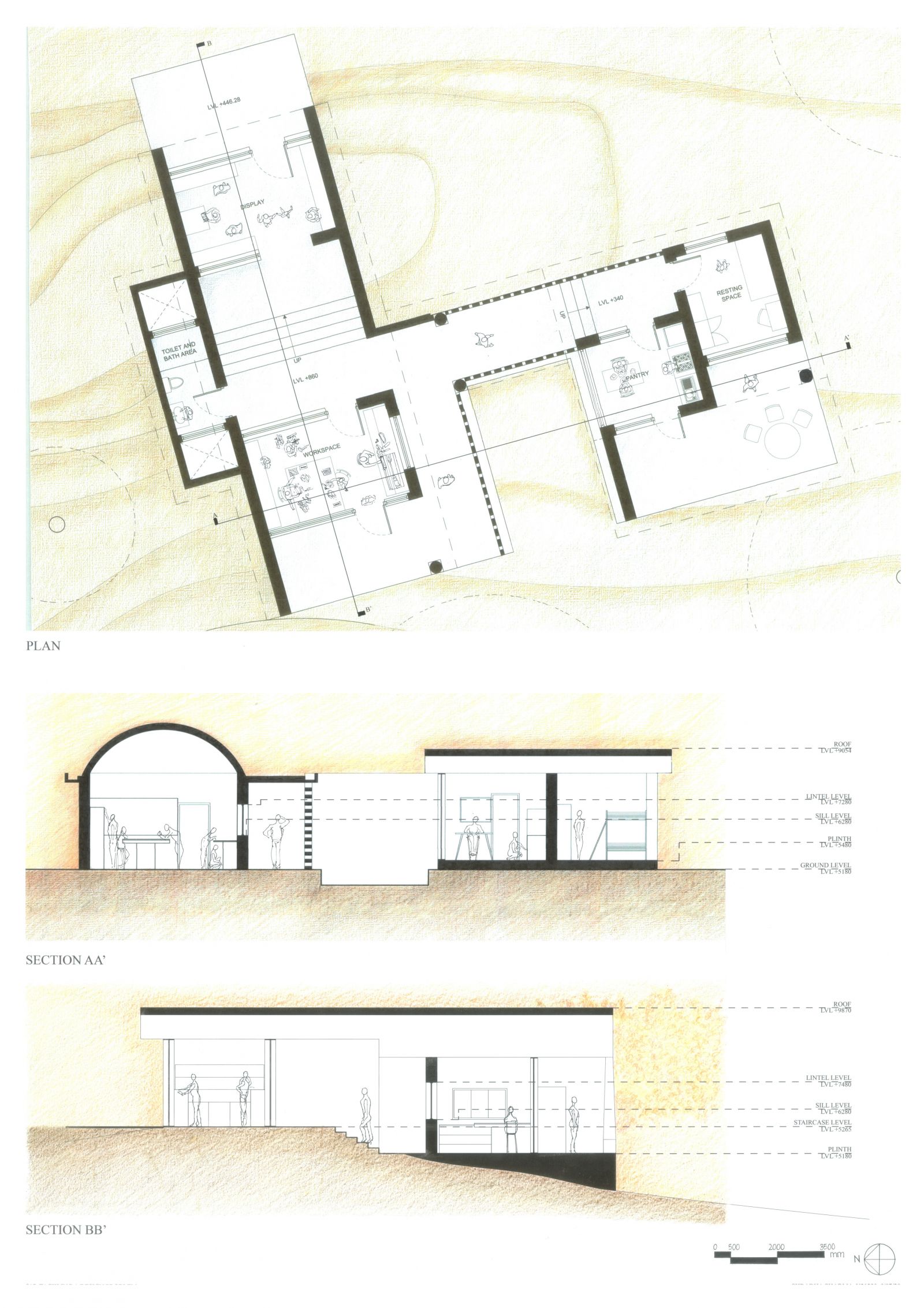
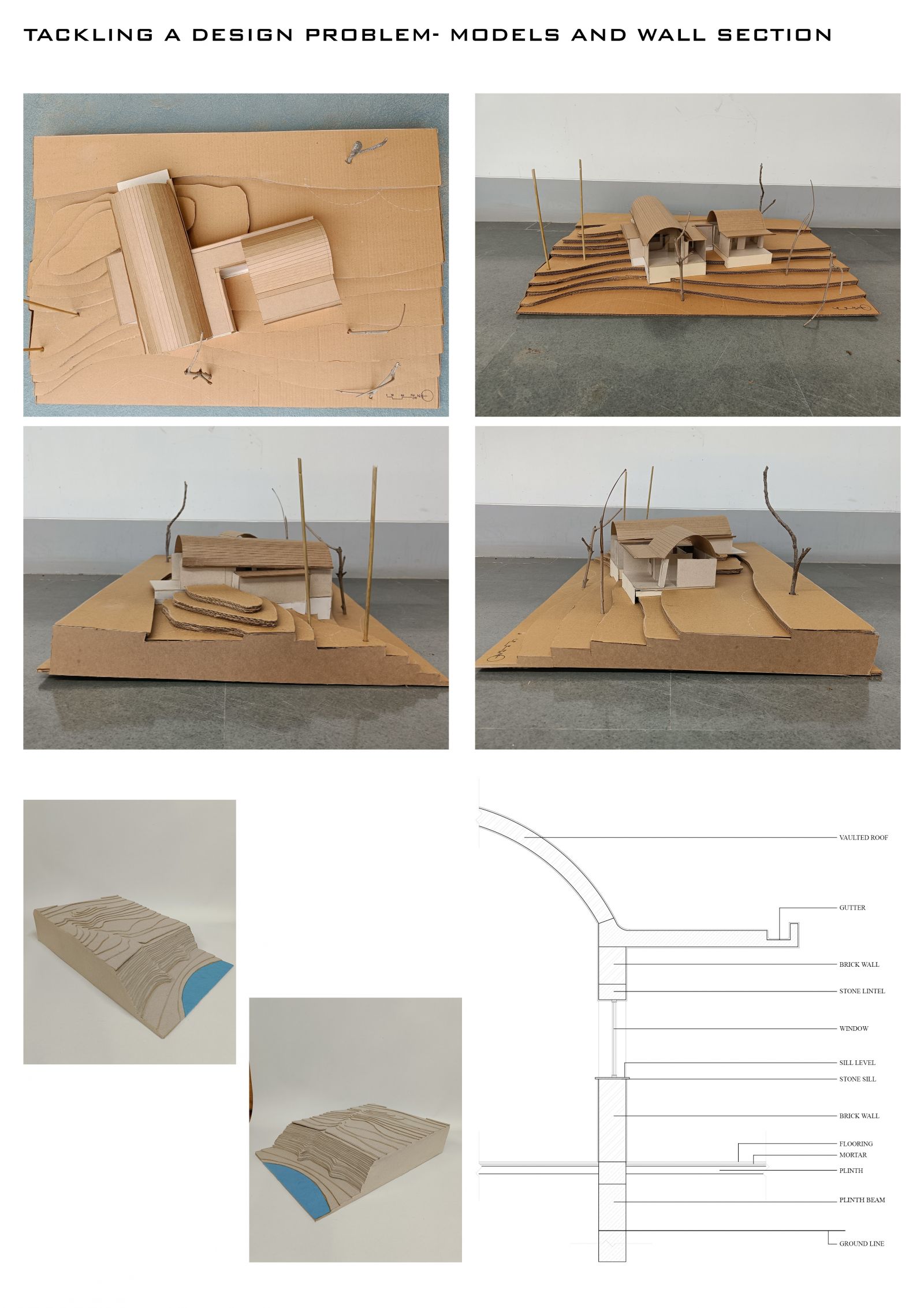
Foundation Studio (II), within the CEPT Foundation Programme continues to build upon the skills acquired during the first semester, adding abilities to use digital media in representation; to make models; to understand the assembly of built form through its building elements, materials and structures; to be able to draft architectural and topographical drawings: and eventually leads to bringing the skills and abilities together to tackle a design problem.
View Additional Work