Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
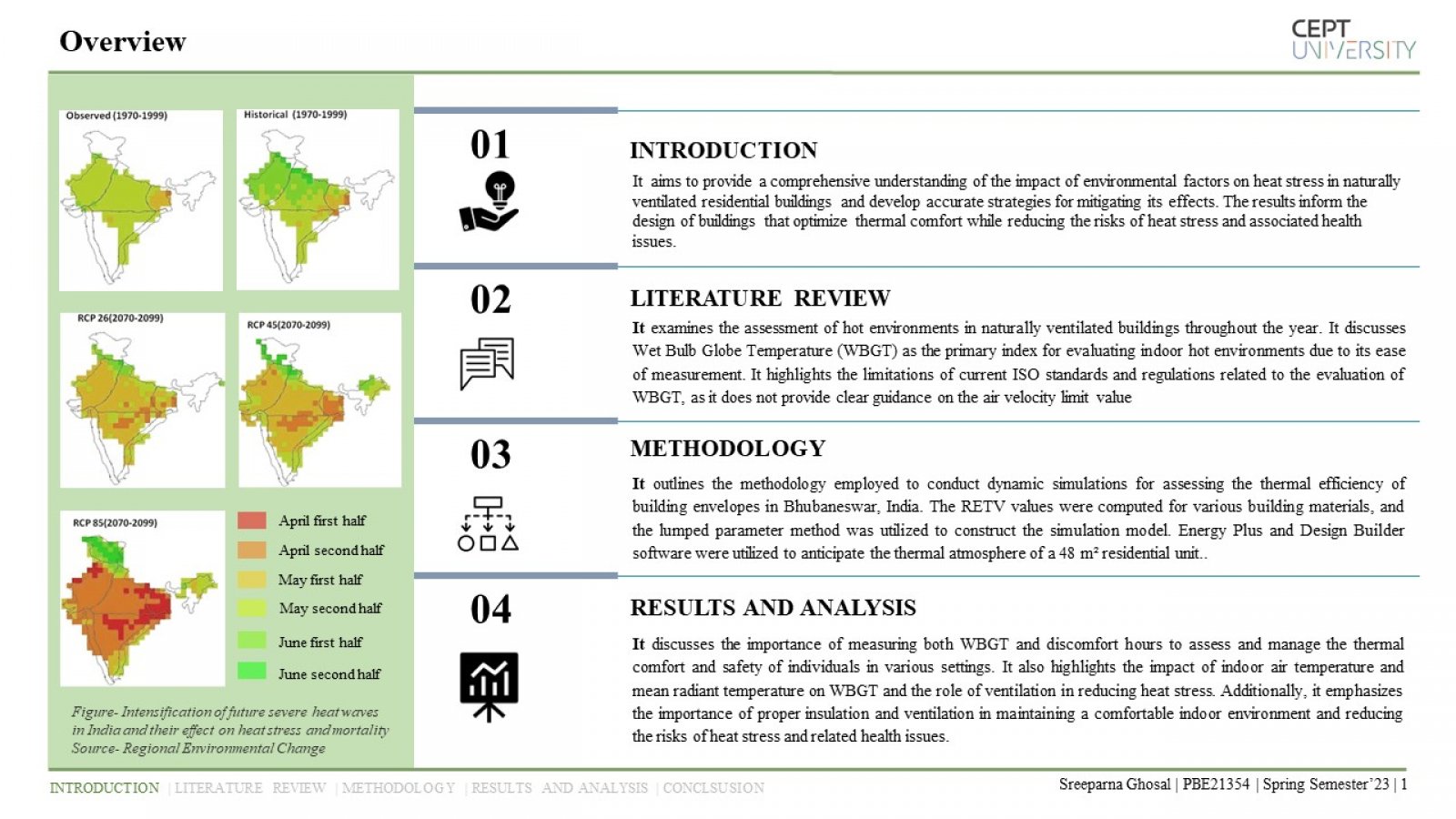
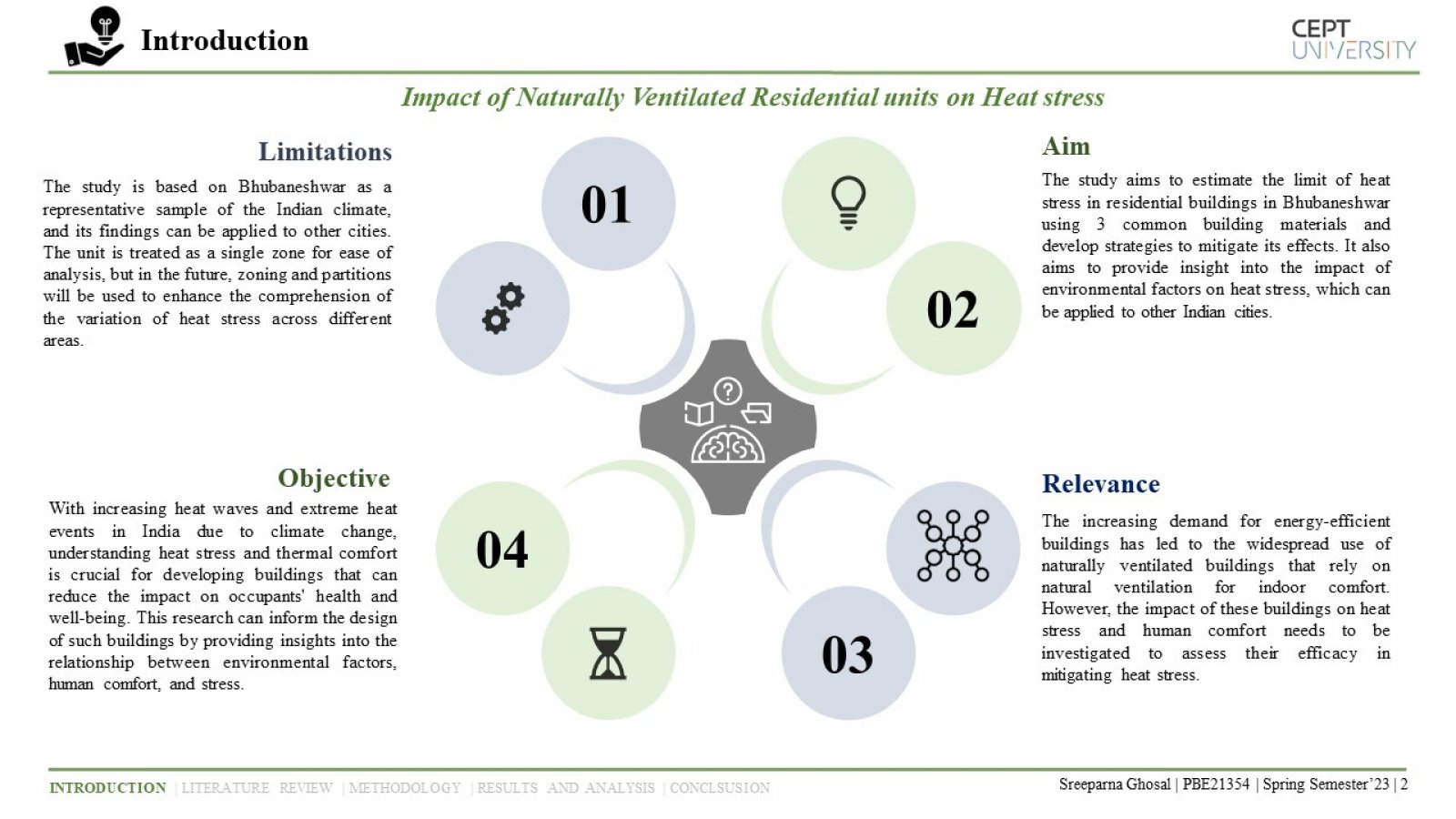
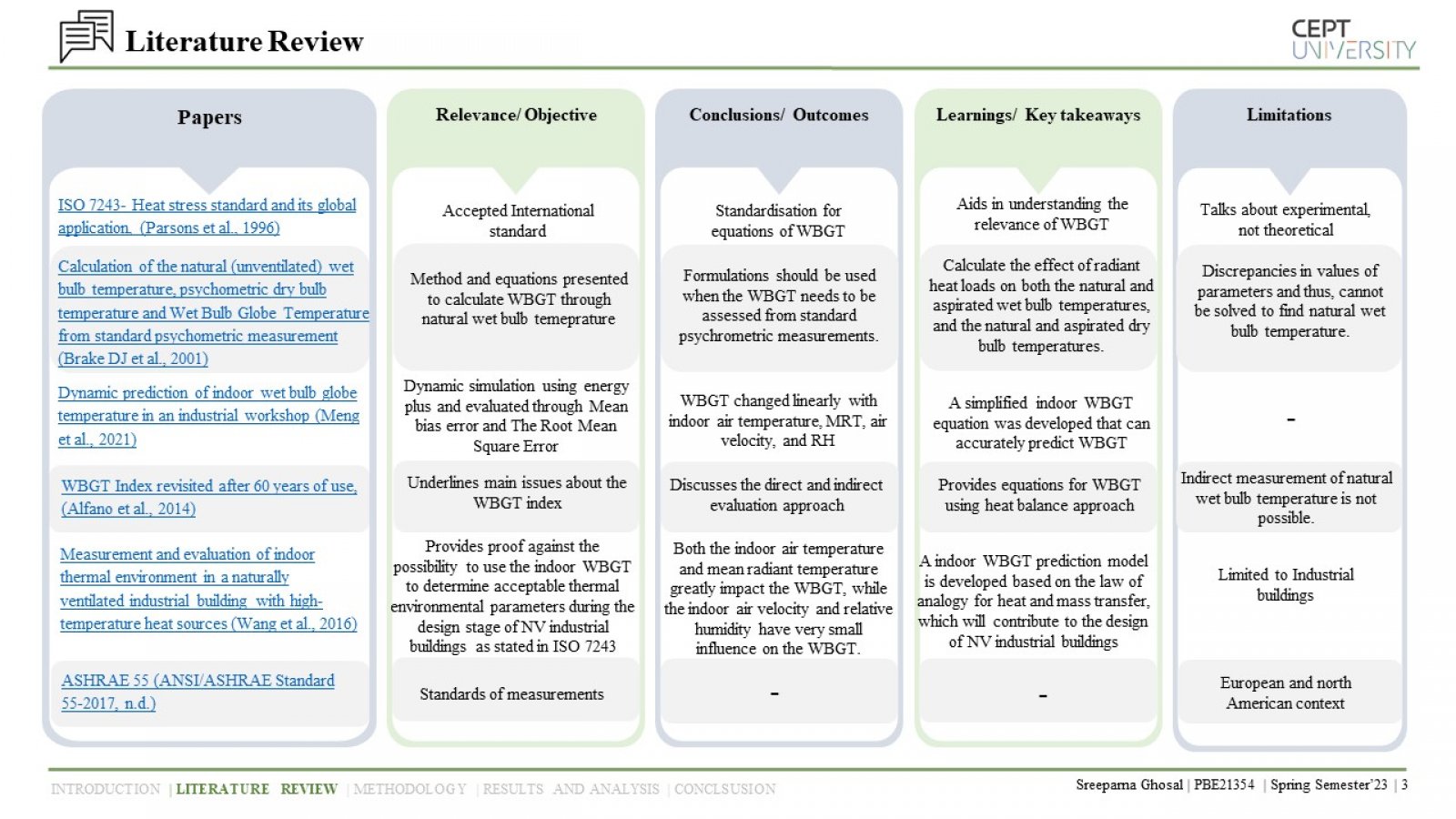
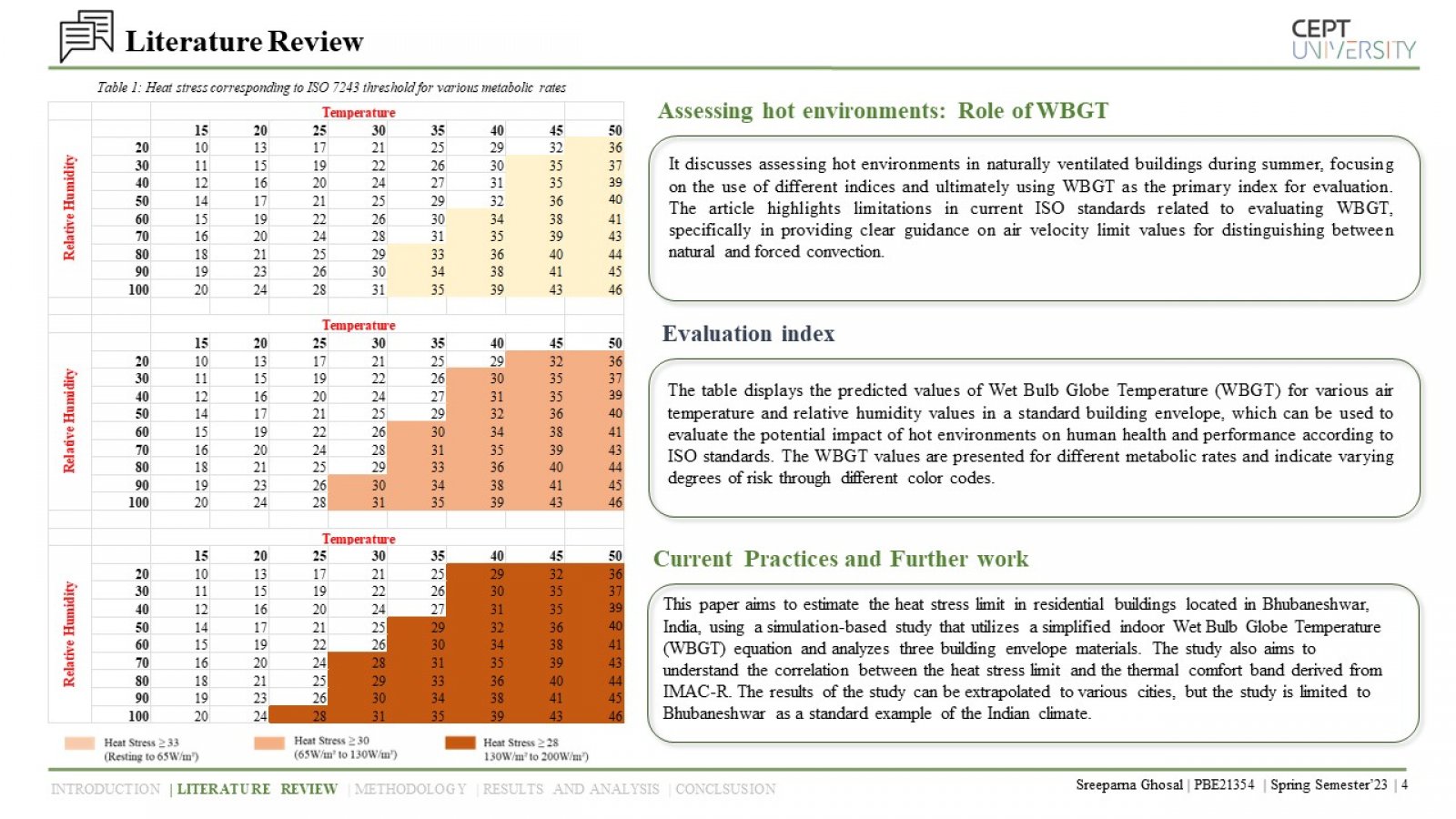
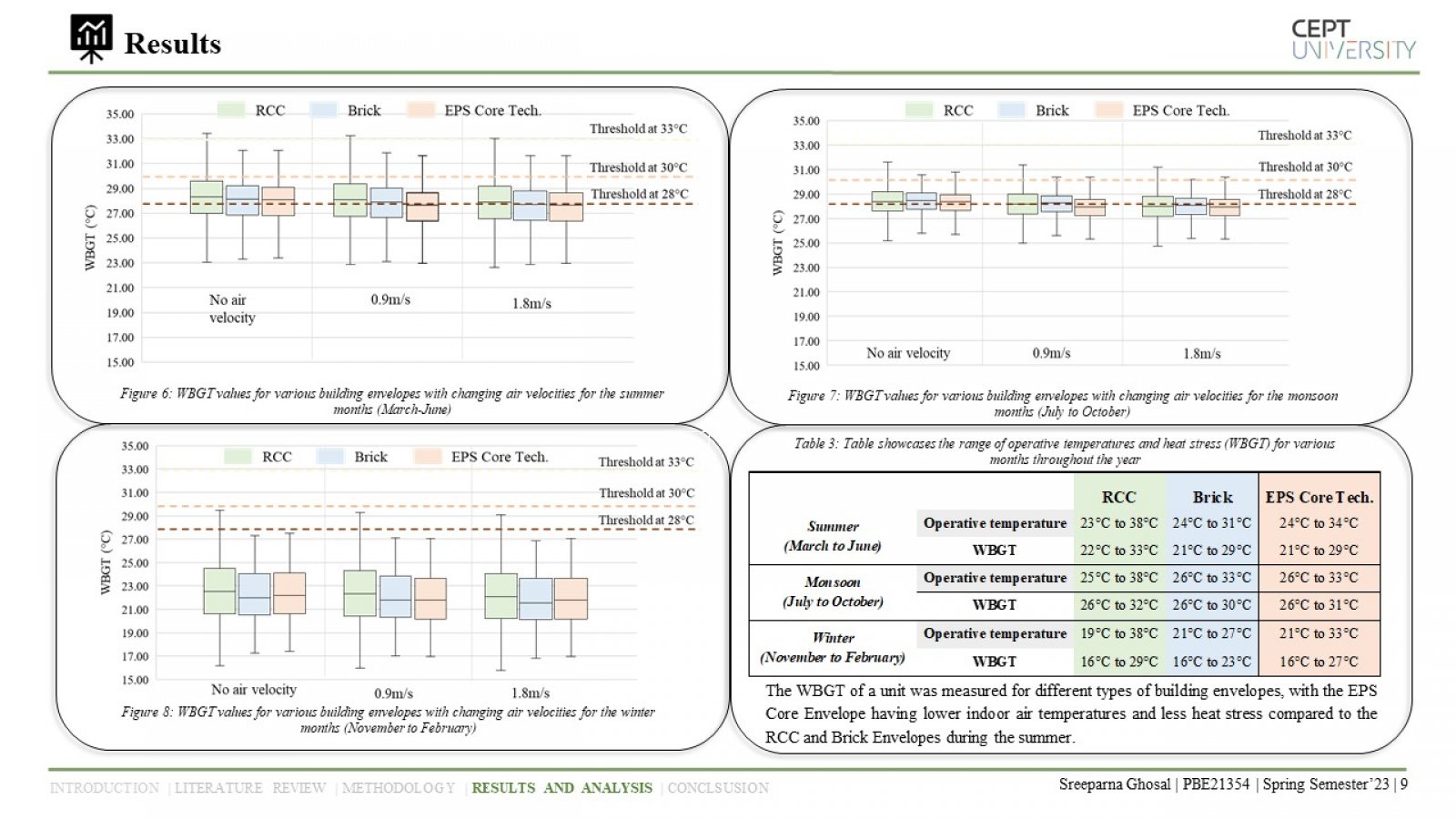
The study examines the impact of environmental factors on heat stress in naturally ventilated residential units in Bhubaneshwar, India, using a dynamic method of predicting heat stress. The study analyzes three building envelope materials, and the results underscore the importance of proper insulation and ventilation in reducing the risks of heat stress and associated health issues. The study highlights the significance of adaptive thermal comfort models in designing buildings that optimize thermal comfort while considering multiple factors impacting human comfort.