Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
The effective management of indoor air quality (IAQ) while minimizing energy consumption remains a challenge in building ventilation. This research focuses on developing a Ventilation Rate Prediction (DRP) model for mixed-mode ventilation buildings, particularly in the context of Indian residential setups. The study begins with a comprehensive literature review, examining the merits of natural ventilation (NV) and mechanical ventilation (MV) systems and their integration into concurrent mixed-mode ventilation. The ongoing debate between energy efficiency and IAQ management is explored, highlighting the resurgence of natural ventilation with advancements in control systems.
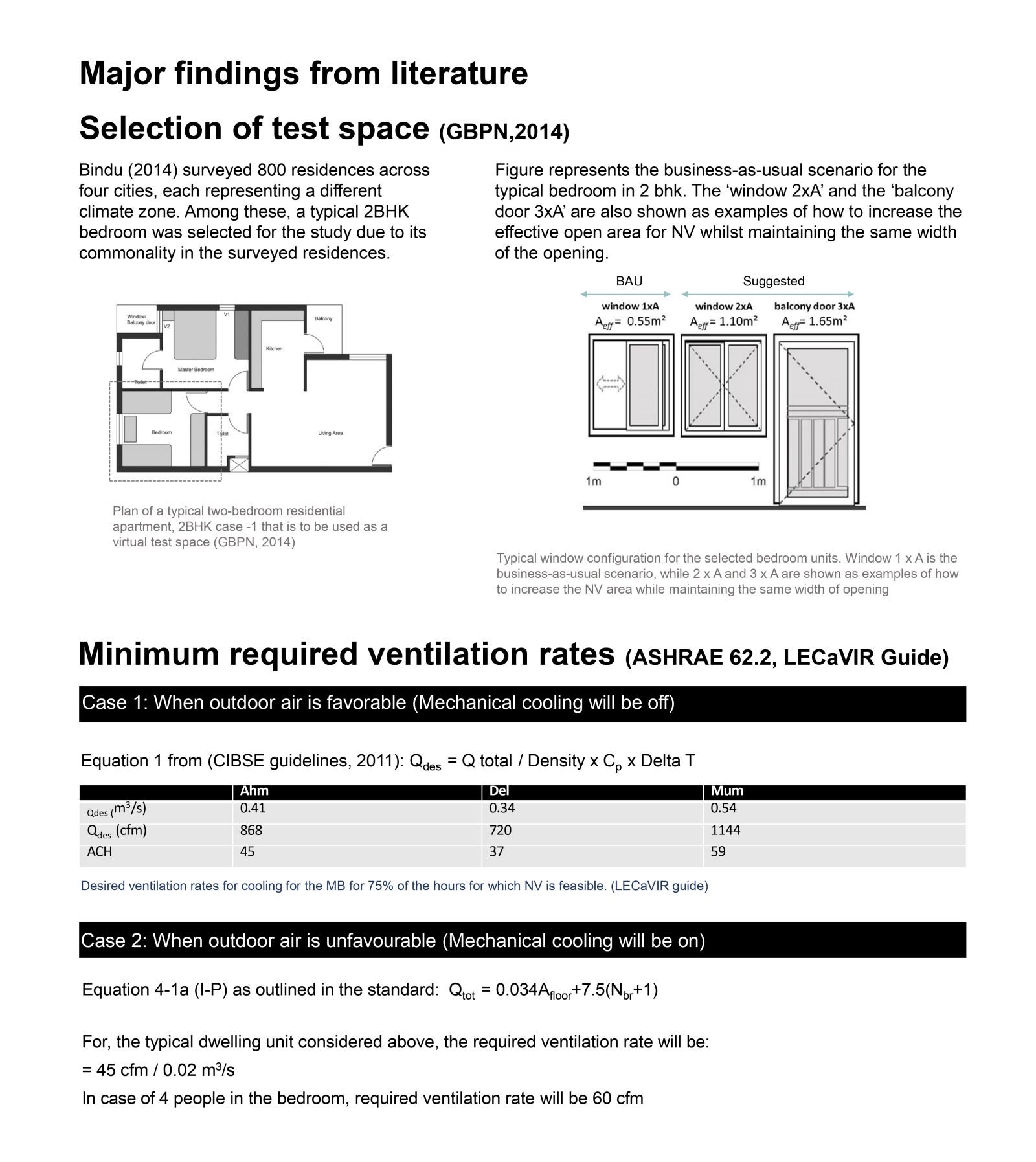
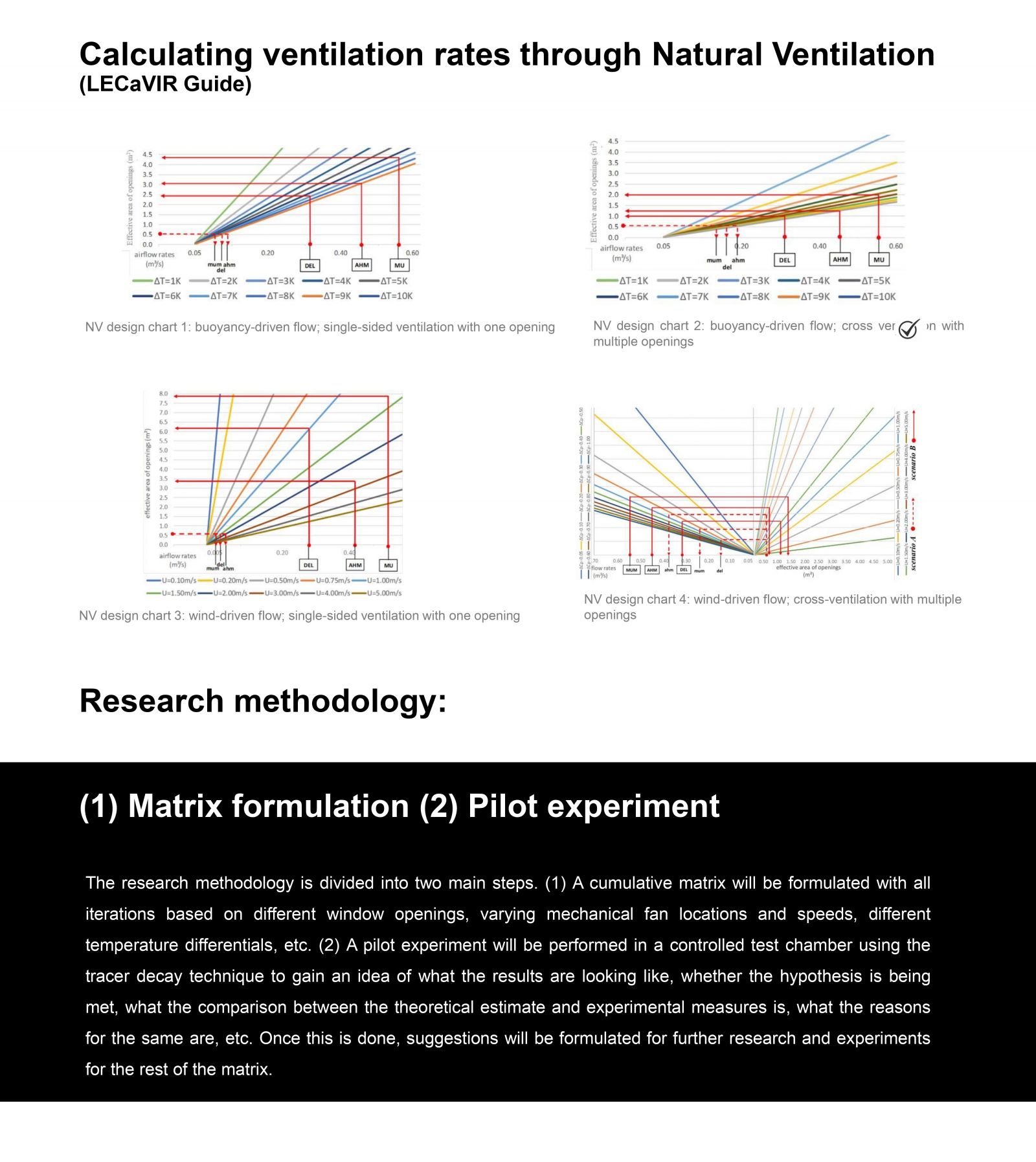
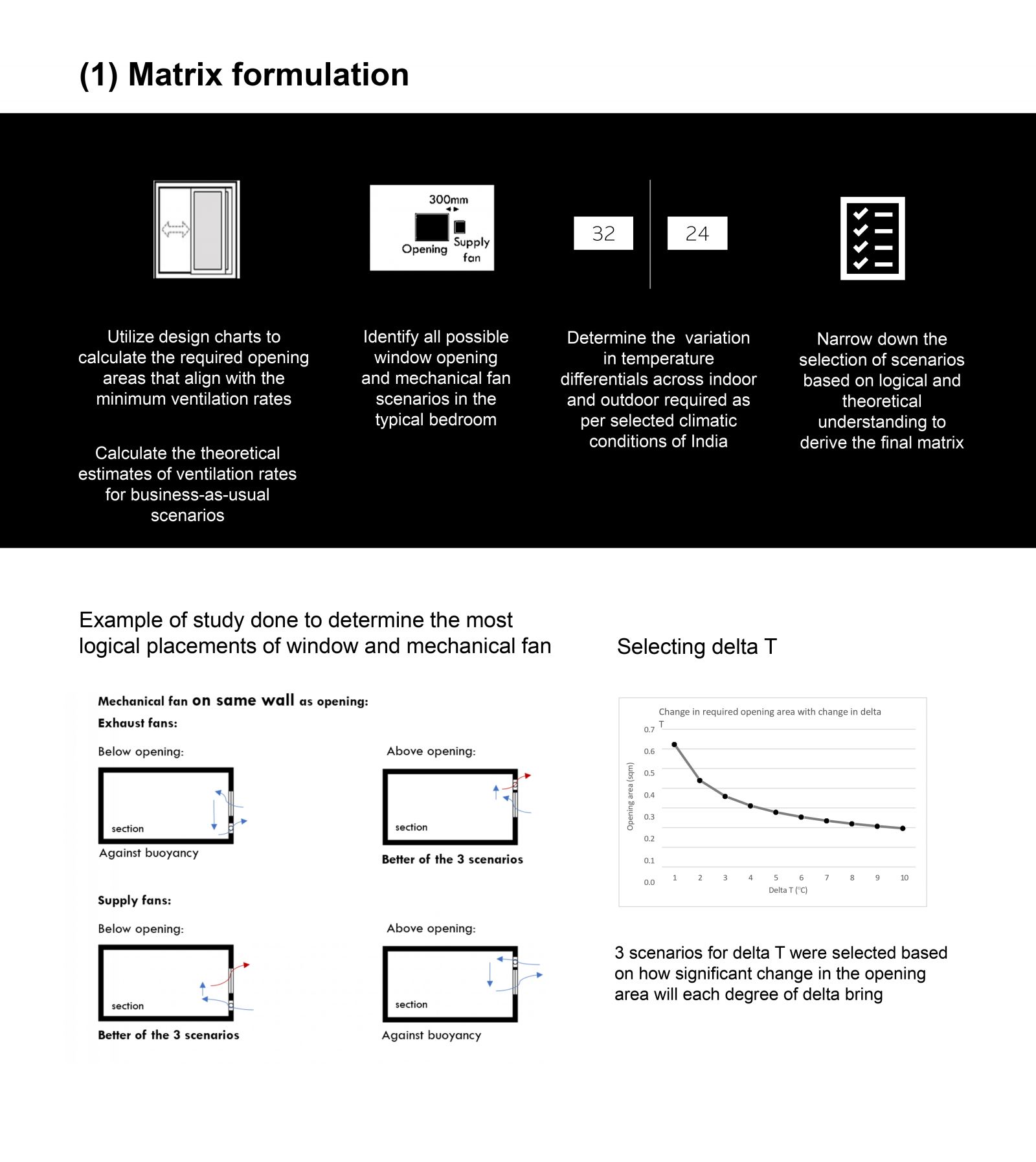
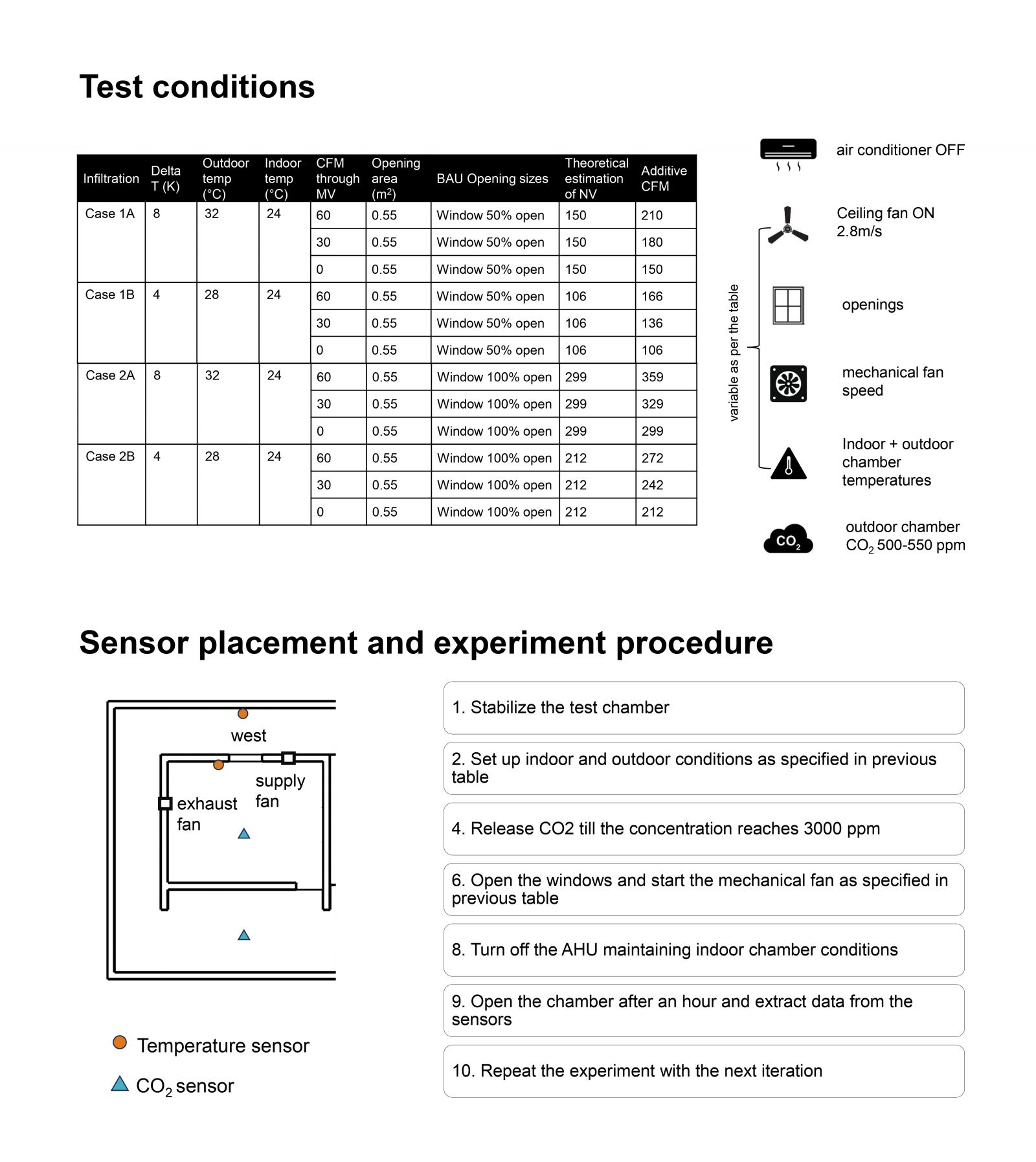
The research methodology involves formulating a matrix of possible ventilation scenarios based on window opening configurations, mechanical fan setups, and temperature differentials across indoor and outdoor conditions across various climatic conditions in India. Utilizing design charts and theoretical calculations, required window opening areas and theoretical ventilation rate estimates are determined. The matrix guides the selection of iterations for pilot experiments, conducted using the Tracer Decay Technique for Ventilation Rate measurement in a controlled chamber setup.
The pilot experiments focus on representative scenarios, establishing insights into hybrid ventilation scenarios and their potential application in Indian residential environments. The outcomes of the pilot experiments inform the establishment of a protocol for subsequent iterations, including scope for additions, removals, or changes to the methodology.