Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
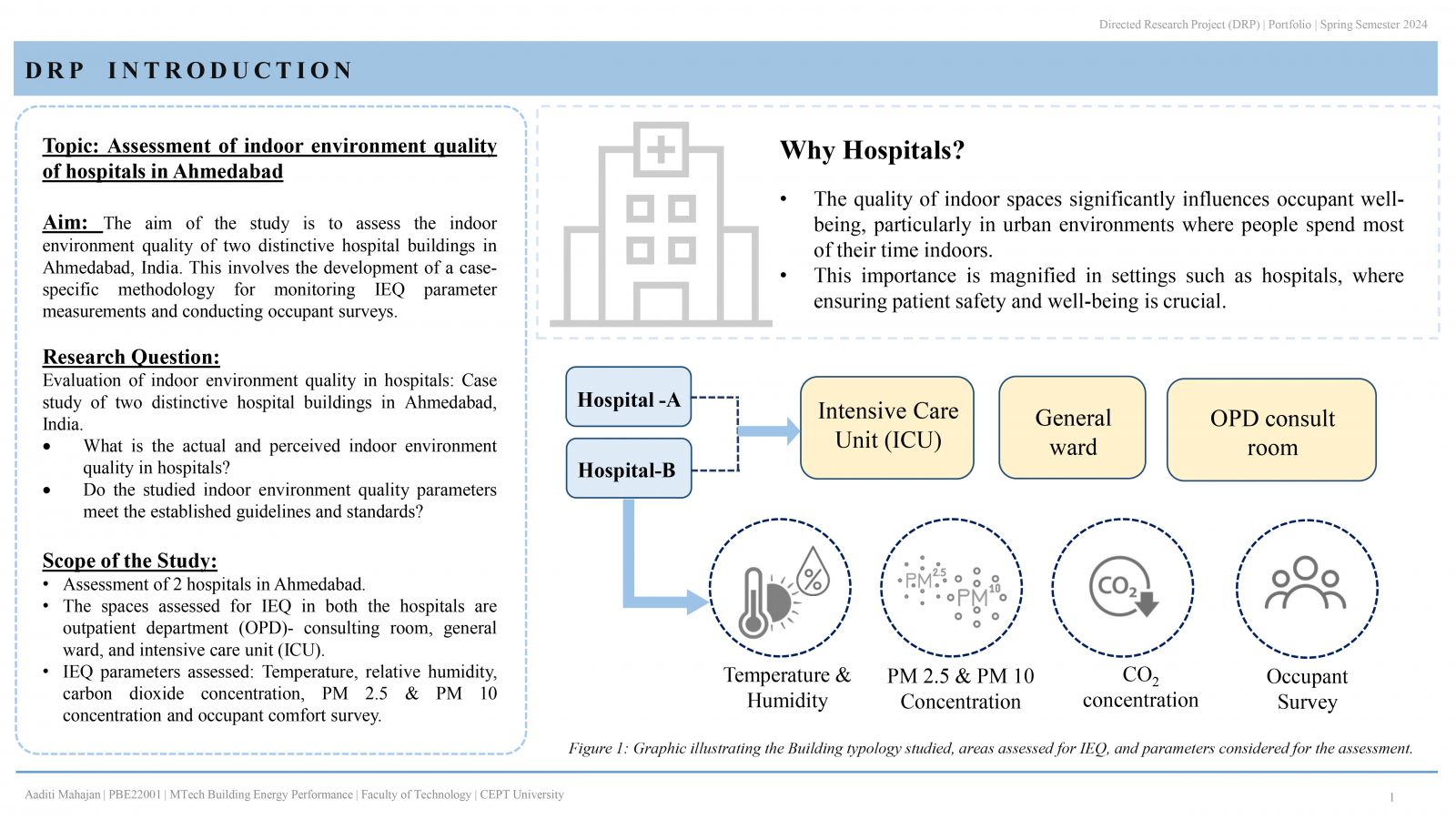
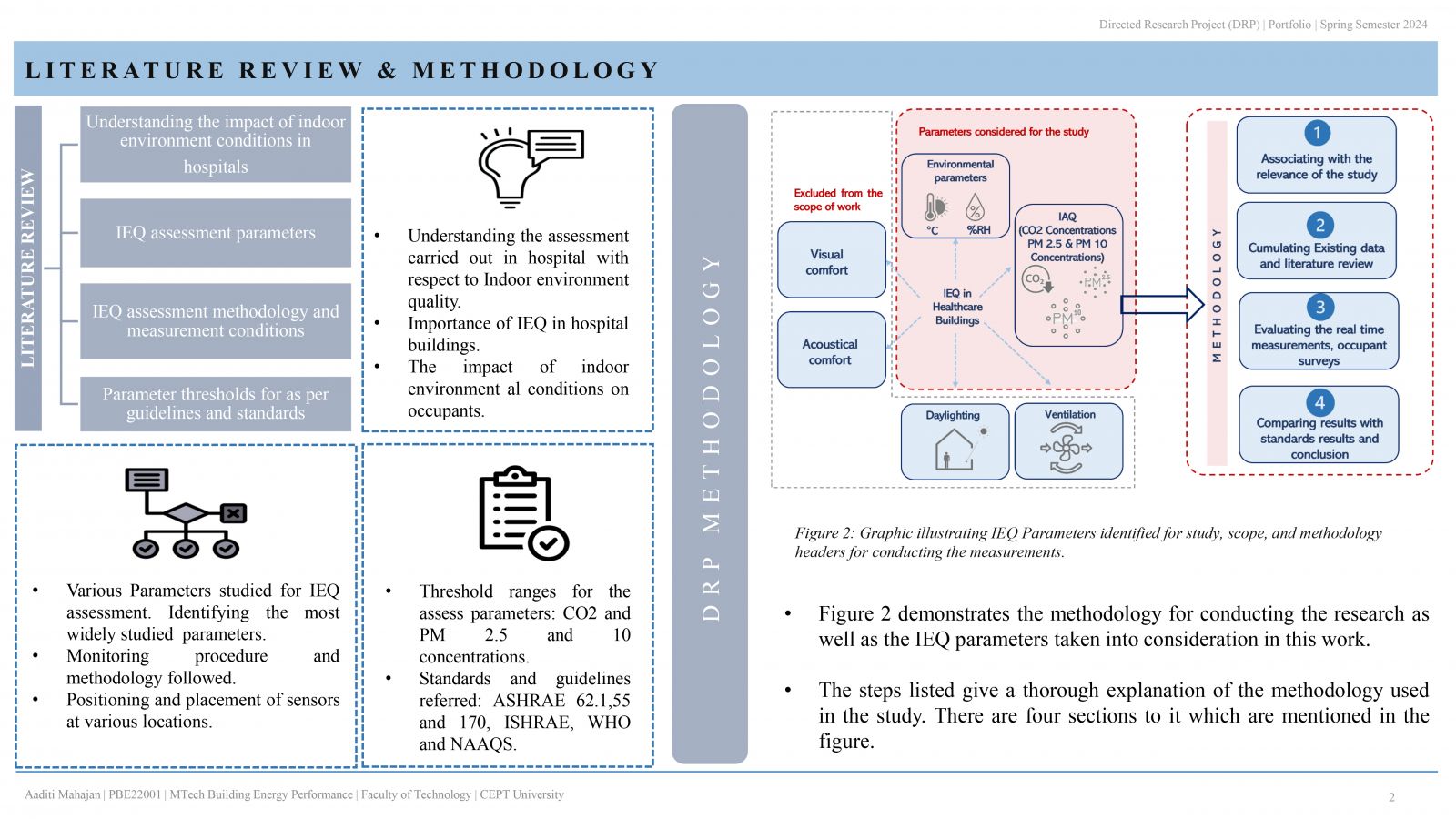
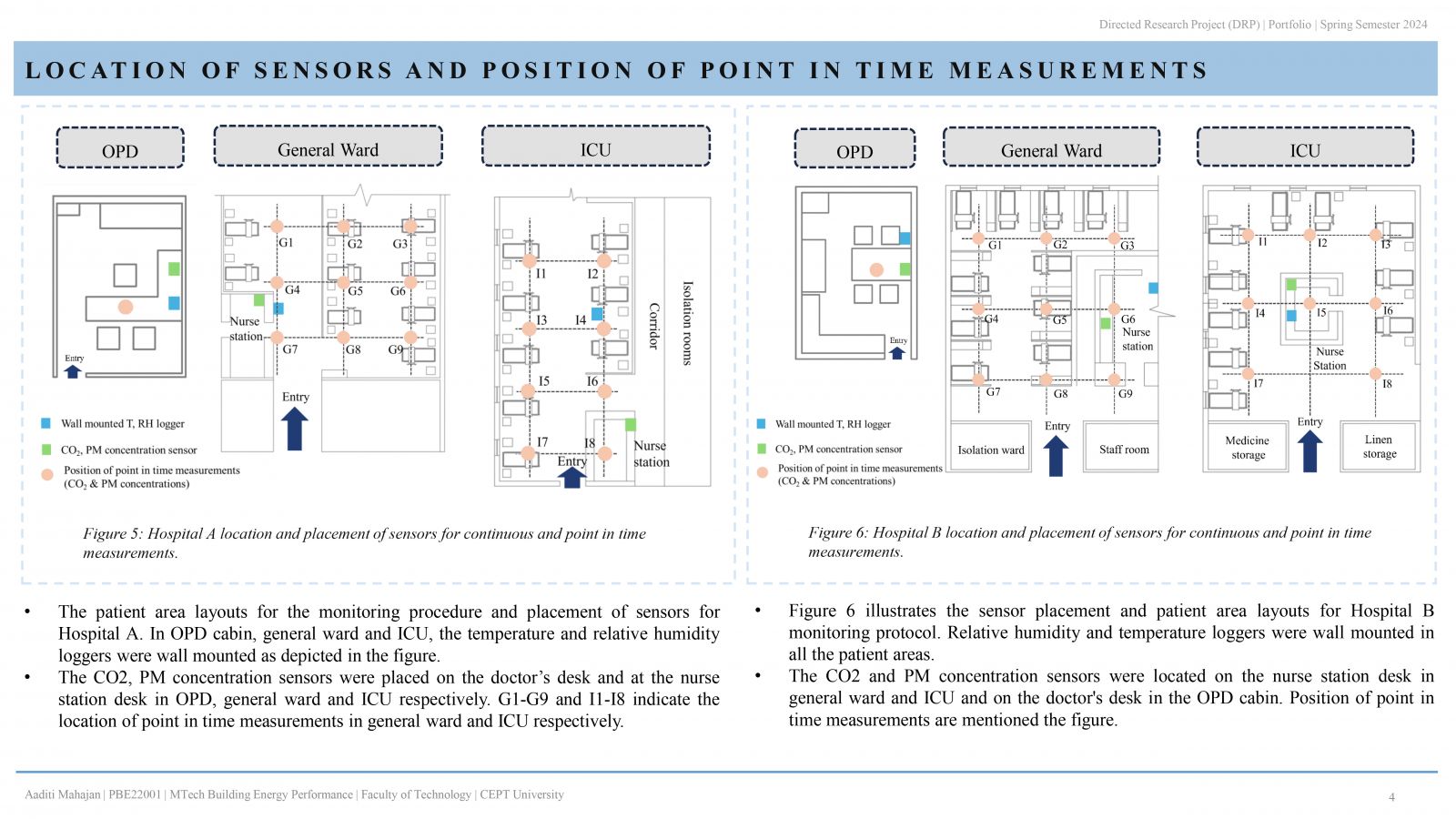
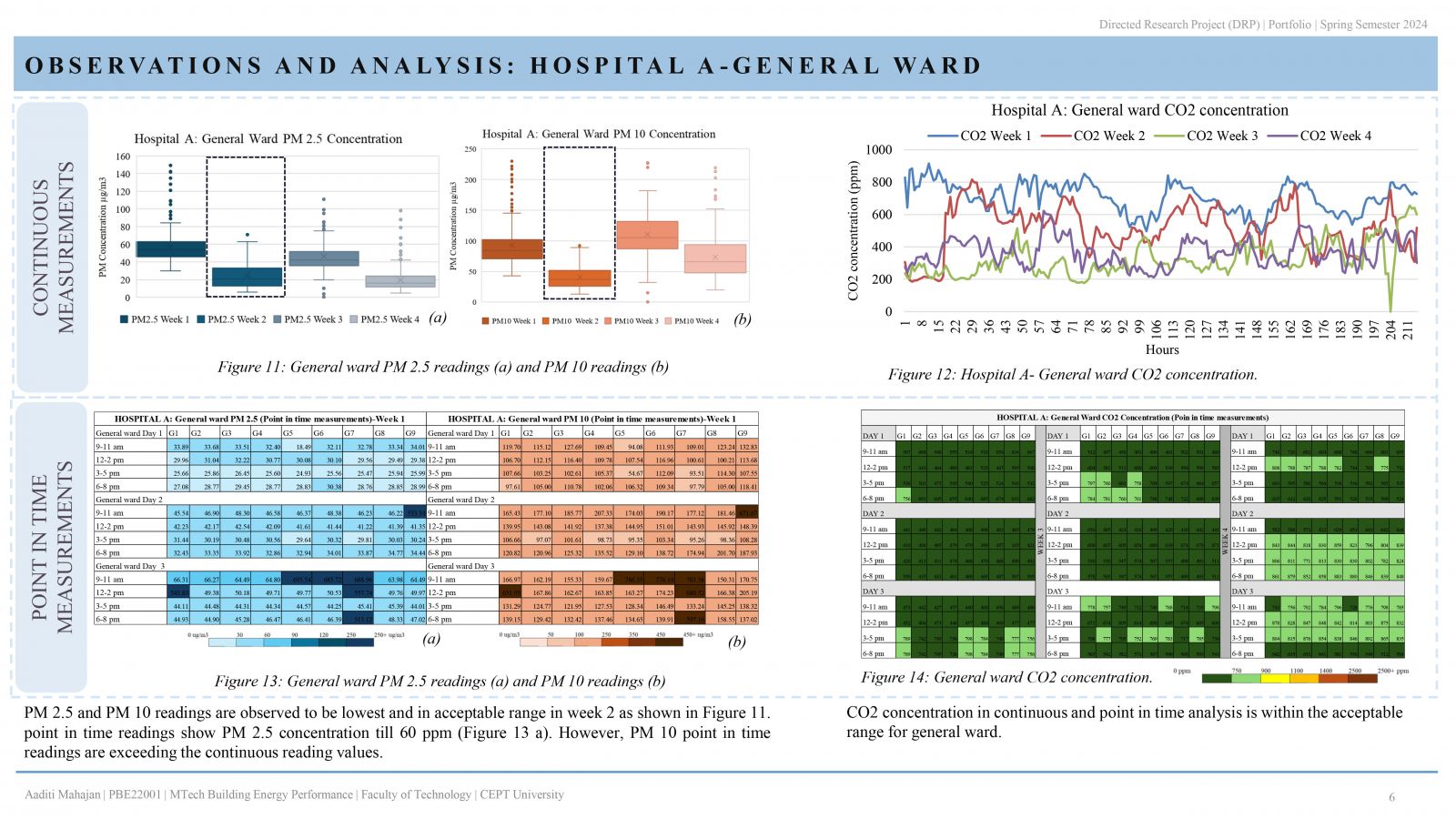
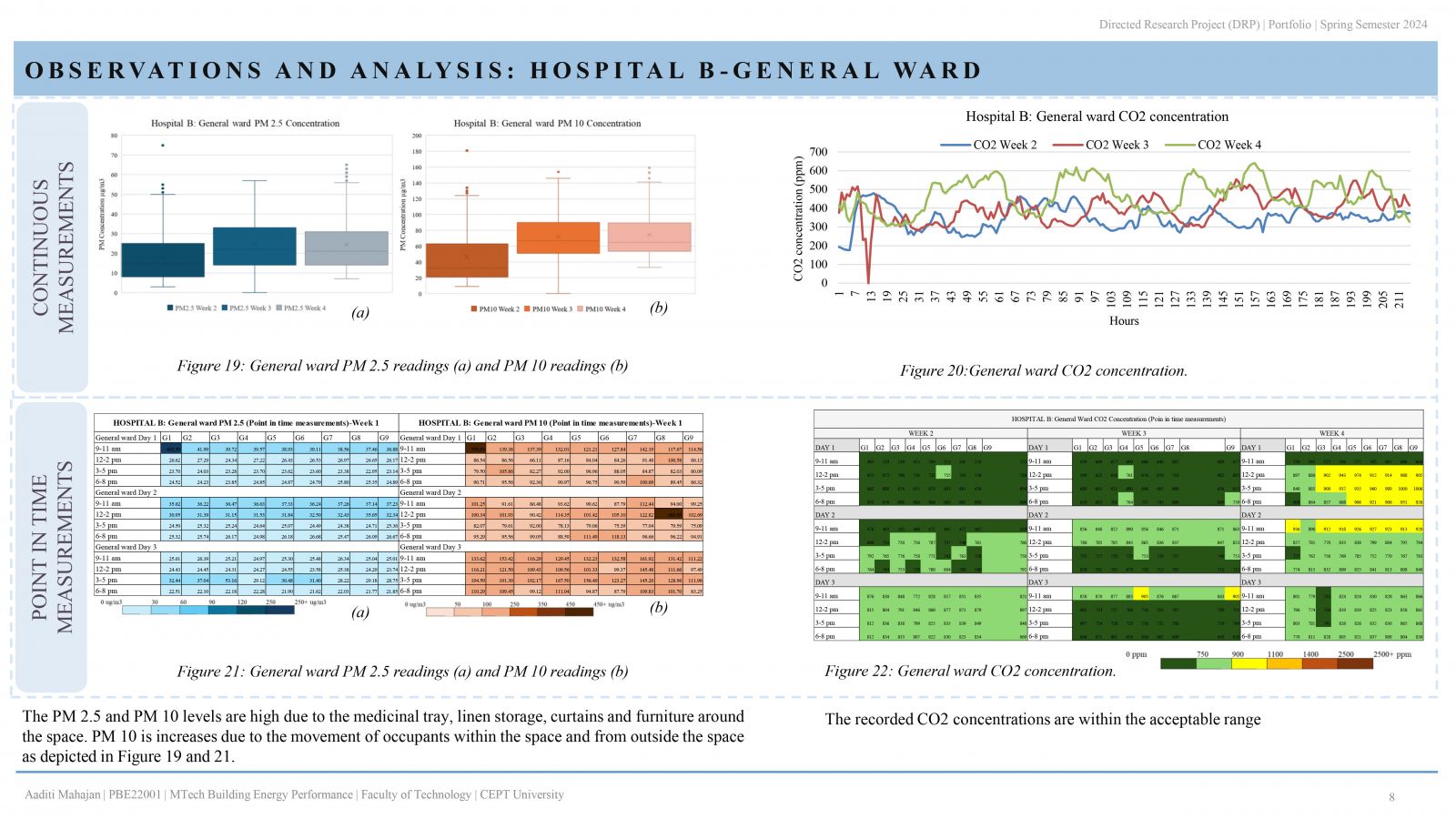
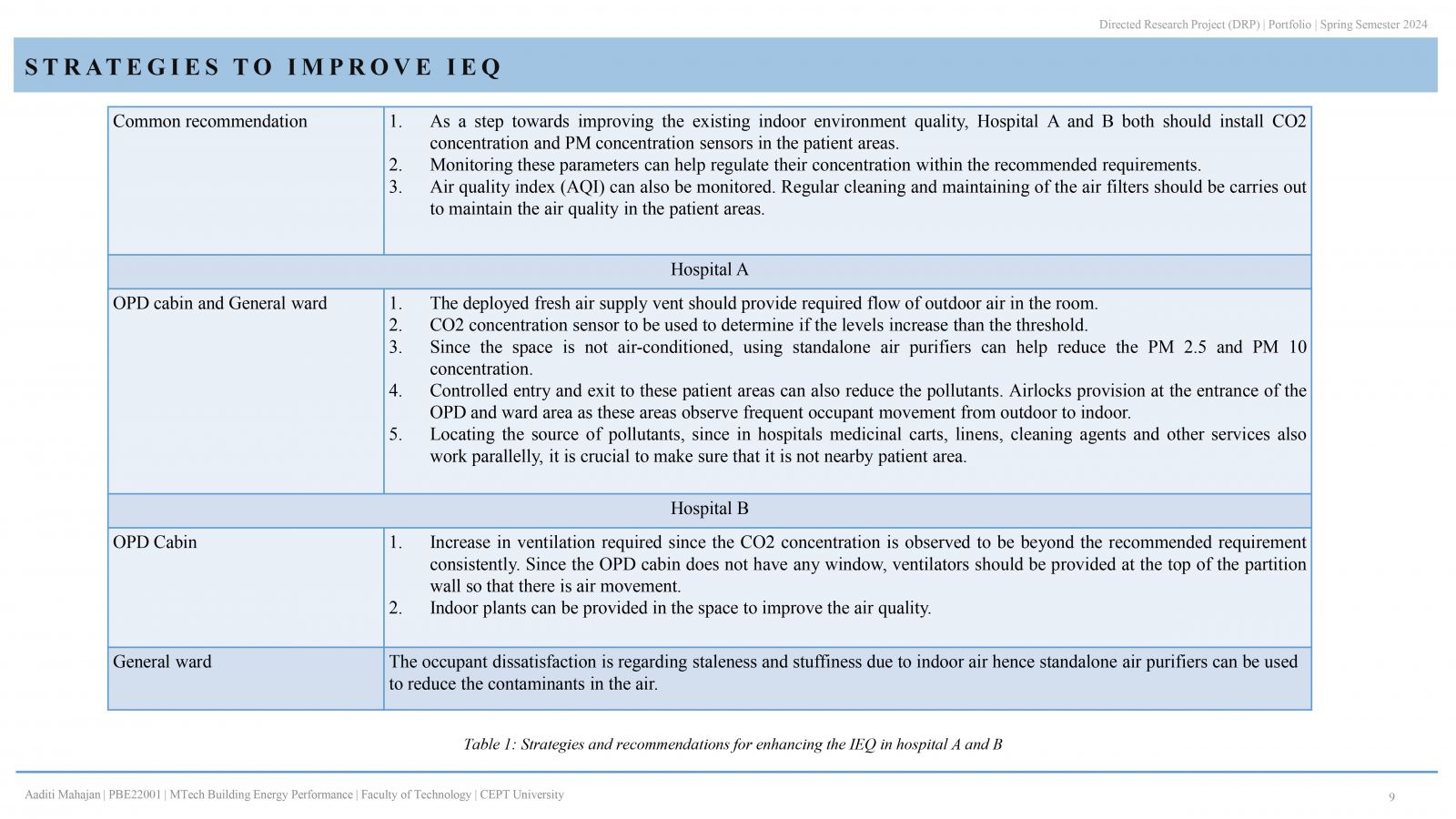
People spend most of their time indoors in the urban environment, hence, occupant wellbeing is greatly impacted by the quality of the indoor space. IEQ becomes significant when hospitals are considered, as patient safety and well-being are the primary objective. This study examines the indoor environment quality in two distinctive hospital buildings in Ahmedabad, India. IEQ is measured in 3 patient areas of both hospitals: outpatient department (OPD), general ward, and intensive care unit (ICU). The evaluation that is carried out, focuses on the measurement of environmental parameters (temperature, relative humidity), indoor air quality; carbon dioxide, PM 2.5 & PM 10 concentration. Additionally, occupant comfort analysis through occupant satisfaction survey is conducted. . It is therefore possible to determine if the parameters meet standards and guidelines and whether they are within acceptable limits.