Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
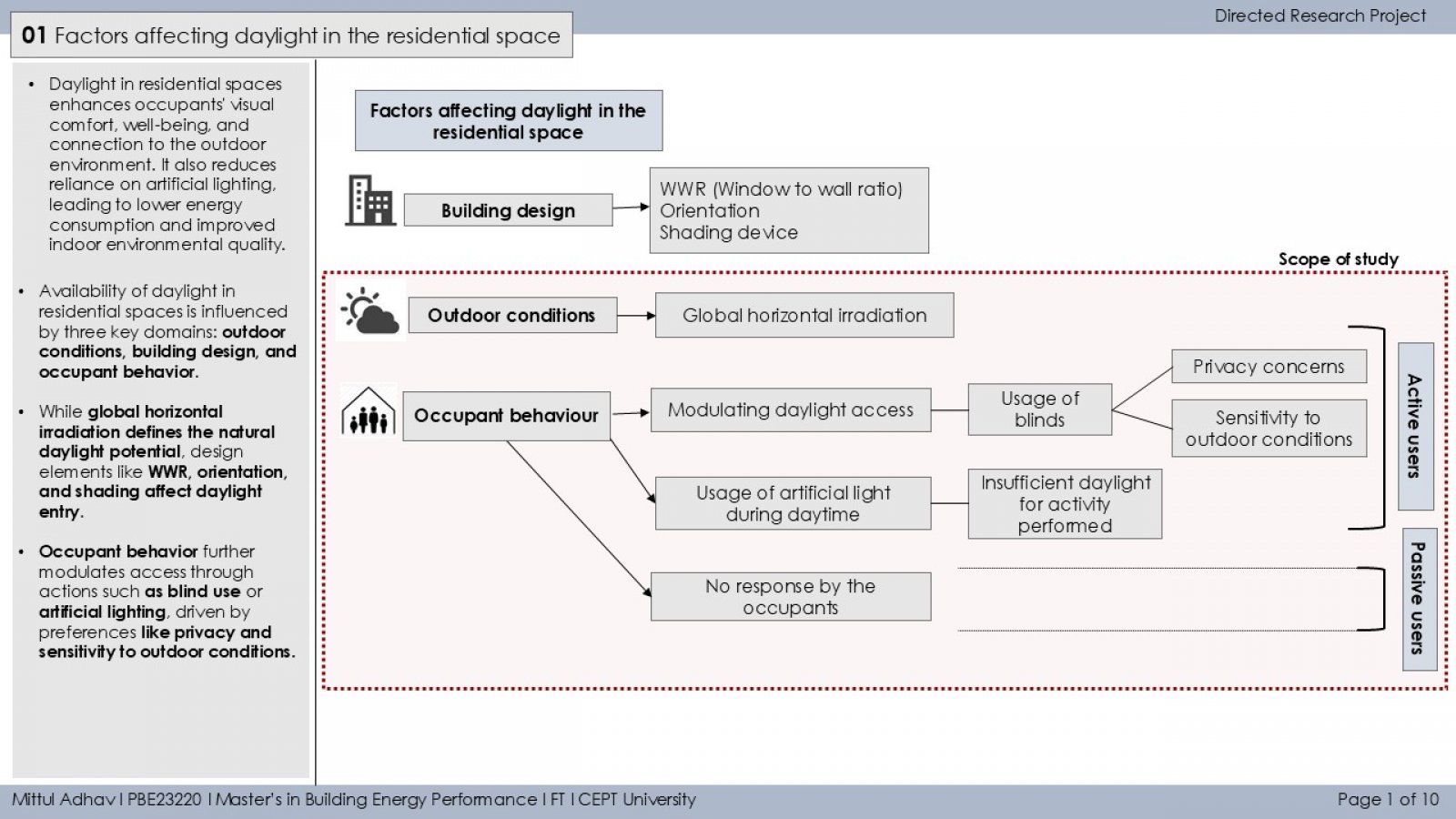
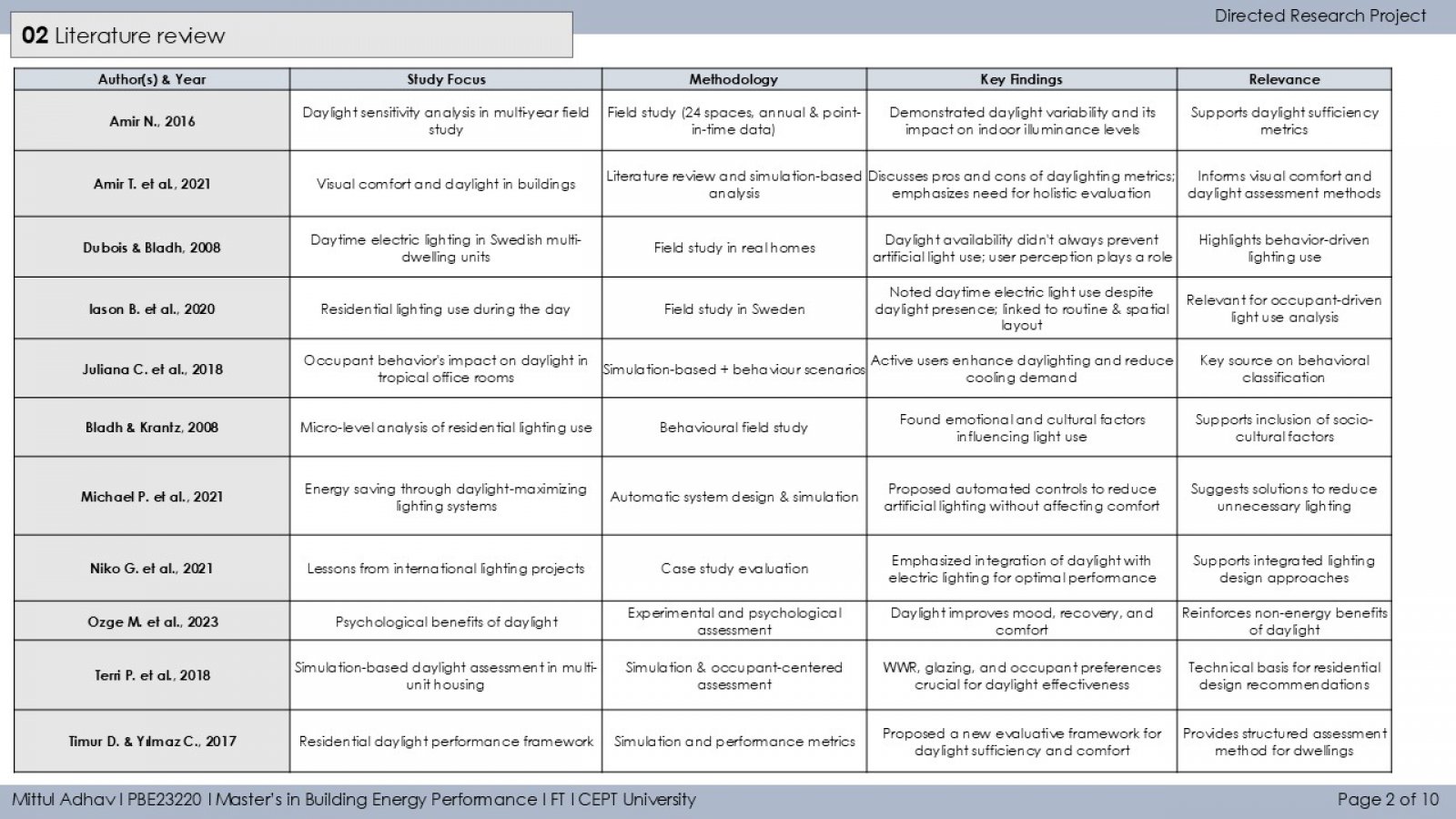
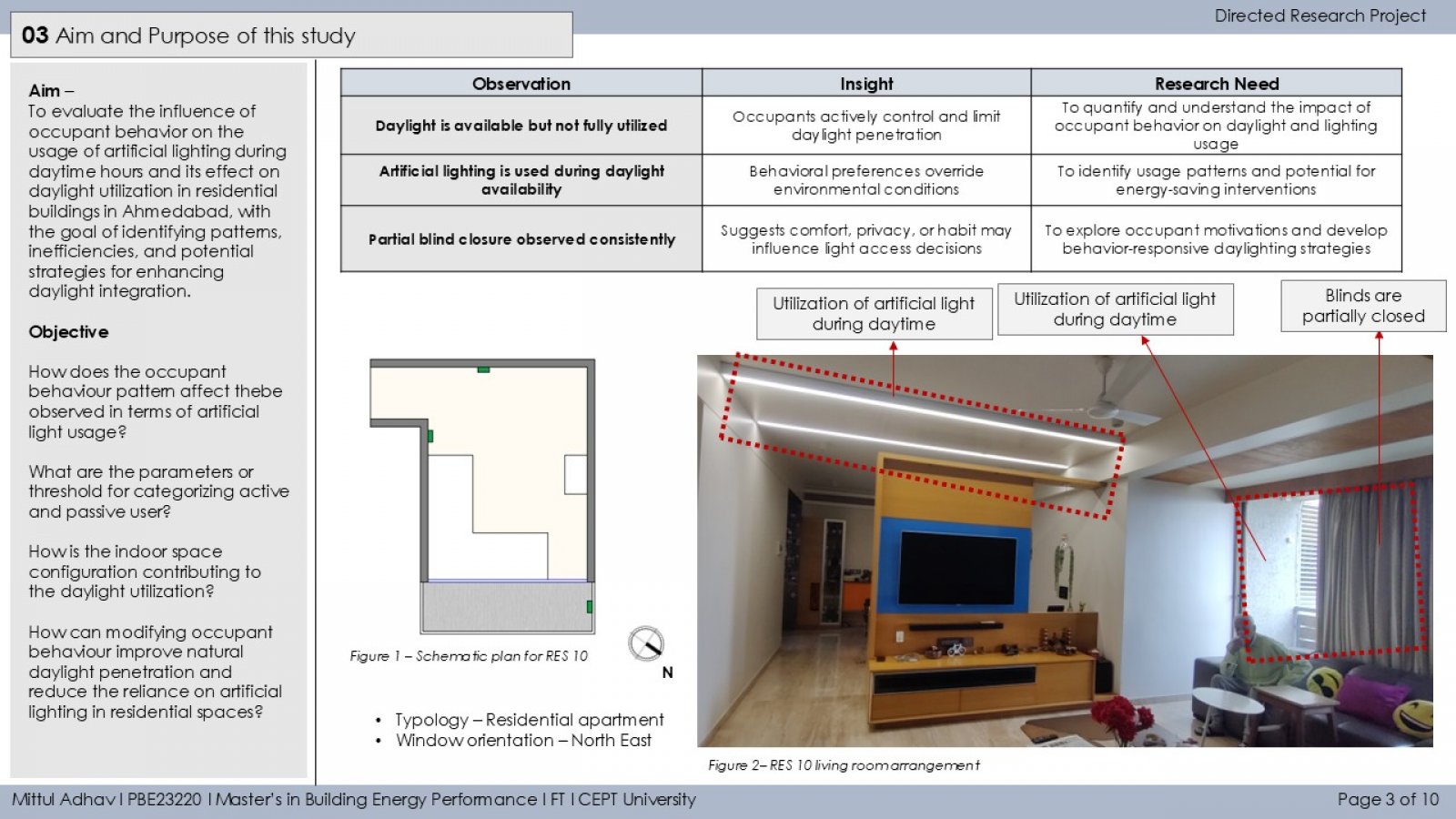
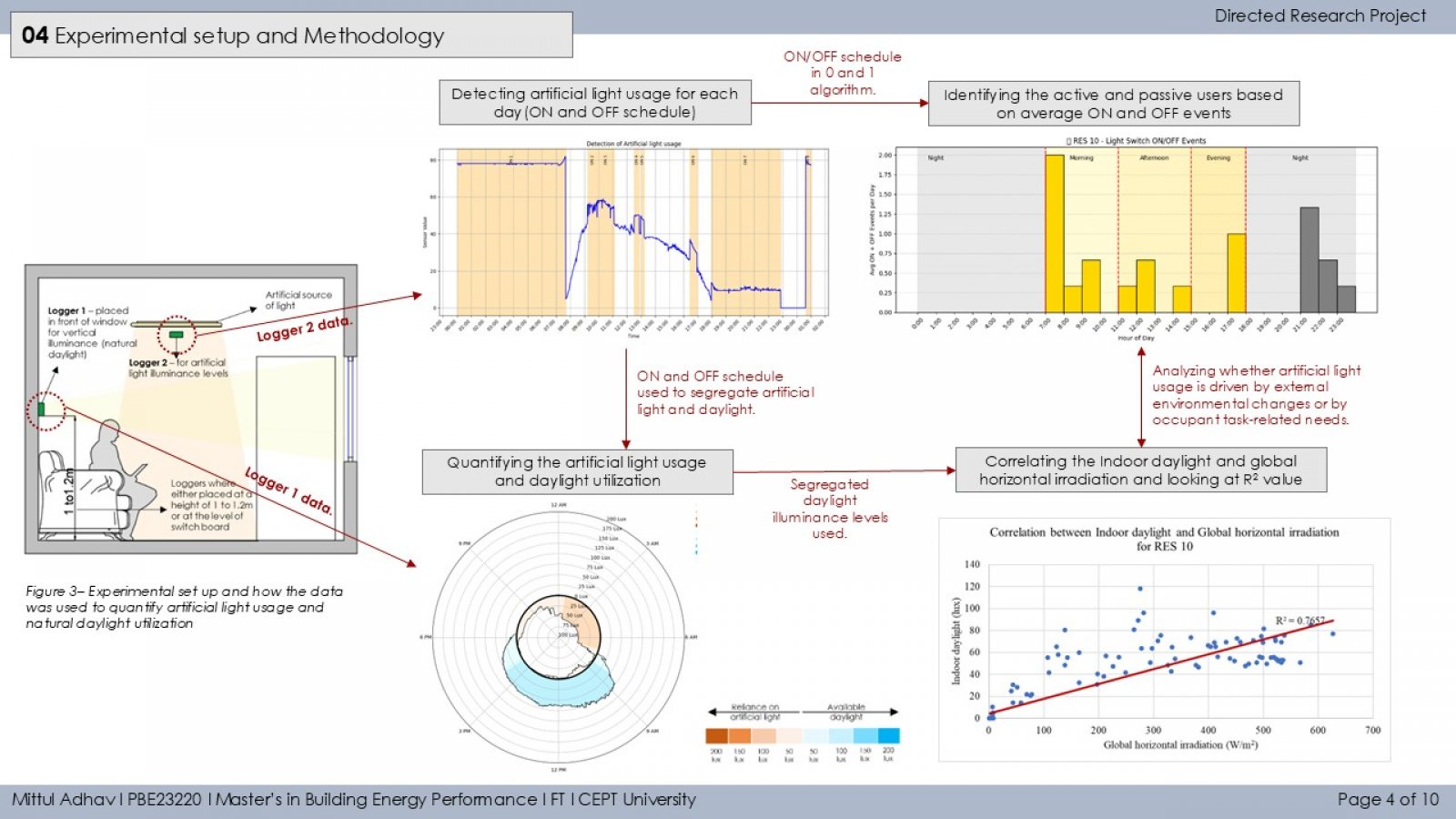
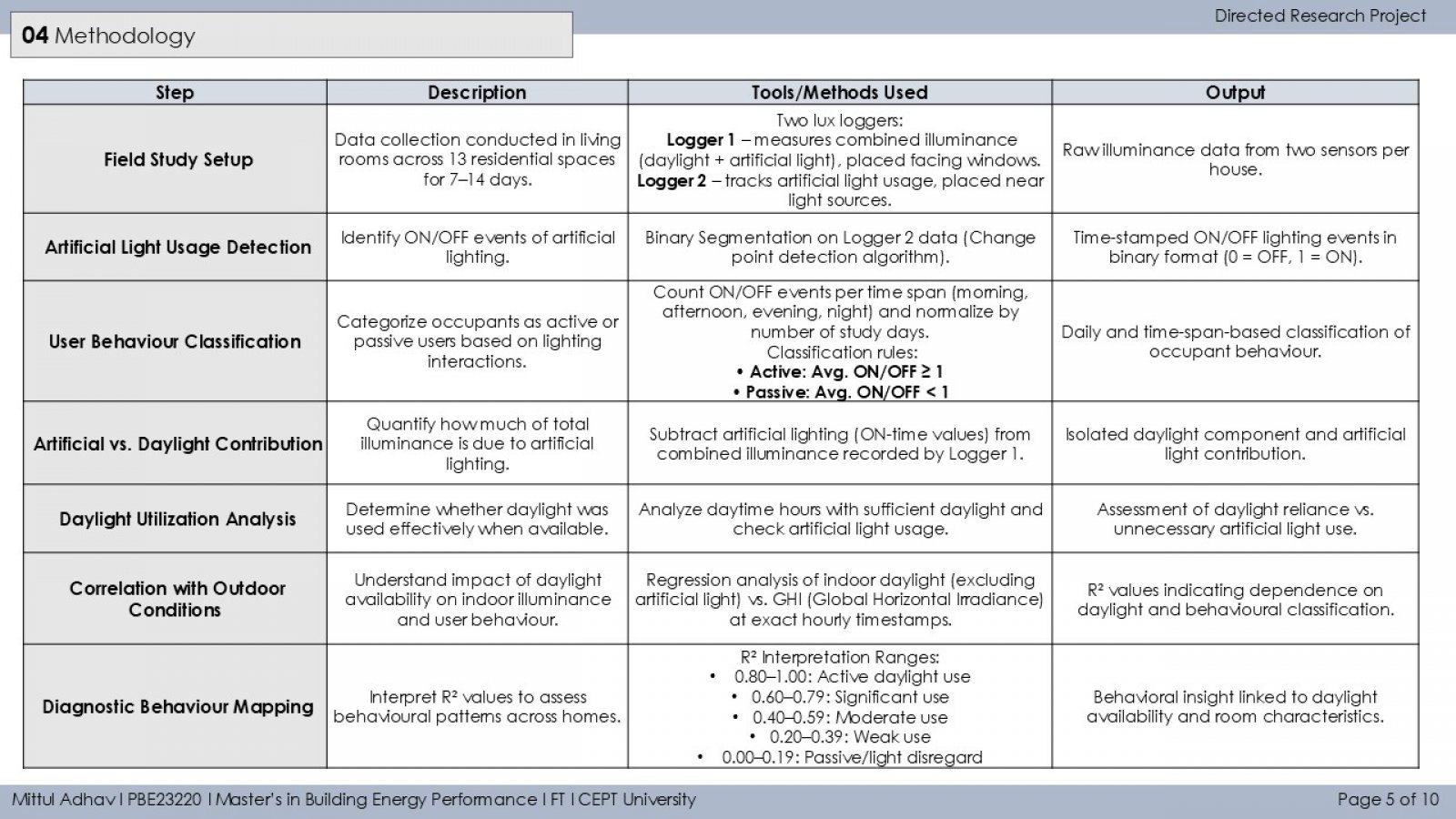
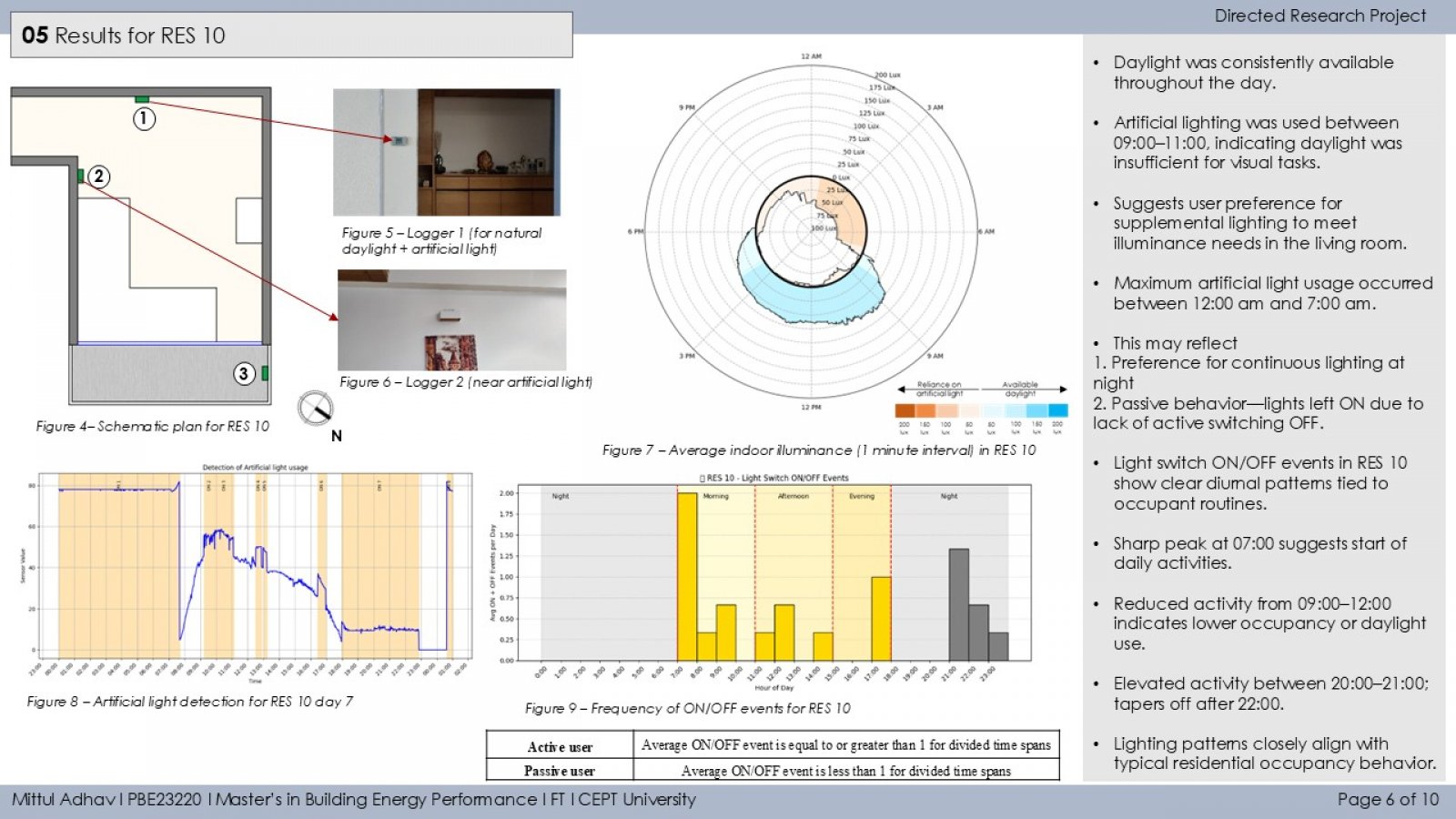
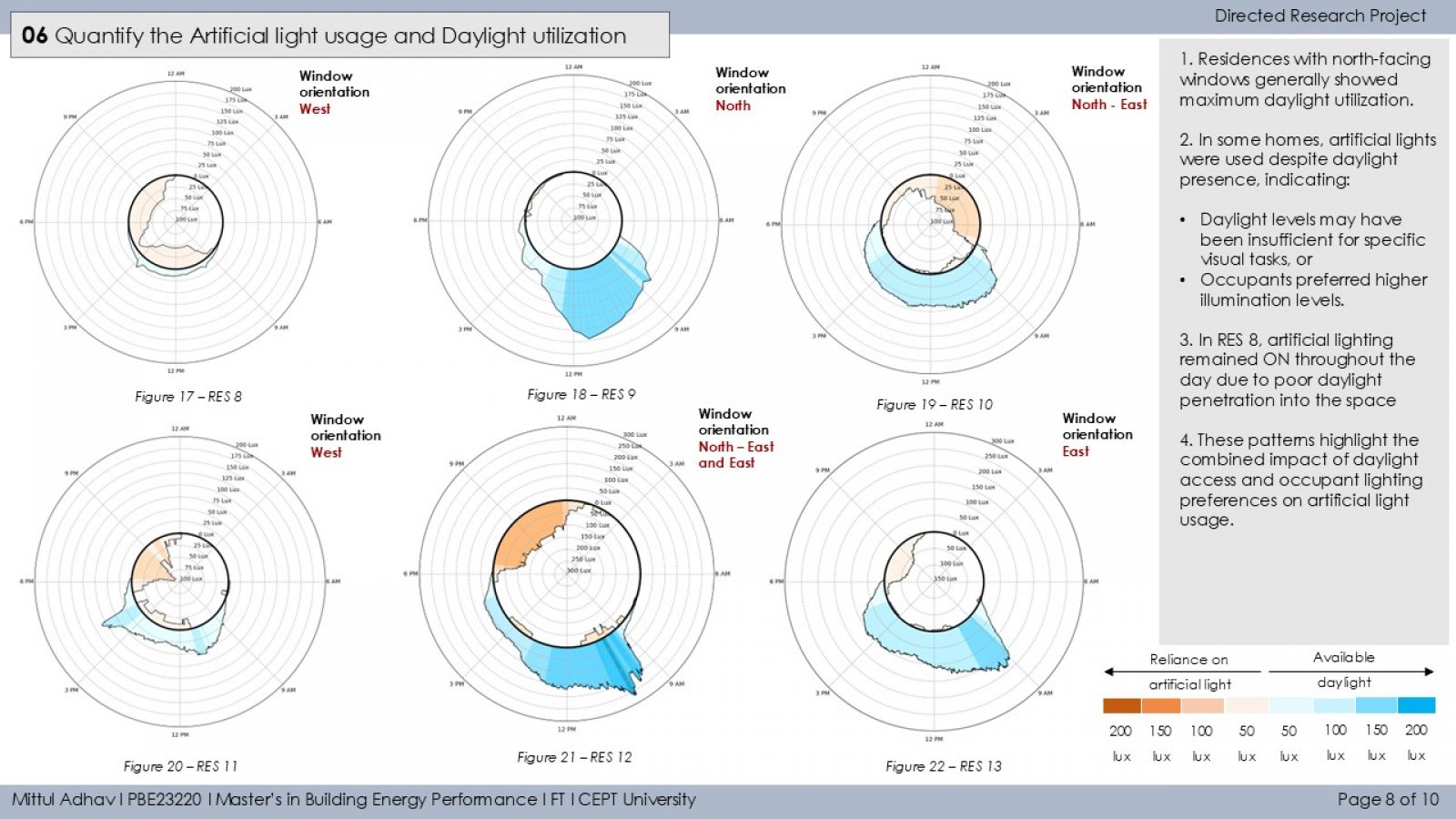
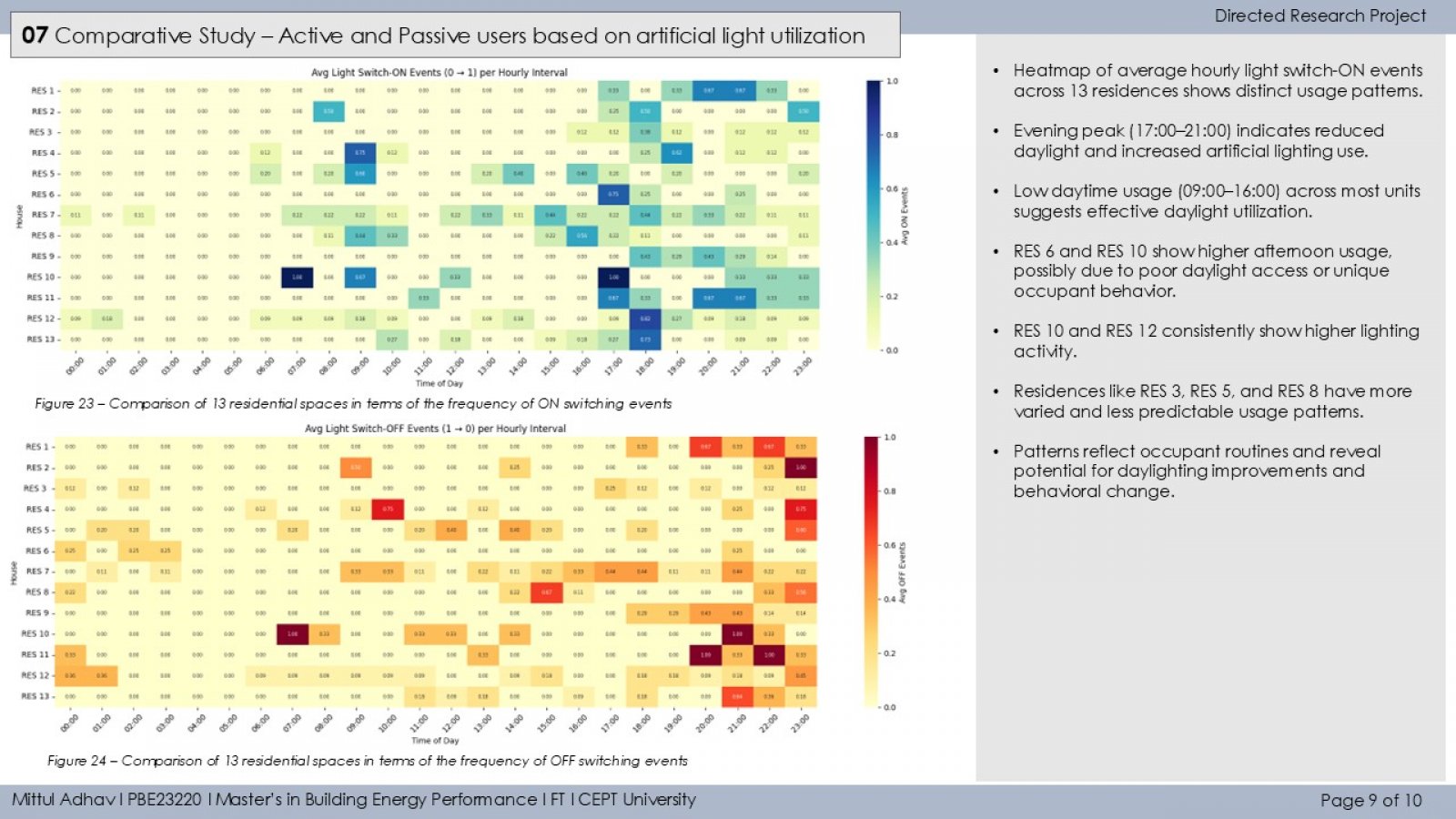
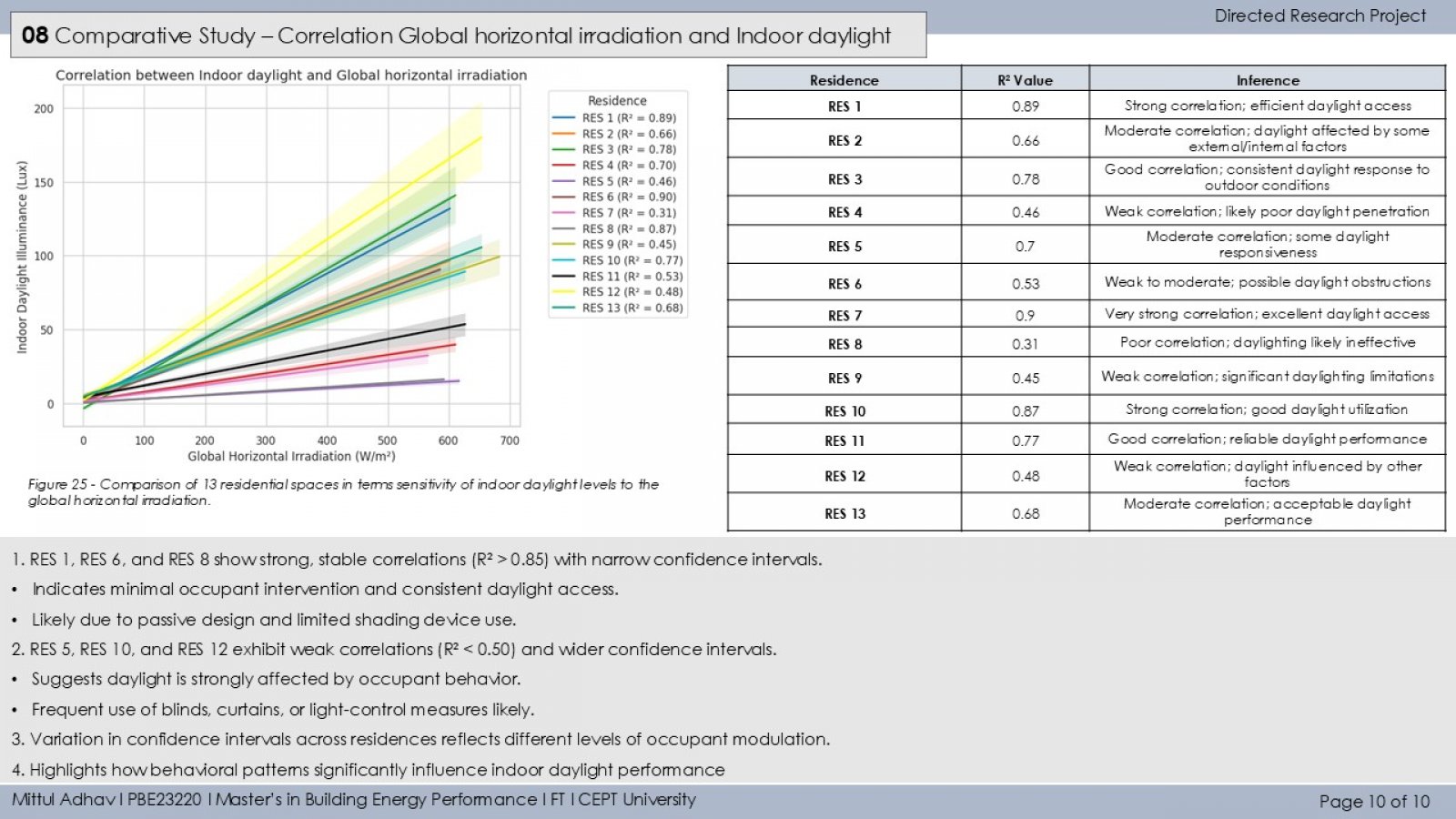
The study investigates how occupant behavior influences the use of artificial lighting and daylight in residential buildings during daytime in Ahmedabad. It monitors lighting patterns in 13 households using illuminance loggers placed near windows and artificial light sources. A binary segmentation technique detects ON/OFF lighting events, and occupants are classified as active or passive users based on interaction frequency. The study also examines the relationship between indoor daylight and outdoor solar irradiance (GHI), revealing that both environmental conditions and personal habits significantly impact daylight reliance. Findings aim to guide occupant-centric design and lighting strategies to improve energy efficiency and comfort.