Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
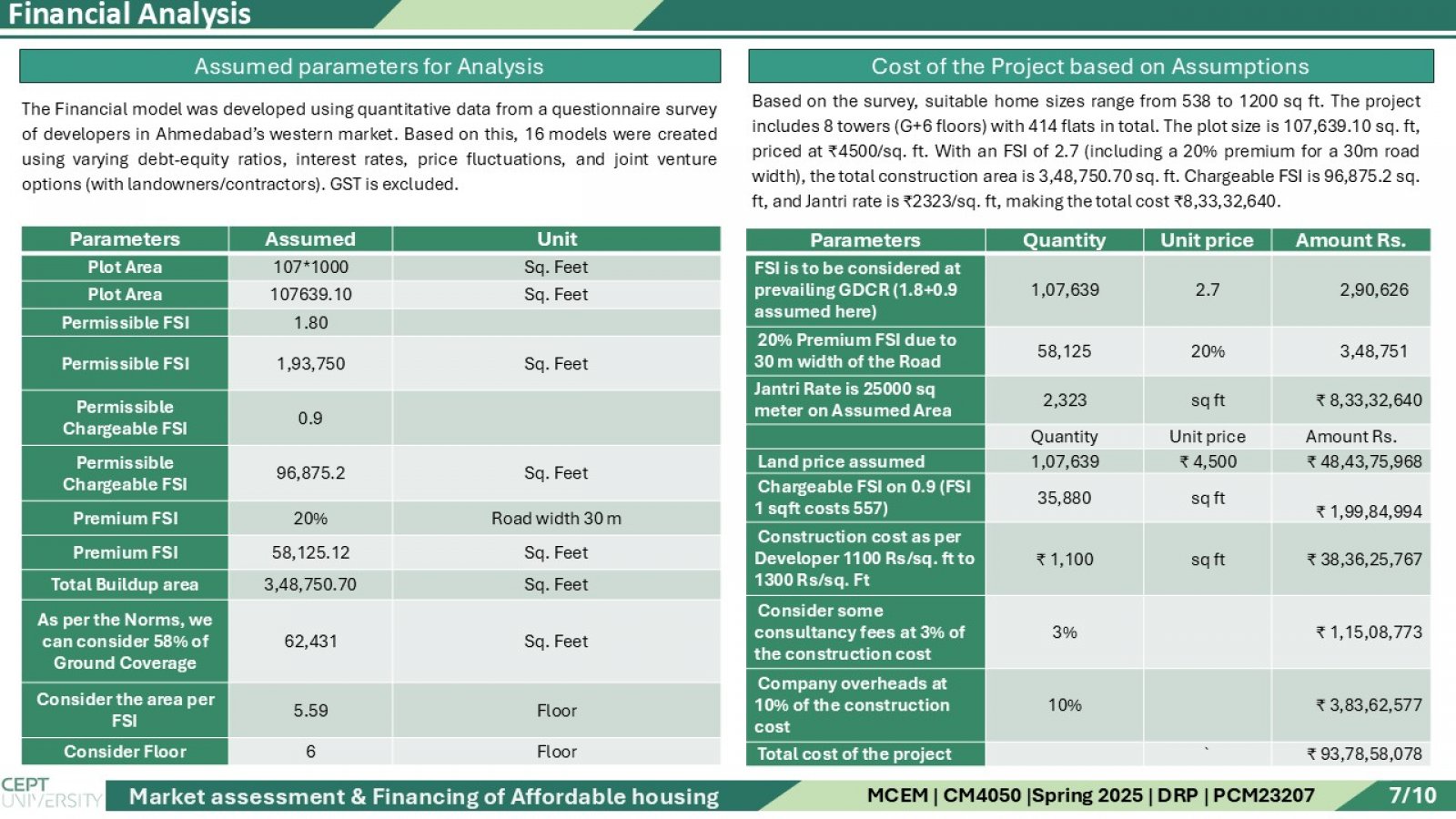
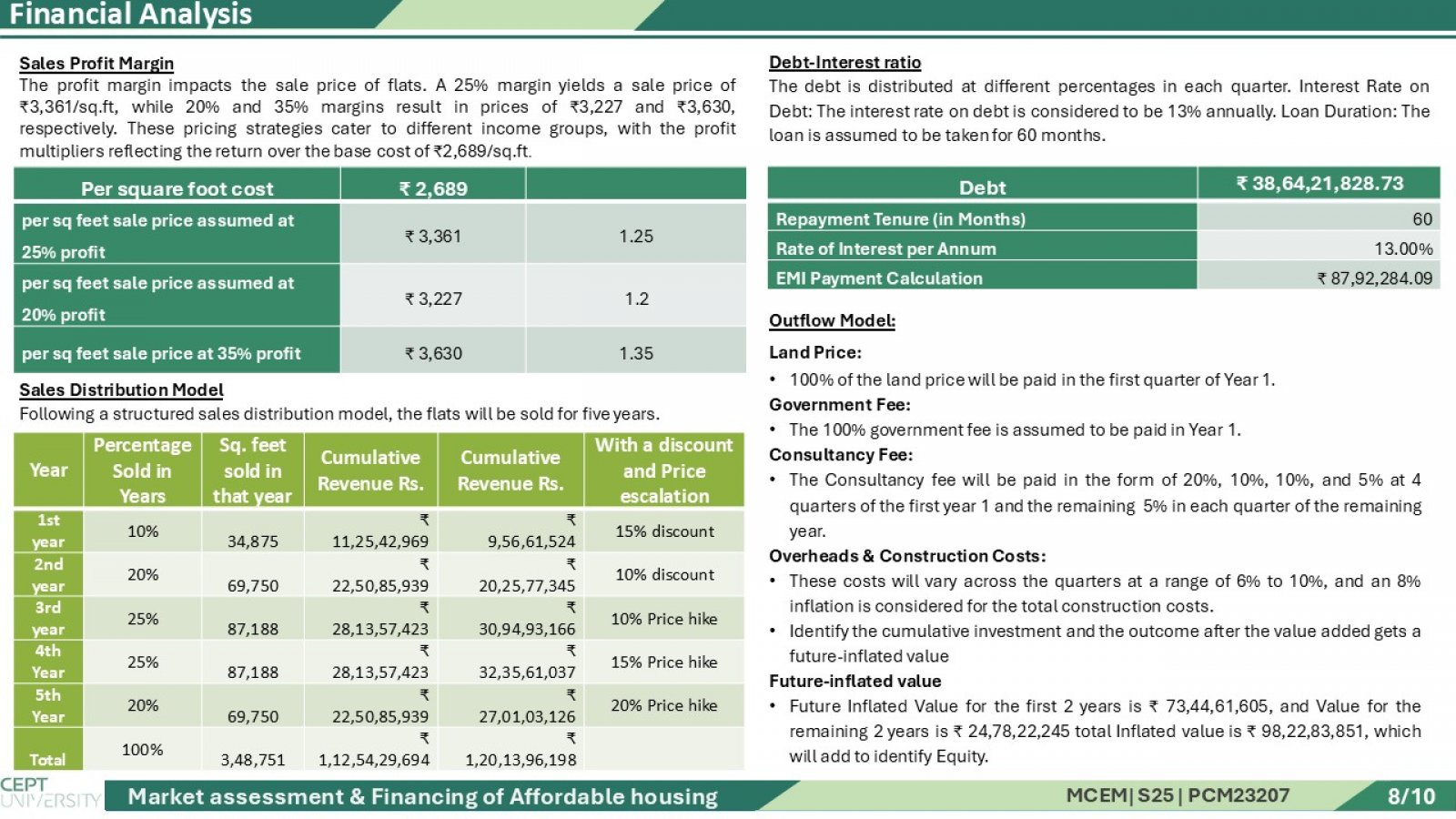
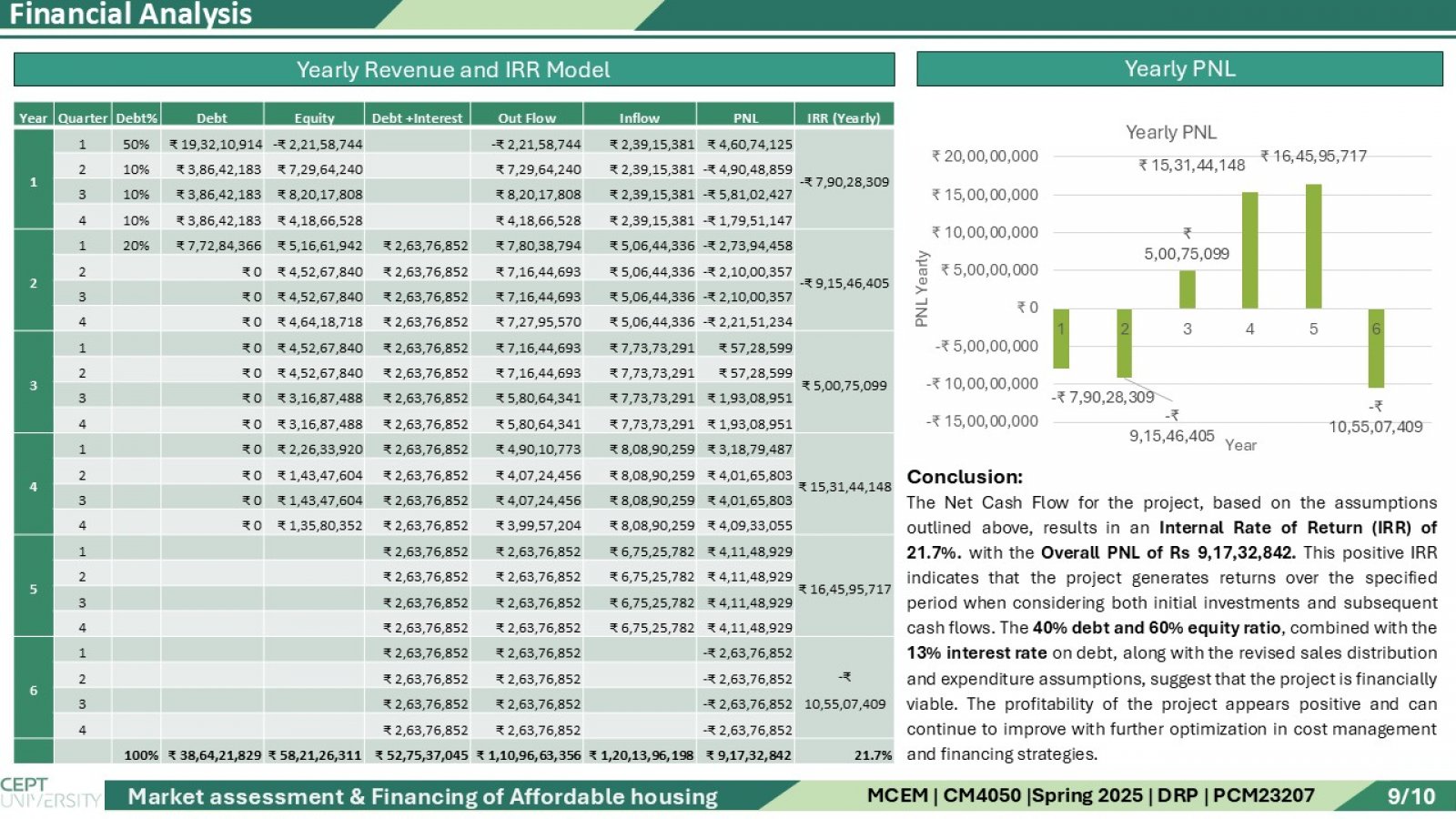
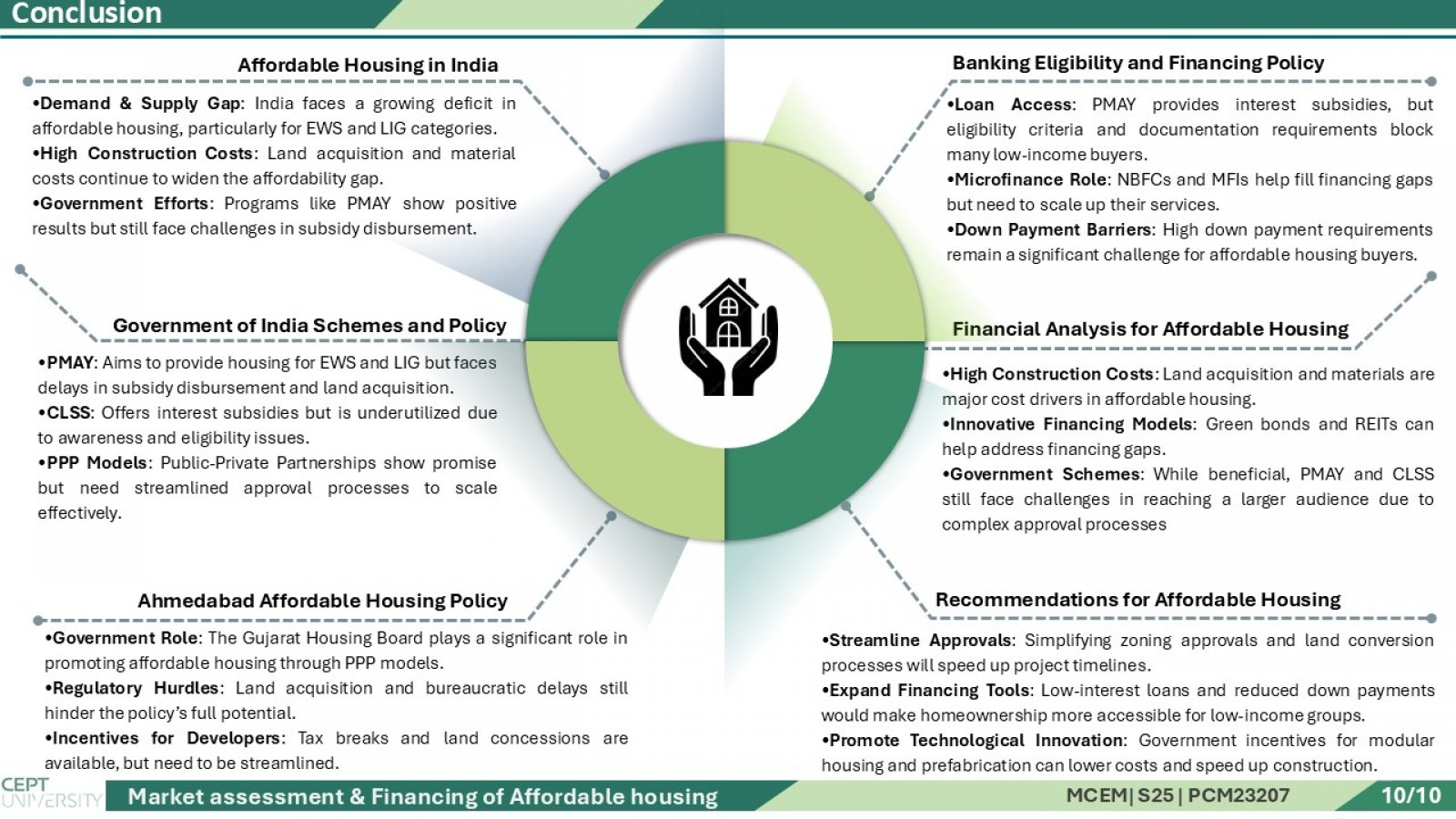
This study presents an integrated analysis of the affordable housing ecosystem in India, with a focused case on Gujarat. It combines primary surveys conducted with developers and end users, alongside a comprehensive secondary market review of national and state-level policies. The research evaluates how central schemes like PMAY (Urban & Gramin), CLSS, and AMRUT 2.0, alongside Gujarat-specific planning instruments and incentives, facilitate affordable housing development. Special attention is given to how the Gujarat Government supports private developers through zoning relaxations, bonus FSI, and township policies to ensure viable and scalable projects. Further, the study explores the role of the banking sector, housing finance companies (HFCs), and the RBI’s priority sector lending criteria in improving mortgage accessibility for EWS and LIG beneficiaries. The financial aspect includes developing 16 financial models, where land cost assumptions, FSI utilization, consultant and construction costs are used to forecast project cash flows and compute the Internal Rate of Return (IRR). Each model's output is analyzed through IRR graphs to identify the most financially sustainable and beneficiary-friendly structure for affordable housing delivery.