Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
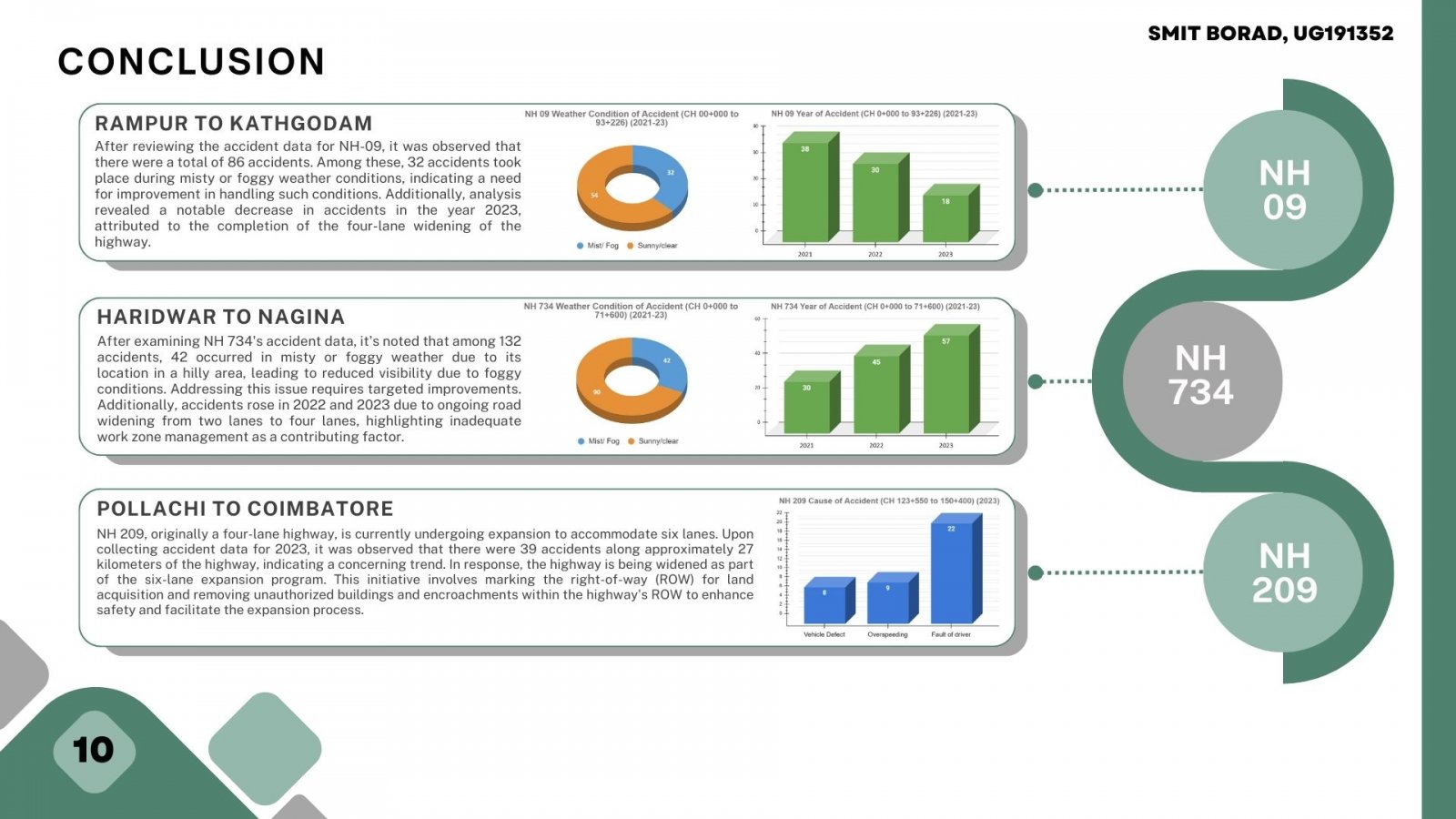
This study investigates the alarming rise in road accidents, fatalities, and injuries on two-lane and four-lane National Highways (NHs) in India, focusing on NH 09, NH 734, and NH 209. Analysis of accident data from these highways reveals significant insights into the contributing factors and highlights the urgent need for effective mitigation measures. Factors such as weather conditions, road infrastructure development, and human error play pivotal roles in the occurrence of accidents. Notably, the transition from two-lane to four-lane roads on NH 09 and NH 734 saw contrasting effects on accident rates, emphasizing the importance of safety measures during road expansion projects. Moreover, the prevalence of mist and fog exacerbates road safety challenges, as evidenced by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways' report indicating a surge in accidents under such conditions. The findings underscore the imperative for comprehensive blackspot management processes and targeted interventions to address localized risk factors and reduce road accidents. Implementation of access control measures, geometric design improvements, and enhanced enforcement of traffic regulations are crucial steps towards creating safer road environments and mitigating the escalating trend of road accidents on Indian highways.