Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
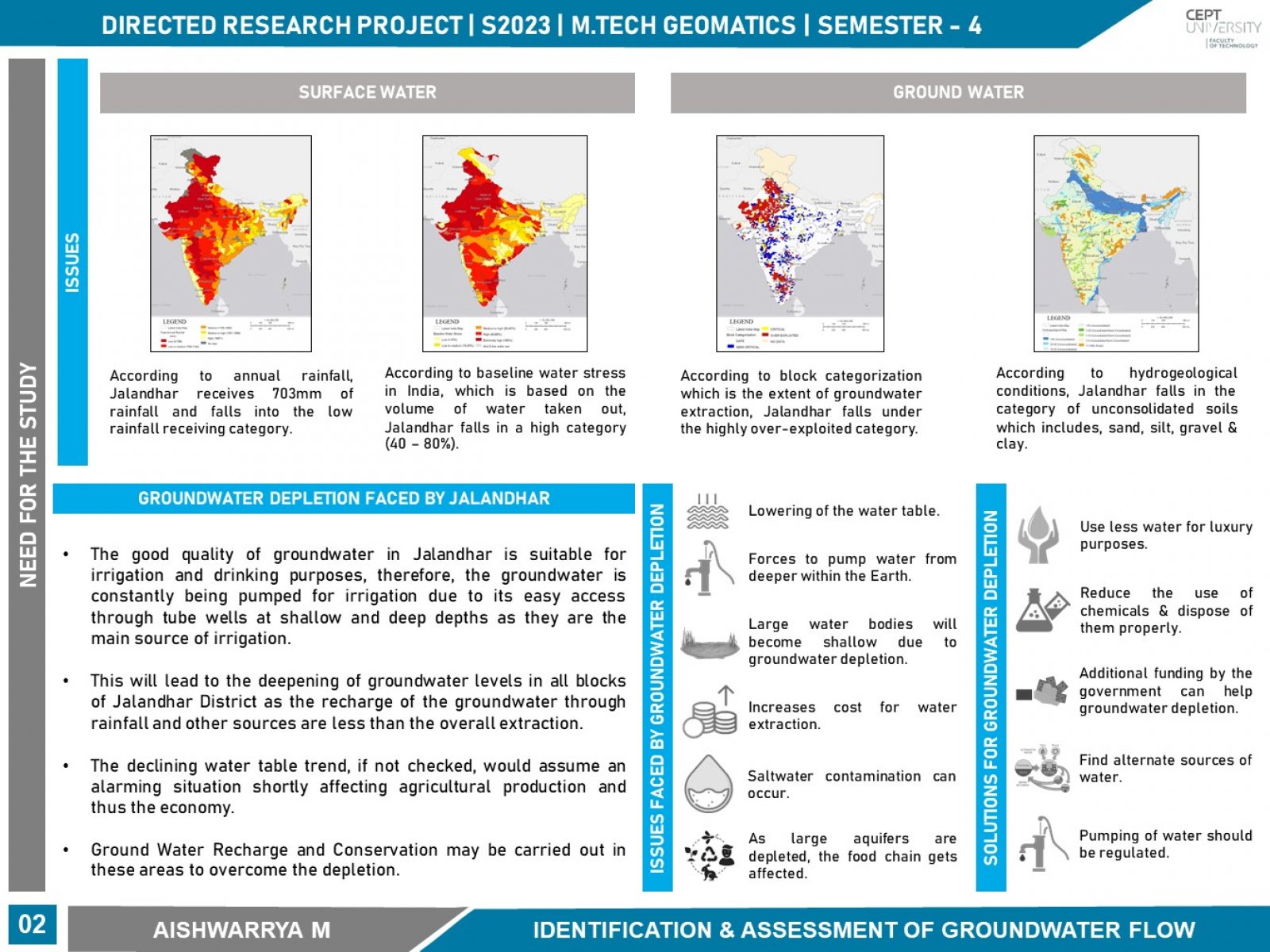
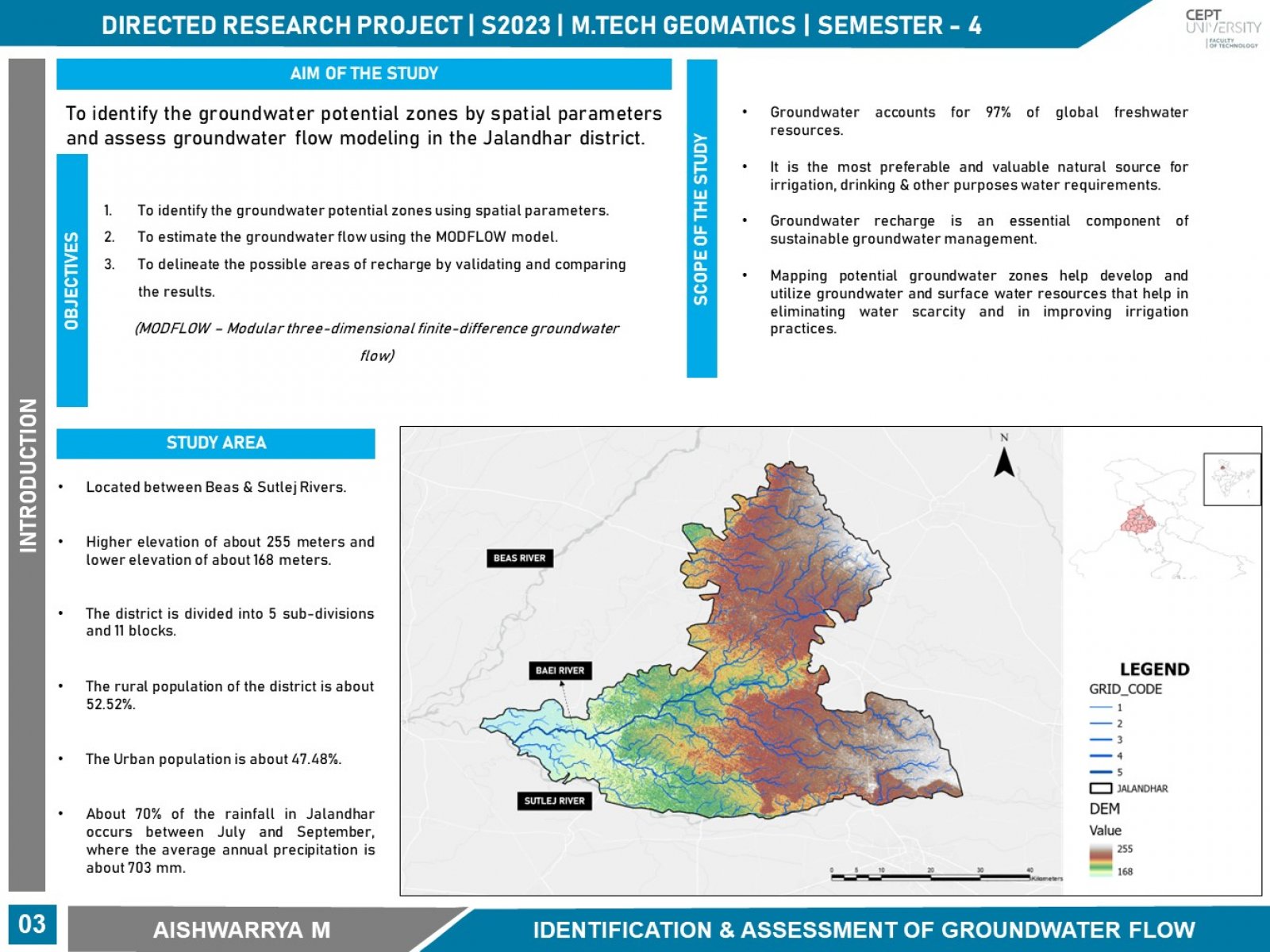
The concept of a sponge city is defined as a city that is designed to absorb, clean and reuse rainfall to reduce runoff. Sponge City helps in reducing surface runoff and increases the groundwater level. As groundwater is the most essential for agriculture, irrigation, drinking, and other purposes of water. The recharge of groundwater is an essential component of sustainable groundwater management. Thus, mapping potential groundwater zones helps develop and utilize groundwater and surface water resources. The groundwater table has been declining in Punjab over the past decades and in the Jalandhar district. The baseline water stress for the Jalandhar district is relatively higher. The annual rainfall received in Jalandhar is about 703 mm with an average of 35 days as its rainy days. According to the Indiawatertool, Jalandhar belongs to the low rainfall category. Based on the Baseline water stress categorization, Jalandhar falls in a high category which is about 40 – 80%. Based on the groundwater block categorization, many districts in Punjab have been highly over-exploited and so is Jalandhar. According to groundwater hydrological conditions, Jalandhar falls under the category of unconsolidated soils category which includes that the area is covered fully with sand, silt & clay. These are the factors that led to the identification of the potential zones for groundwater with the help of GIS spatial analysis and modeling.