Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
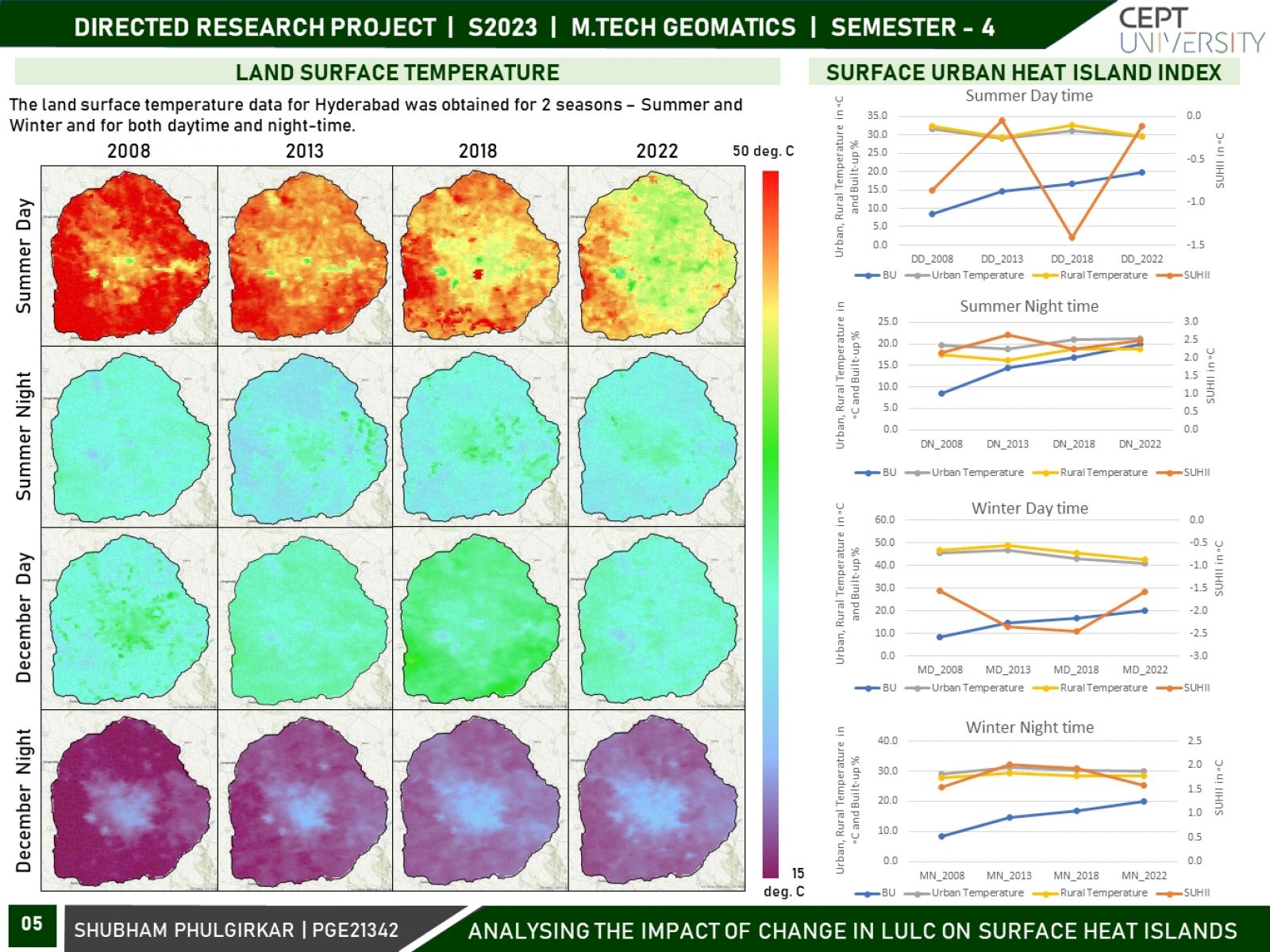
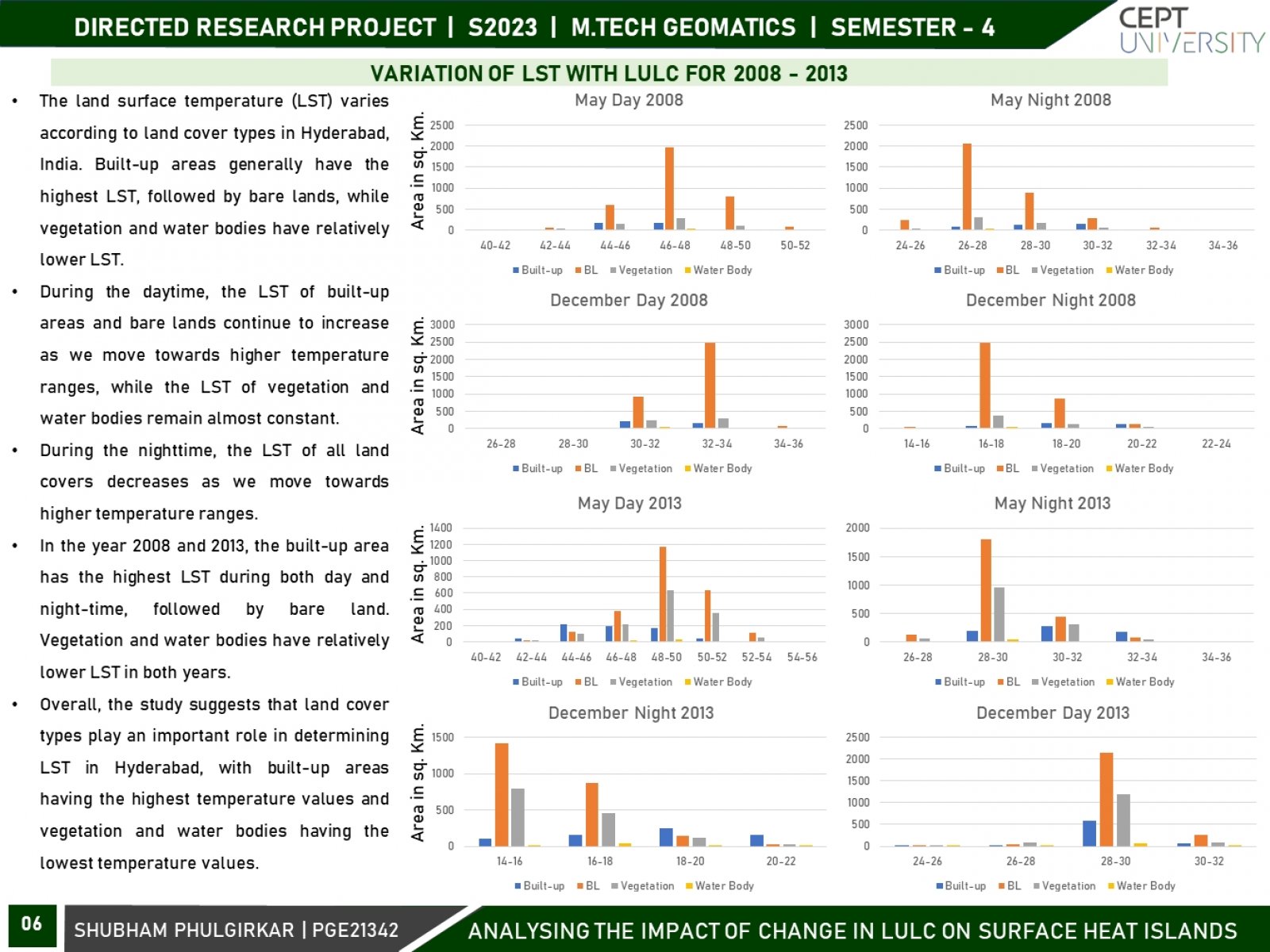
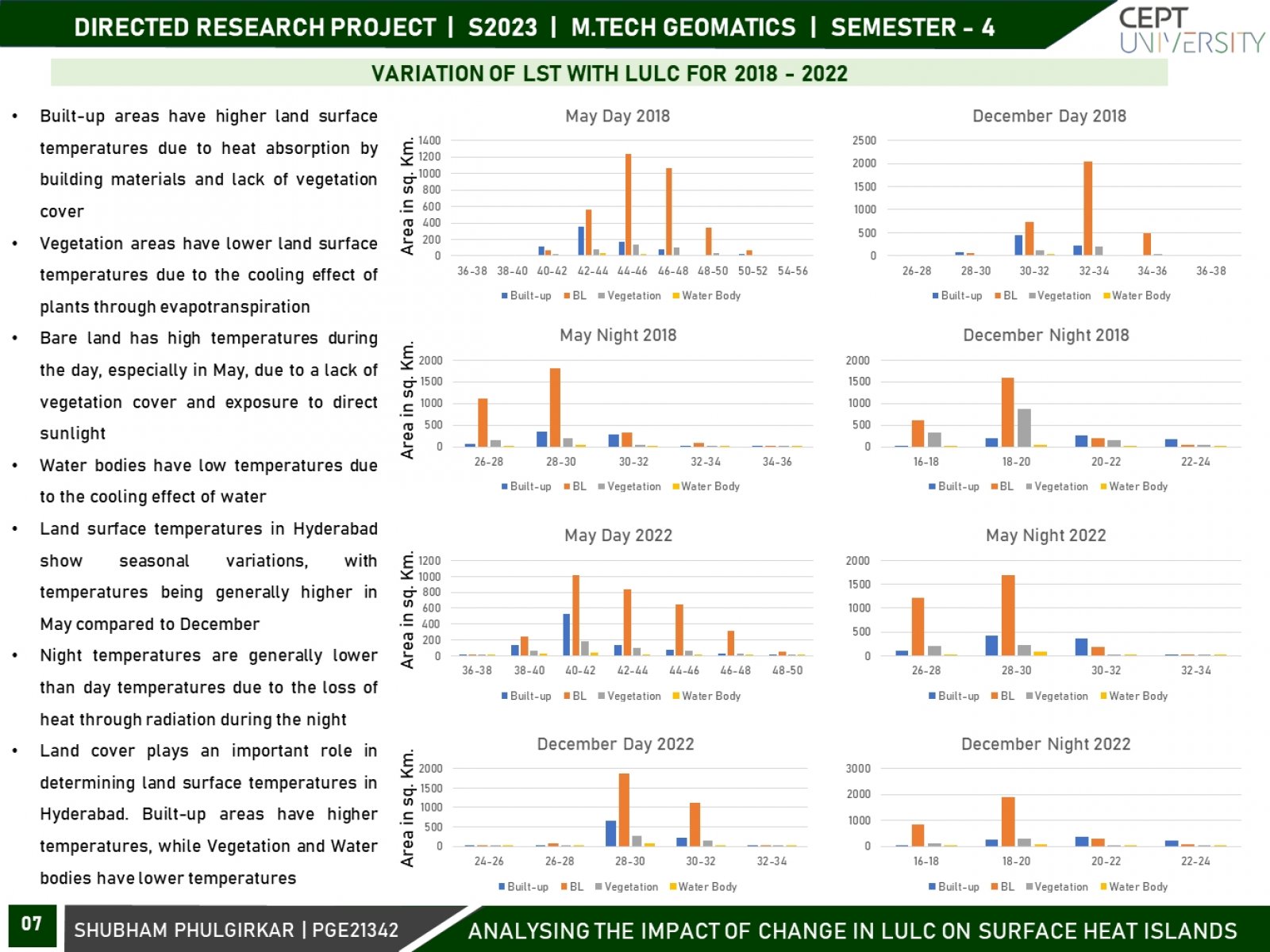
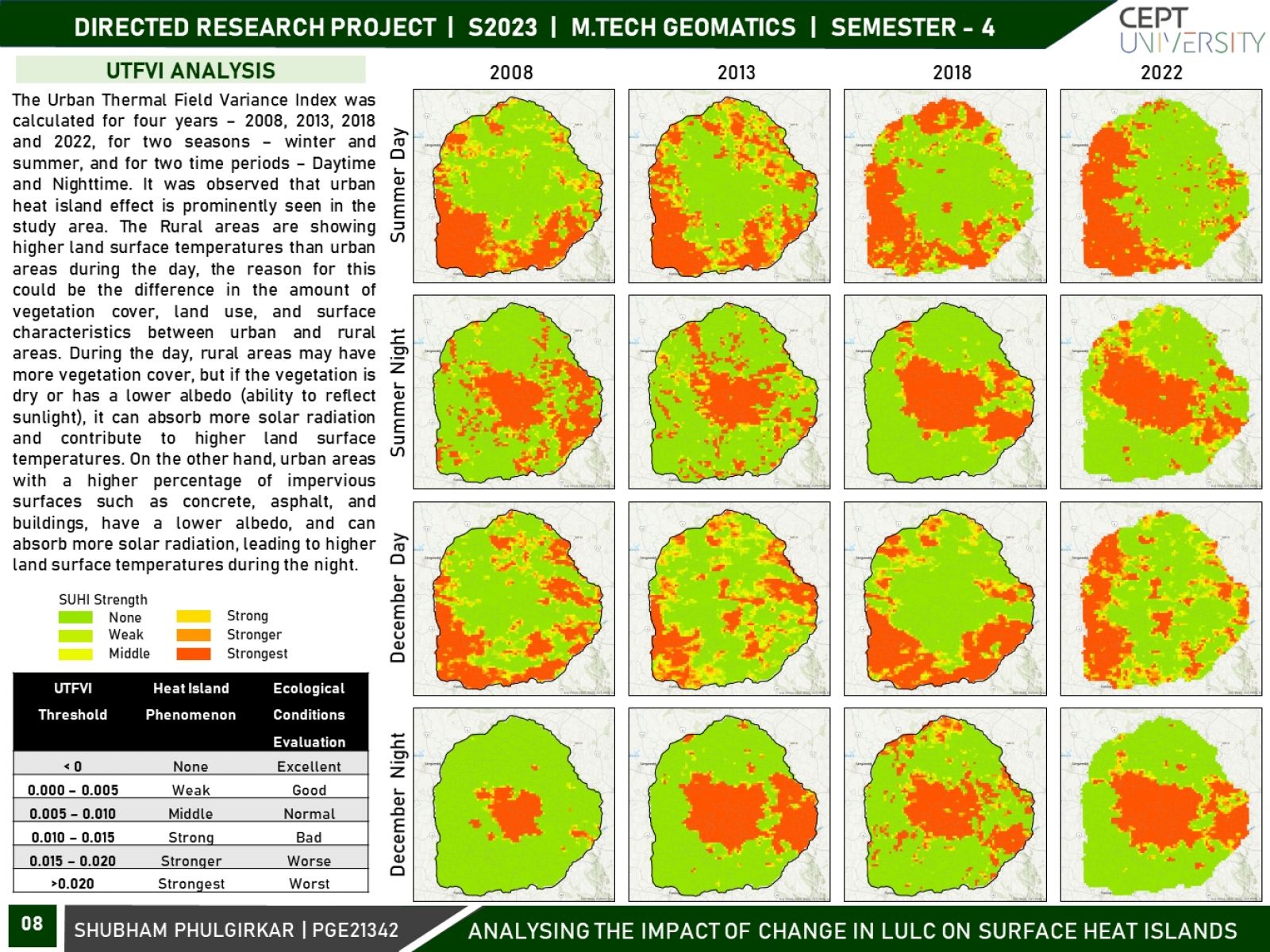
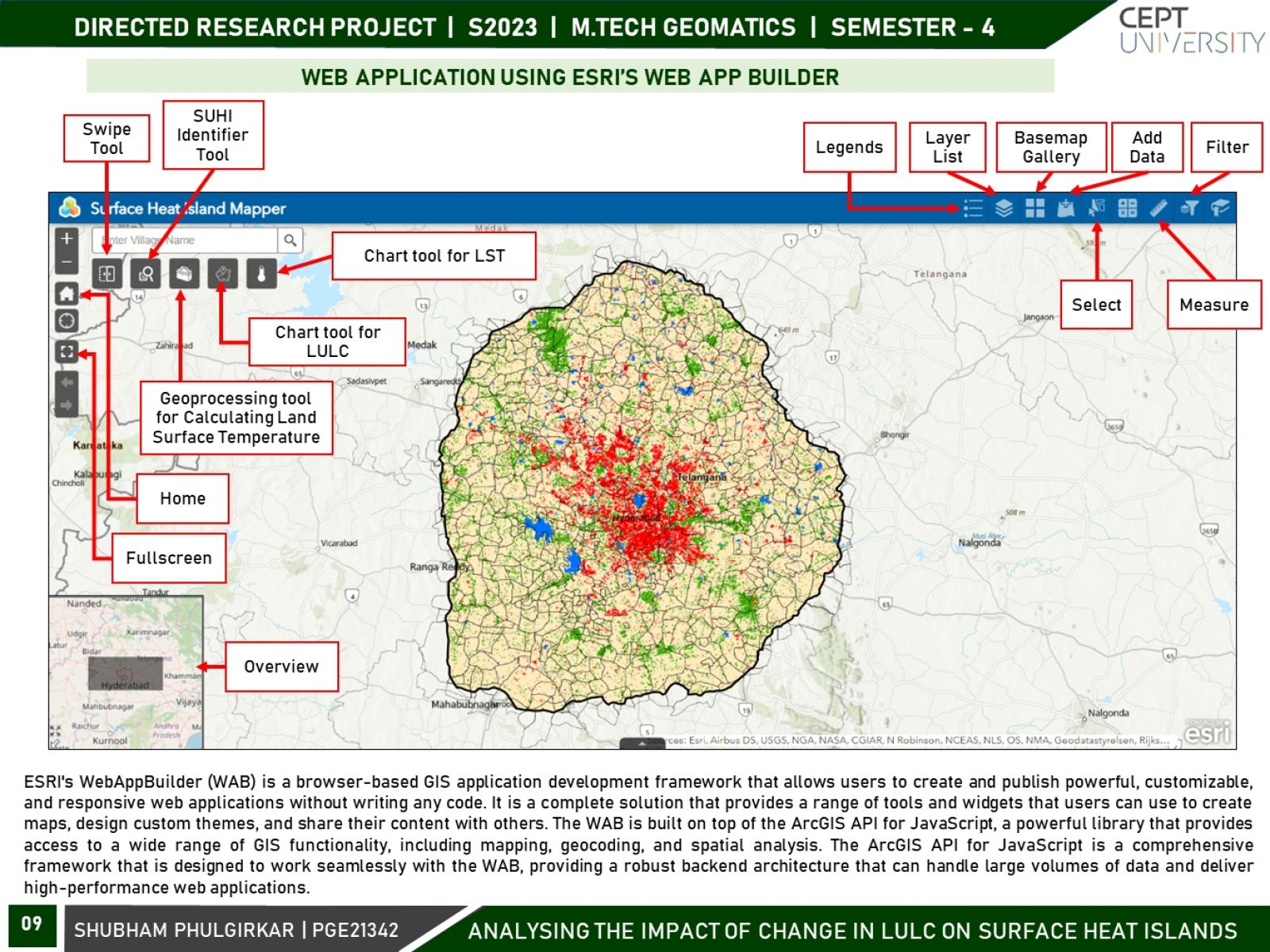
The land surface temperature (LST) pattern is regarded as one of the most important indicators of the environmental consequences of land use/land cover change. Land use and land cover (LULC) changes significantly influence land surface temperature (LST), which is a crucial indicator of the earth’s environmental condition. This research focuses on variations in surface urban heat islands (SUHIs) over the course of two seasons, i.e., winter and summer, and two times - daytime and night-time. Using remotely sensed datasets and geospatial techniques, an attempt will be made to analyze the spatiotemporal variation in urban heat islands (UHIs) and its association with LULC over two decades for Hyderabad City.