Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
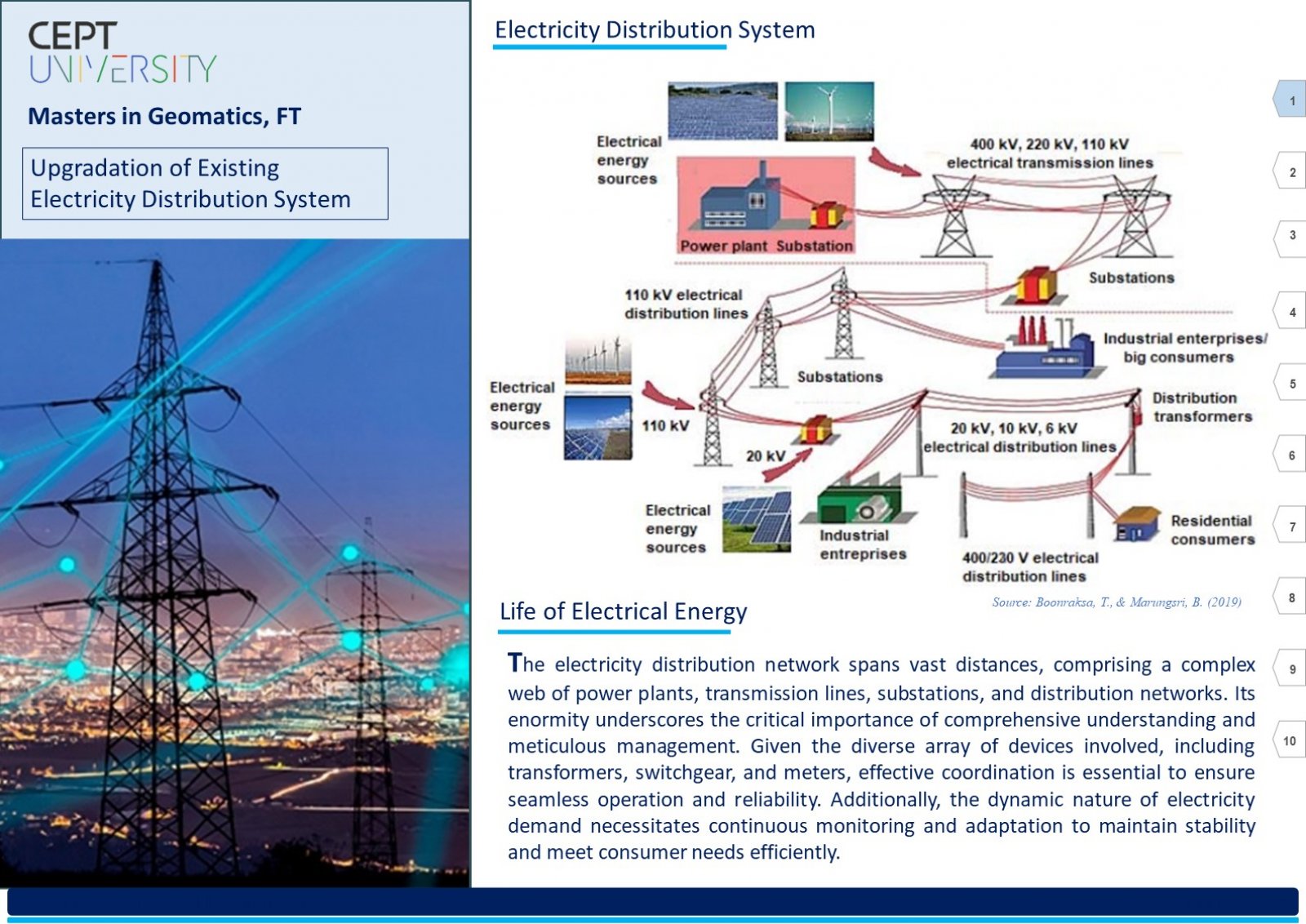
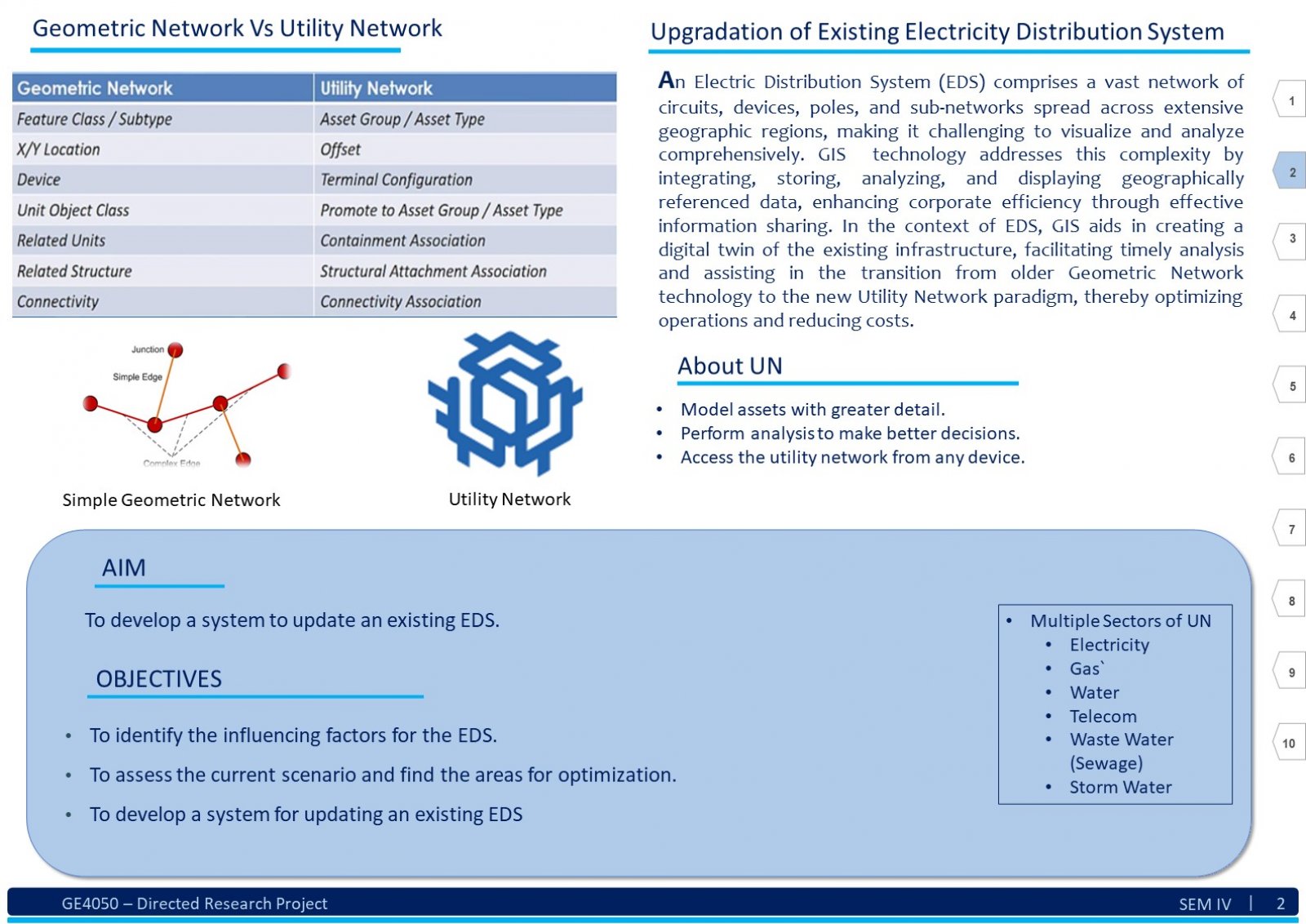
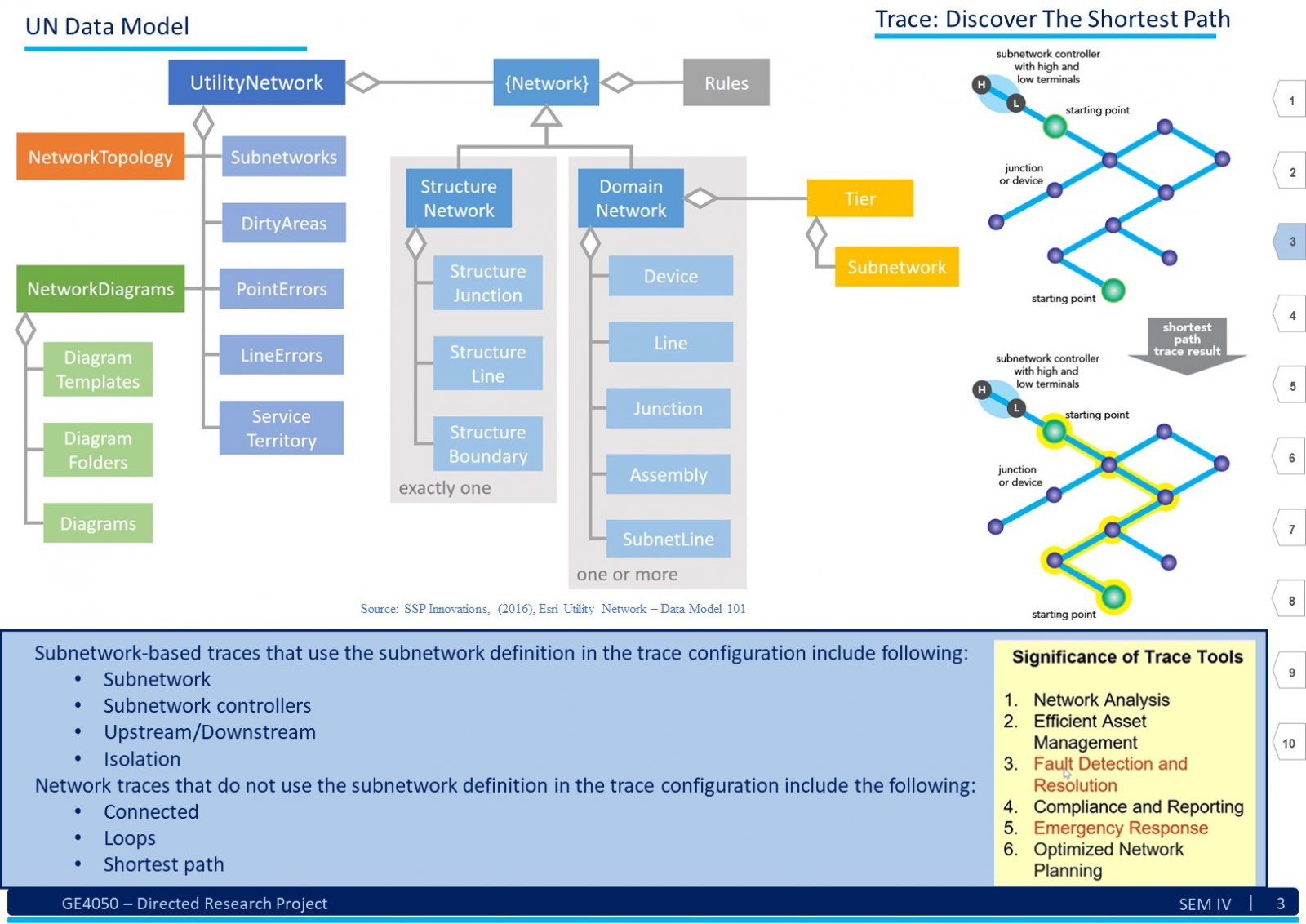
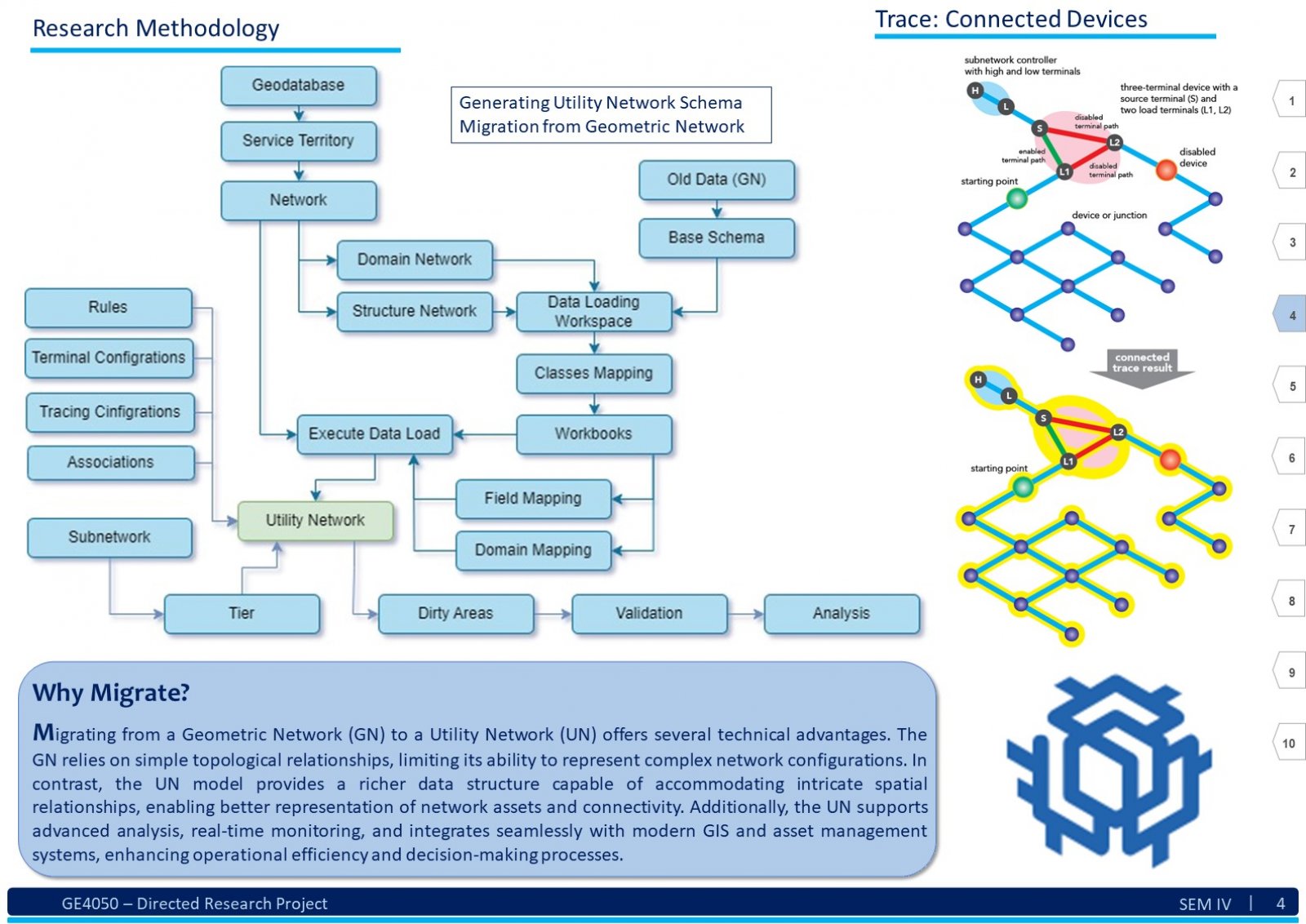
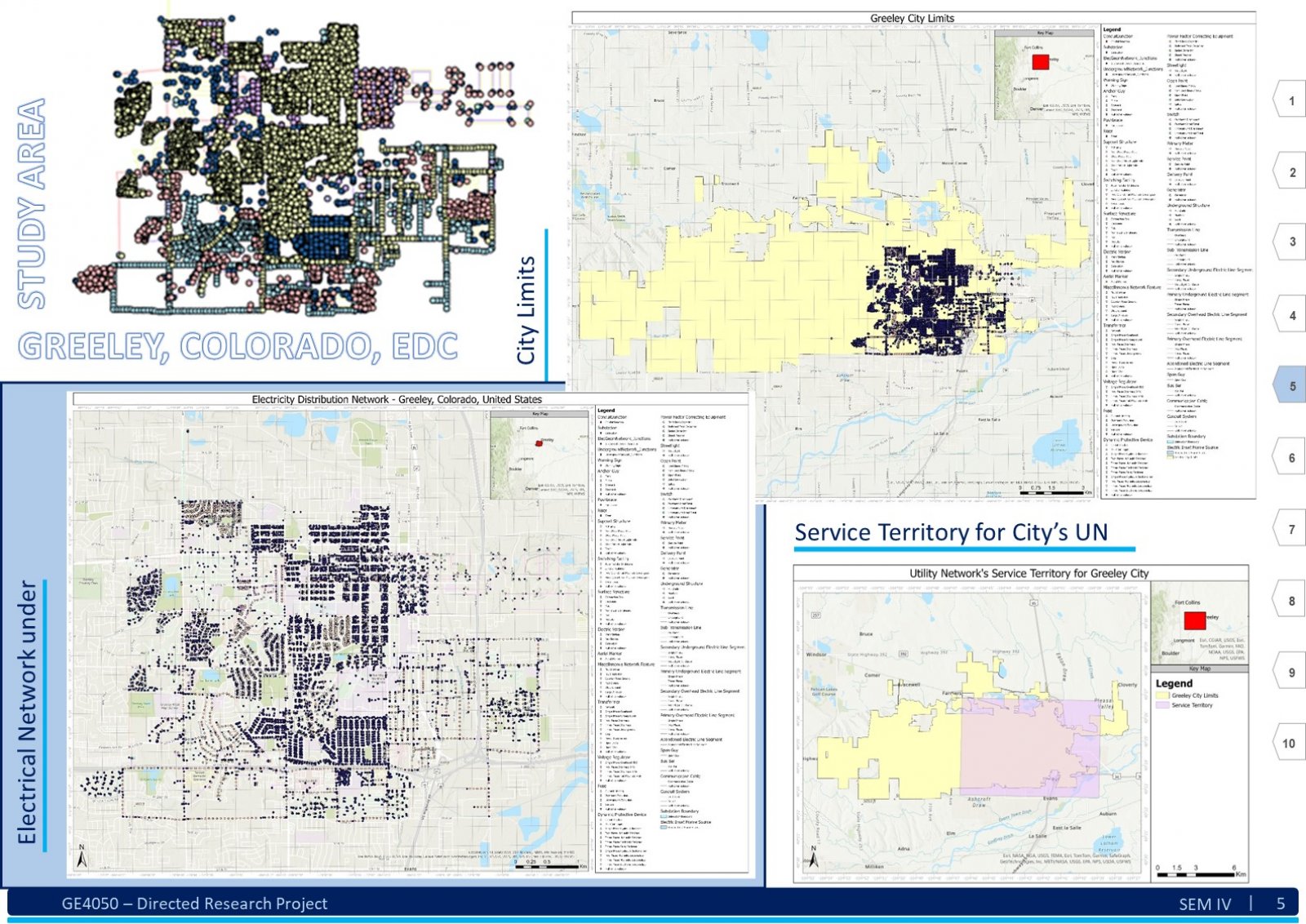
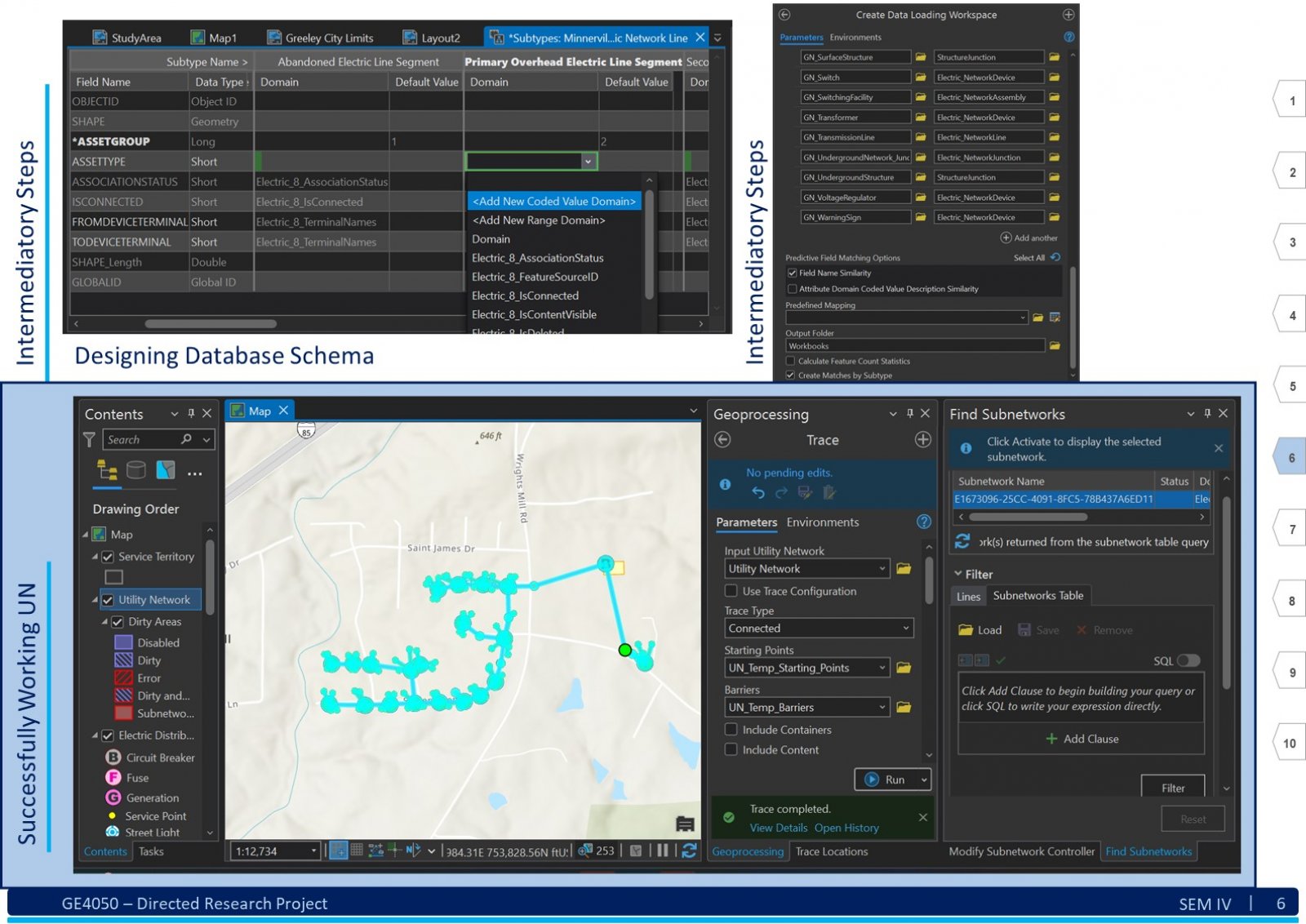
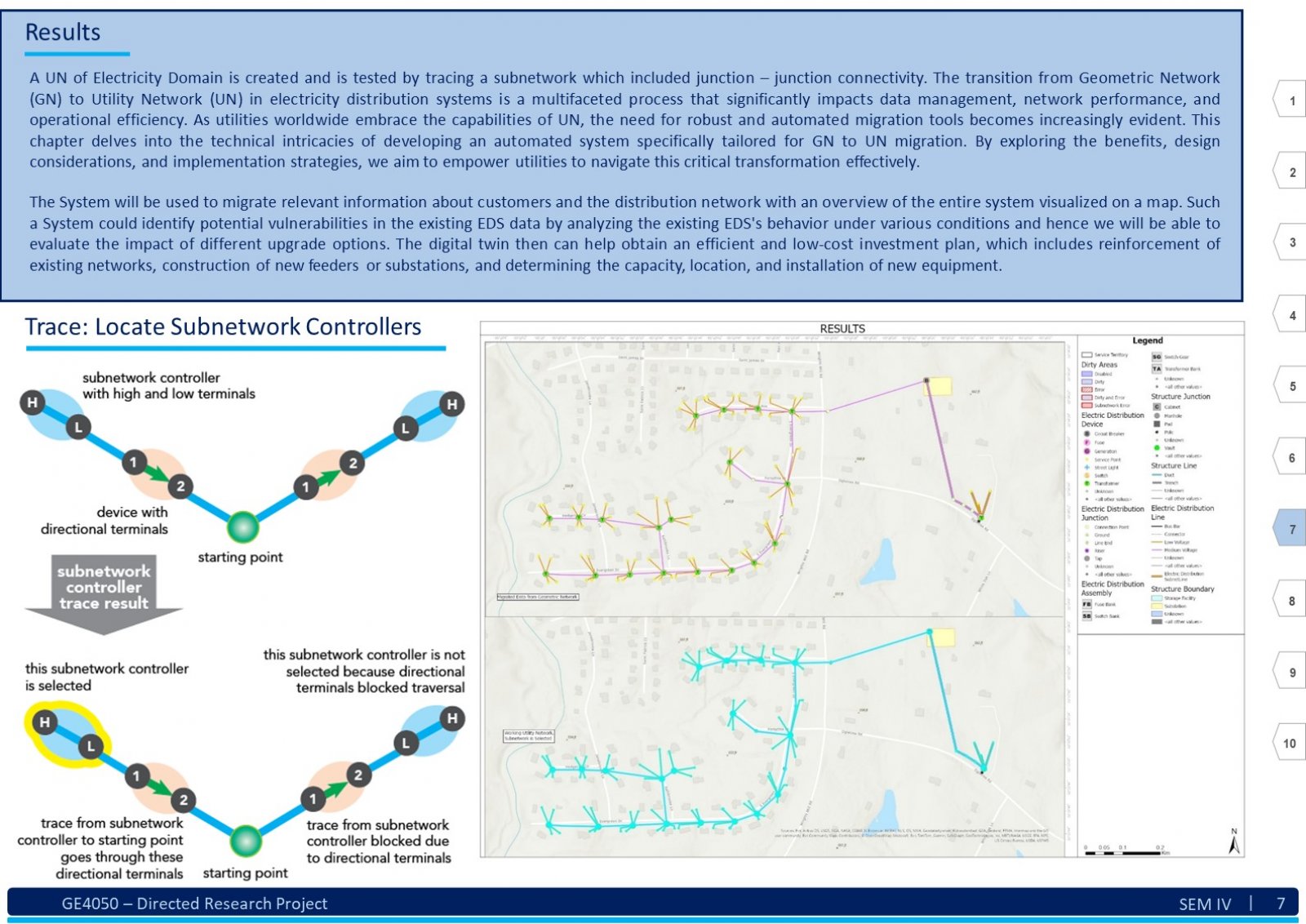
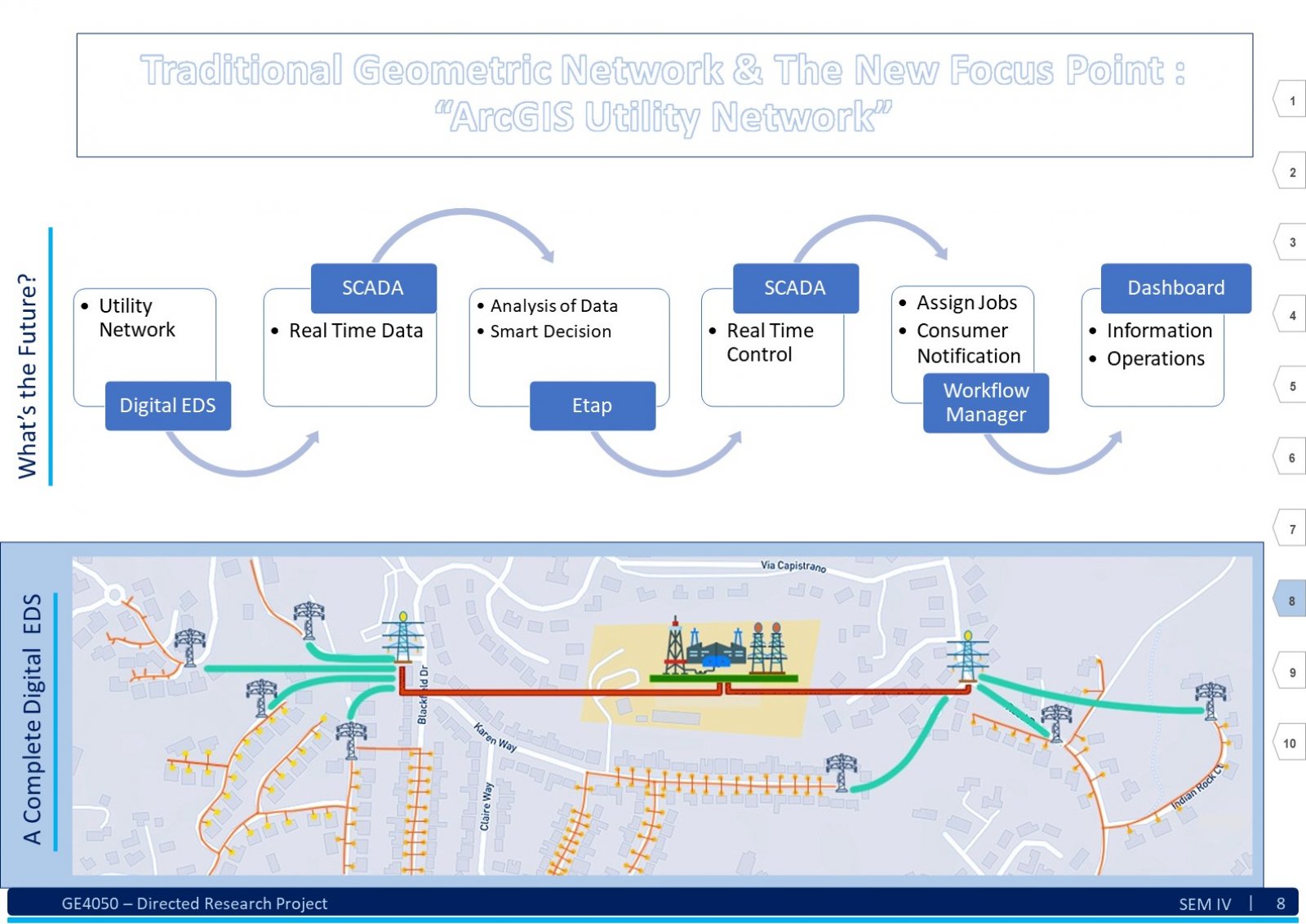
An Electric Distribution System (EDS) is a complex network that encompasses various circuits, devices, poles, structures, and sub-networks across a large geographical area. Due to its scale and intricacy, visualizing, comprehending, sharing, and analyzing the entire EDS simultaneously can be challenging. Here, Geographic Information System (GIS) technology comes into play. GIS as an information system integrates, stores, analyses, shares, and displays geographically referenced data. It enables greater corporate efficiency by facilitating effective information sharing and distribution. In the context of EDS, GIS can be beneficial in creating a digital twin of the existing EDS data. This digital twin ensures productive and timely analysis. The tools and advancements of GIS software will play a significant role in visualizing, understanding, and implementing specific business rules, hence analyzing the data by generating a technology termed Utility Network (UN). This report explores understanding of the EDS and GIS, focusing on developing a System. This system assists users in migrating an existing EDS from the older Geometric Network (GN) technology to the new UN paradigm. To illustrate this transition, we use a practical example from a geometrically networked EDS. Certainly! The demography significantly impacts the analysis of a GIS-based digital electric distribution system. Population density, geographical terrain, and urban vs. rural areas affect load distribution, asset management, and emergency response. Accurate data collection and understanding of consumer behavior are crucial for effective system planning and operation. This System will help the users follow a dedicated path to develop a clear and working UN for the EDS.