Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
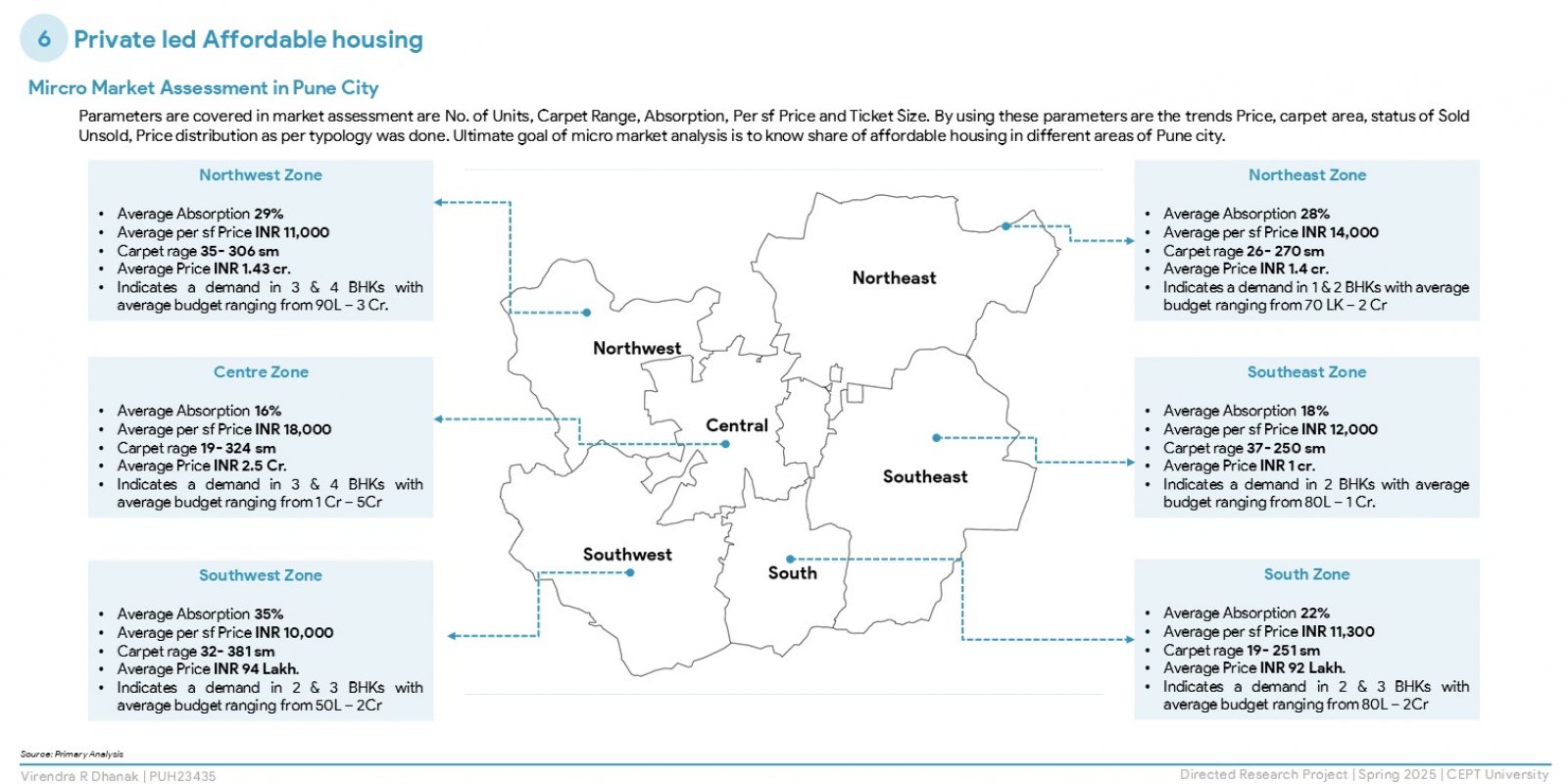
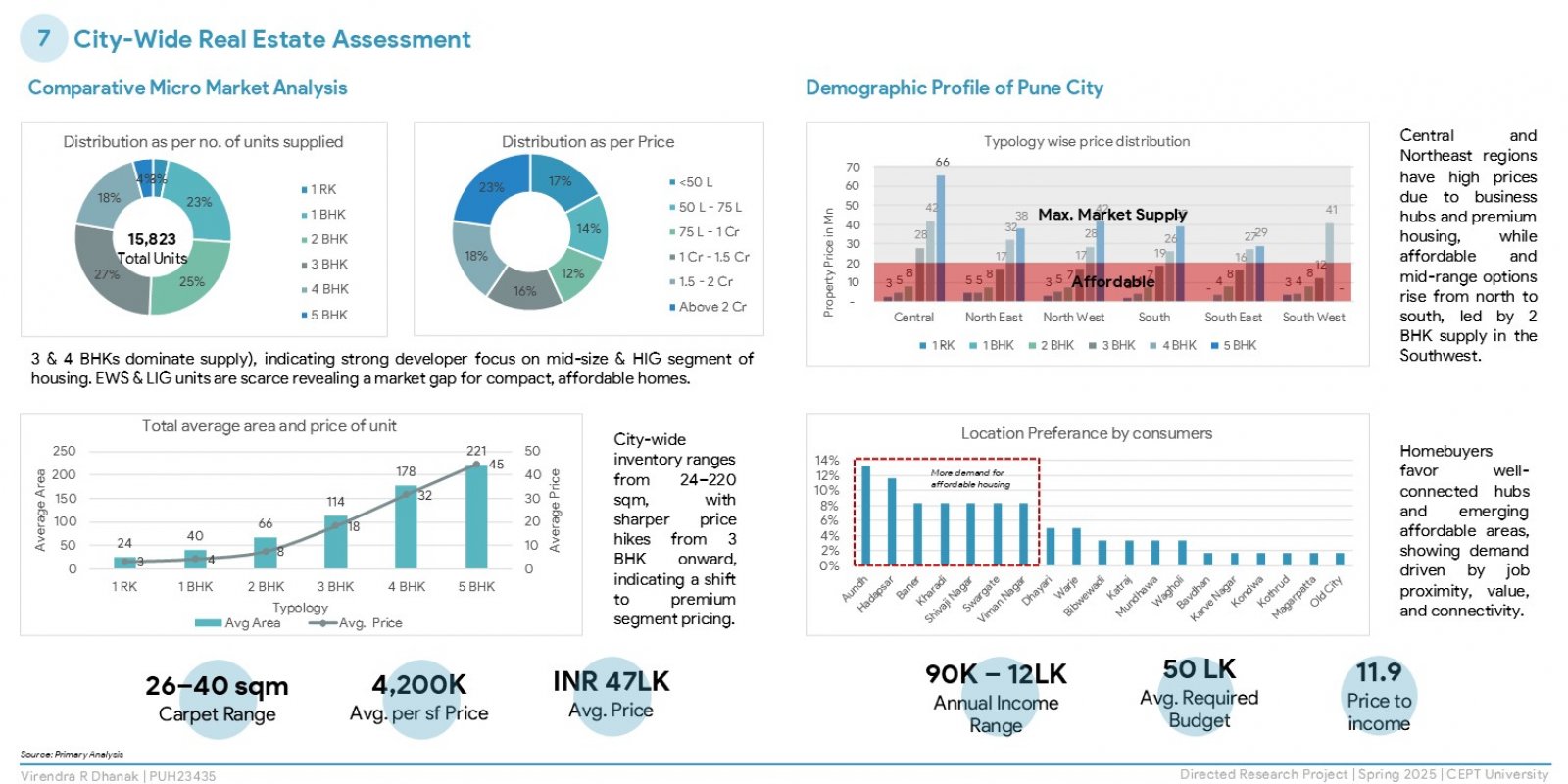
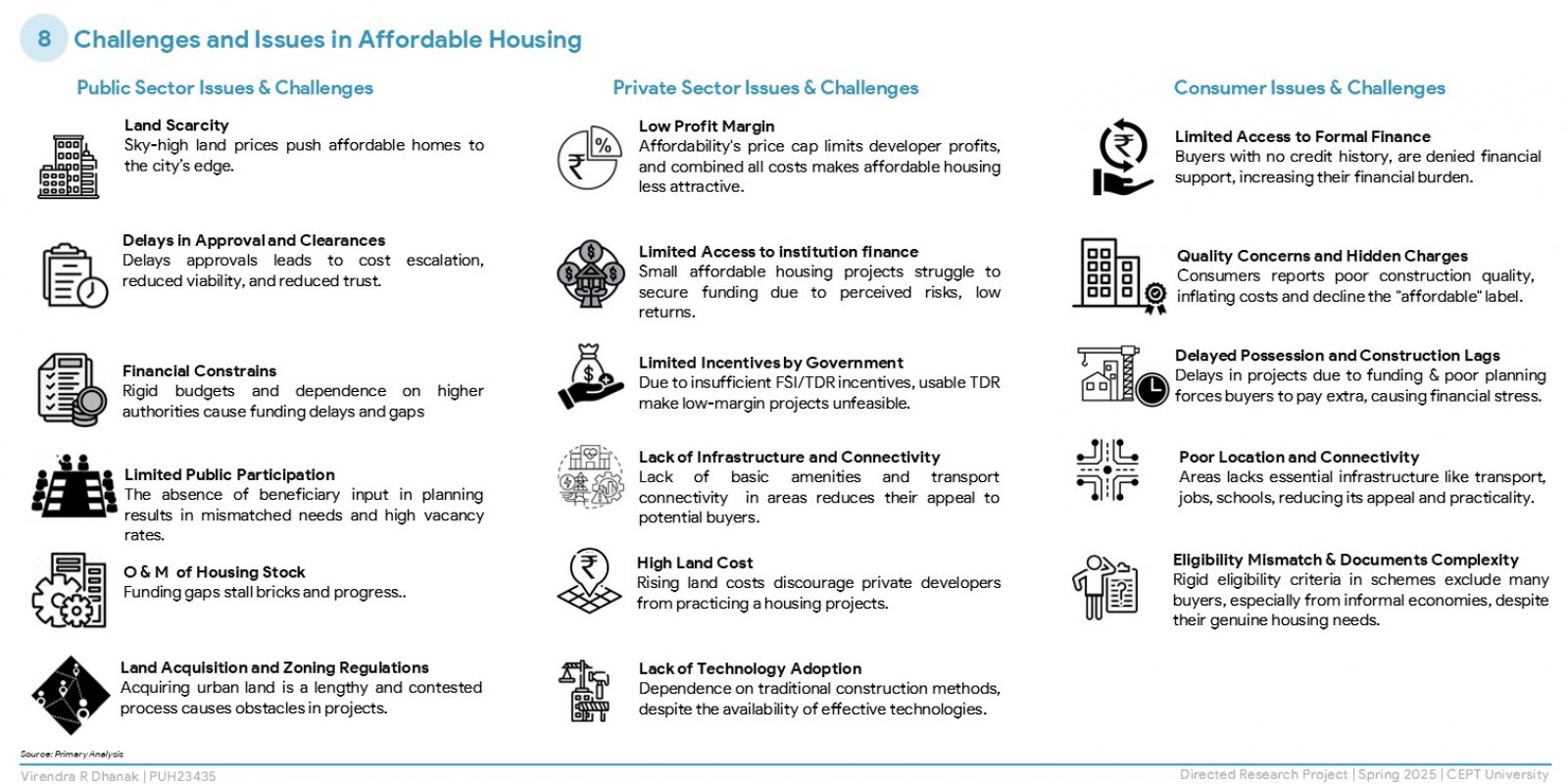
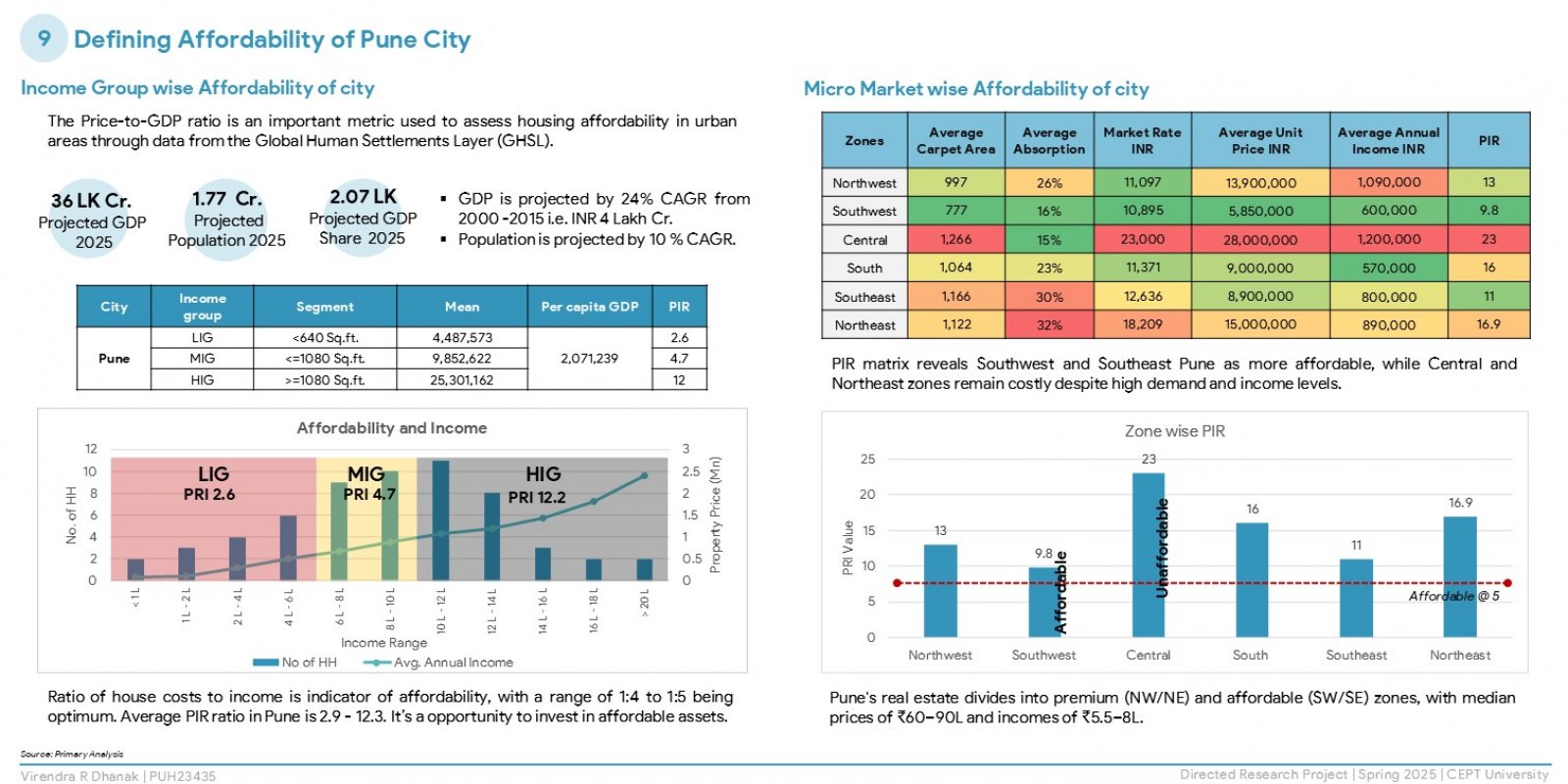
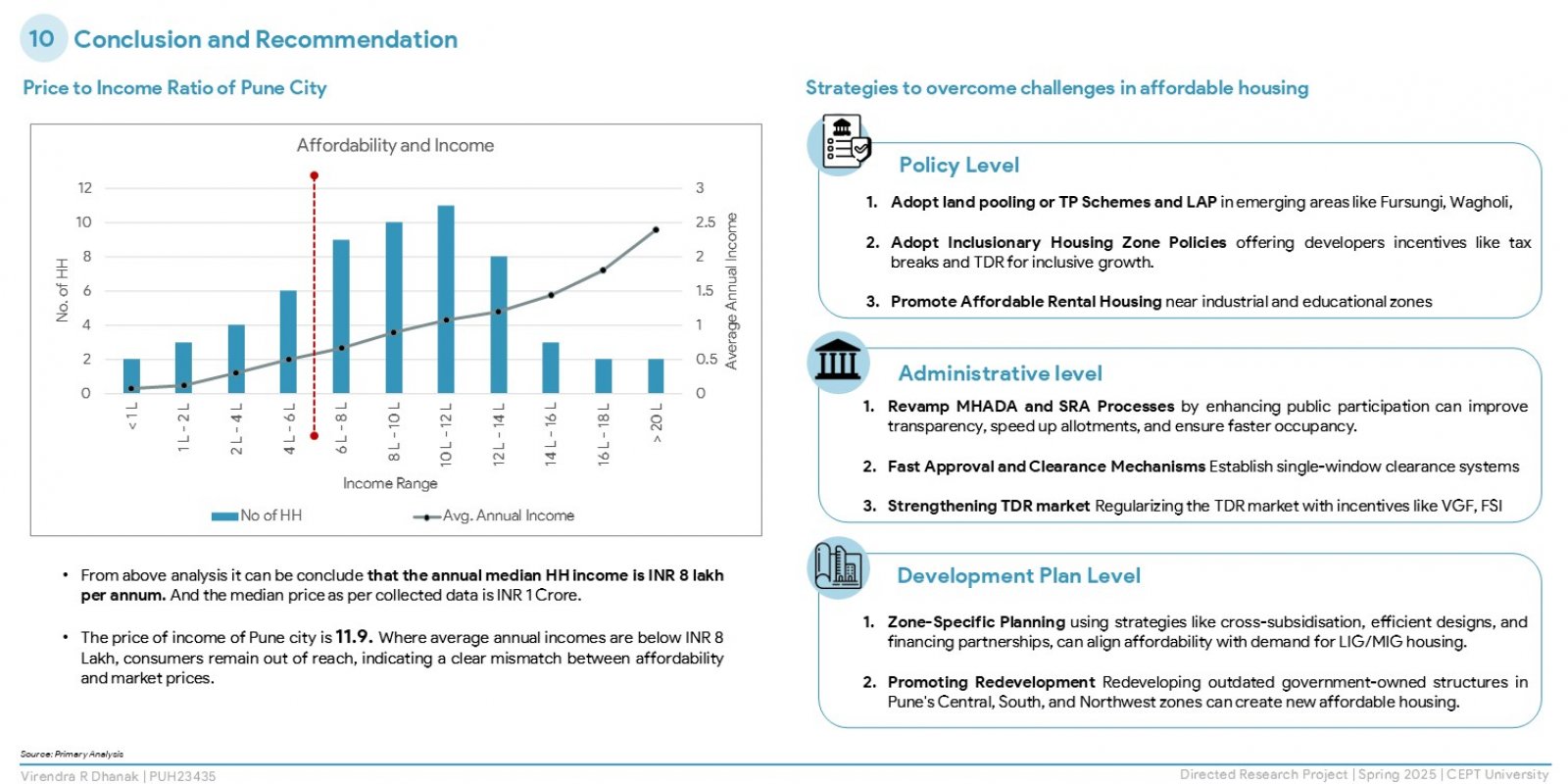
The research explores housing affordability in Pune, a fast-urbanising Indian city, using global and national indicators. It examines supply- and demand-side factors, including government policies, private sector roles, land costs, household incomes, and aspirations through field surveys. Findings reveal a mismatch between affordable housing supply and actual demand, with lower-income groups facing inaccessibility due to credit barriers and policy gaps. The study concludes that affordability is not just financial but also a spatial and governance issue. It recommends regulatory reforms, better spatial planning, and active community participation to bridge the affordability gap and foster inclusive urban development.