Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
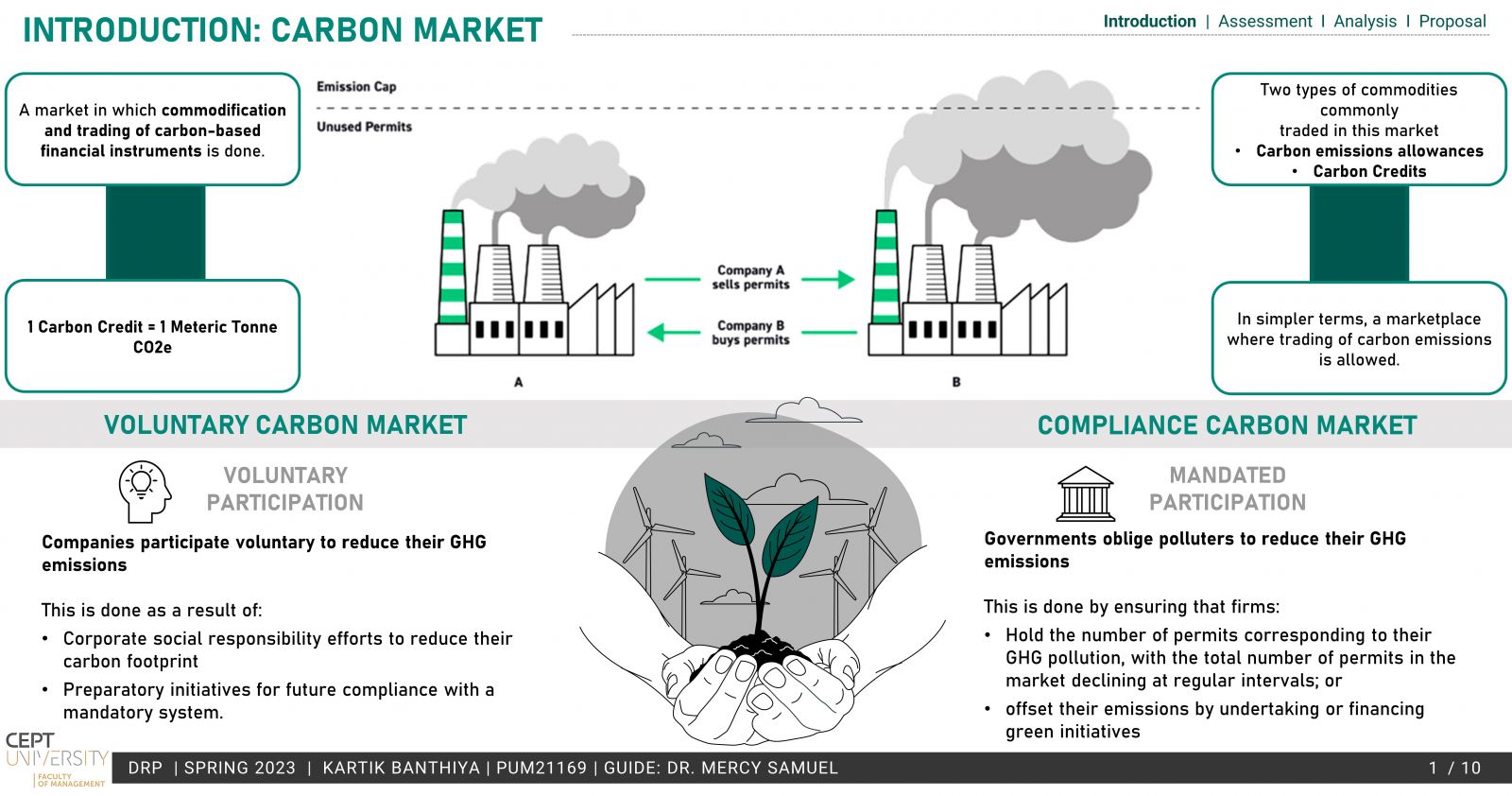
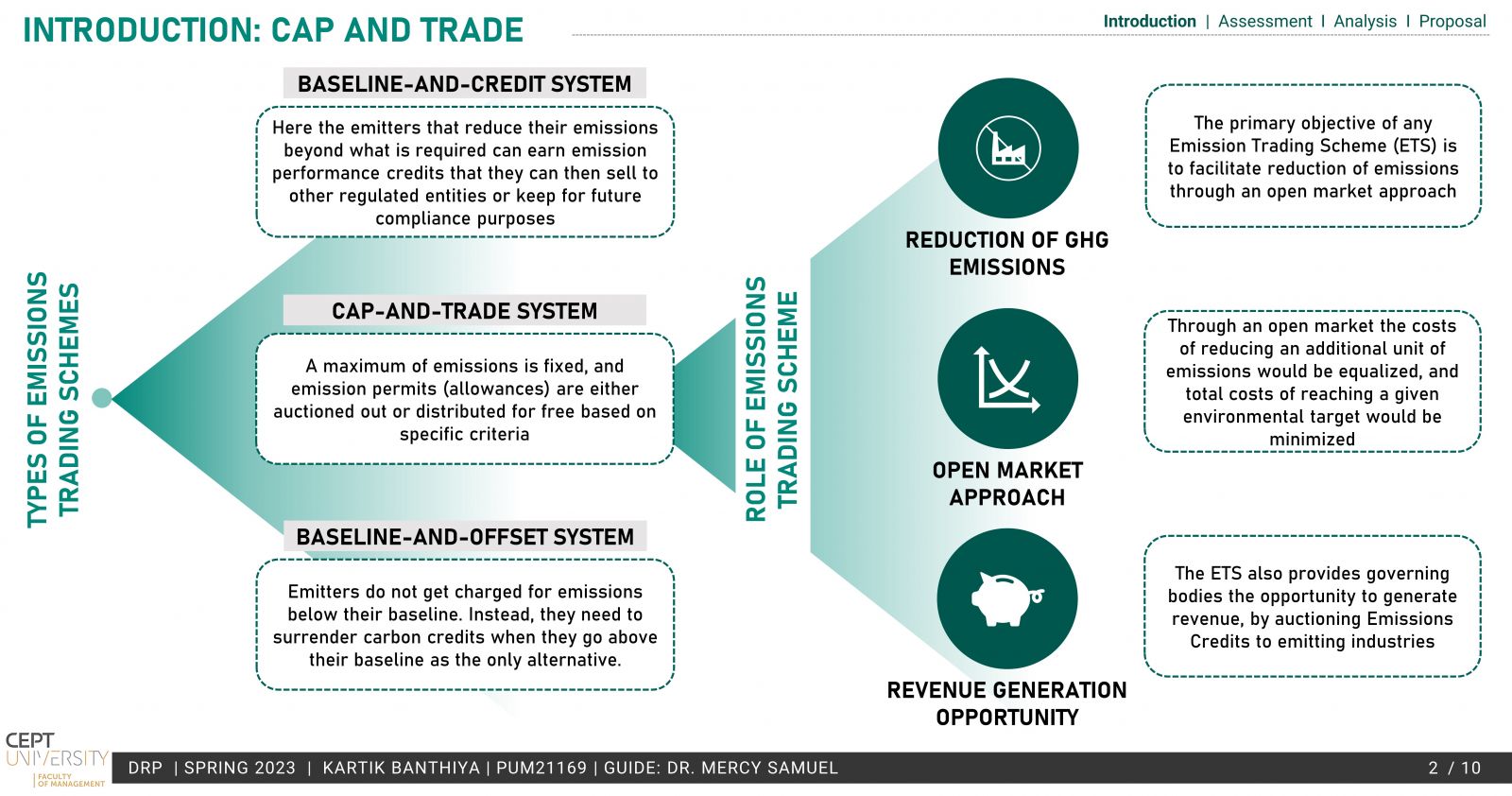
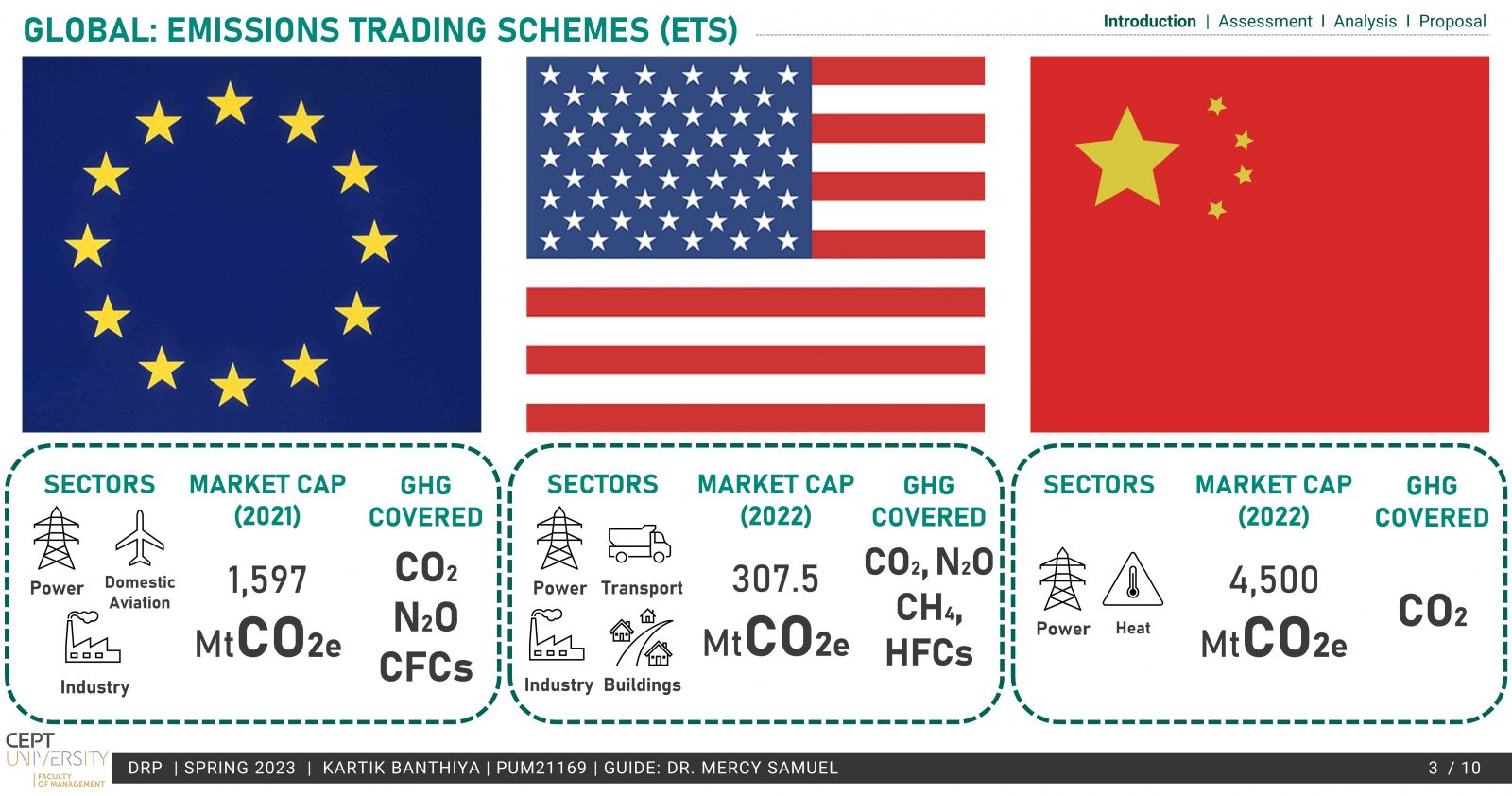
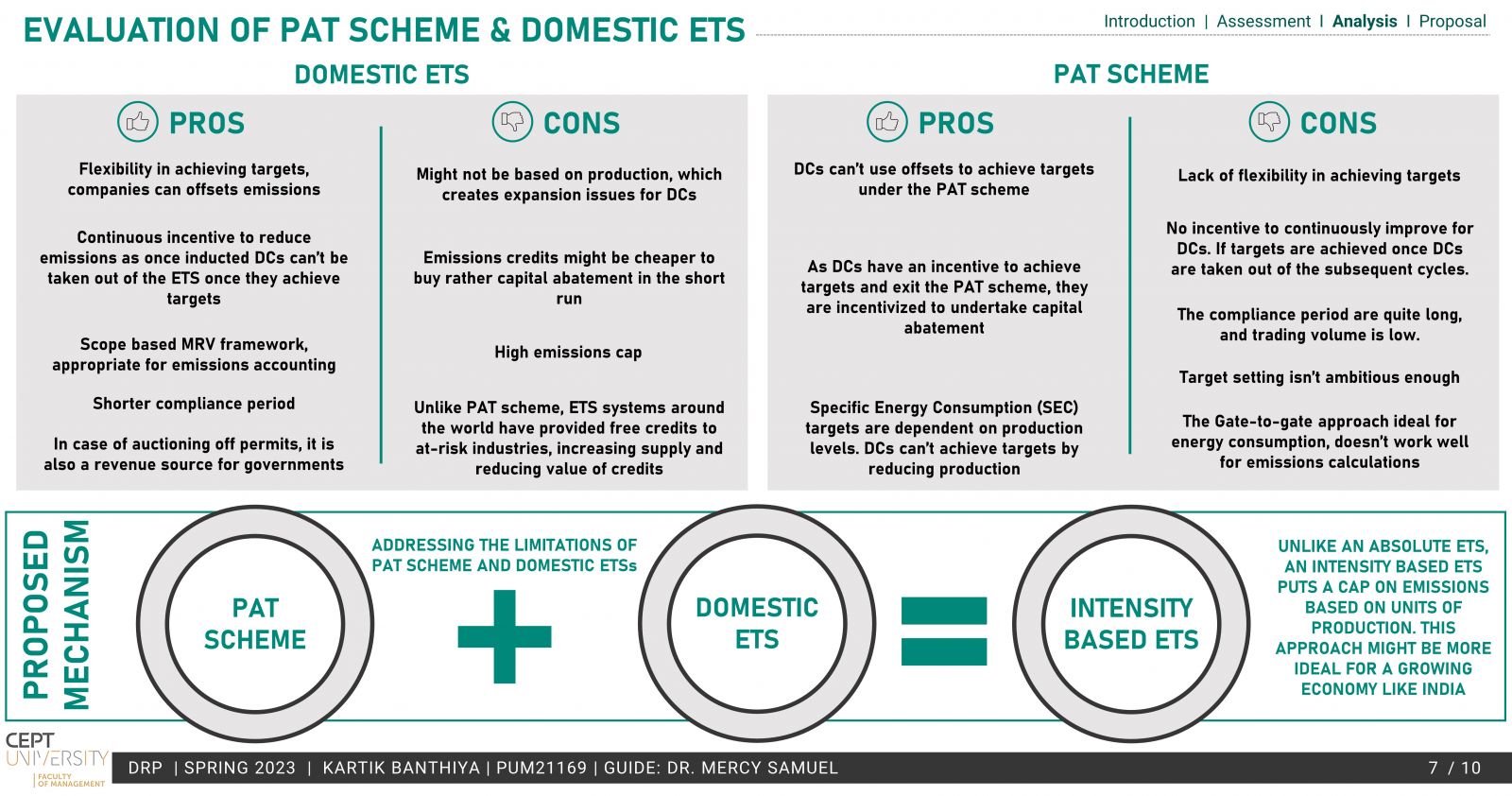
A developing country, India needs measures that can aid the country’s NDCs with low levels of intervention and costs, making a domestic ETS a viable option. Apart from being a low-cost alternative, it also offers additional revenue for the government.
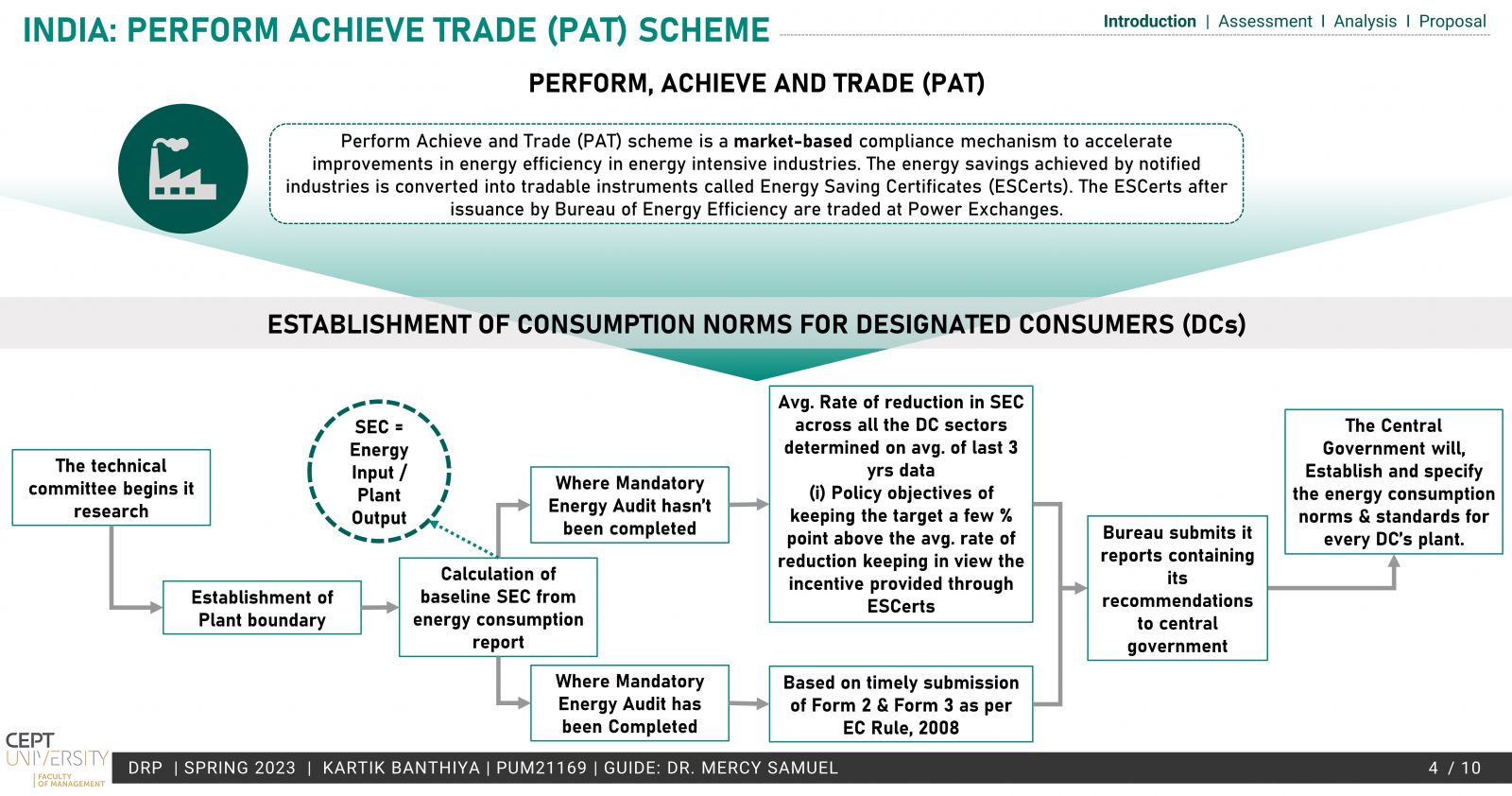
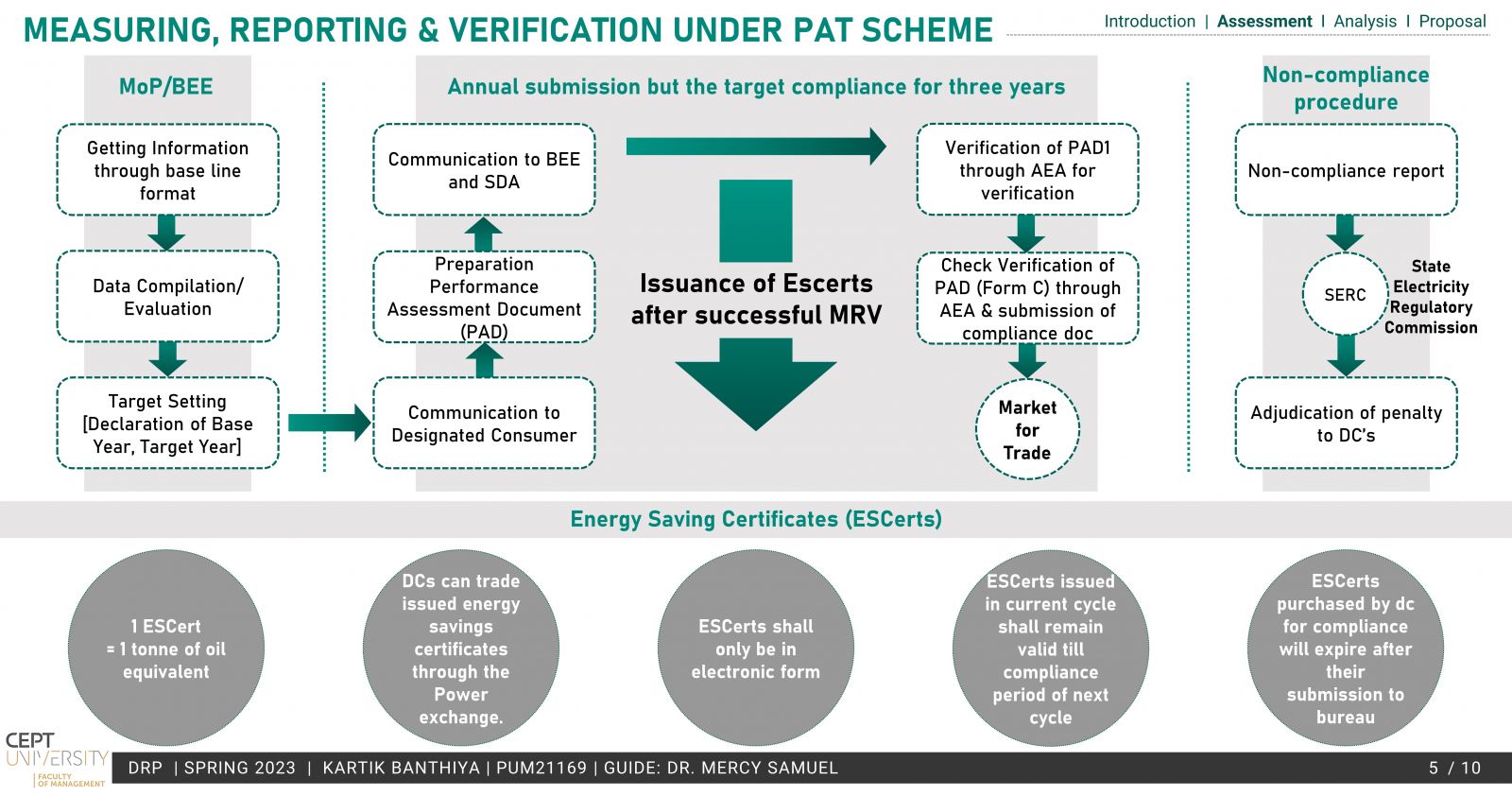
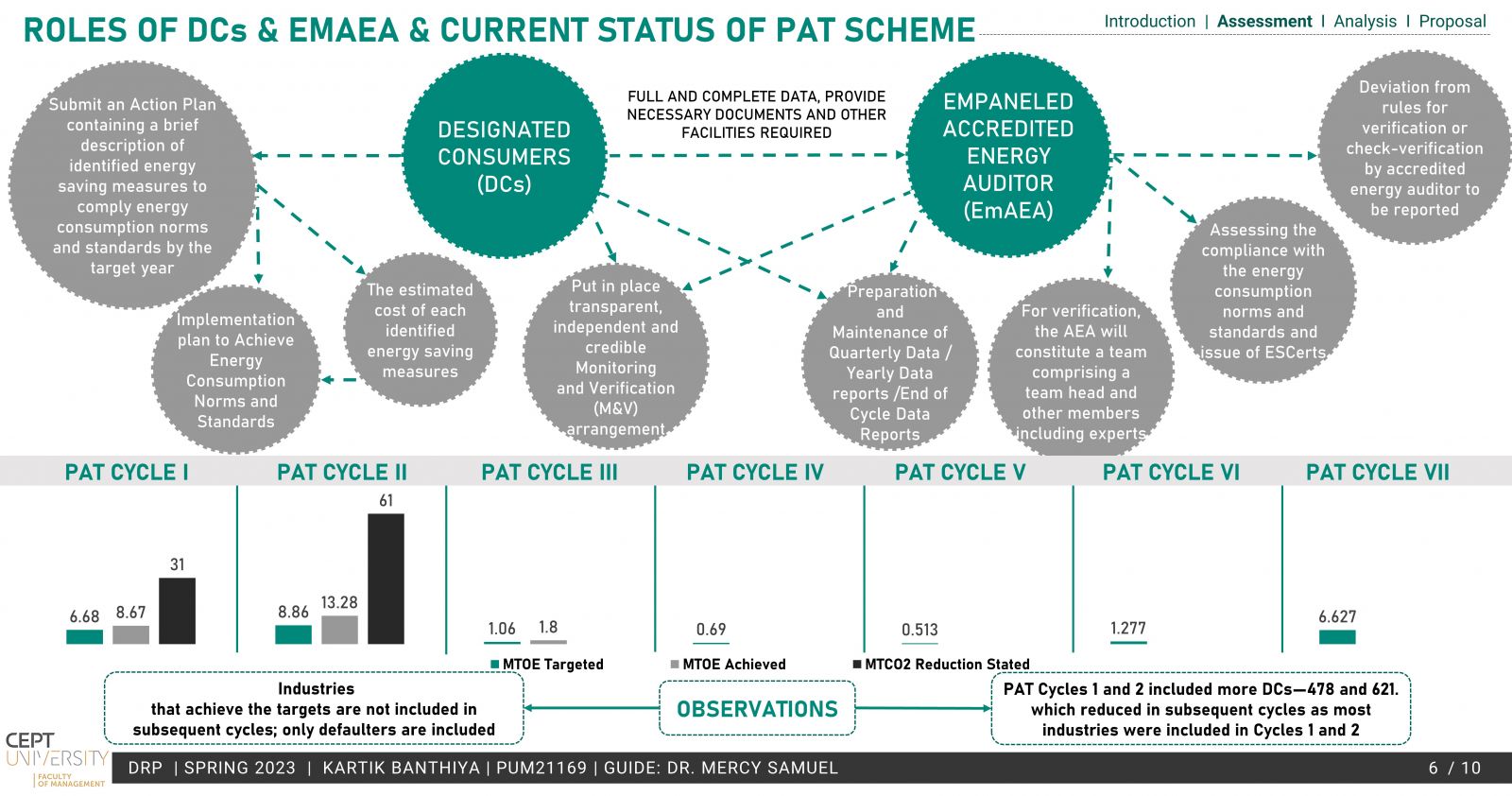
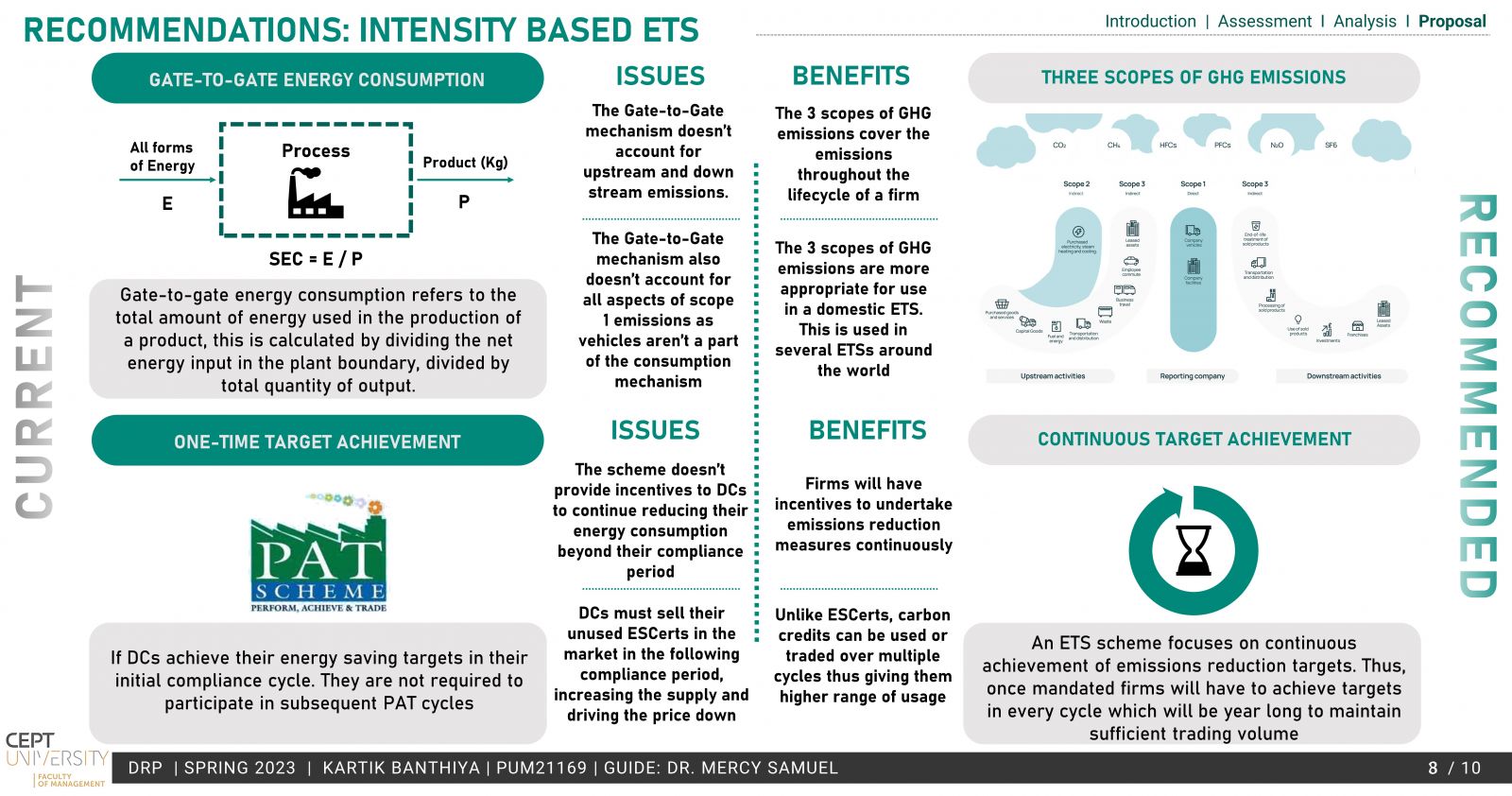
The existing PAT scheme by BEE is based on energy efficiency and provides a market-based mechanism much like ETS but lacks the emission reduction aspect, which is the need of the hour. To operationalize a domestic ETS, the conversion of the PAT scheme to an ETS has been explored in the study. Taking into account the MRV, Compliance cycle & mechanisms.