Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
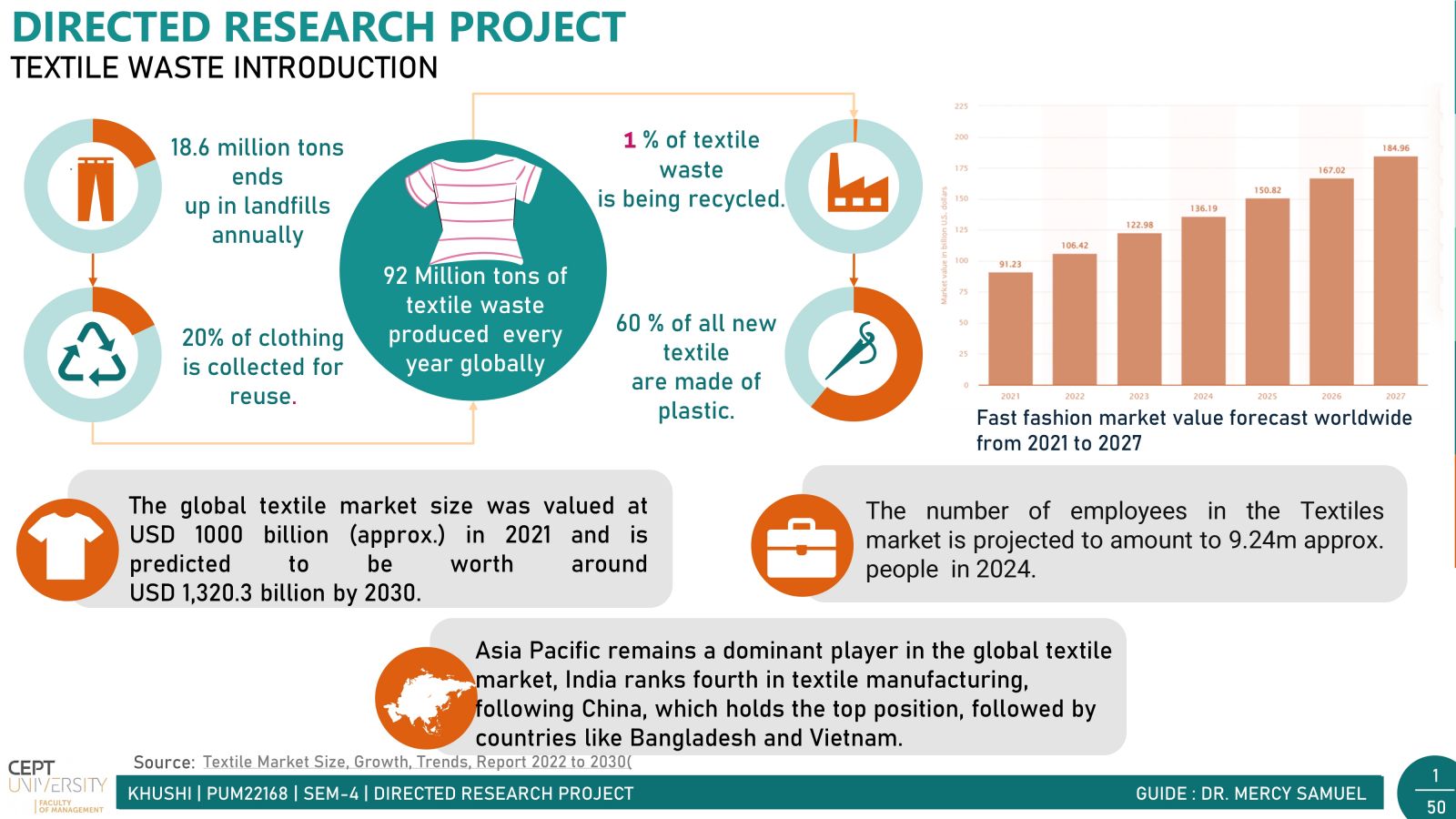
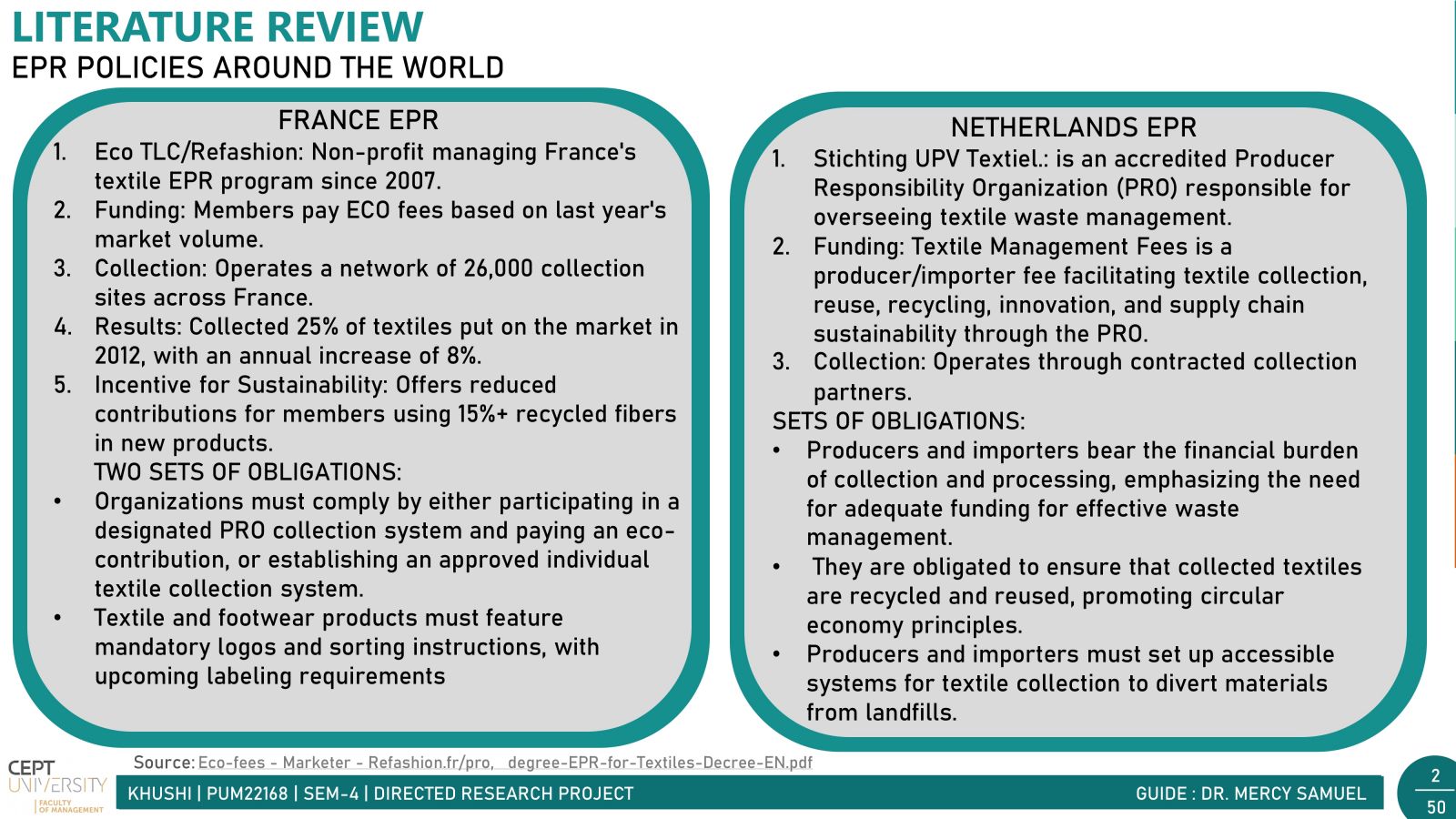
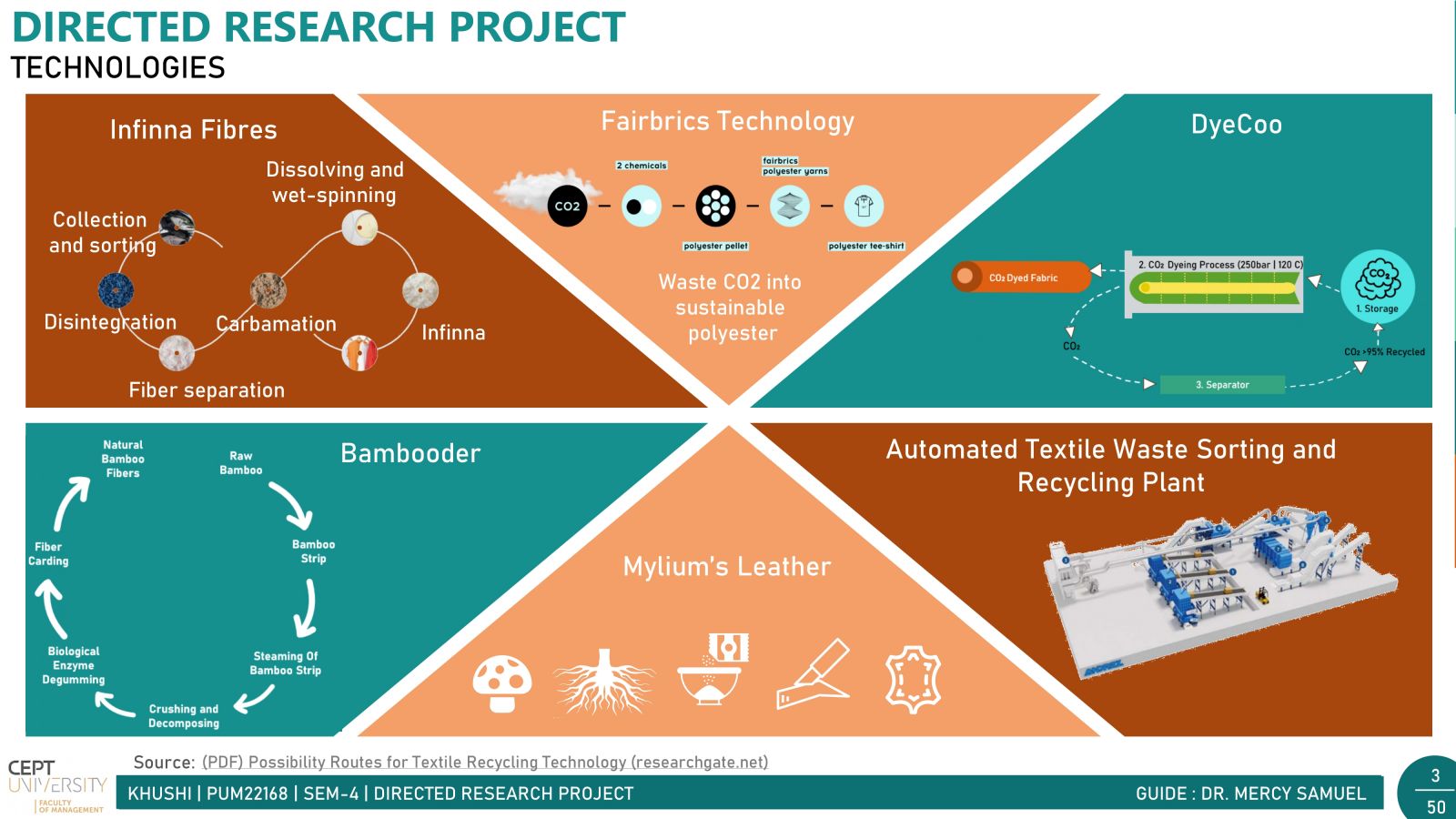
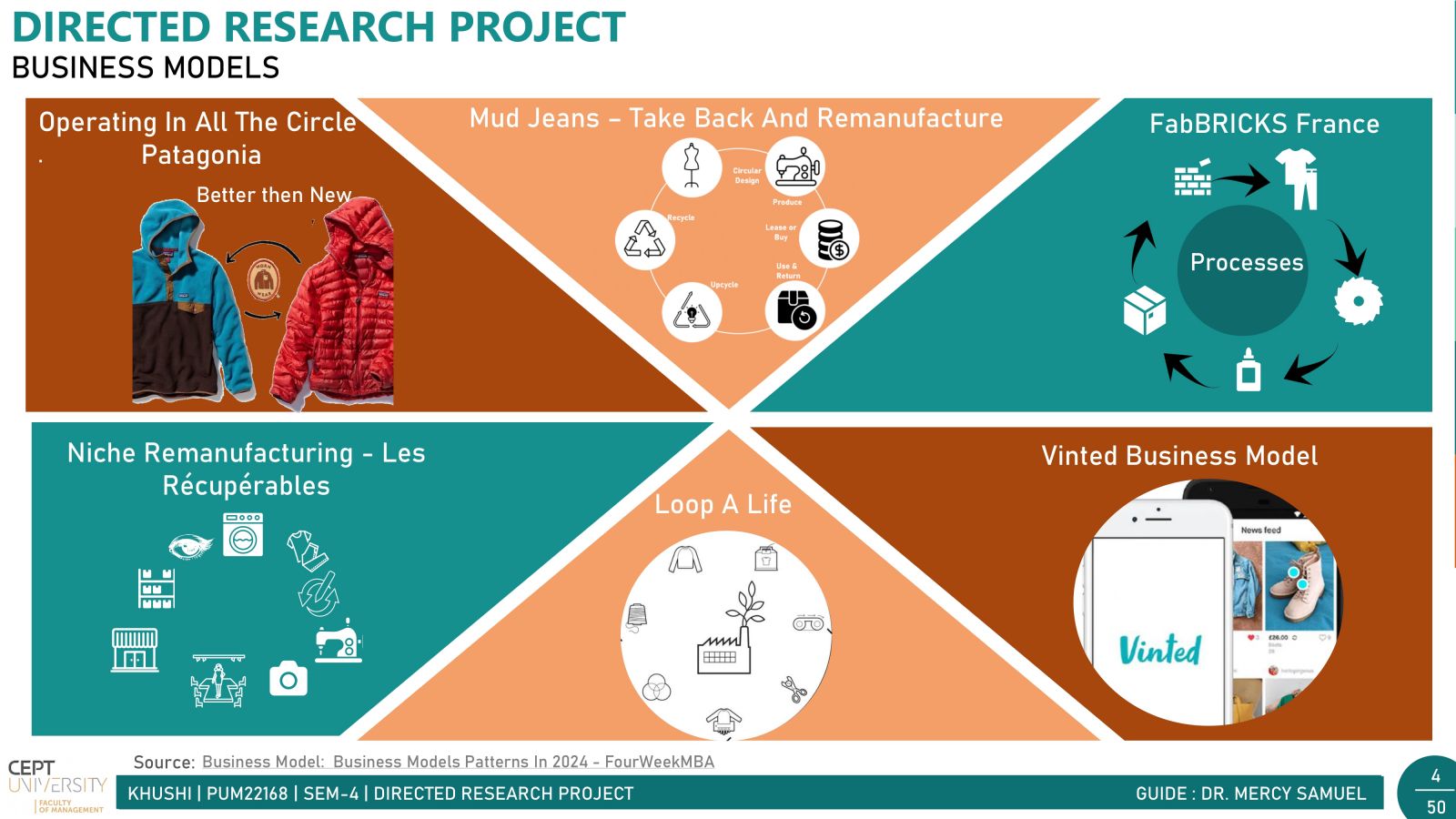
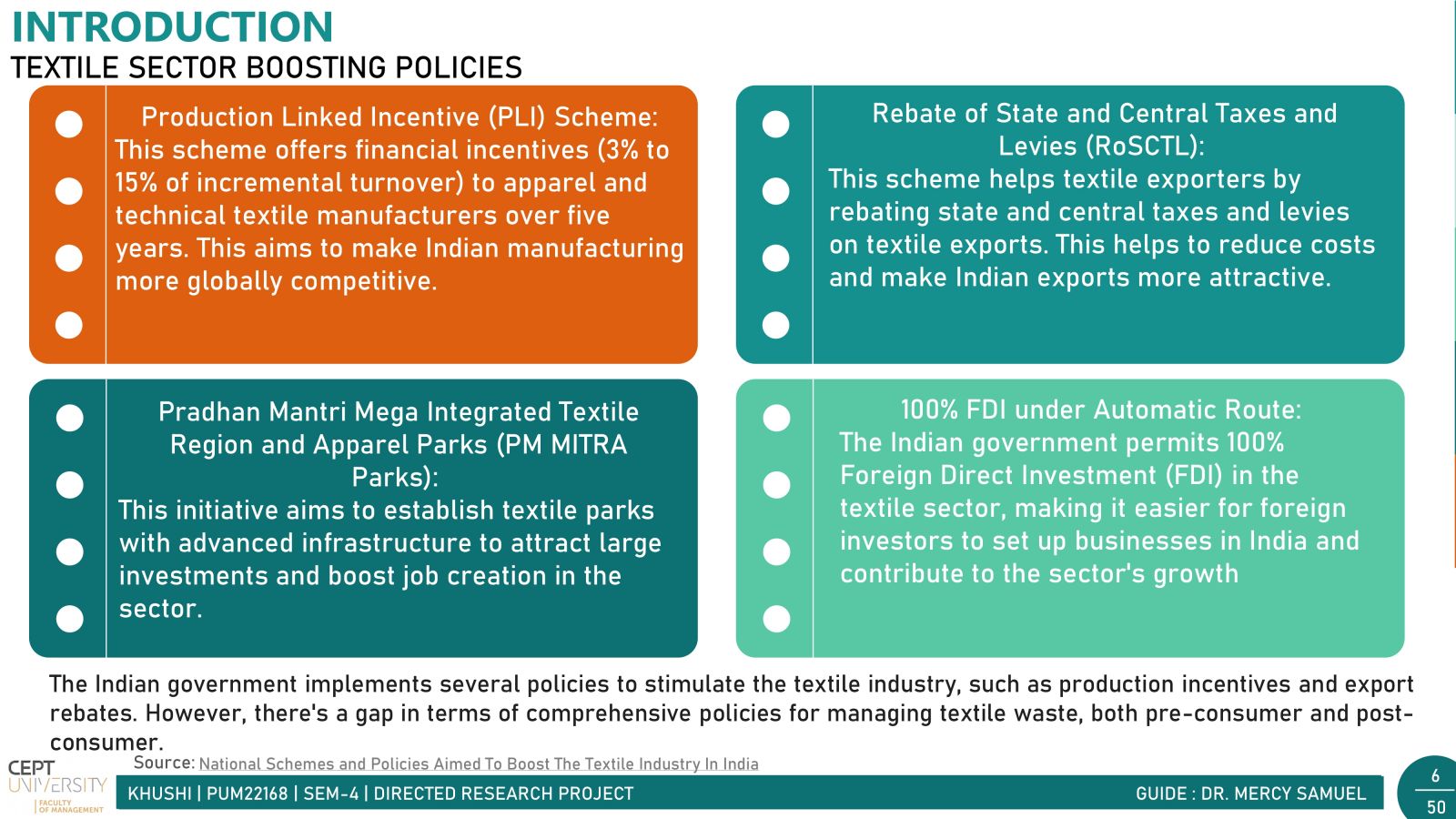
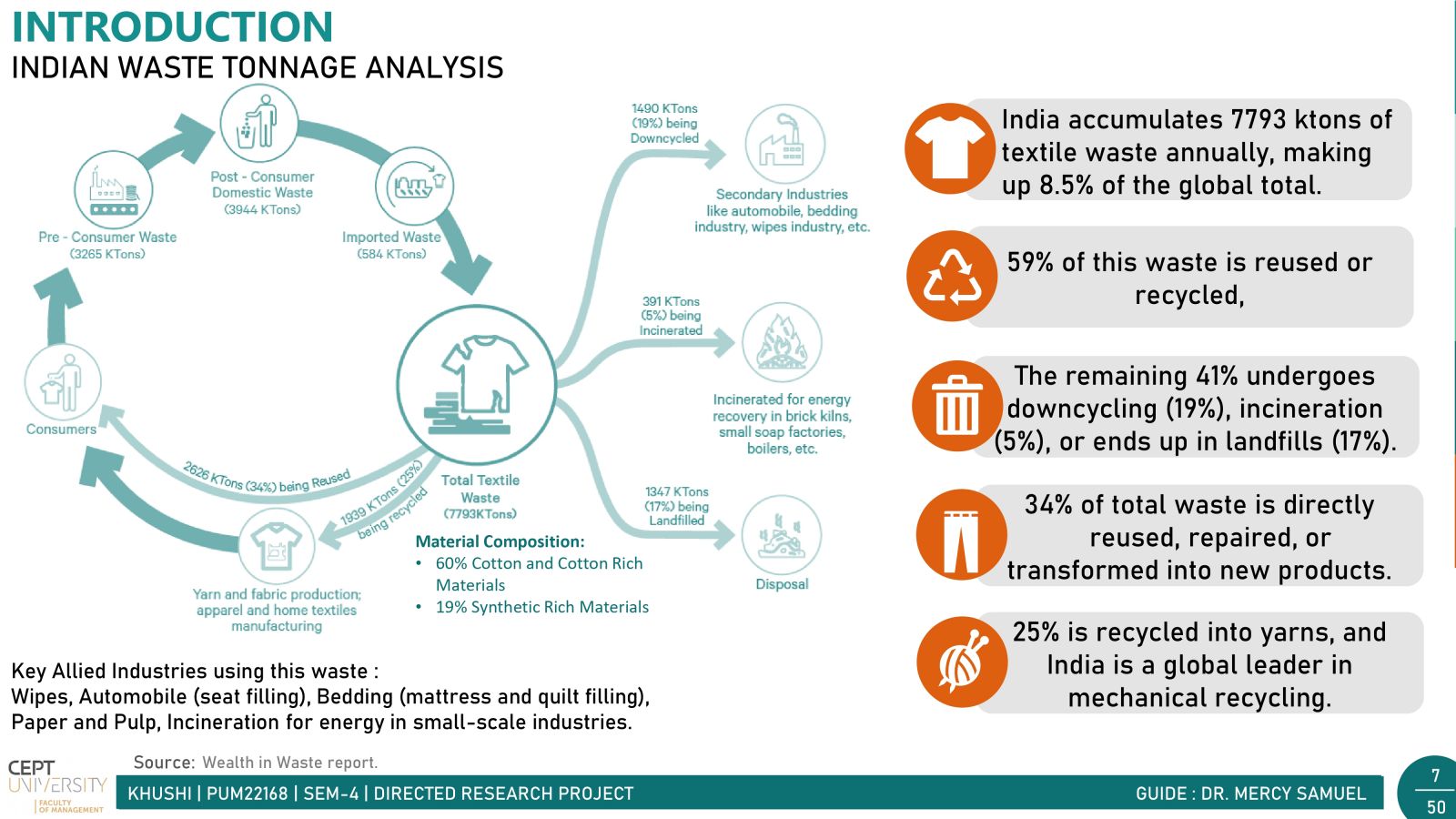
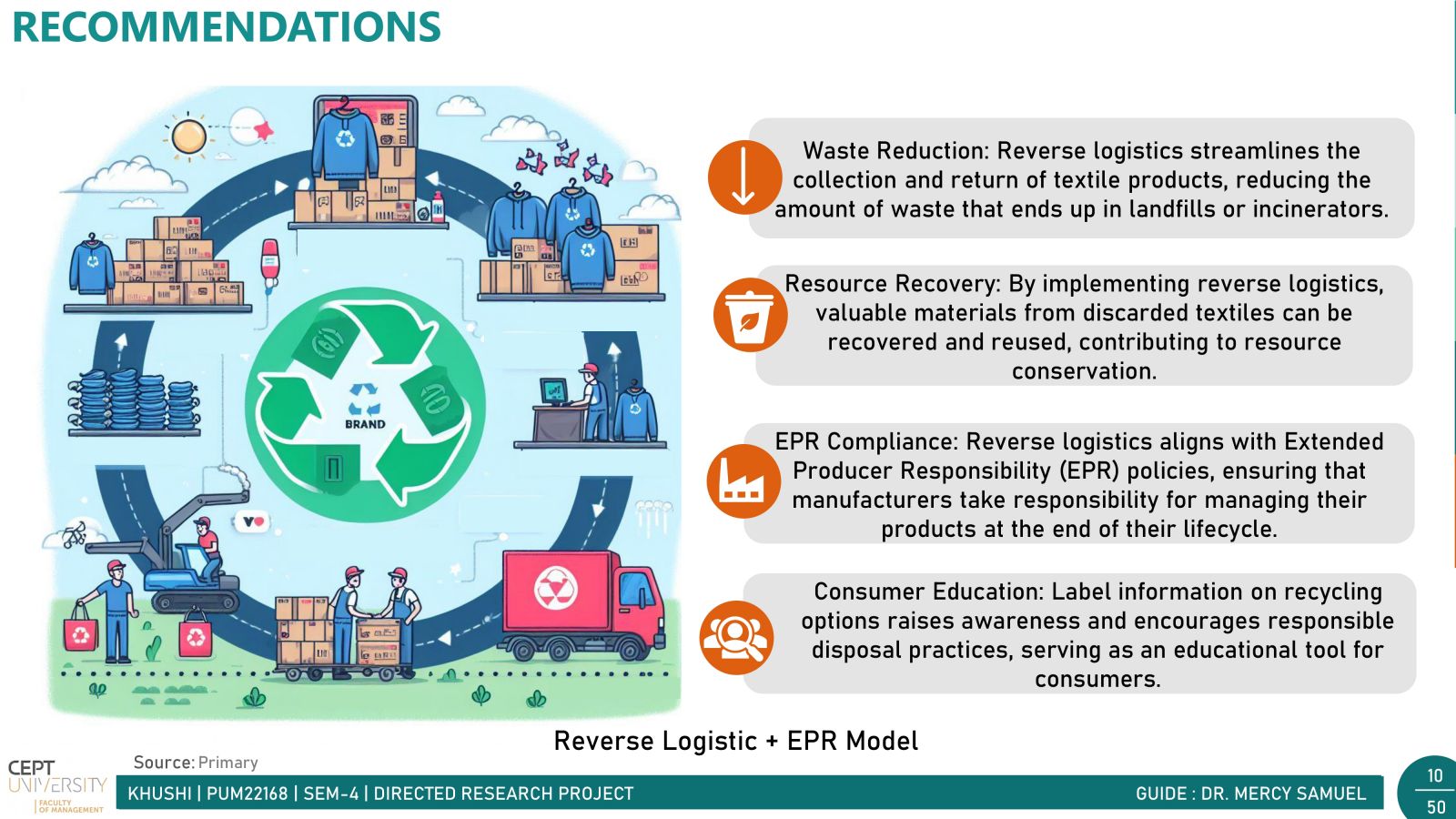
In today's fast-paced world, fast fashion is all the rage. But with it comes a hidden problem: textile waste. Every year, tons of clothing end up in landfills, causing big environmental headaches. India, a powerhouse in the textile industry, contributes significantly to this waste. There are two main types: waste generated before products reach consumers (pre-consumer) and waste from consumers (post-consumer).Post-consumer waste poses a significant challenge due to its diverse mix of materials, making sorting and recycling difficult. However, solutions like Reverse Logistics incentivize customers with discounts for returning clothes for recycling, alongside the crucial push from government in the form of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for waste management. Together, these initiatives pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future in the fashion industry.