Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
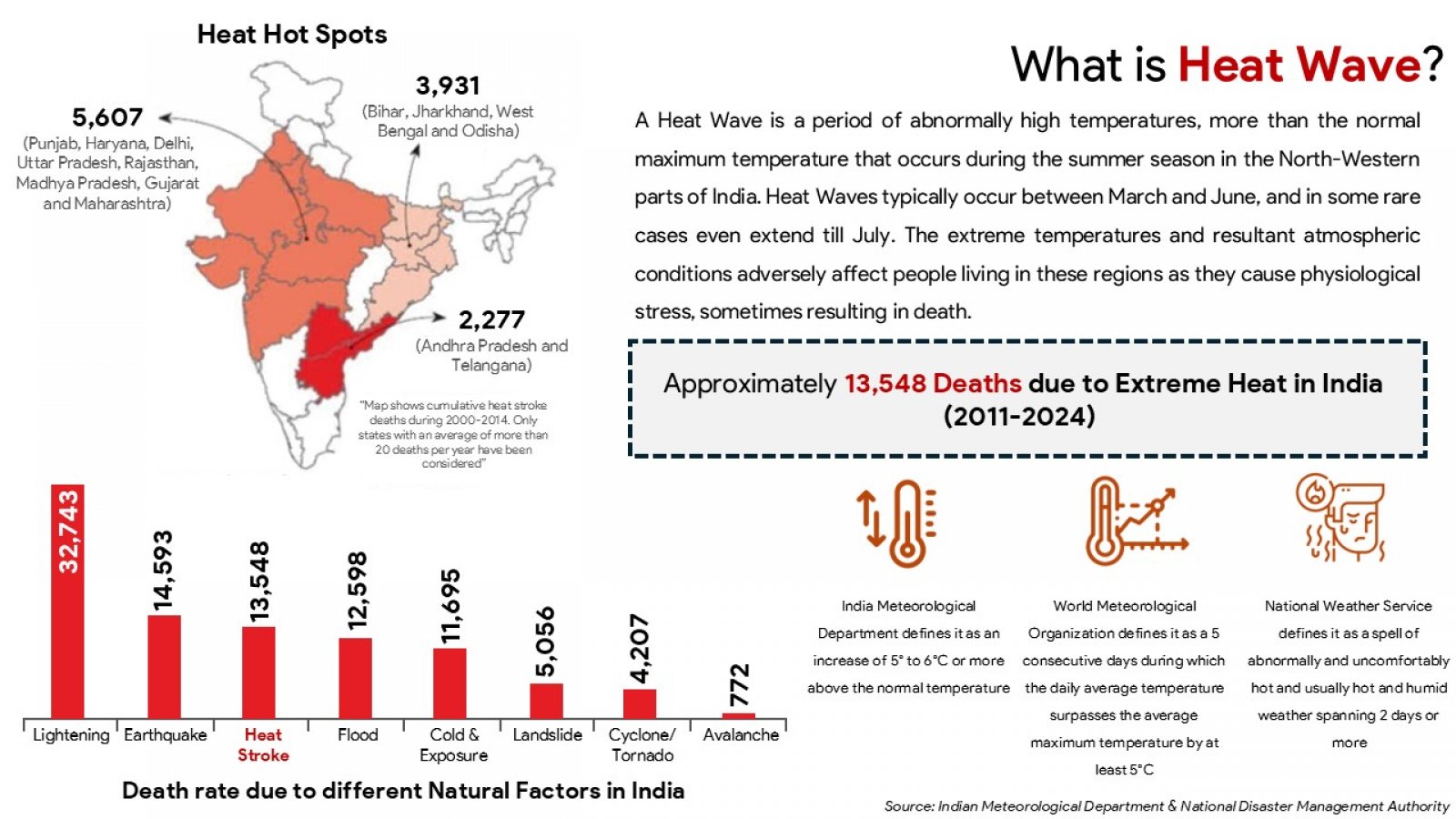
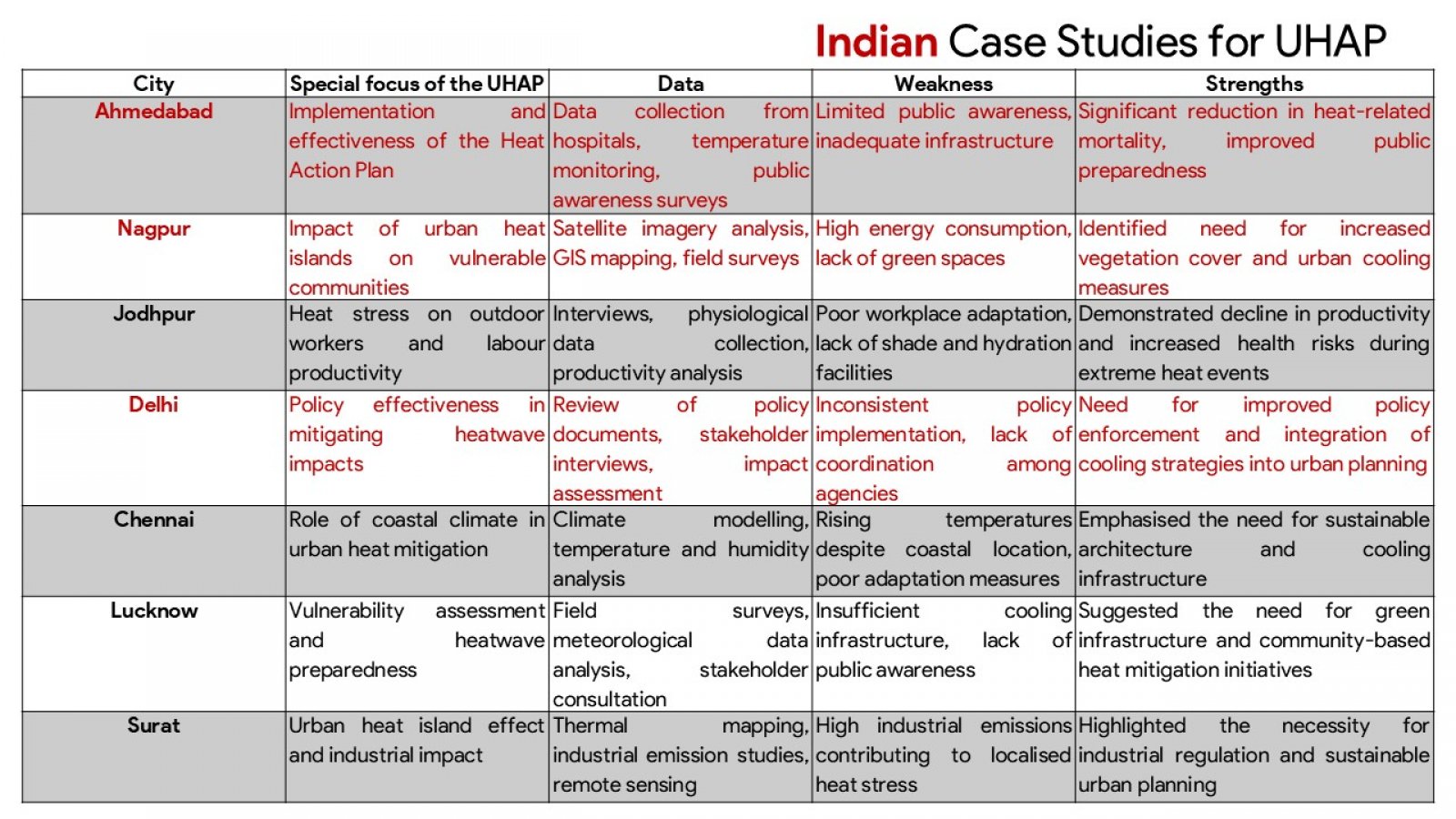
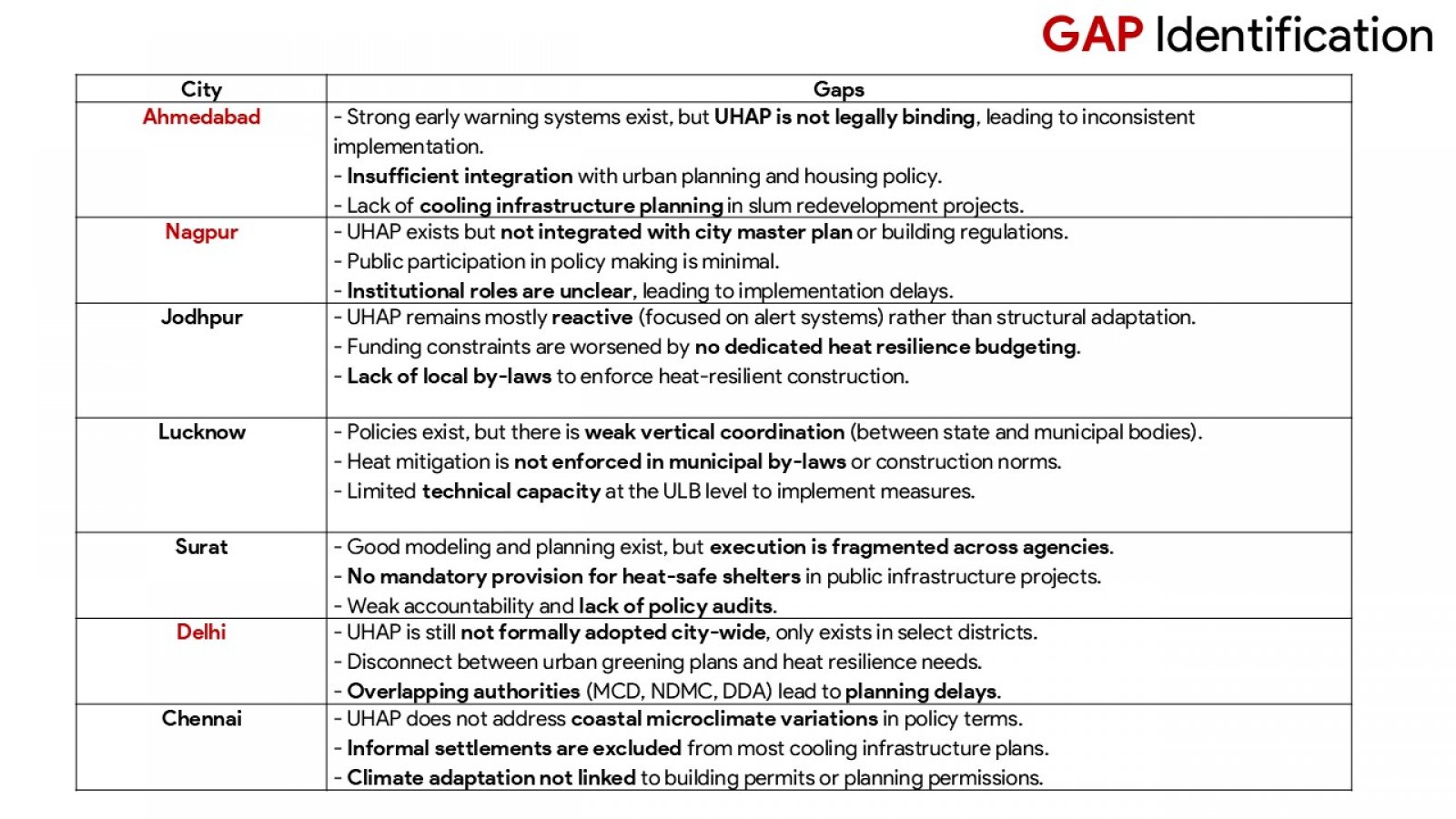
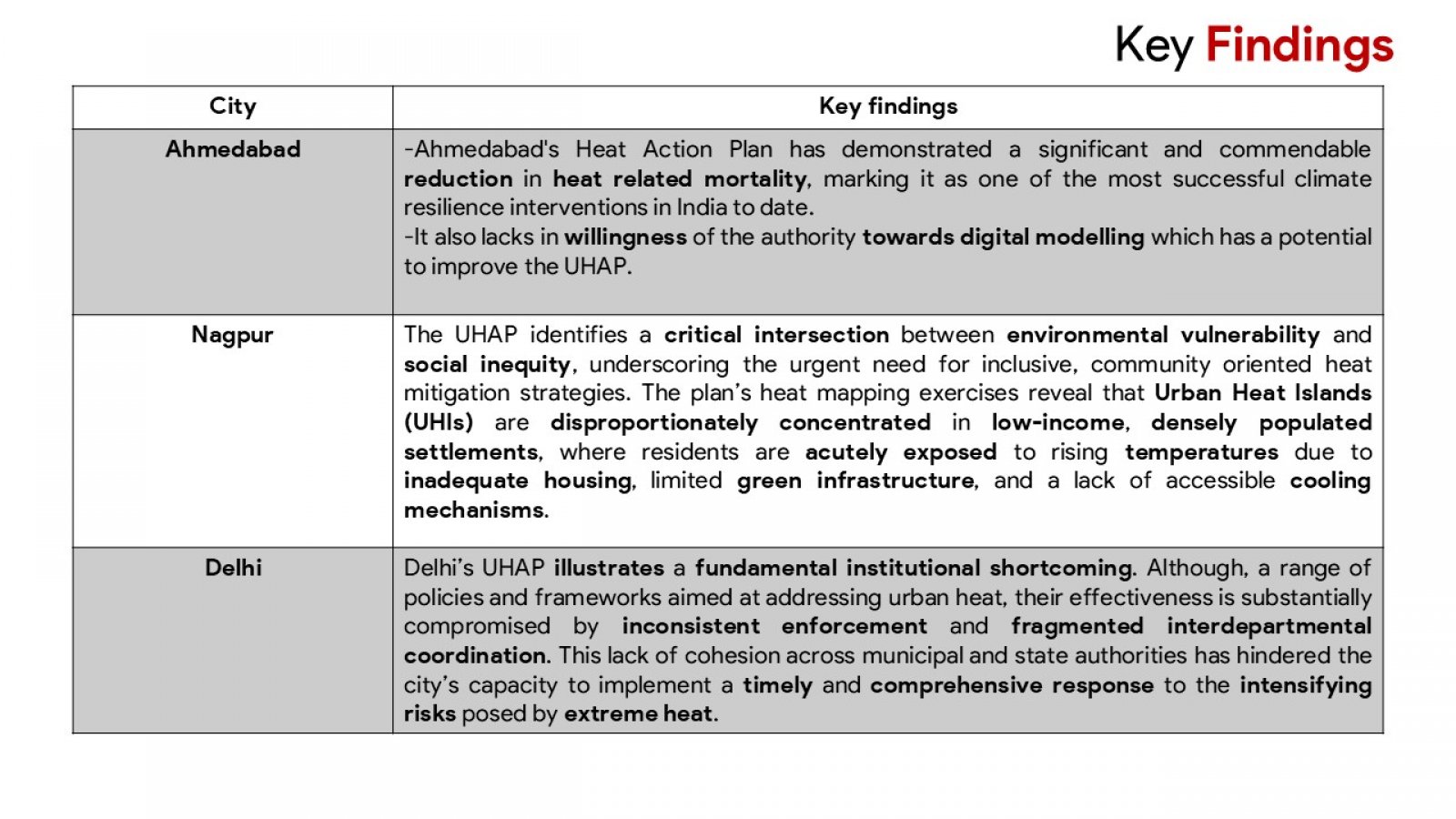
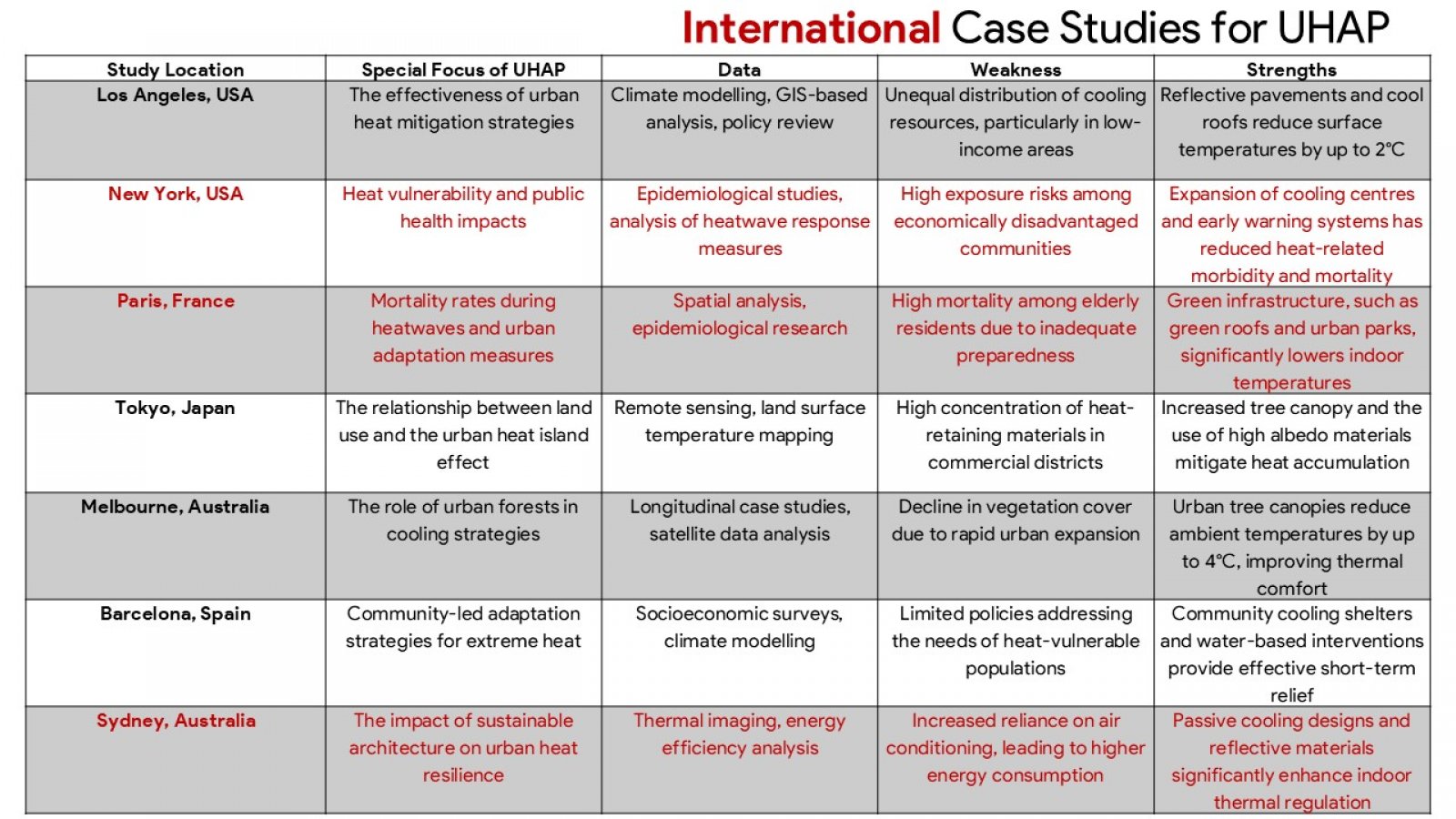
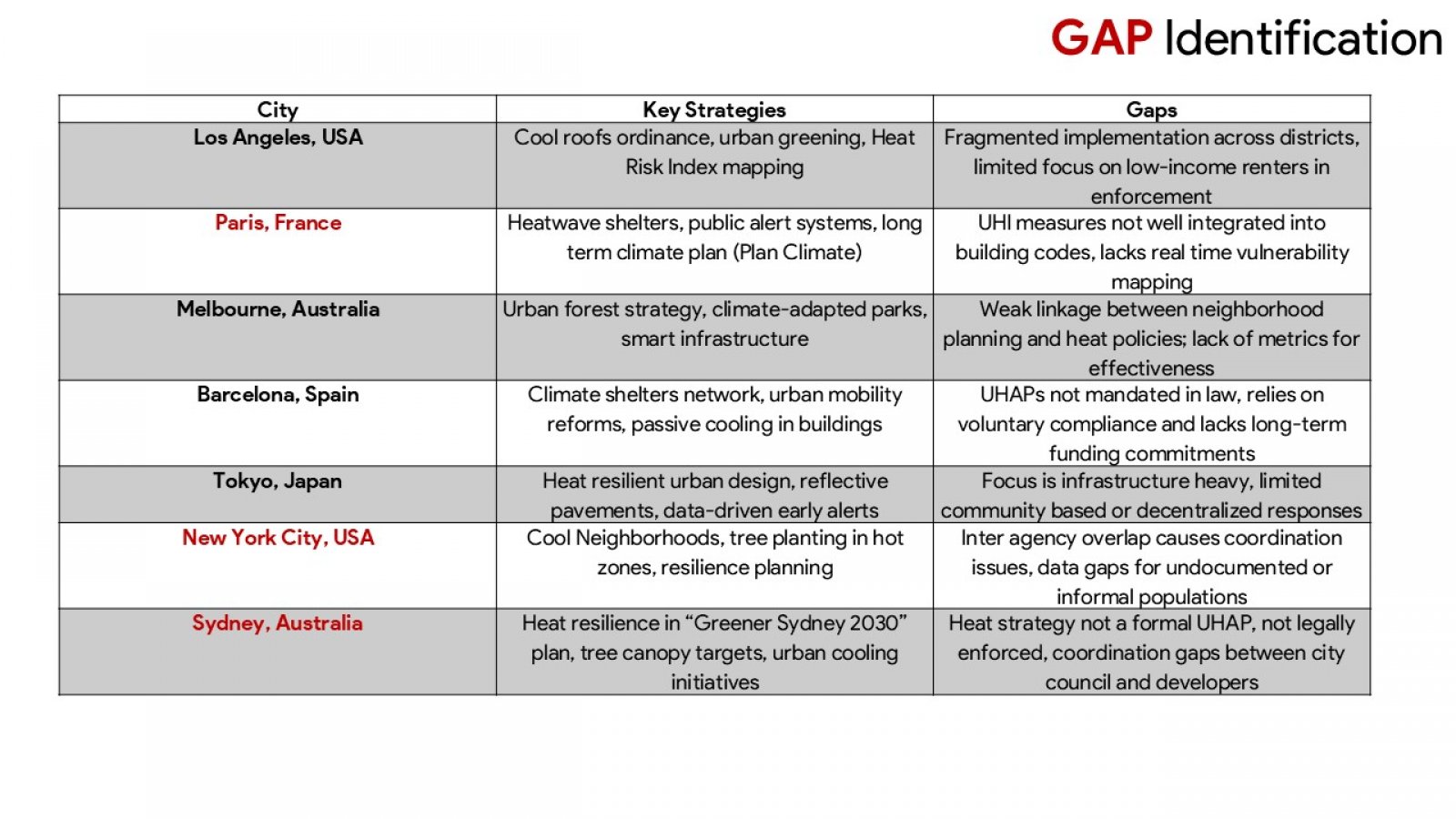
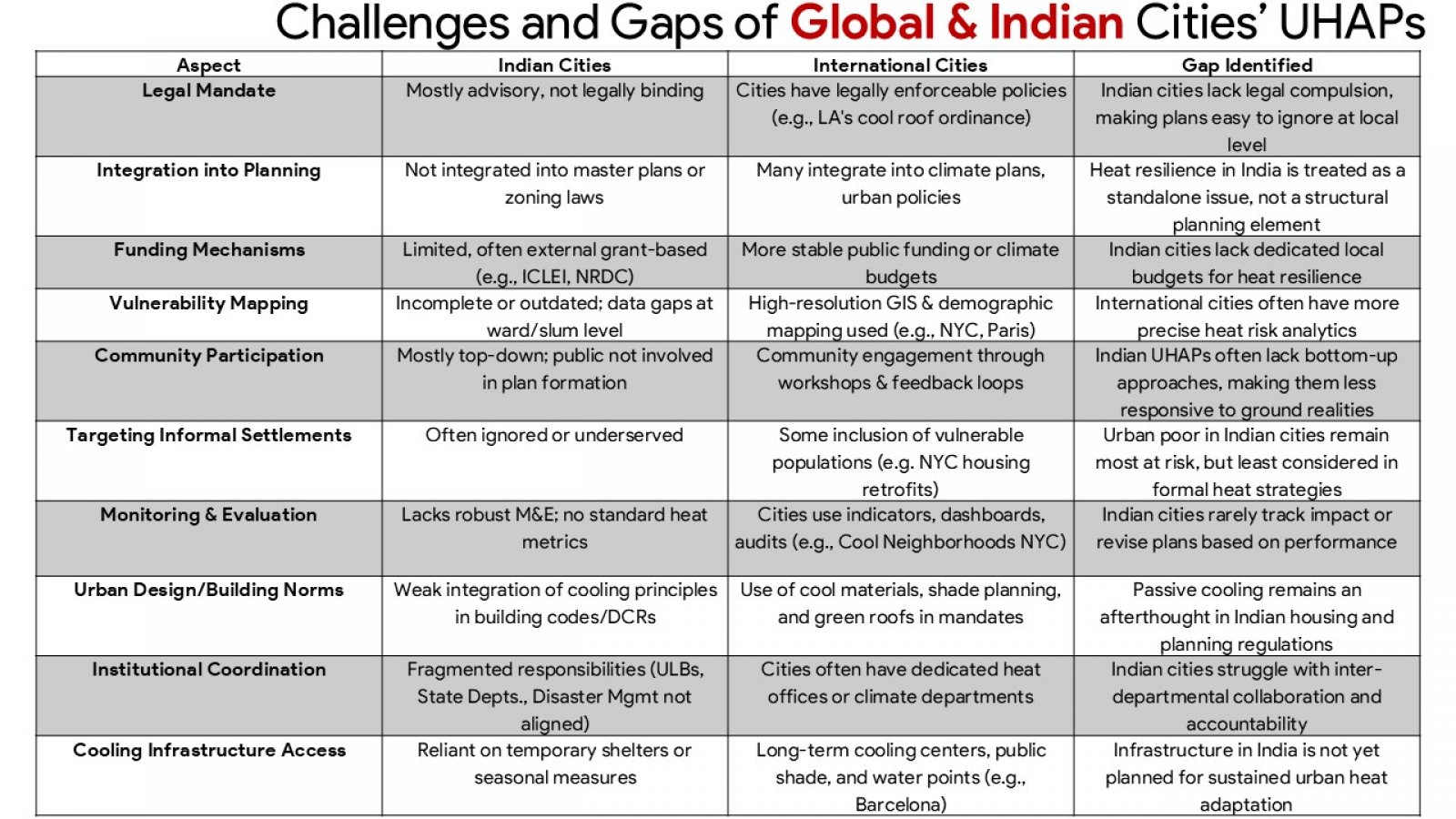
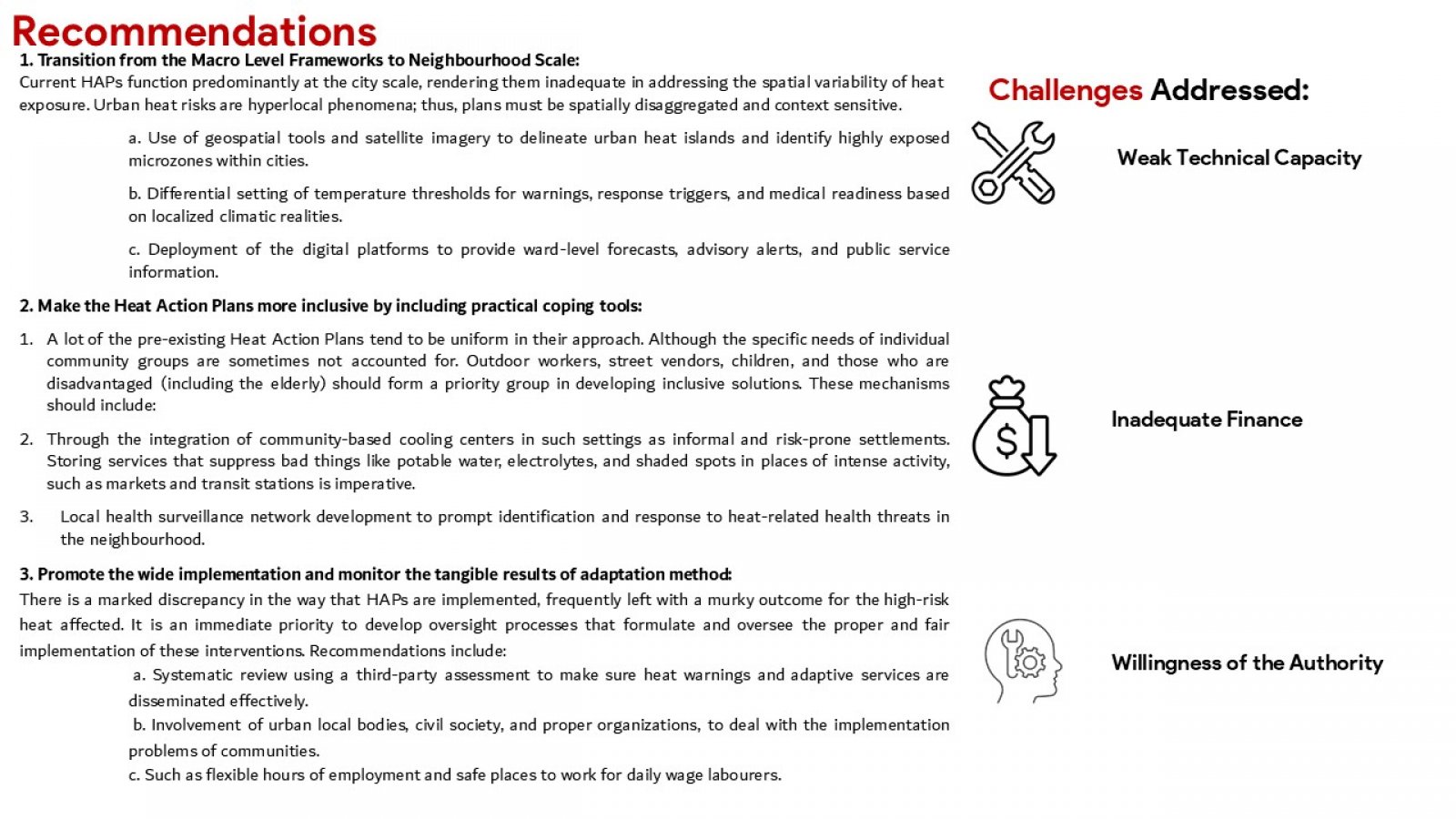
The discussion presented hereunder critically evaluates the urban heat action plans (UHAPs) in the face of the increasing occurrence of extreme heat incidents throughout Indian urban centres. Adopting a comprehensive analysis of Ahmedabad, Nagpur, and Delhi, the study evaluates how UHAPs have been designed, implemented, and assessed to mitigate health risks and heat stress on urban infrastructures. In addition, the analysis uses global examples from Paris, New York, or Sydney to illustrate beneficial strategies and systemic constraints. Although the research recognizes the advancement of Indian cities in developing heat preparedness plans, particularly with Ahmedabad where such activities resulted in fewer casualties due to the heat, major deficits are still present. These challenges include a fragmented approach to institutions, a thin cover on regulatory oversight, lack of cooperation with urban developments’ plans, and inadequacies of ensuring protection to vulnerable groups, such as those living in informal housing or outdoor occupations. The mixed method approach of the study utilizes a combination of secondary data review and key stakeholders consultations to create the ground for the study to examine the plausibility and potential of UHAPs. In point of fact, critical outcomes indicate the need for targeted vulnerability mapping, binding regulation, stable funding, and responsible OverSight systems. In addition, the focus of the study is on the requirement of participatory governance structures and decentralised strategies for equity and context-specific responses. Failure to act on the suggestions by stakeholders, the report recommends practical measures to make Indian cities resilient to heat. Recommendations include the adoption of heat planning into master plans by way of legislation establishment of organs to monitor urban heat as well as emphasising the use of climate sensitive architecture and design. The report advises that the UHAPs should be formalised into enduring intersectoral instruments for the sustenance of public well-being and sustainable urban advancement in a planet battling accelerated warming.