Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
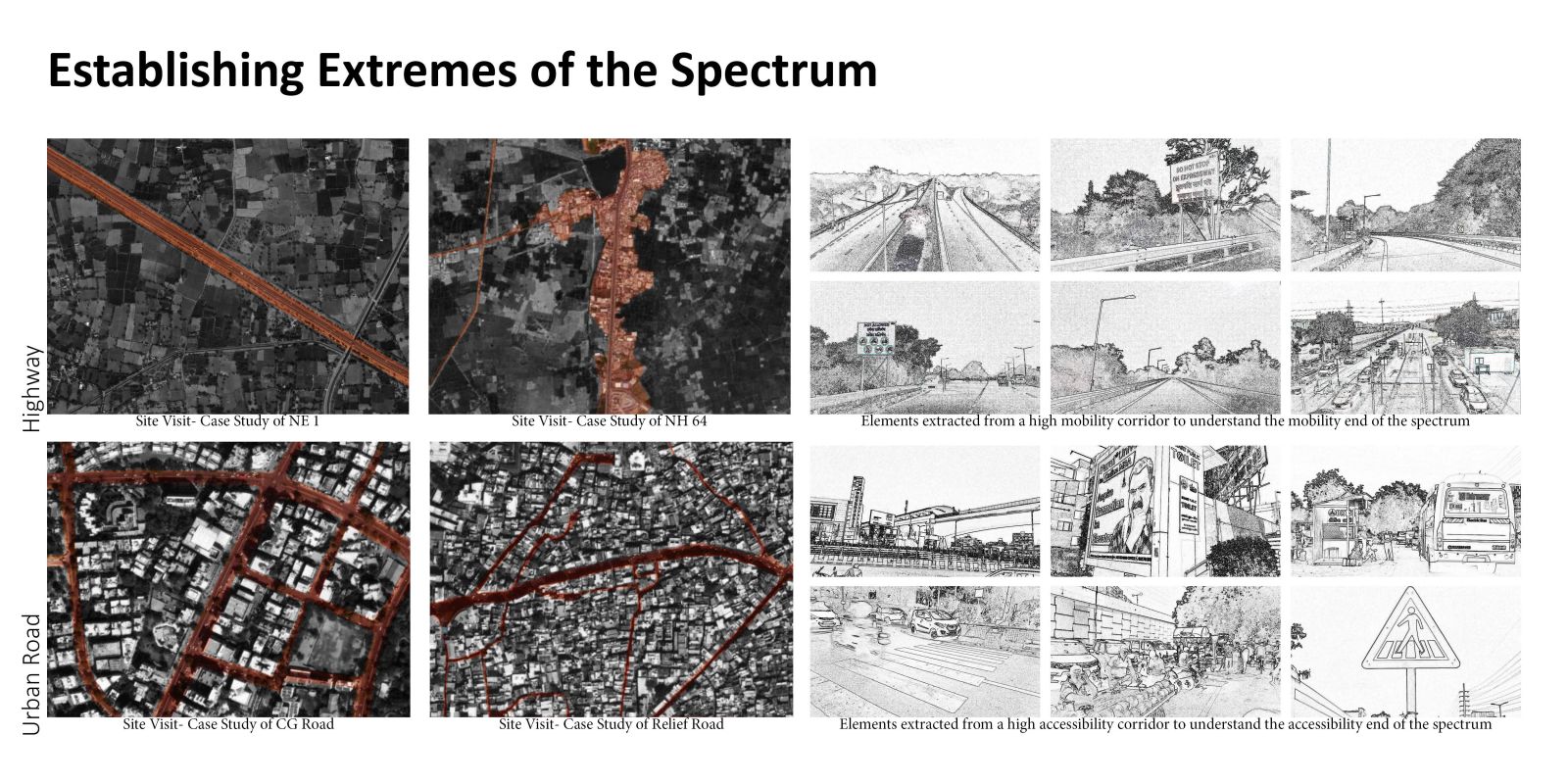
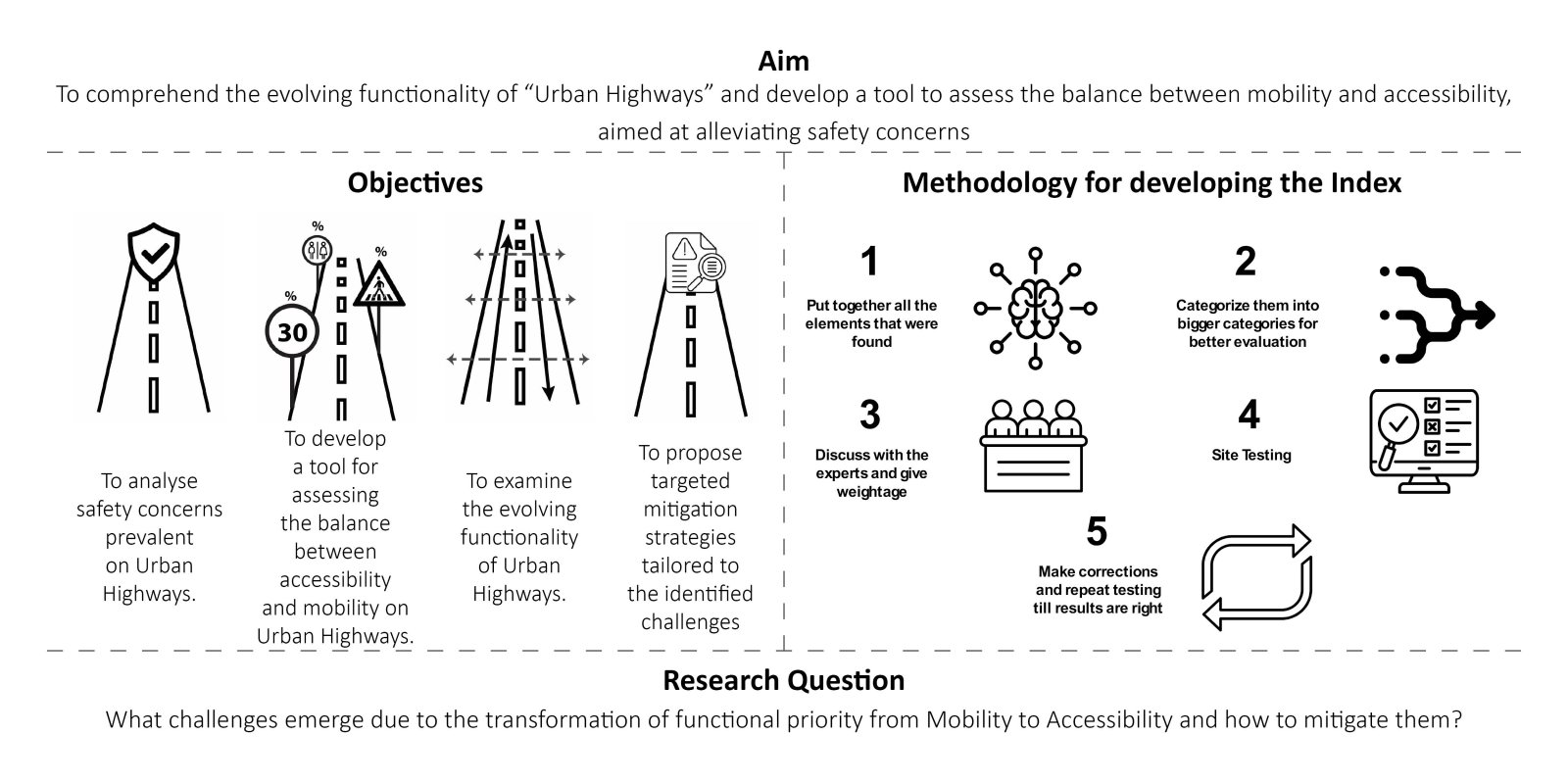
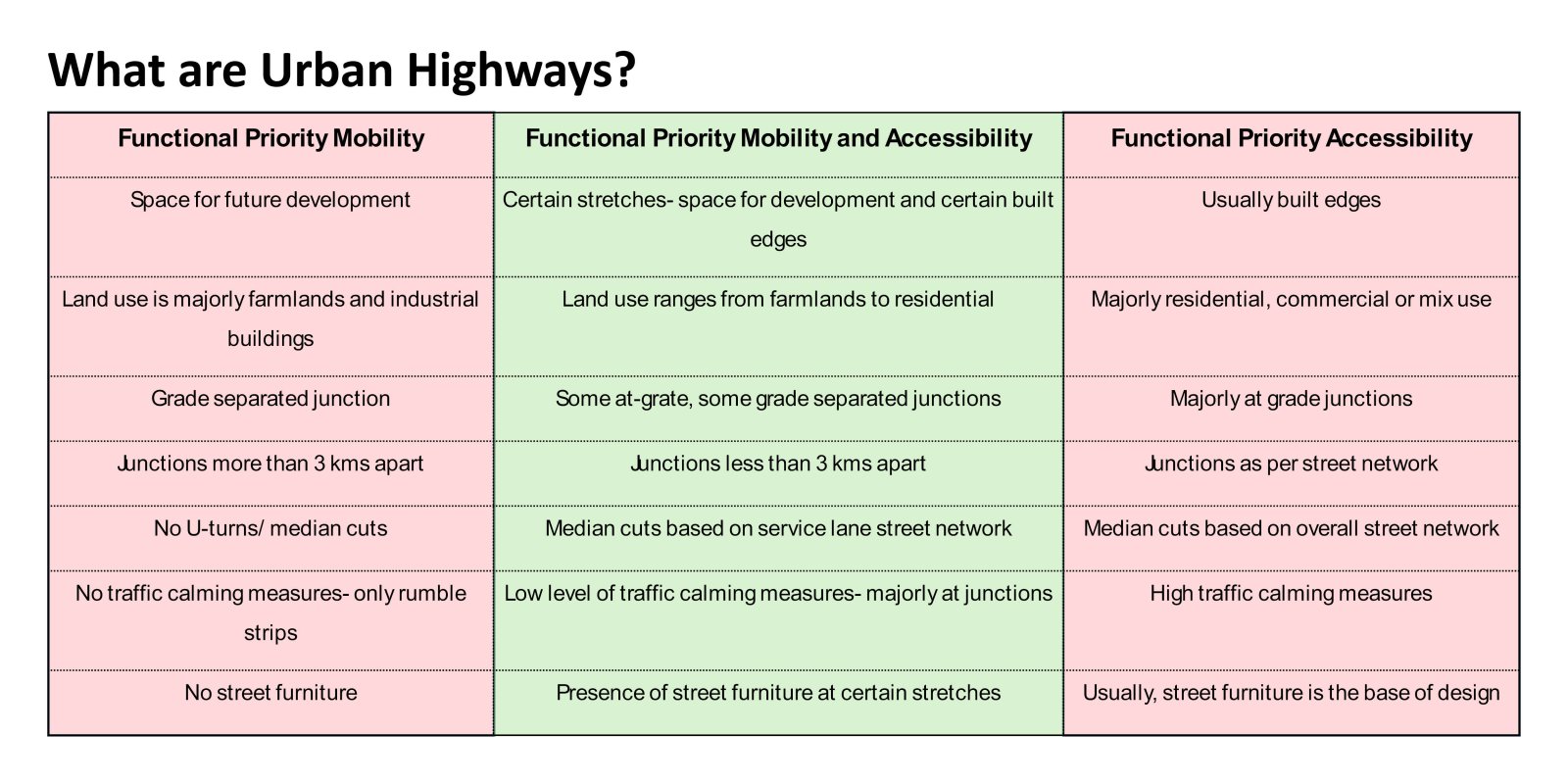
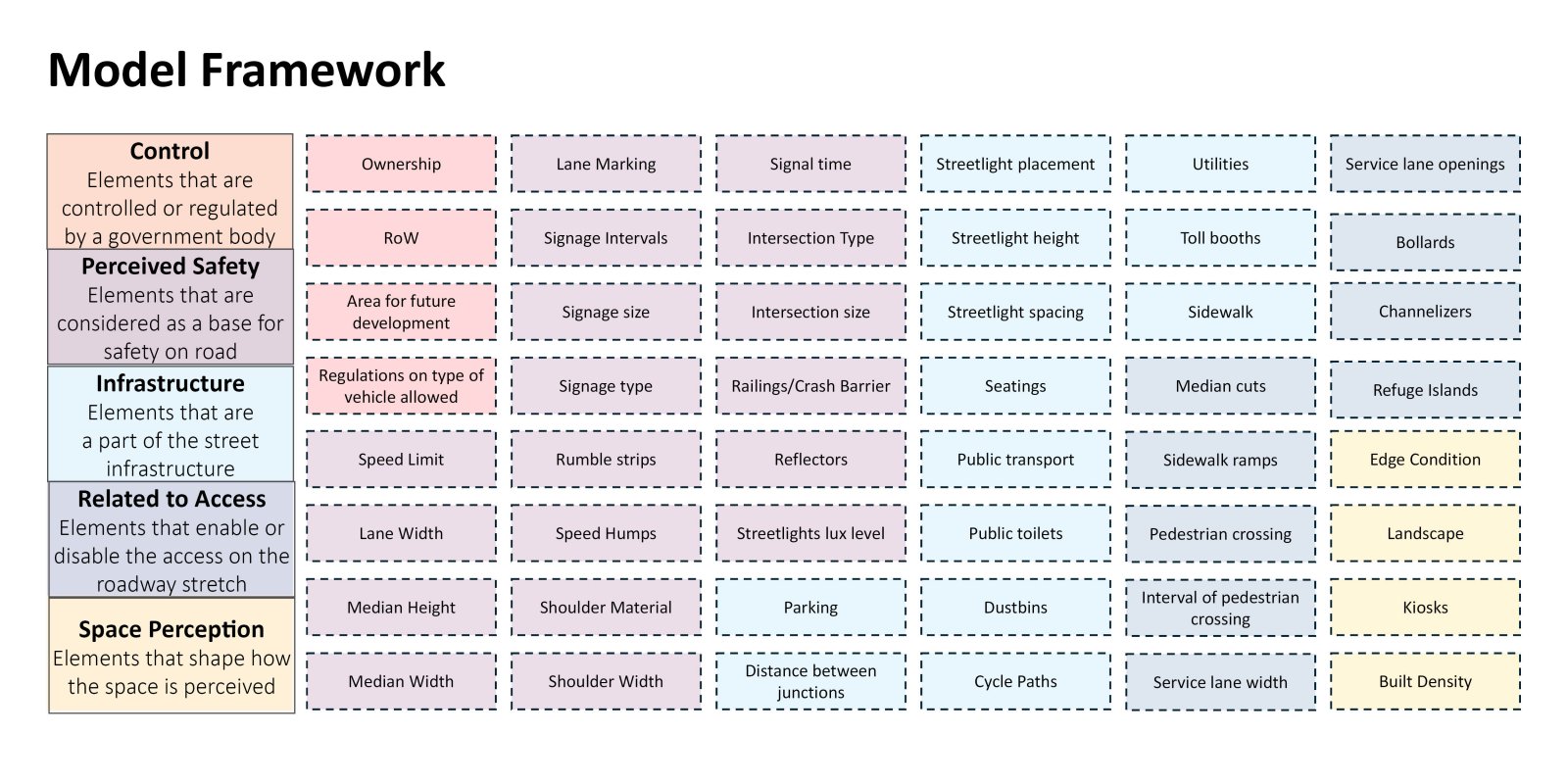
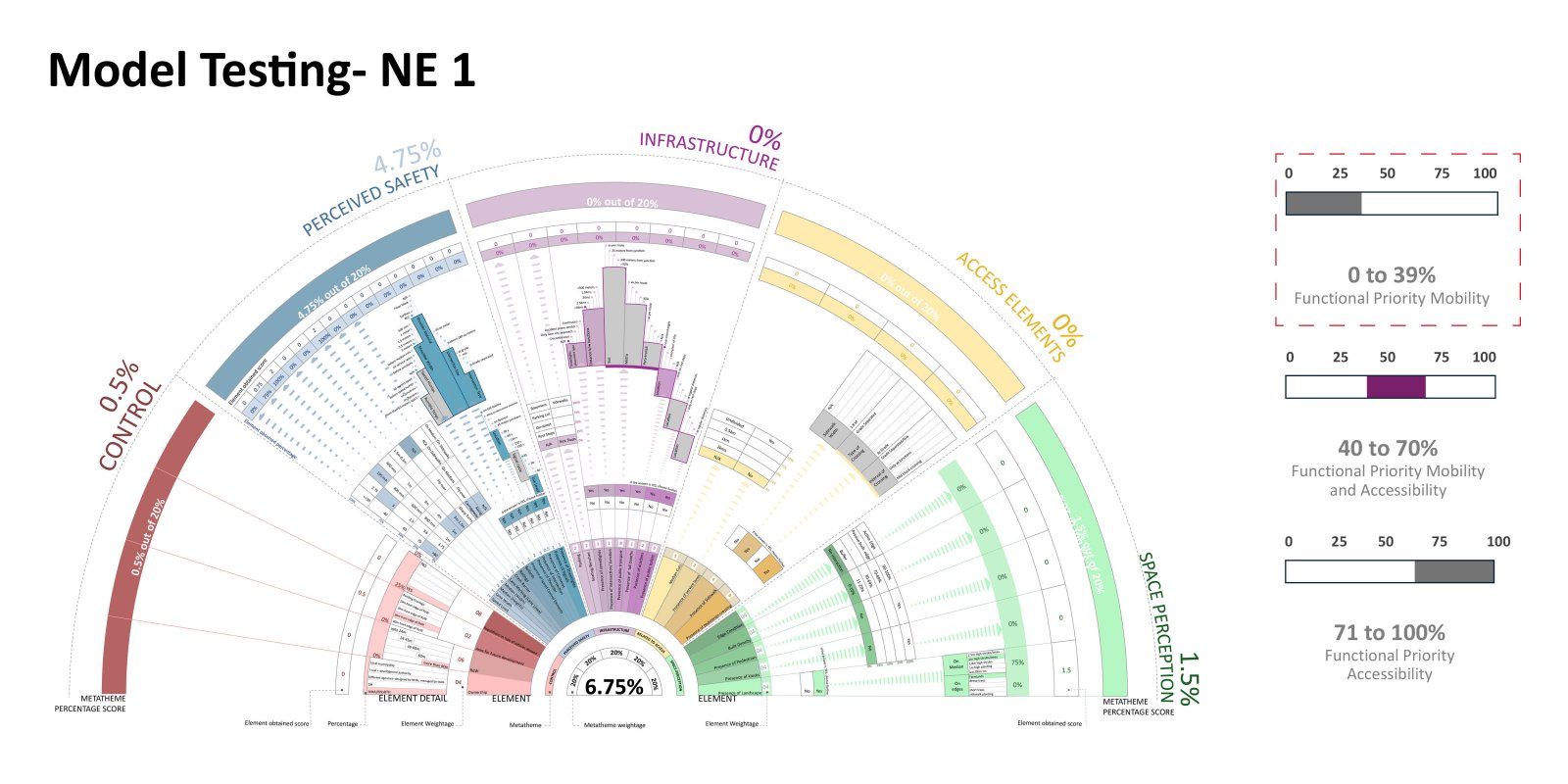
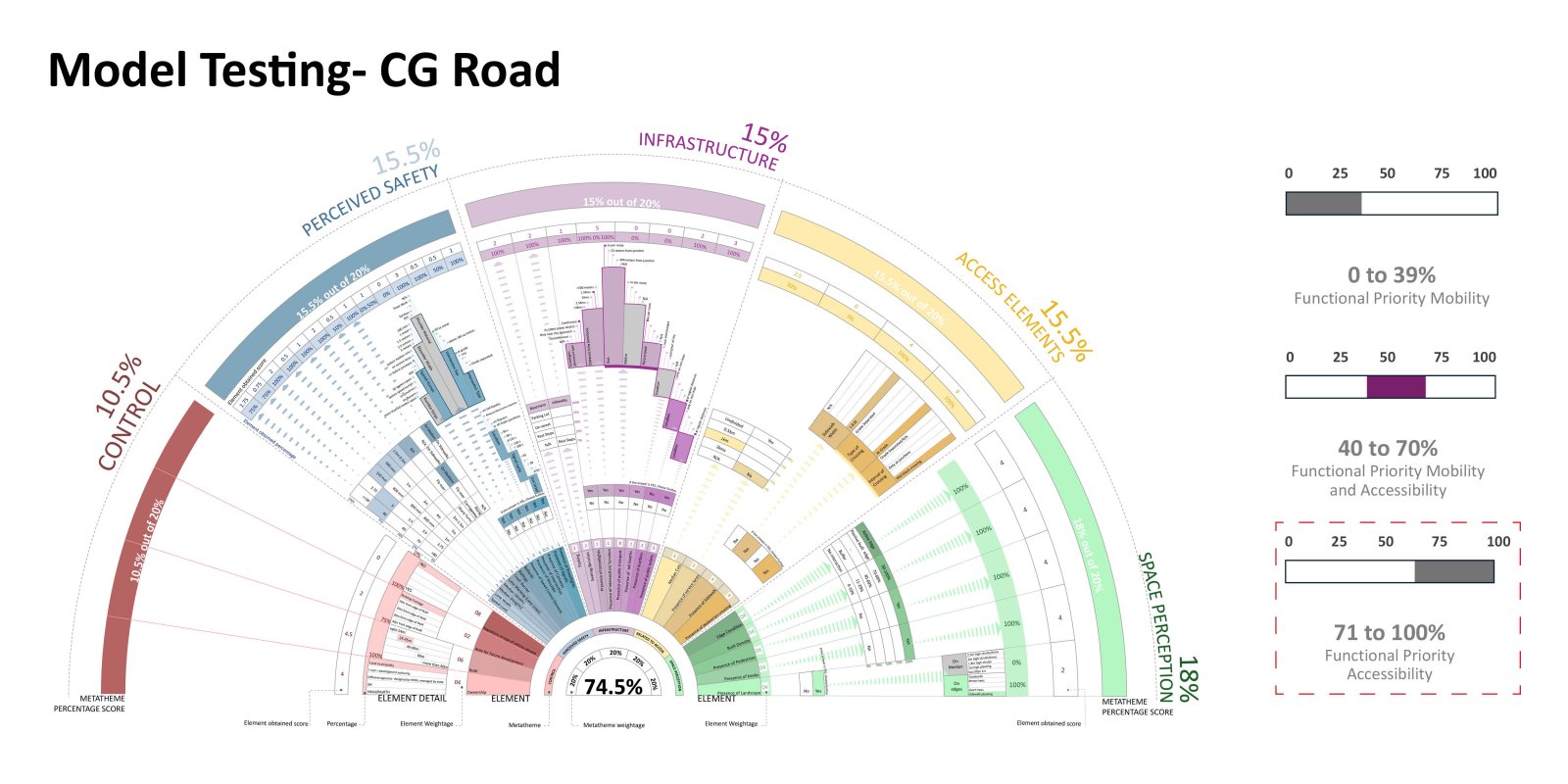
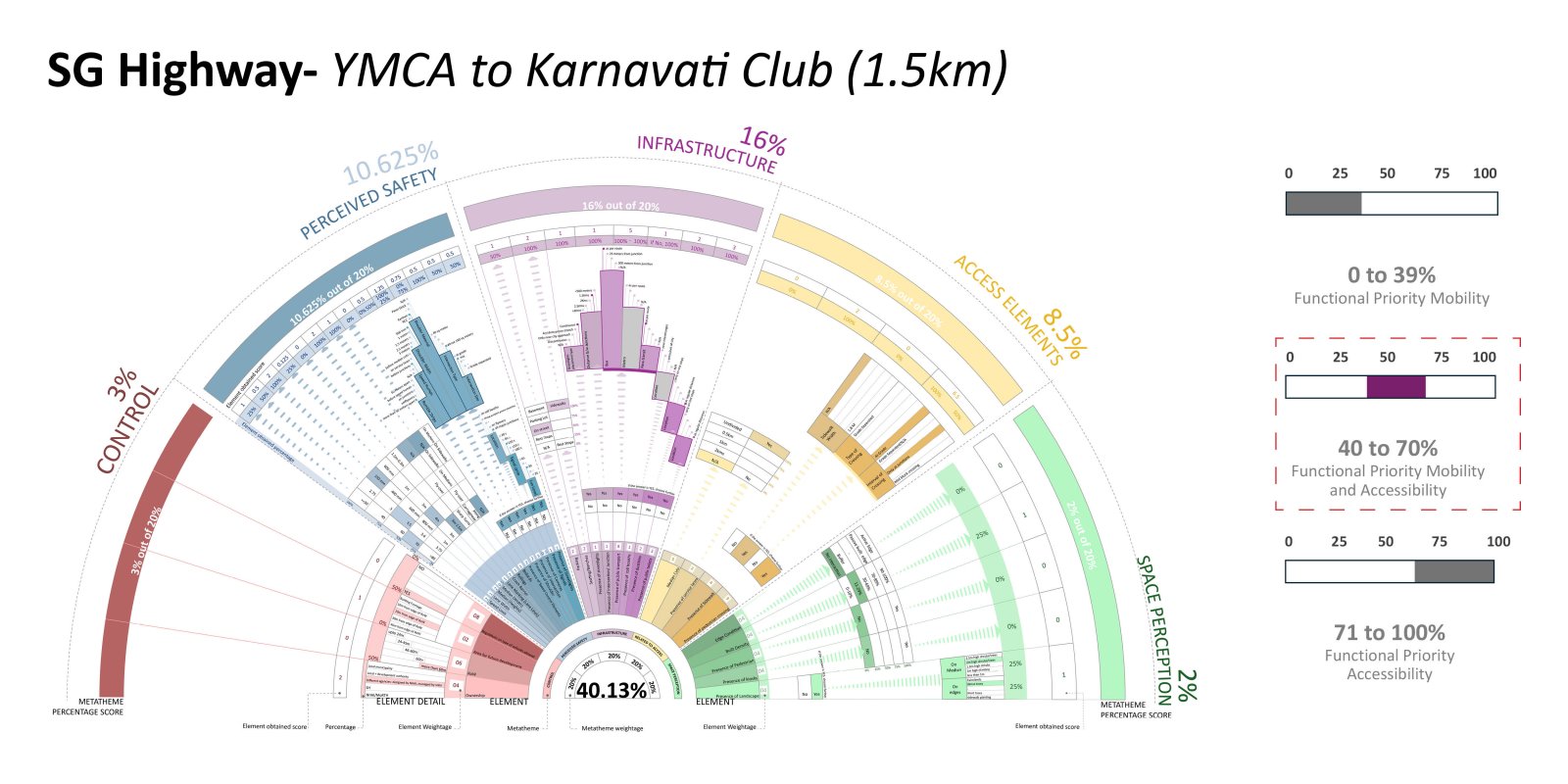
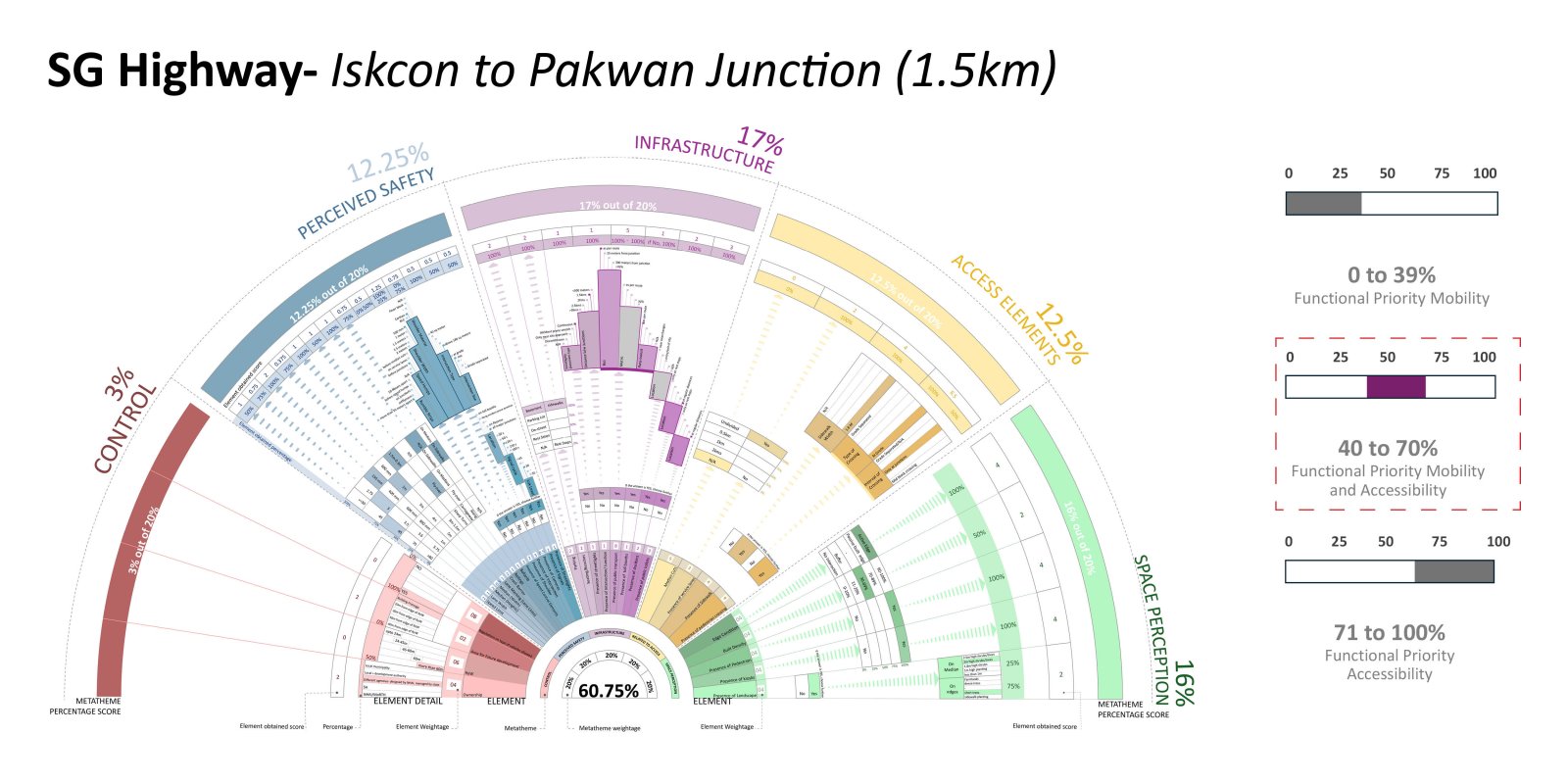
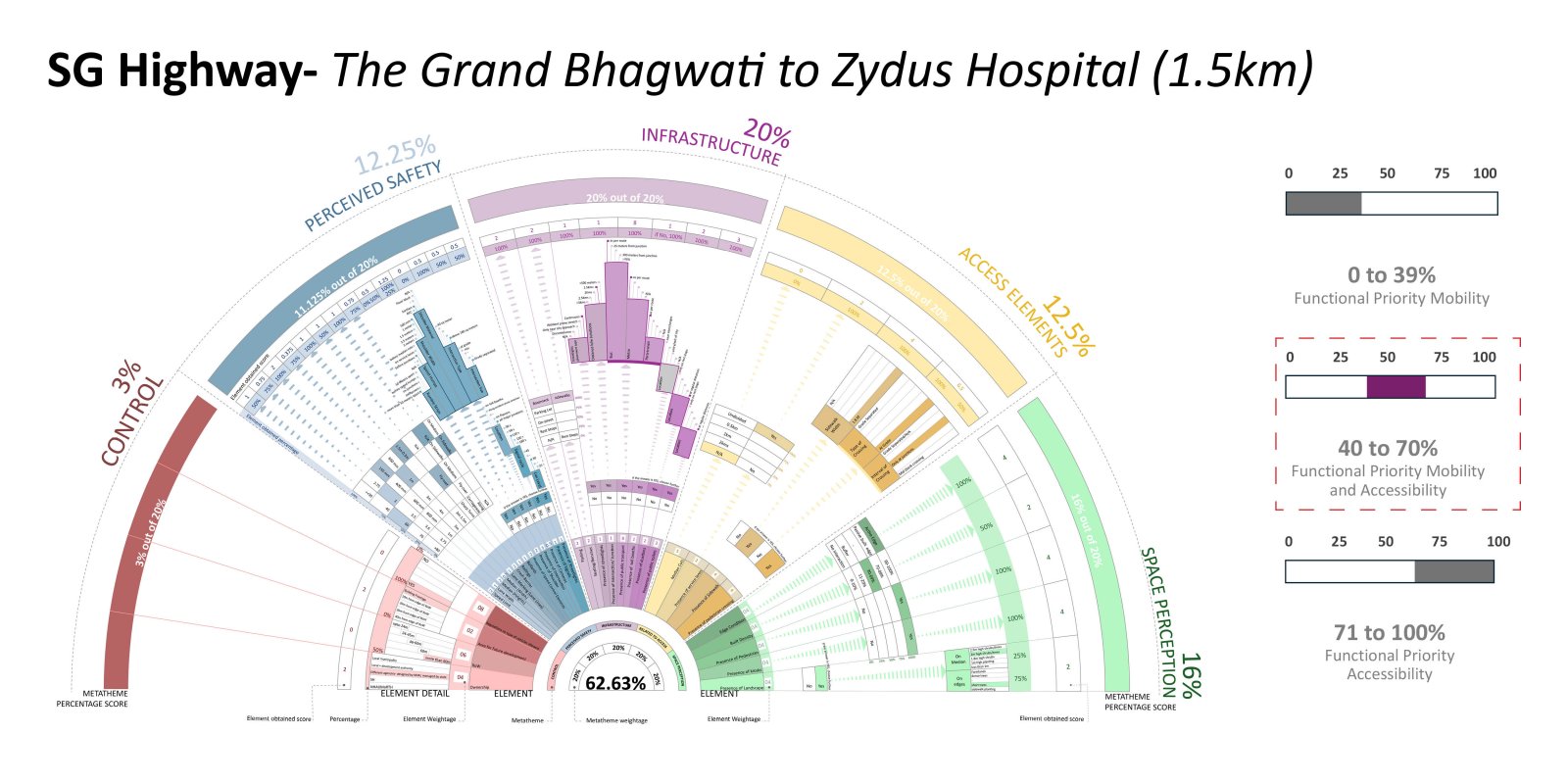
The evolution of roadways, initially designed for high-speed mobility, has led to a critical urban challenge as these corridors have become an integral part of the expanding city. City Sprawl and Urbanization has caused a shift in the high mobility corridors that used to be outside the city limits to function as major urban arterial access in the city. This shift poses a serious safety concern on these “Urban Highway.” The existing design standards and guidelines are operational as individual typologies but fail to accommodate the dynamic nature of these corridors demanding a change in the approach.
The study focuses on the illustrative example of the SG Highway, where the intersection of high-speed travel and urban access has given rise to safety, accessibility, and mobility issues. In a concerning revelation, the SG Highway was among India’s top ten road crashes sites in 2023 by the Indian Road Crashes Data Management System (Irad/eRAD) of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).