Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
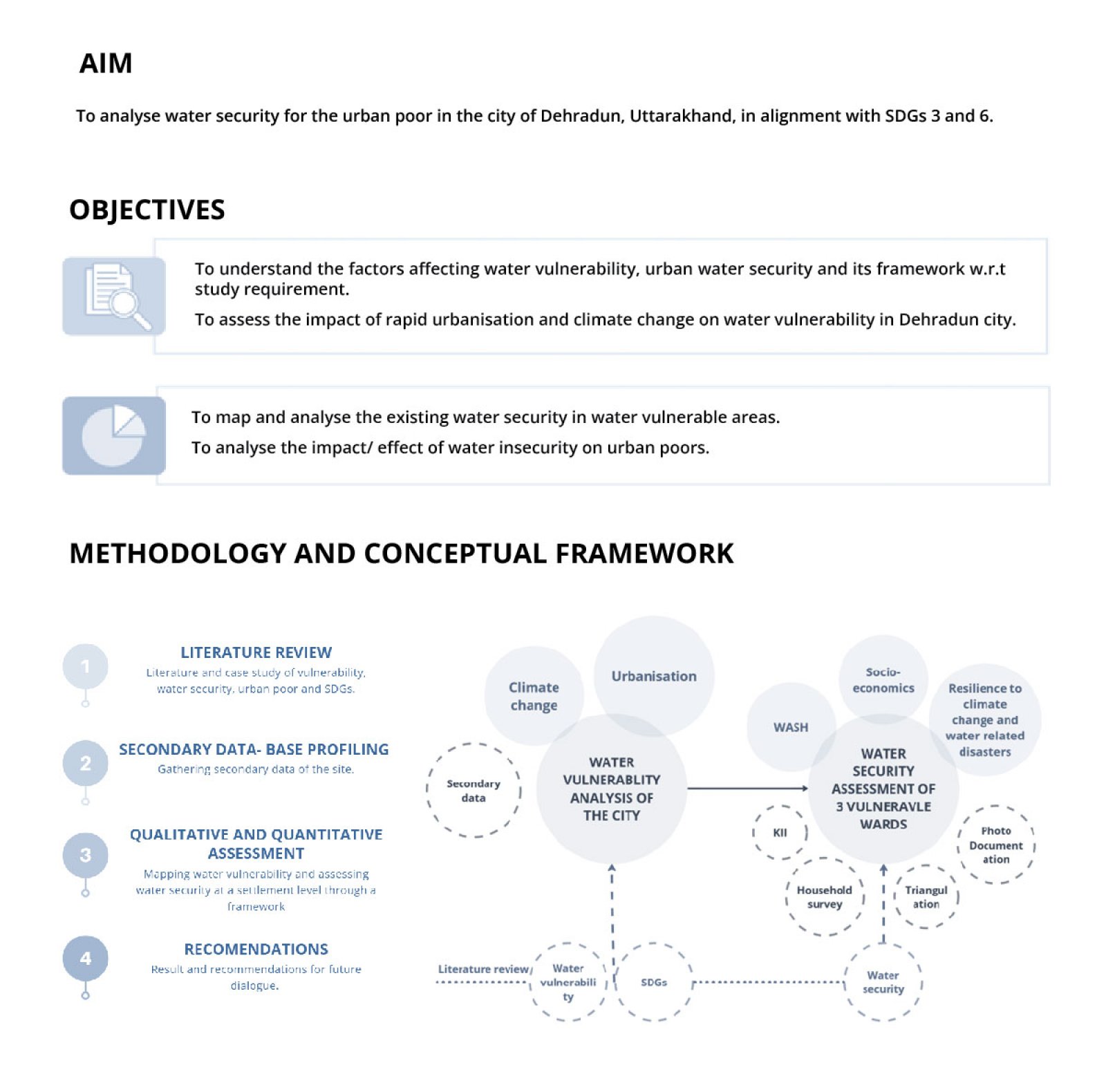
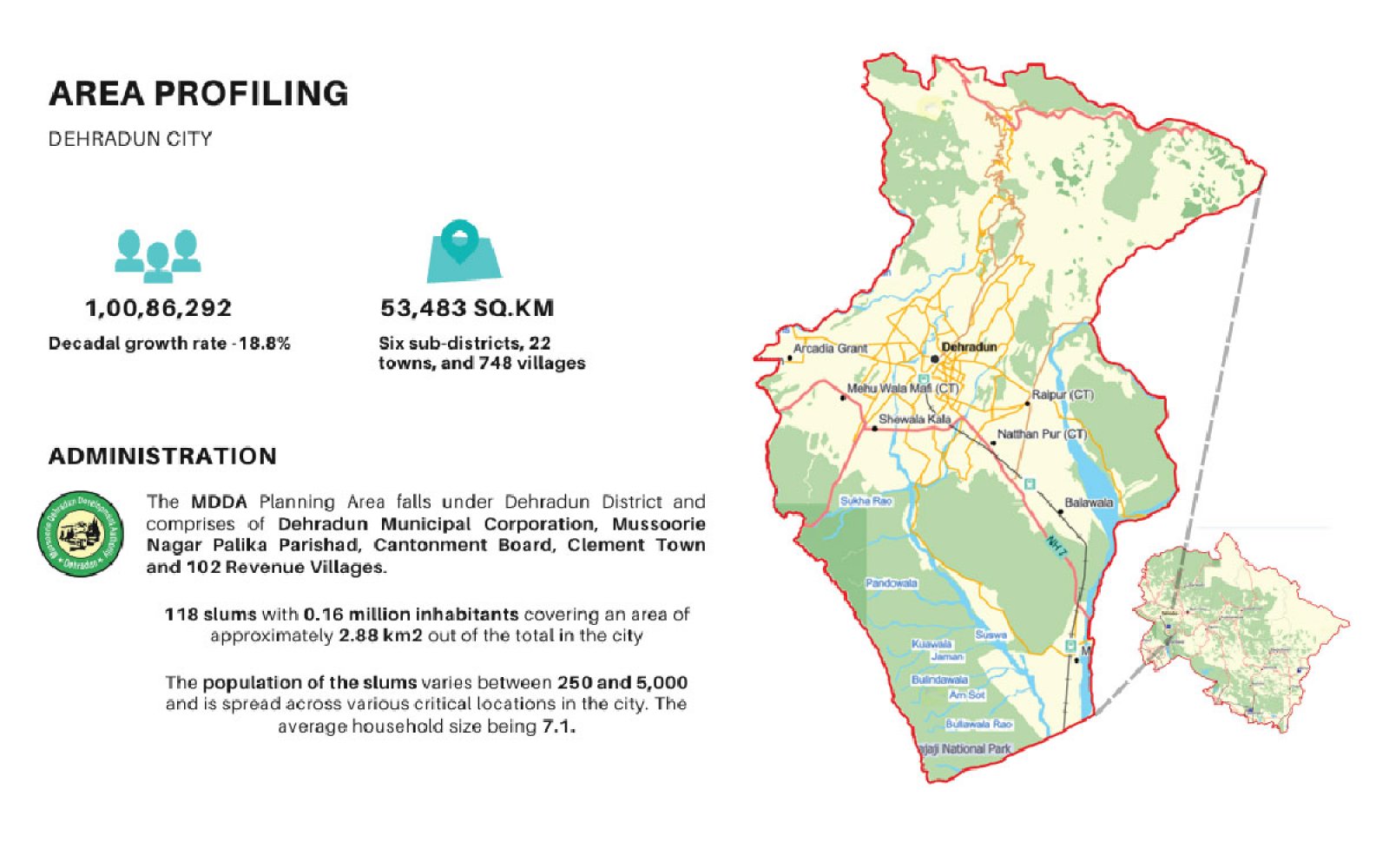
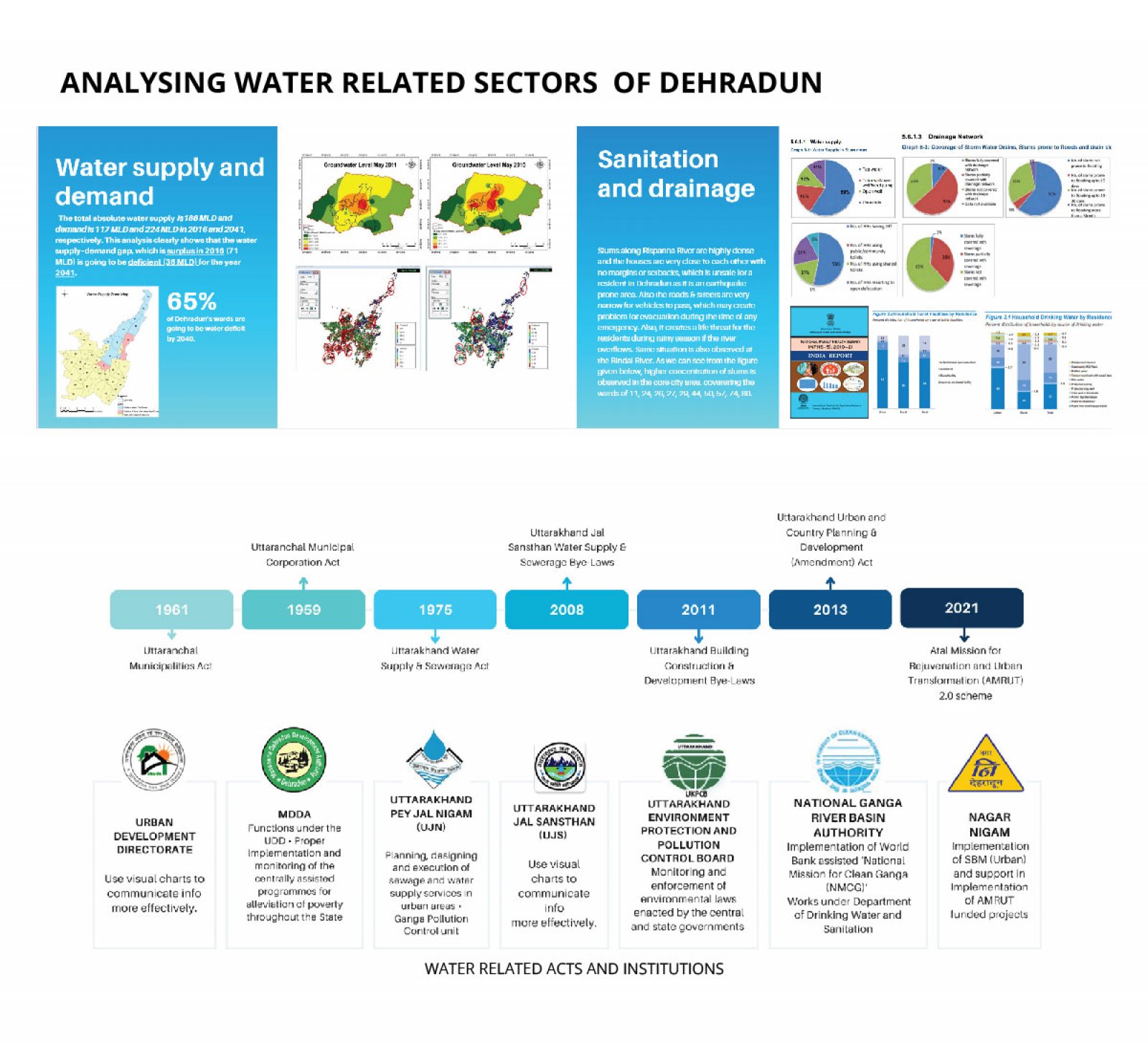
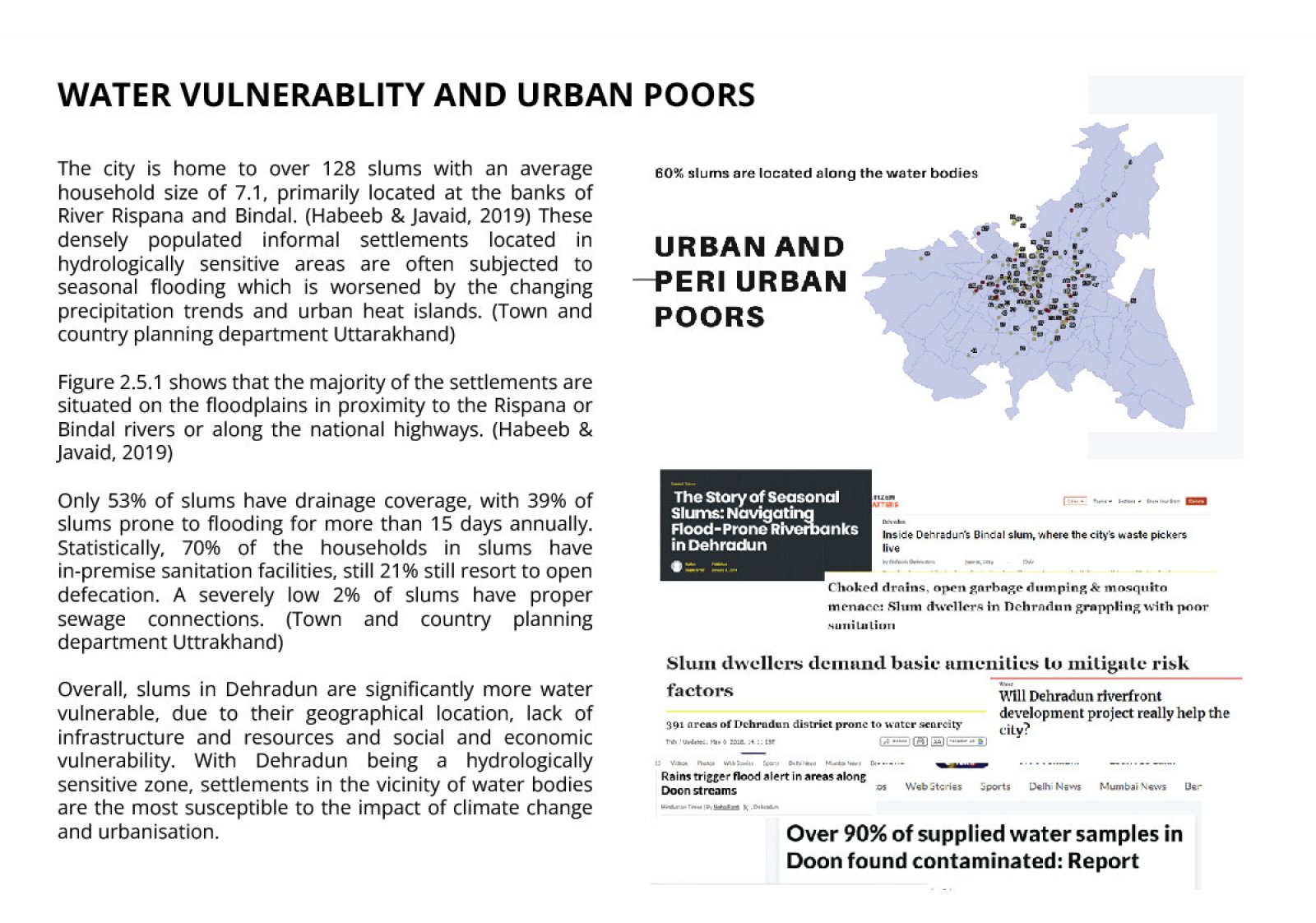
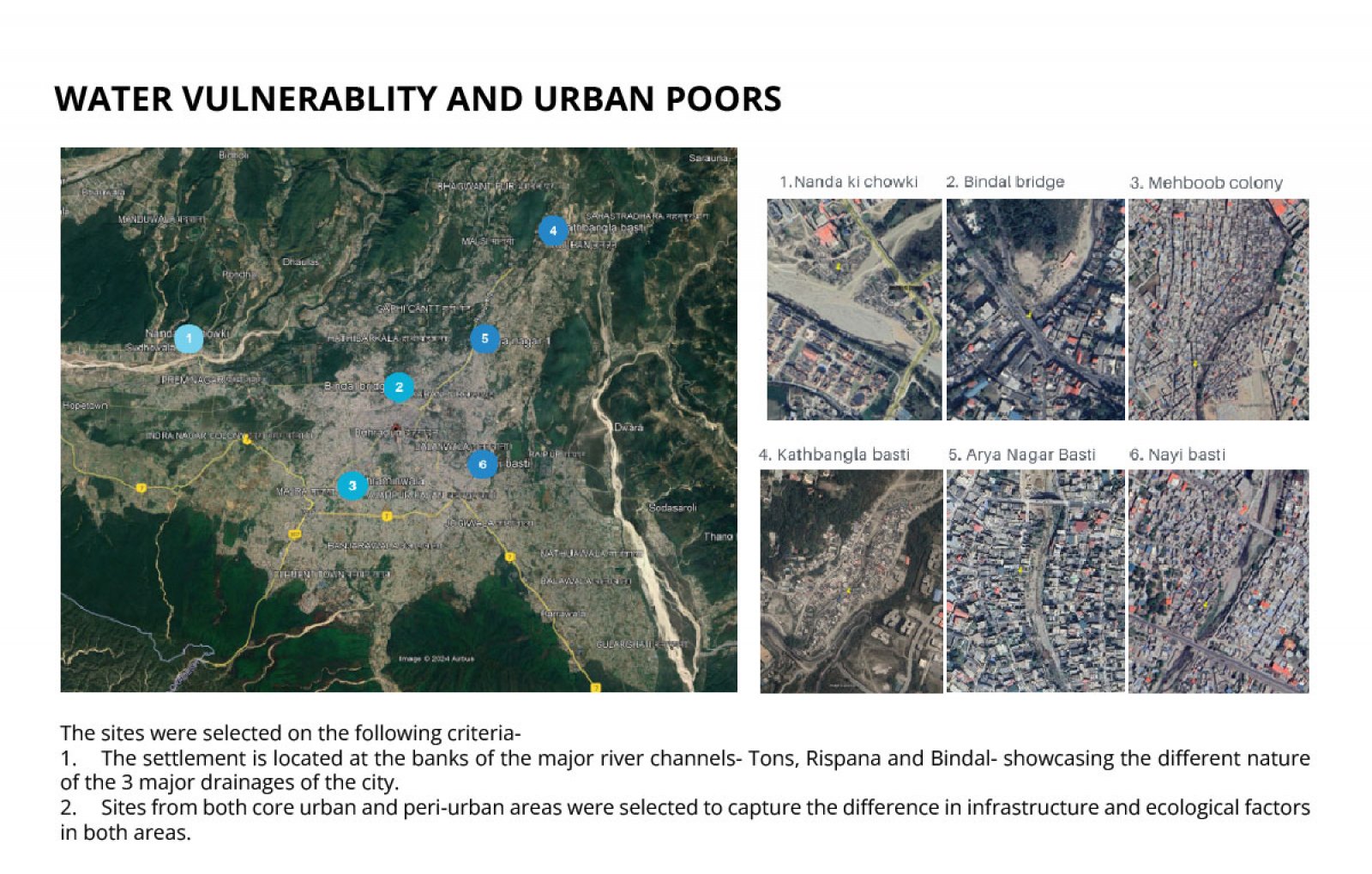
The study examines the impact of rapid urbanization in the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR), particularly focusing on Dehradun, Uttarakhand, where urban populations are expected to exceed 50% by 2050. This growth exacerbates existing infrastructure challenges, especially in water distribution, affecting marginalized communities. The research aligns with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 3 and 6, emphasizing sustainable water management and health promotion. Utilizing GIS mapping and secondary data analysis, the study assesses water vulnerability at six sites through household surveys. It critically evaluates the implications of climate change and urbanization on these communities, advocating for equitable water services and integrated management strategies to address urgent needs.