Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
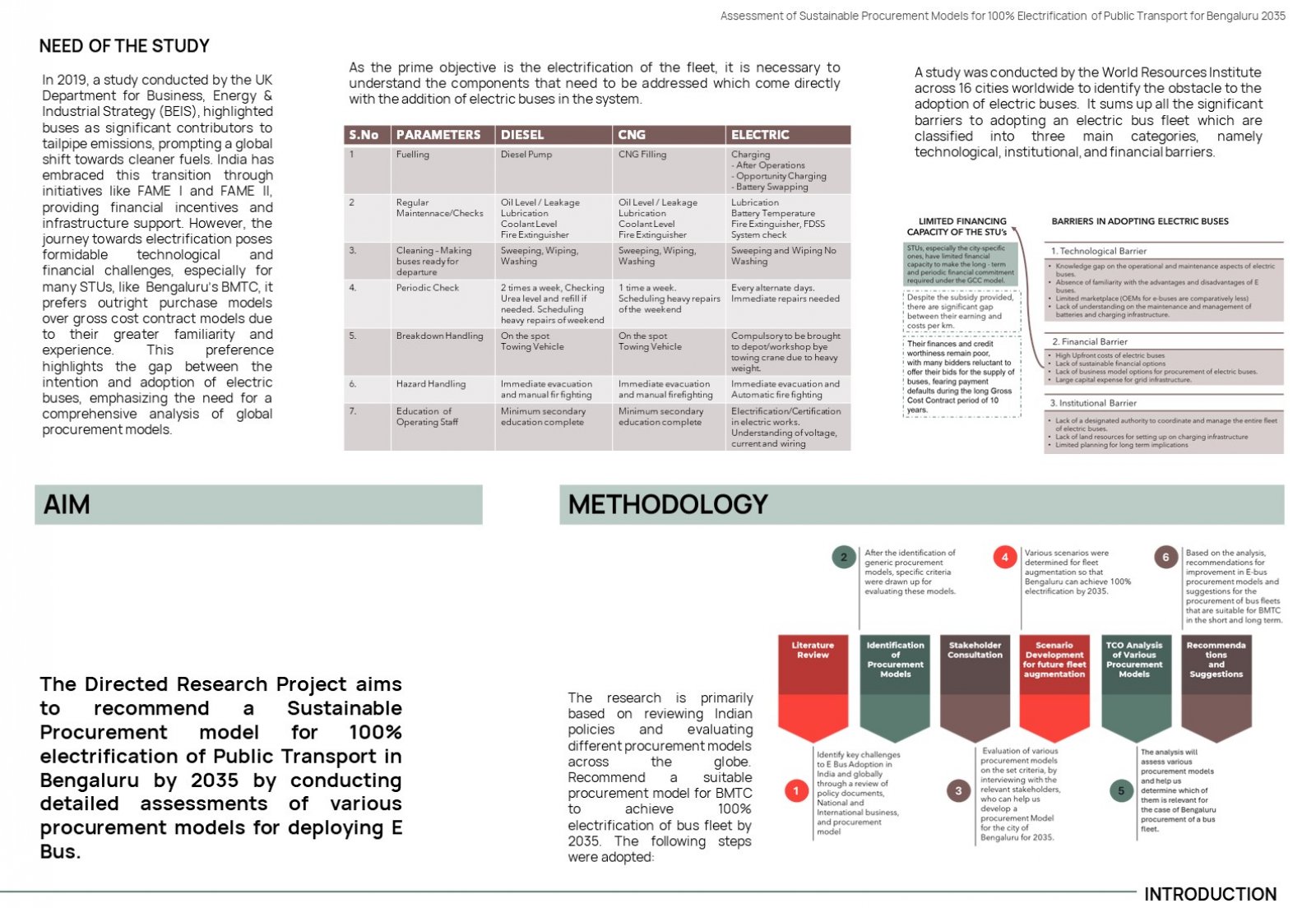
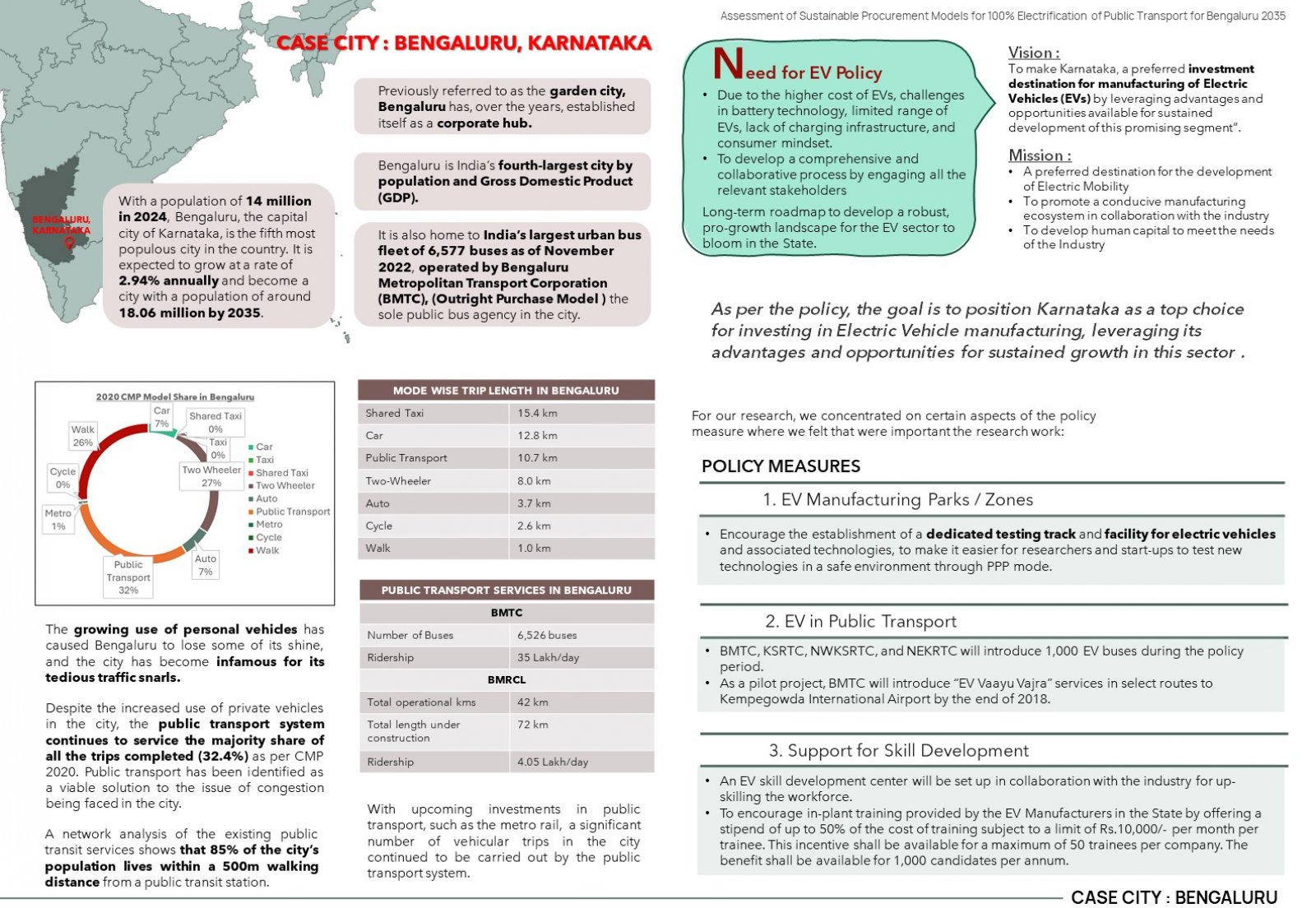
Since 2011, the Government of India has laid down a roadmap for electrification, with the launch of many national-level schemes. These schemes have mandated the procurement process to take place under the Gross Cost Contract. However, many STUs, like Bengaluru’s BMTC prefer outright purchase models over gross cost contract models due to their greater familiarity and experience. This preference highlights the gap between the intention and adoption of electric buses, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive analysis of global procurement models. This research aims to bridge this gap by identifying areas of improvement applicable to Bengaluru and providing actionable insights for BMTC as it gears up for future electrification.