Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
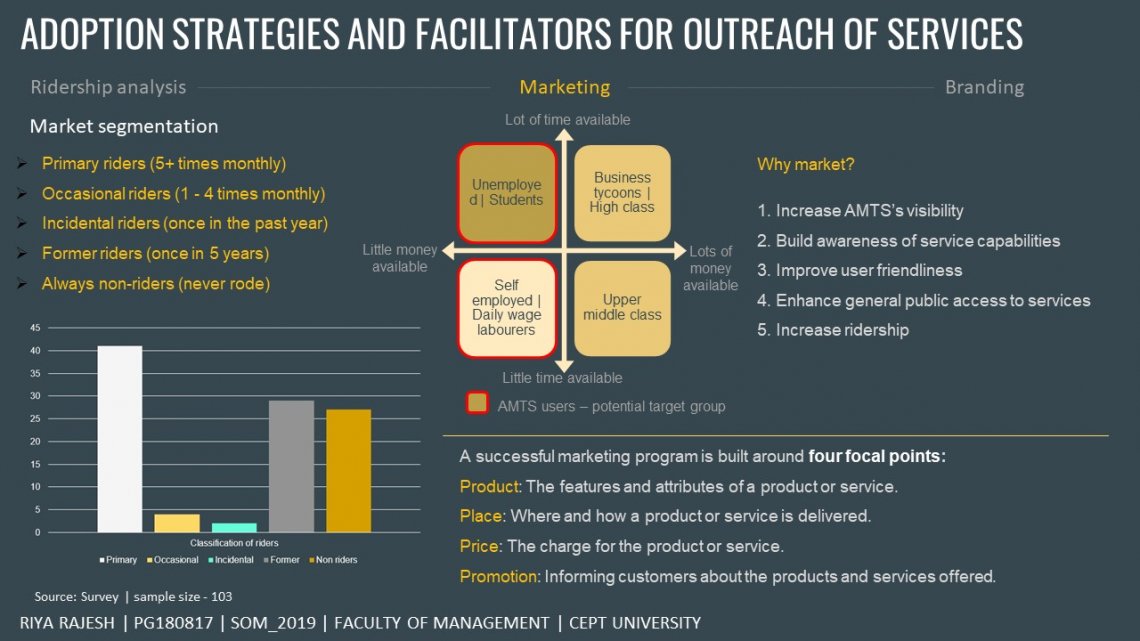
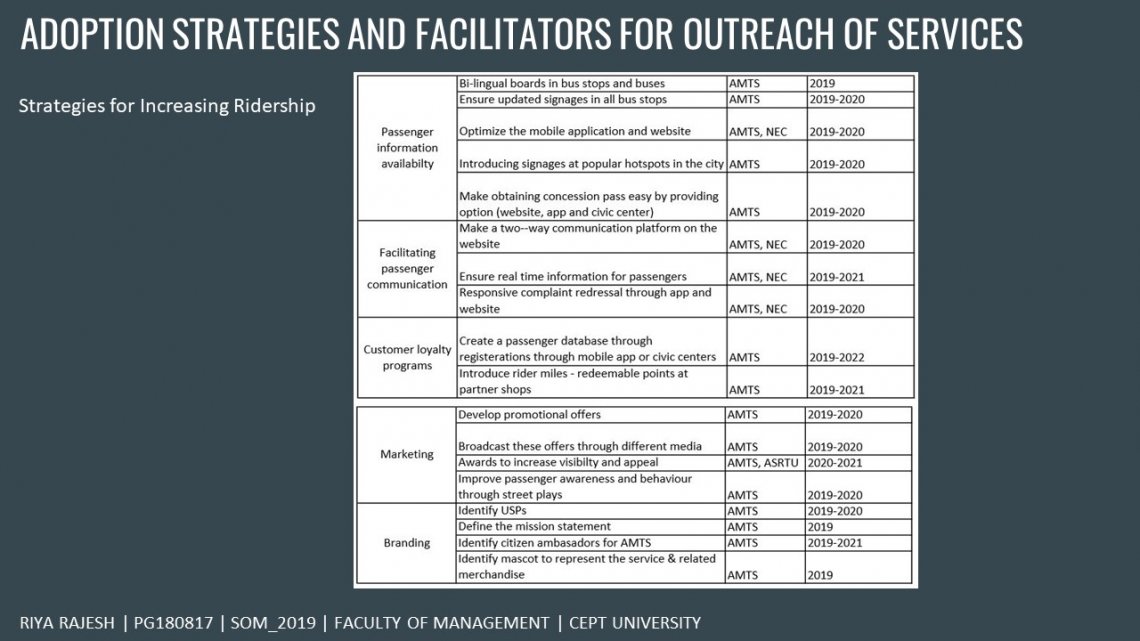
It is essential to analyse the ridership in public transport to understand the shortcomings and potential areas for improvement. The focus of the study was on understanding the stagnation of ridership in the AMTS. Further, the user perception of the service quality of the AMTS was analyzed to identify areas for improvement. Lastly, measures that can be adopted by the service provider to increase the outreach was suggested. The appraisal of theAMTS is a humongous task and requires a large input of data and human resource. The major part of the study involves interaction with the current users of the service and the non-users of public transport systems in general. The research is fragmented into understanding the current ridership and analyzing the travel behaviors. This is done with the help of the survey which is further supported by the in-depth interviews with the people of the city (users of AMTS and the non-users). This is followed by the understanding the market segments and identifying marketing techniques for the various segments. Finally, it concludes with the exploration of the idea of re-branding the AMTS to help with the outreach of services and increasing the visibility of AMTS which will eventually increase ridership.