Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
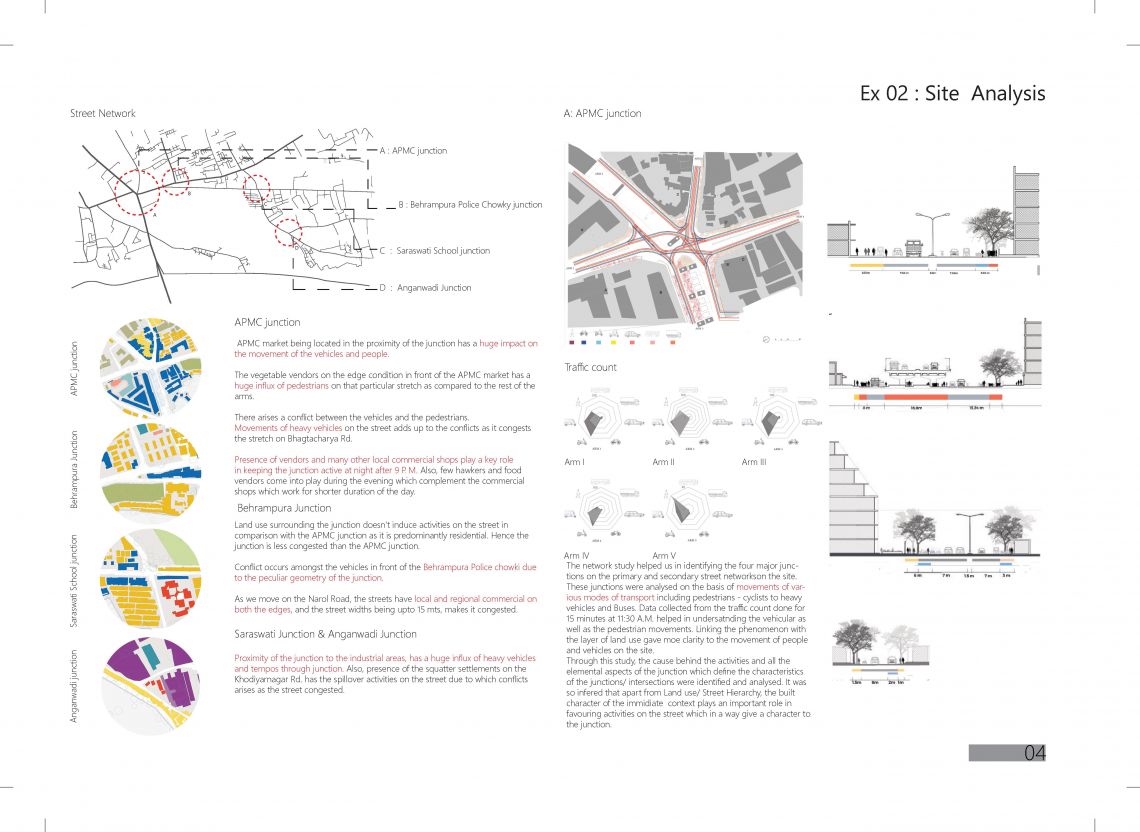
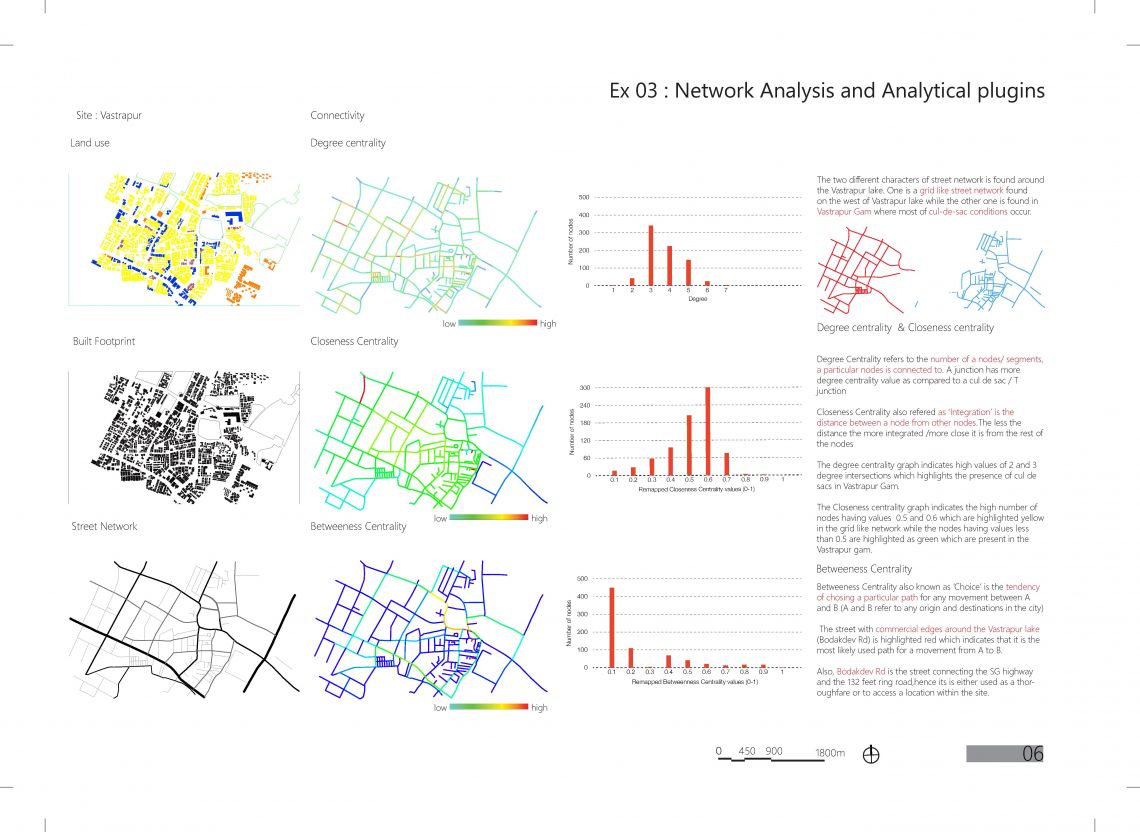
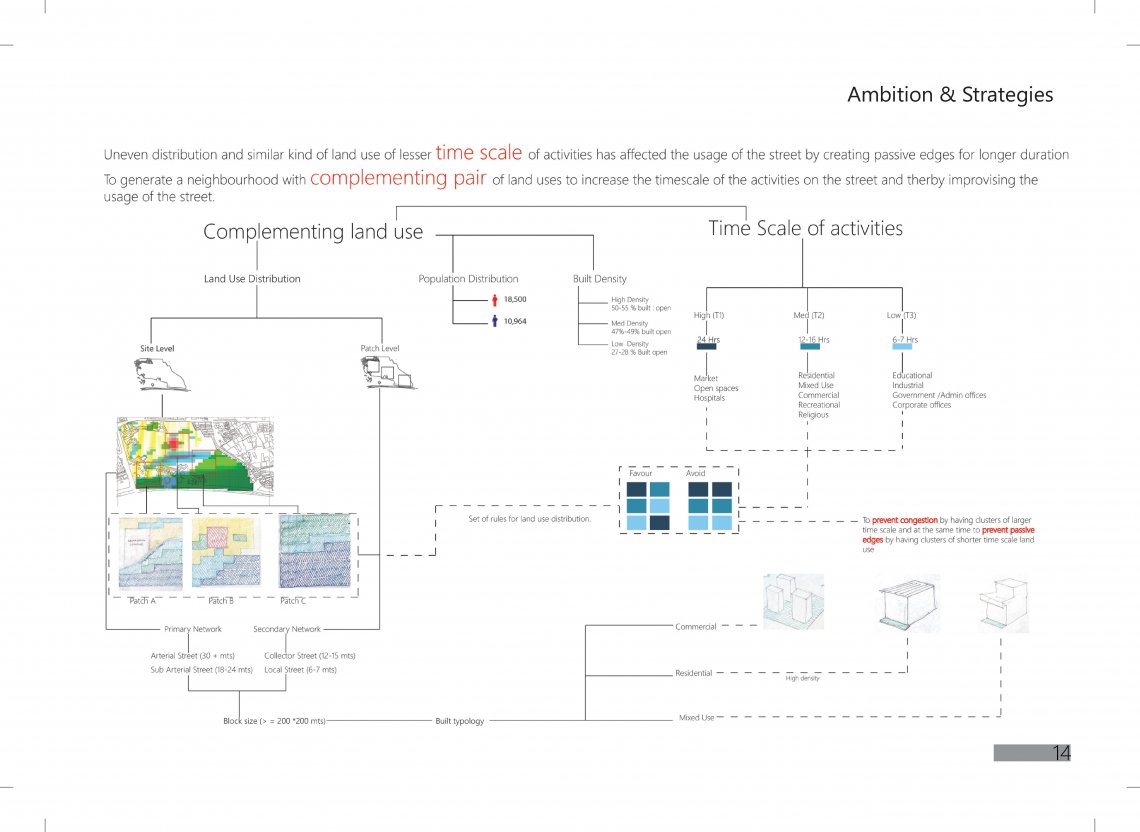
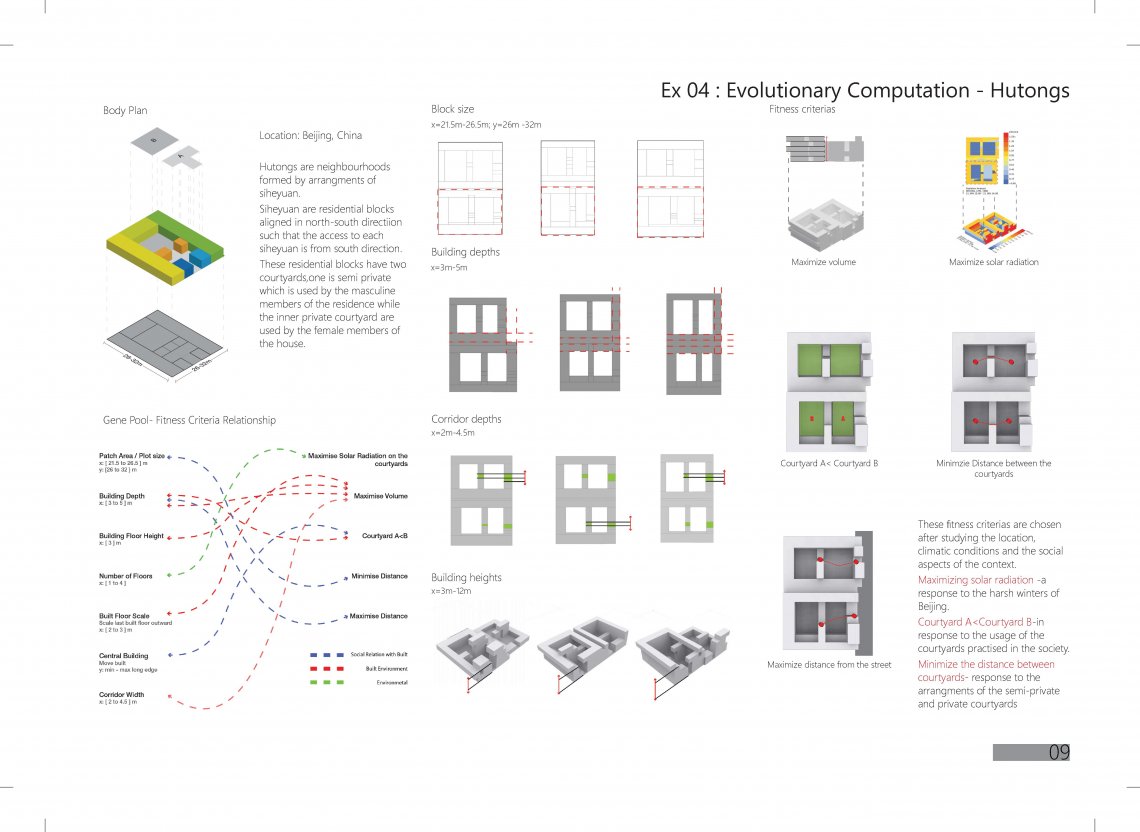
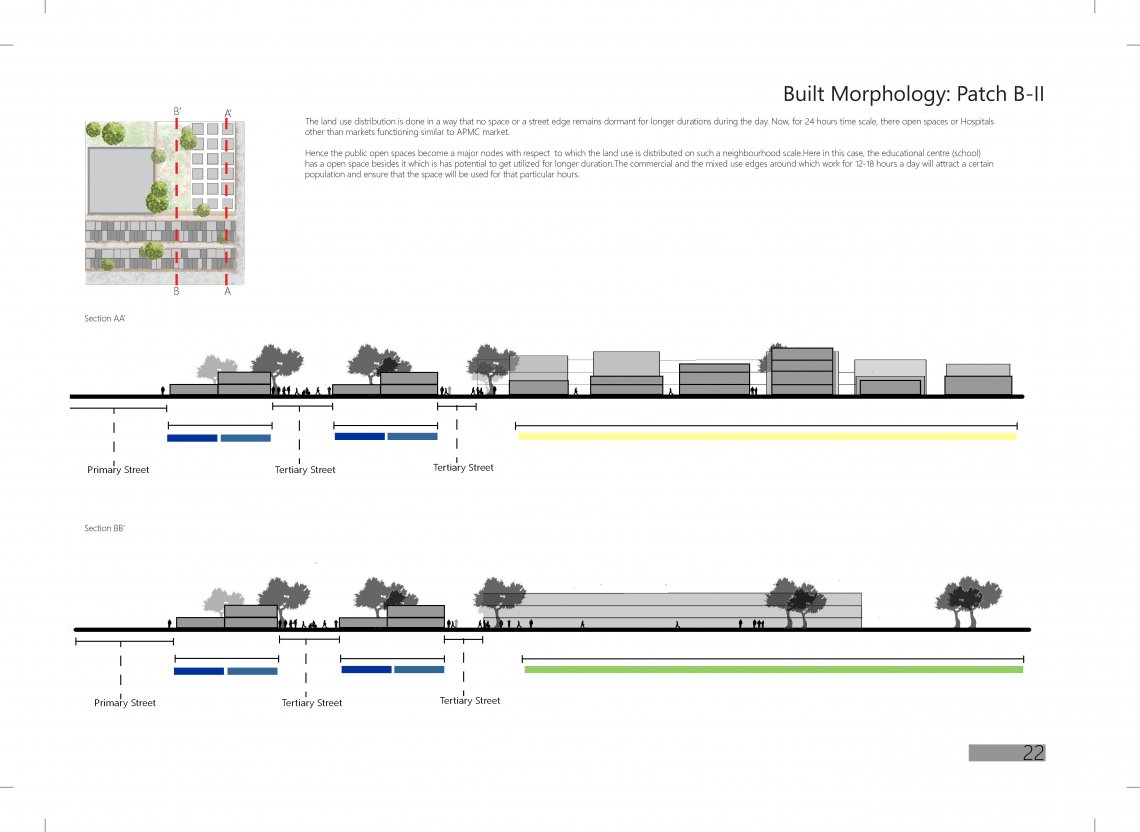
The project focuses on the land use distribution on the basis of their time scale. The proposal suggests to encourage arrangements of land uses with varied time scale instead of clustering of land uses with similar time scale. The reason behind the strategy is to prevent dead spaces on the streets( during non working hours or when the abutting buildings are shut down) and to ensure that the street usage is maximized