Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
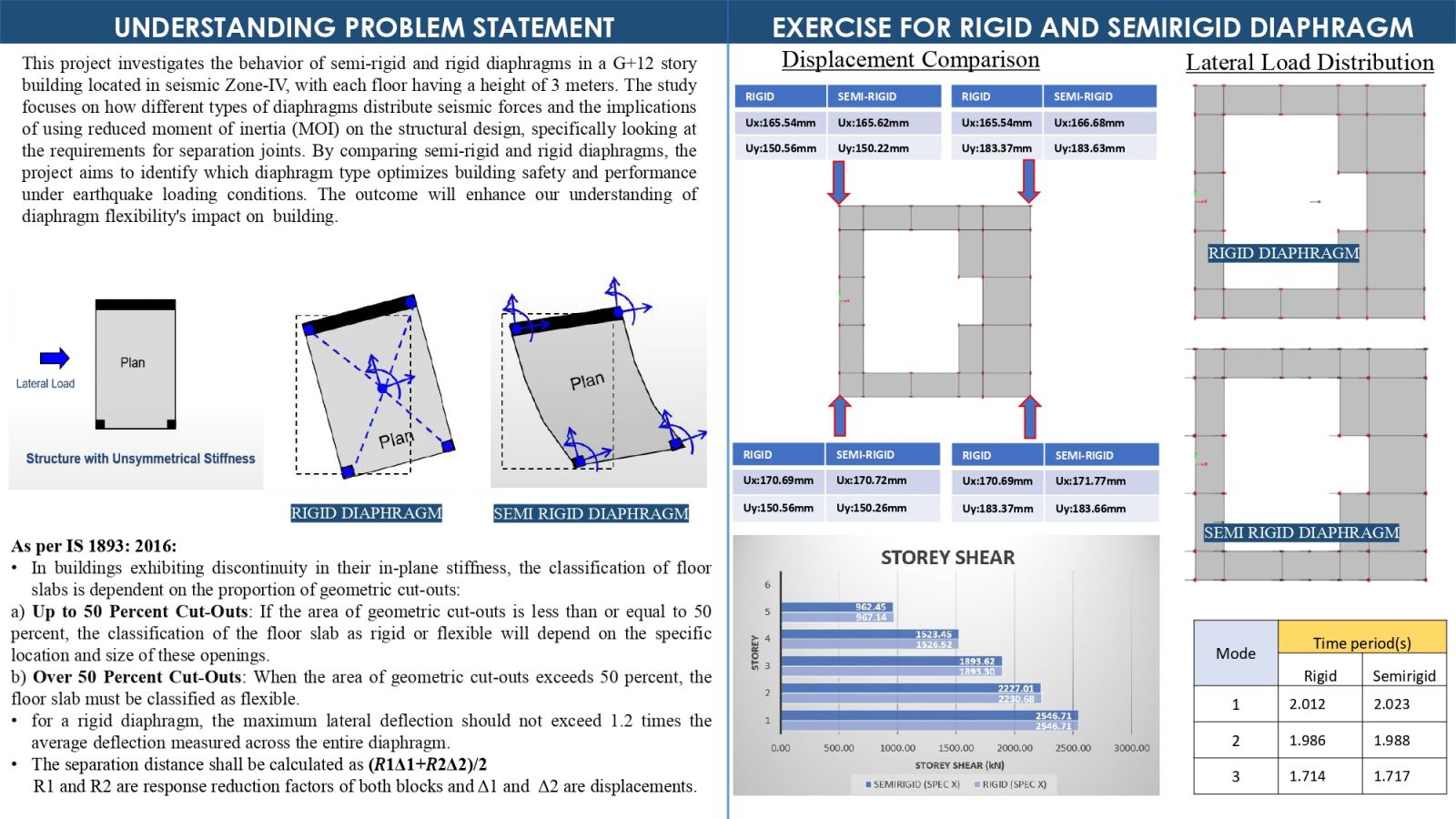
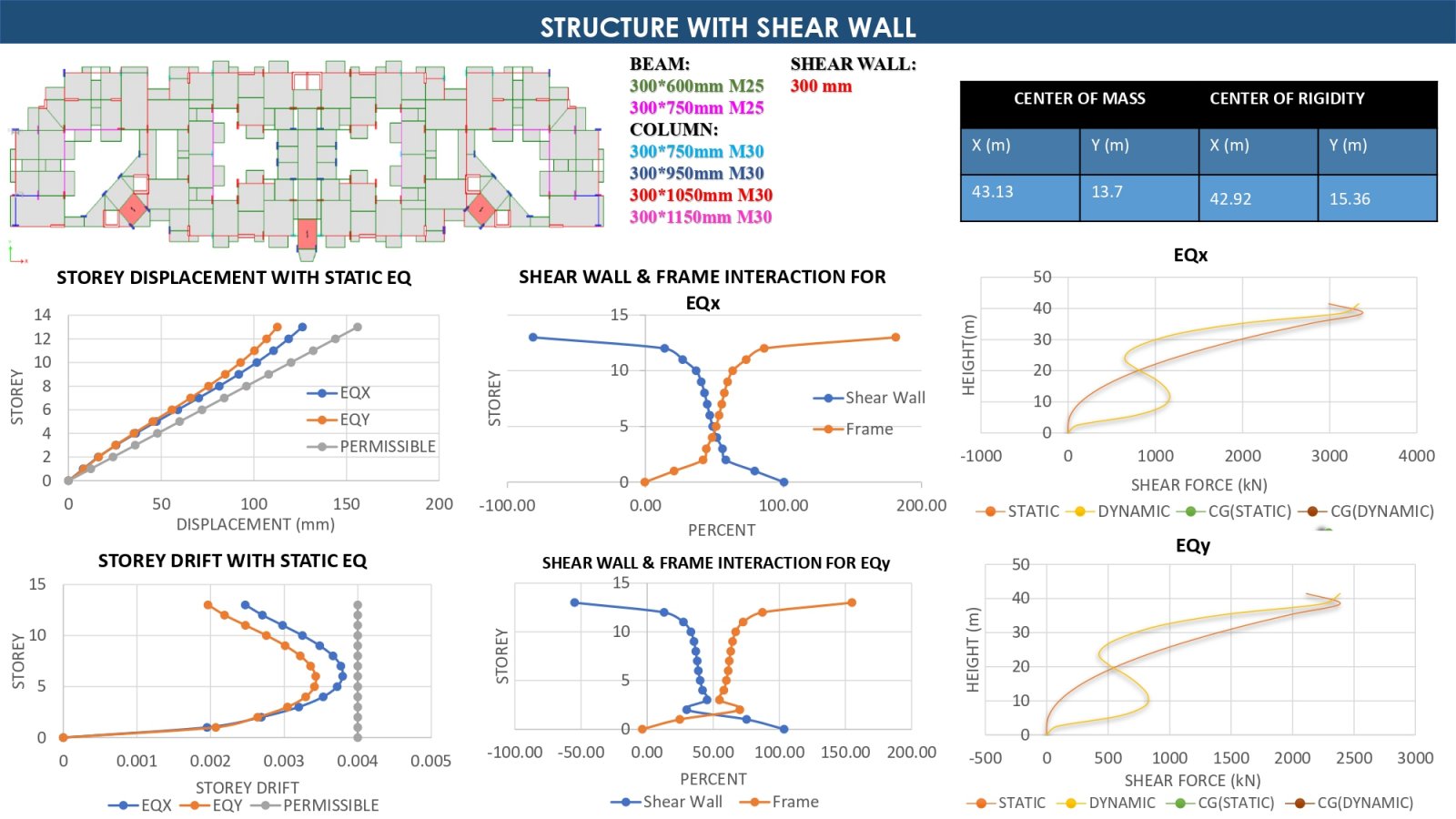
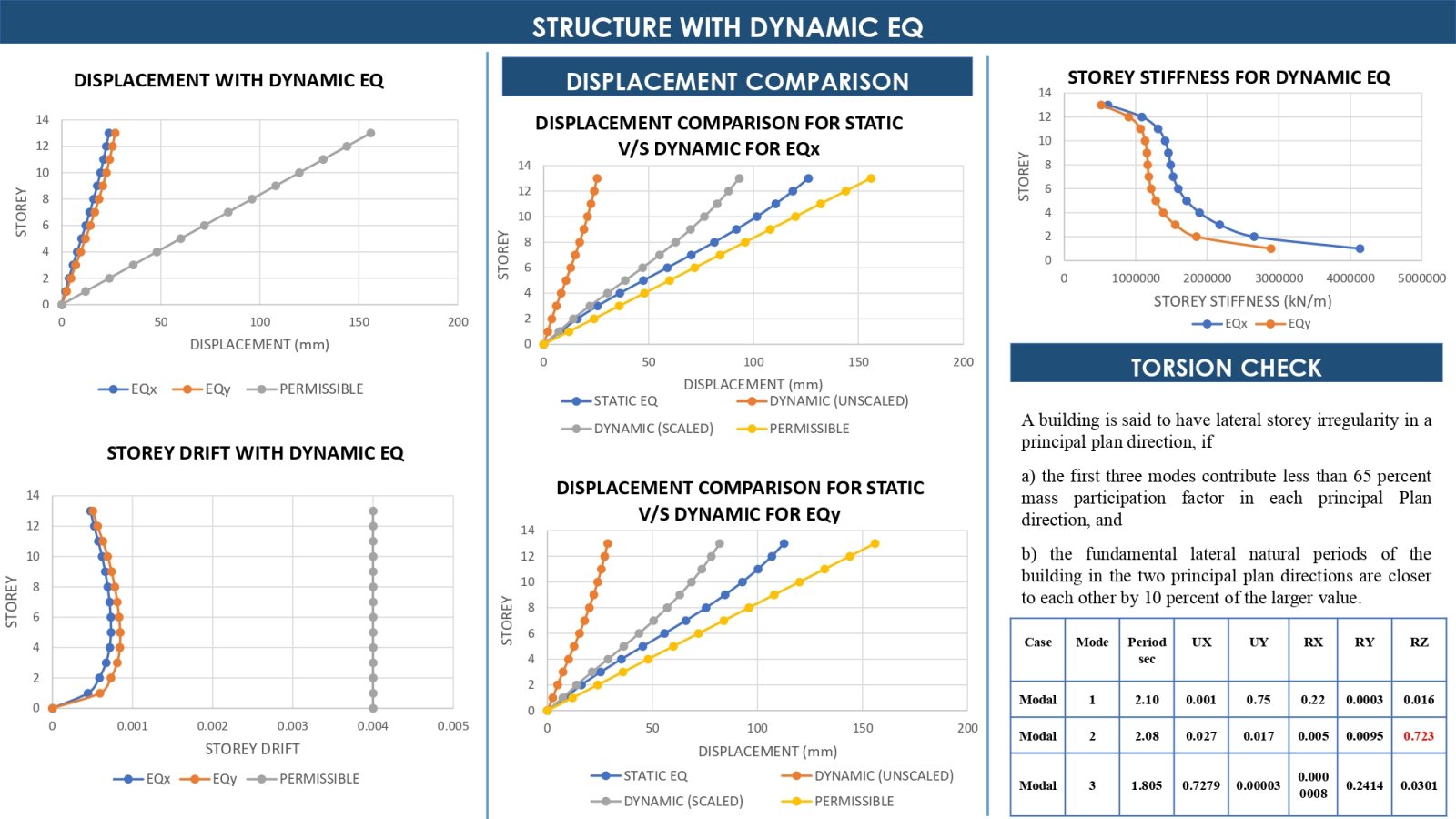
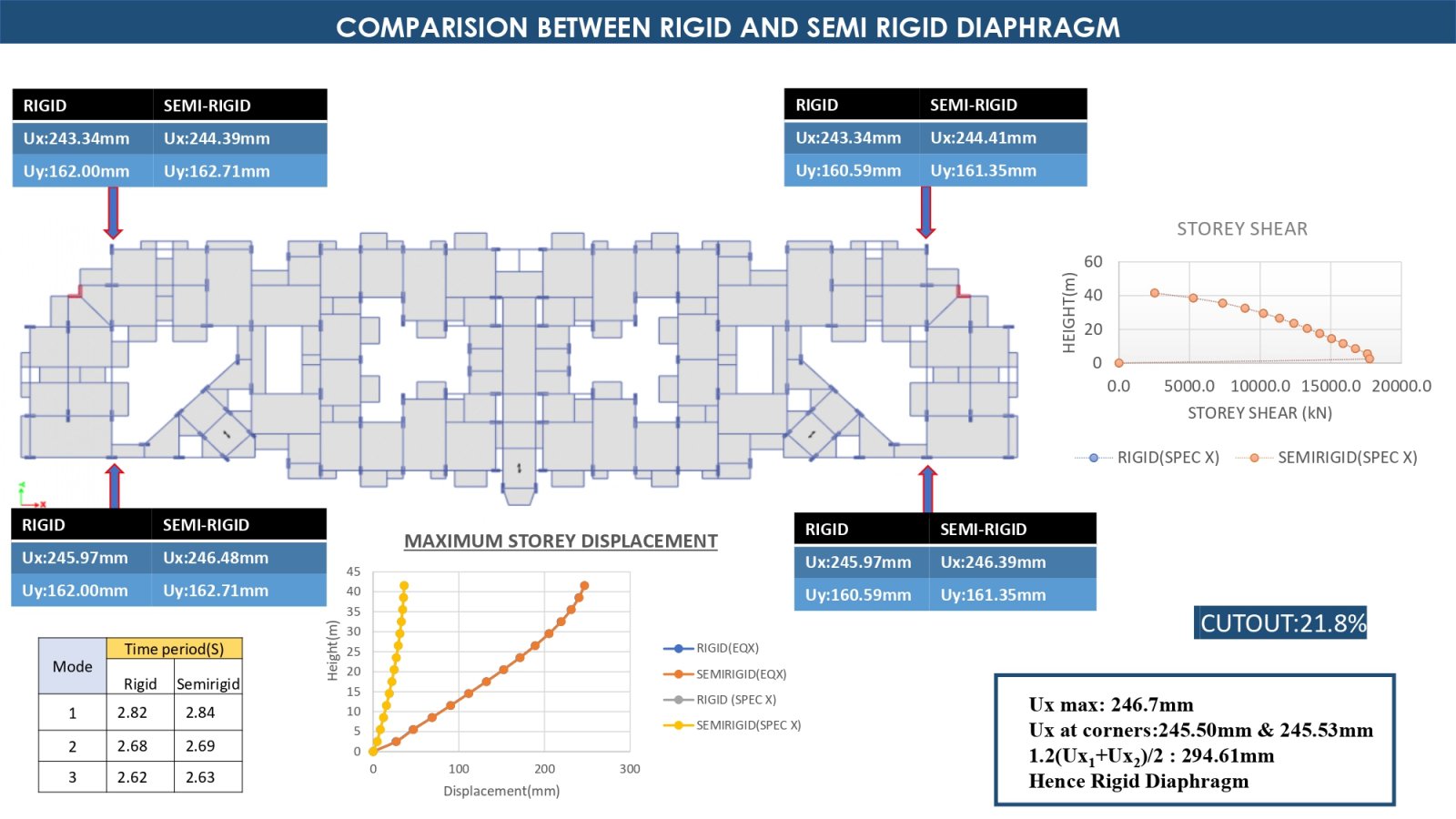
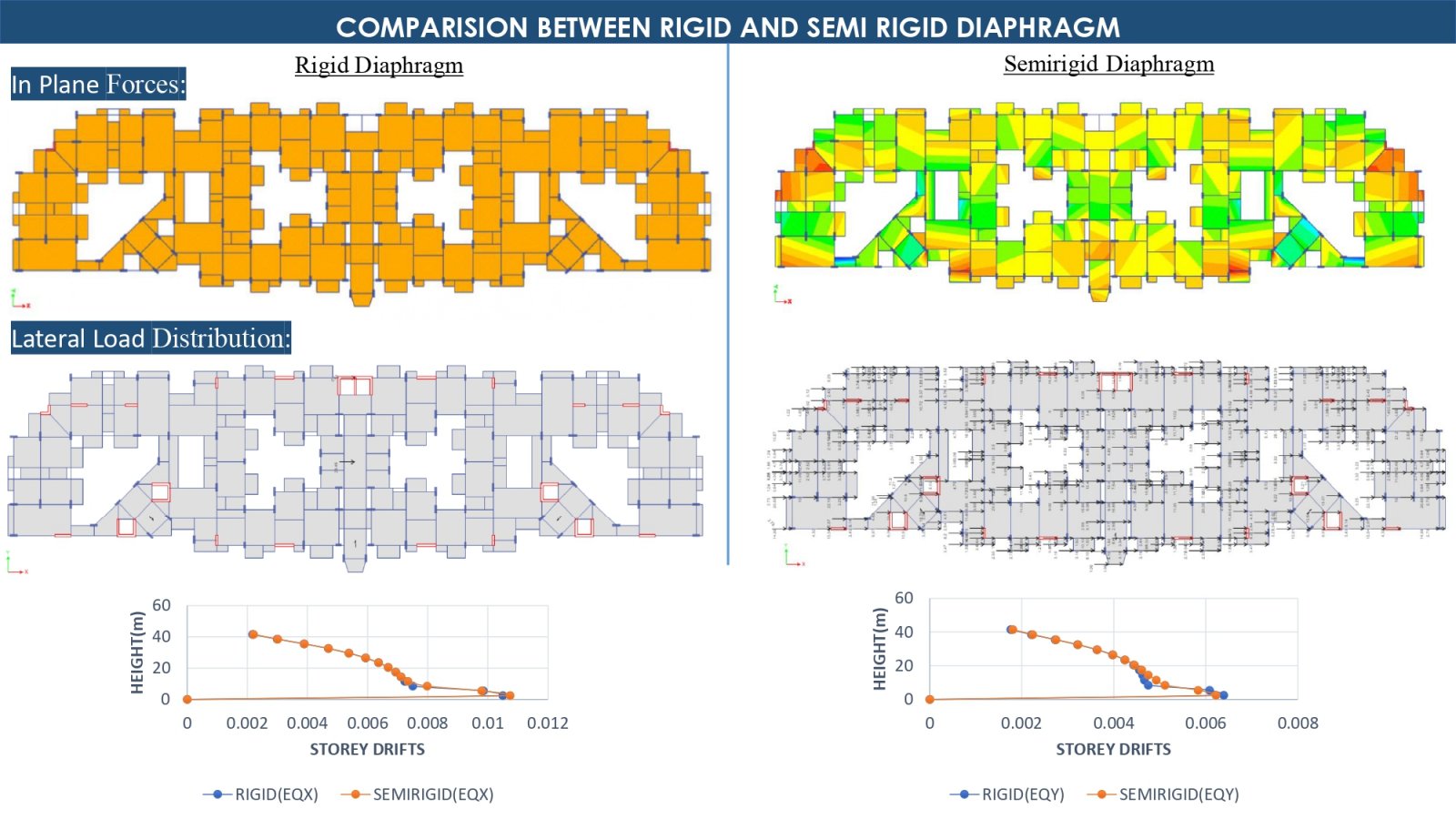
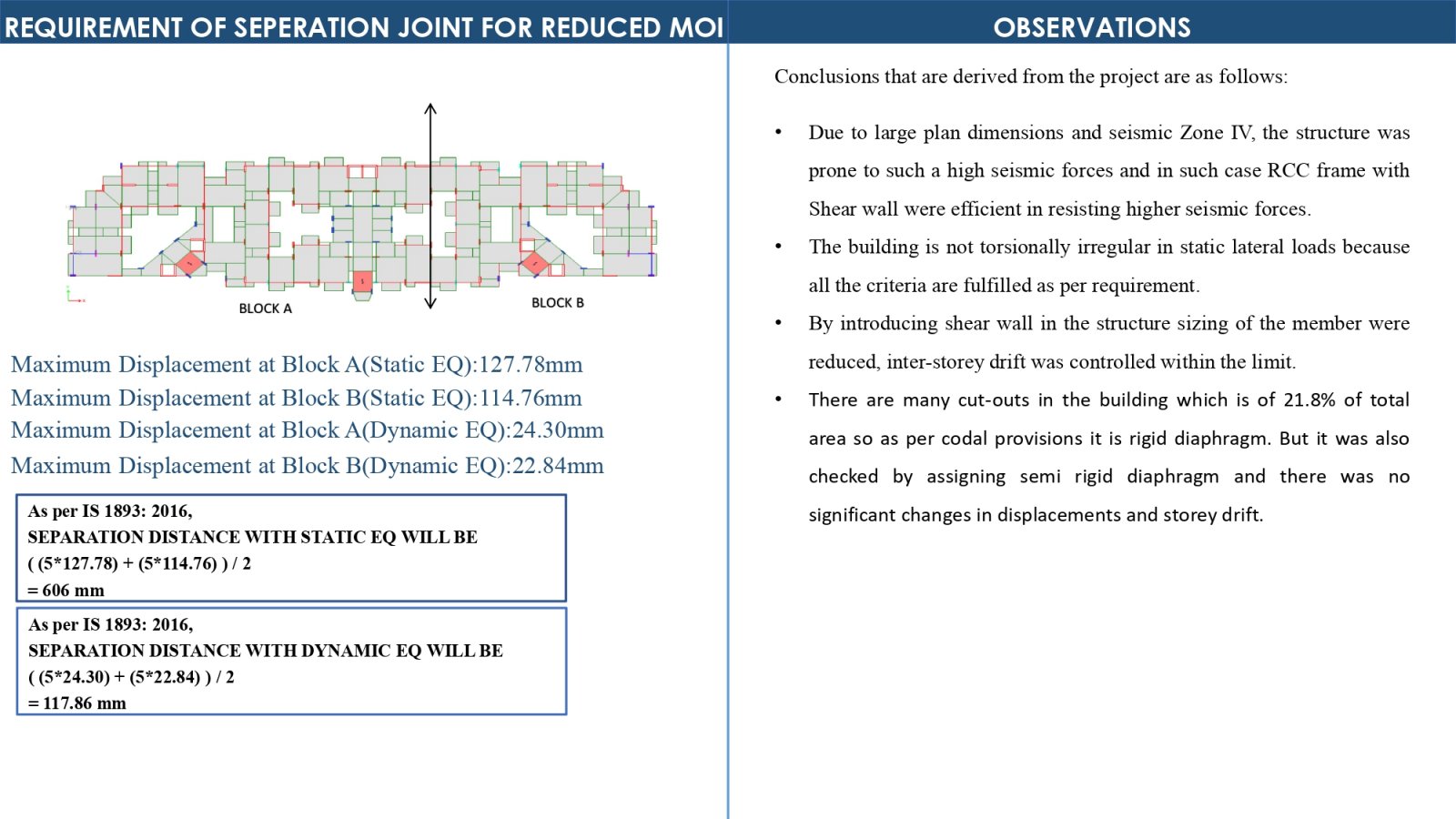
This project investigates the behavior of semi-rigid and rigid diaphragms in a G+12 story Residential building located in seismic Zone-IV, with each floor having a height of 3 meters. The study focuses on how different types of diaphragms distribute seismic forces and the implications of using reduced moment of inertia (MOI) on the structural design, which specifically looking at the requirements for separation joints. By comparing with semi-rigid and rigid diaphragms, the project aims to identify which diaphragm type optimizes building safety and performance under earthquake loading conditions. The outcome will enhance our understanding of diaphragm flexibility's impact on building.