Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
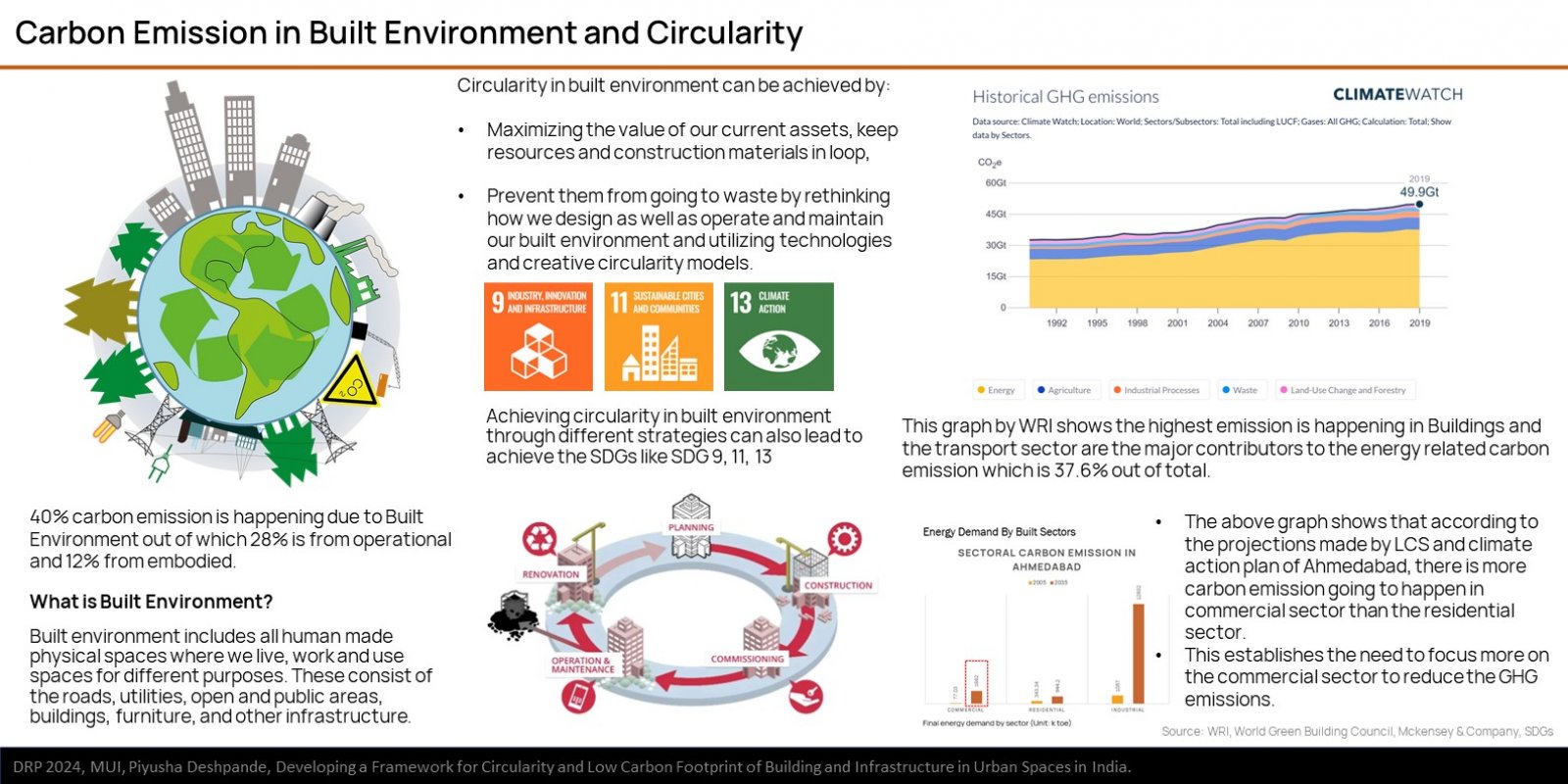
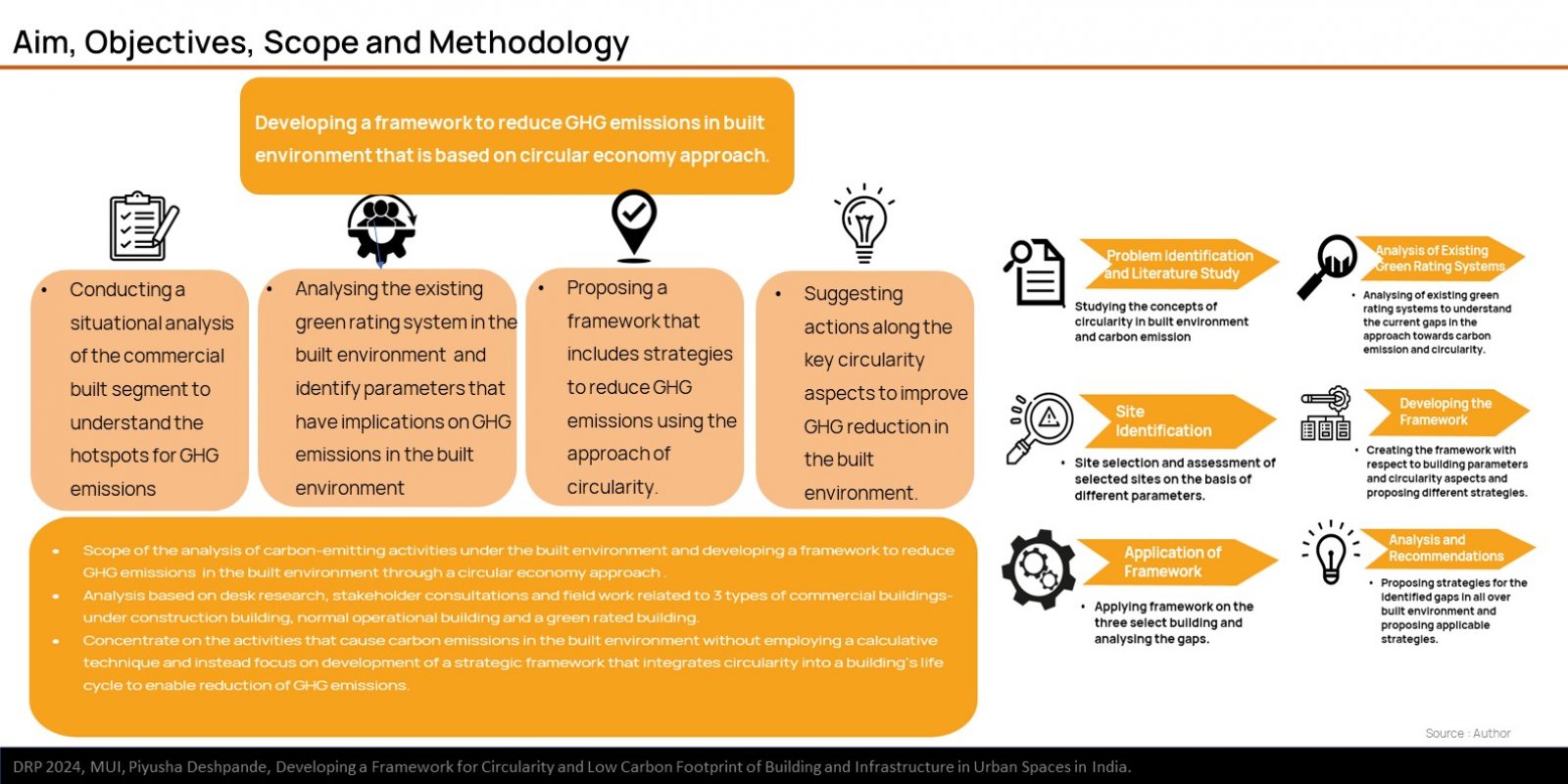
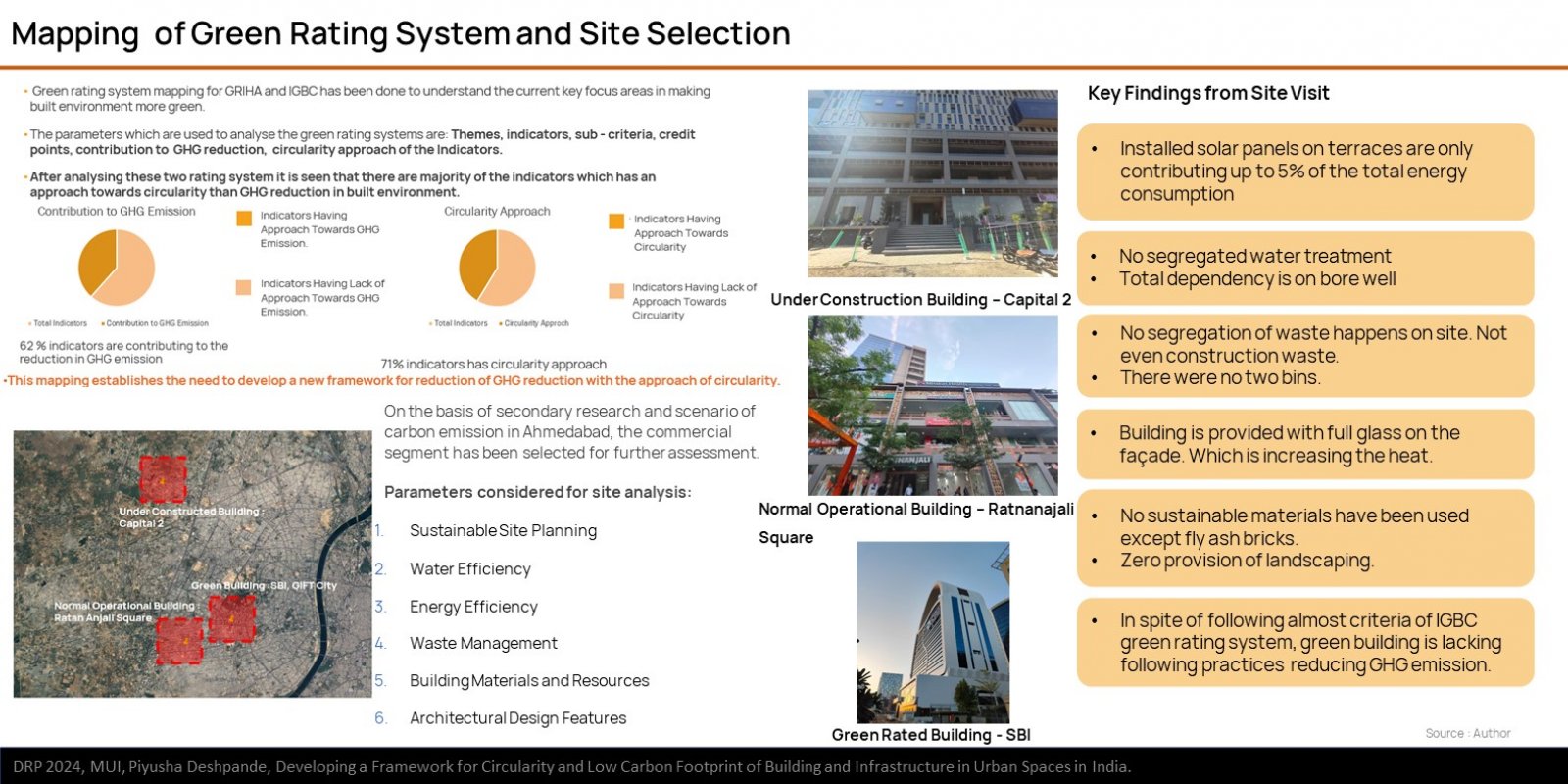
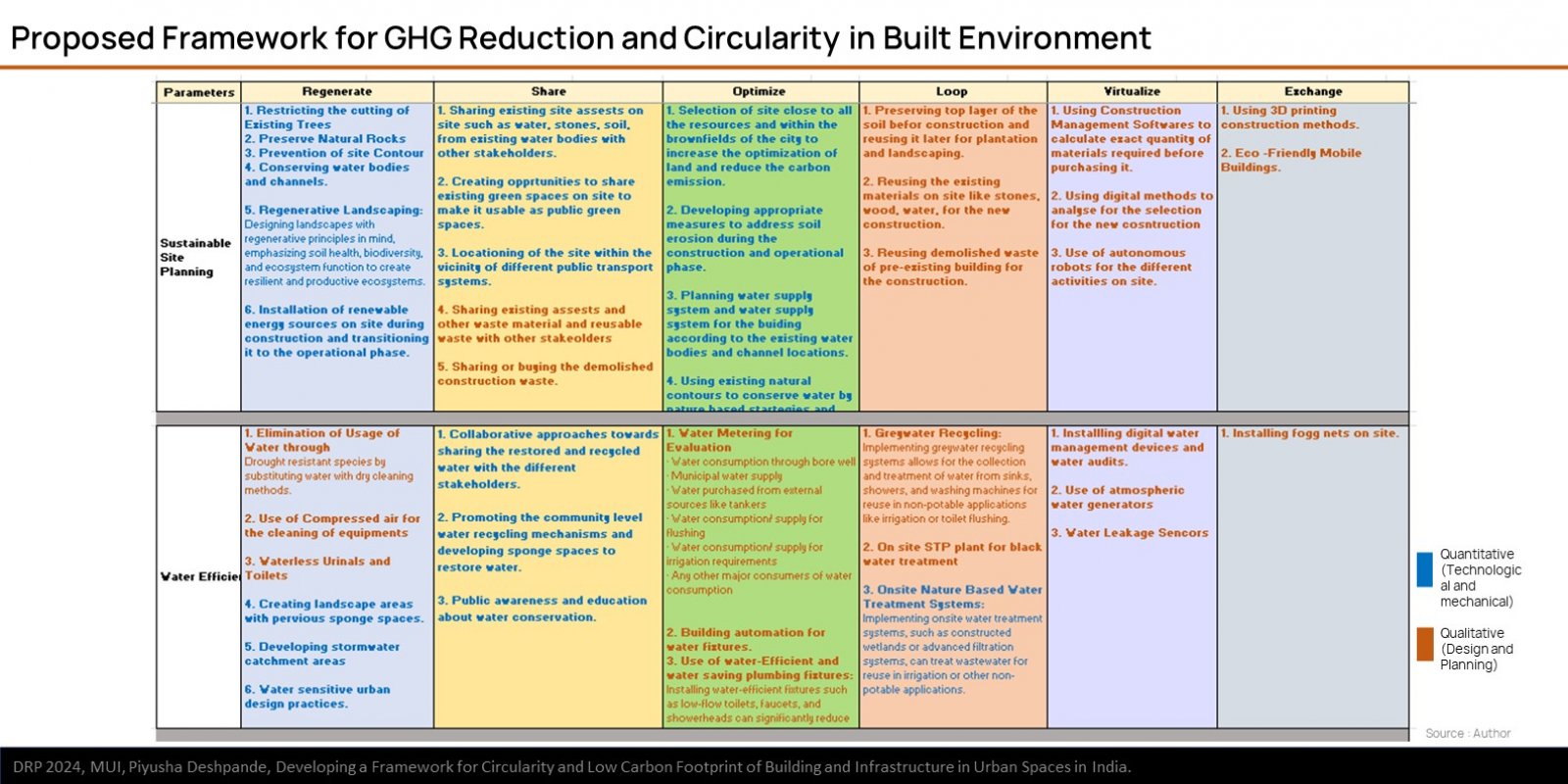
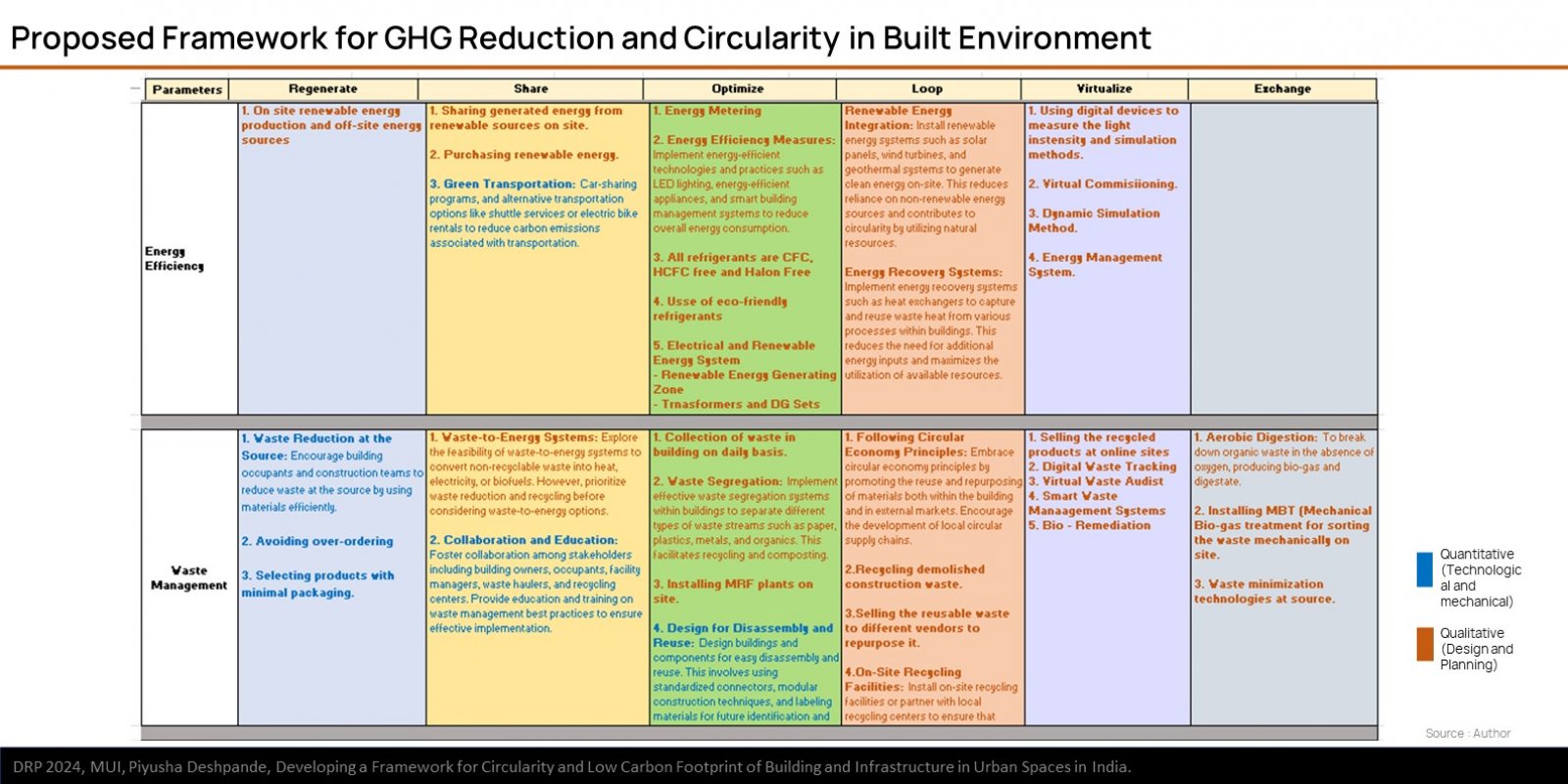
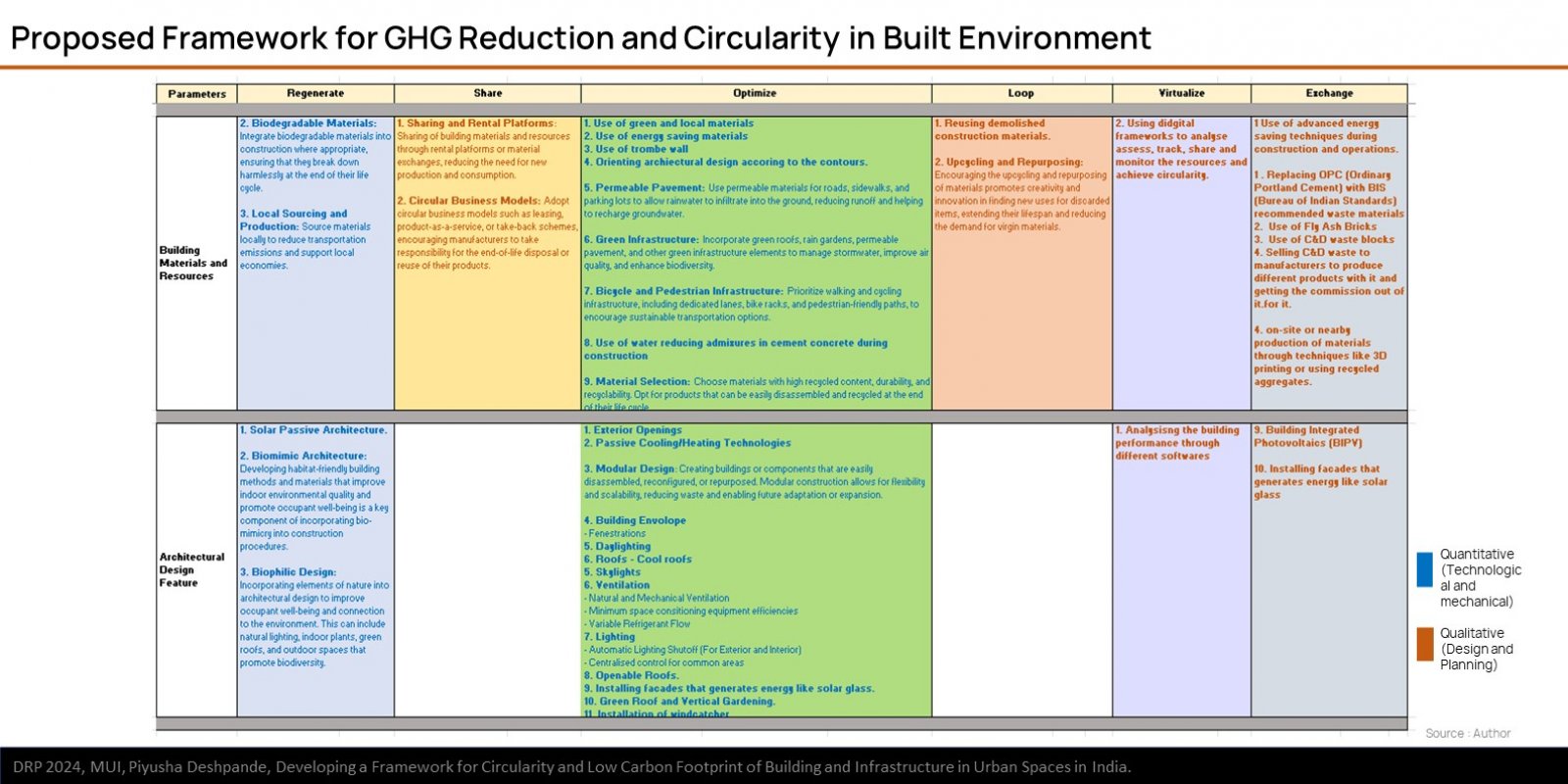
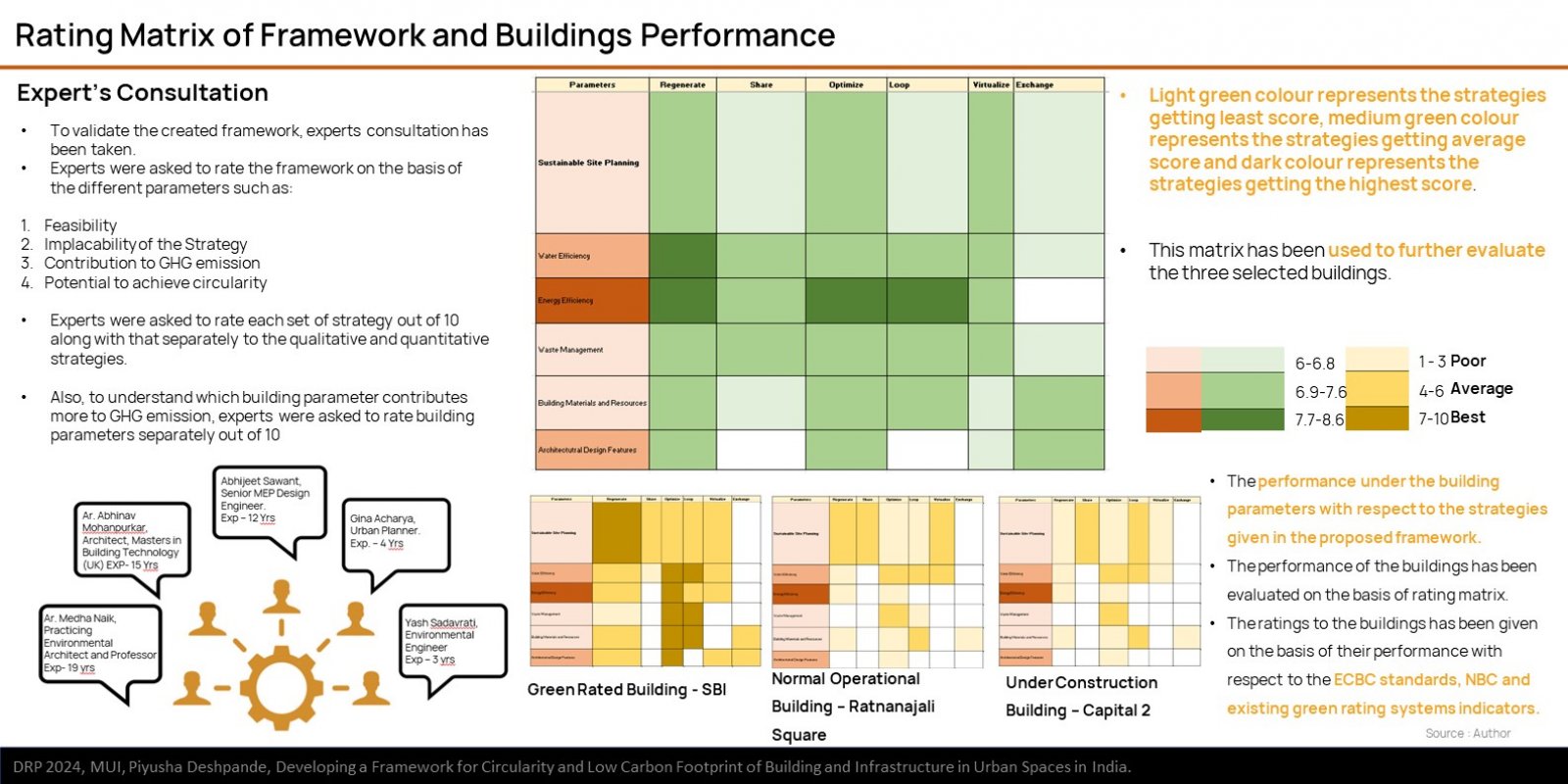
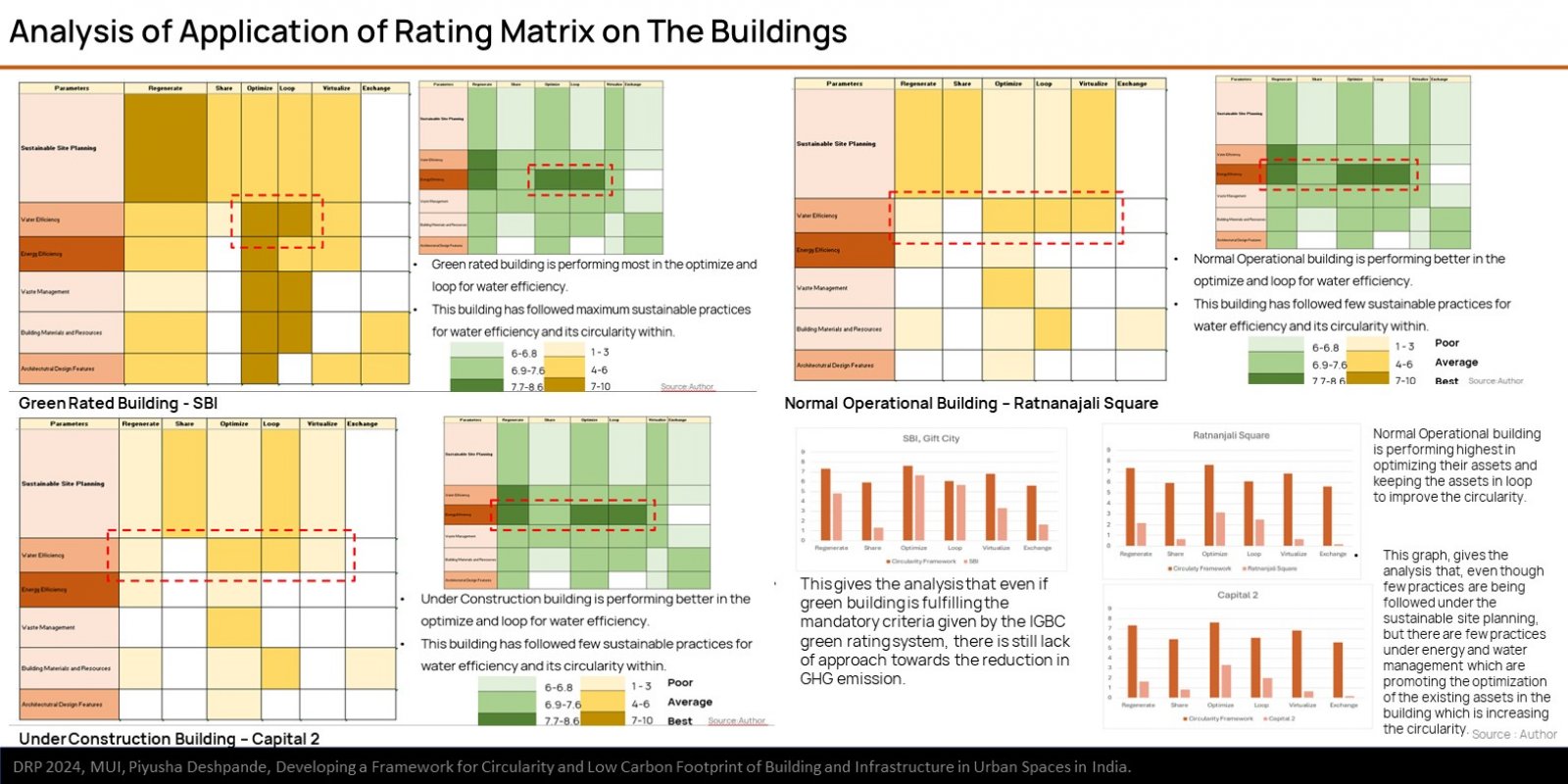
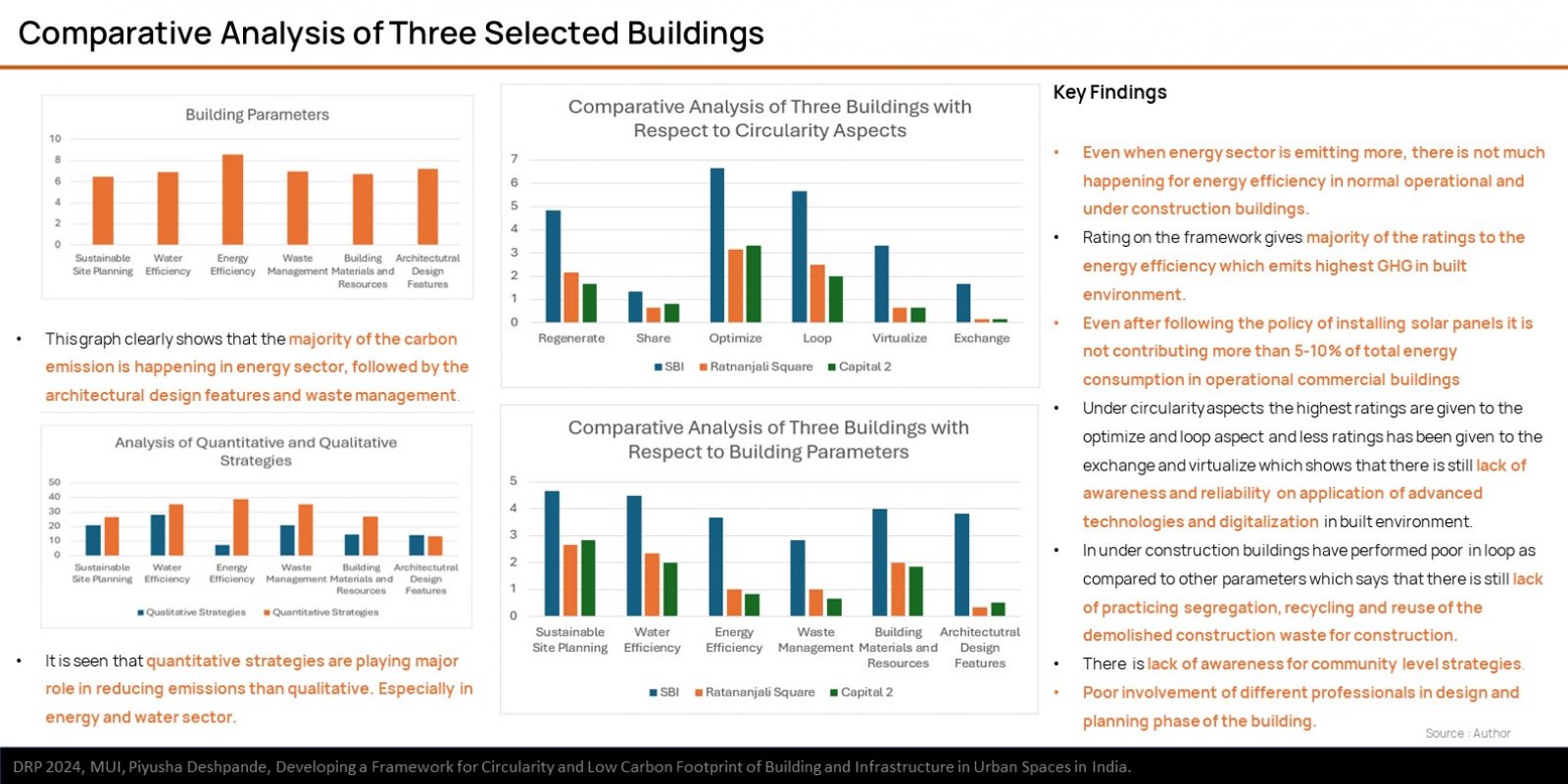
The research explores the challenges and opportunities in reducing GHG emissions in built environment through the approach of circularity. It is based on ReSOLVE Framework, which includes regeneration, sharing, optimization, looping, virtualization, and exchange. The proposed framework was applied to three buildings: green-rated, normal operational, and under-construction. Comparative analysis showed that green-rated buildings performed better in circularity but not significantly in reducing GHG emissions. Whereas, the normal operational building and the under-construction building exhibited poor performance in both circularity and emission reduction. It also emphasizes the importance of implementing strategies across all building life cycle phases to achieve a sustainable, and regenerative built environment. The framework provides a practical pathway for stakeholders to improve building performance.