Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
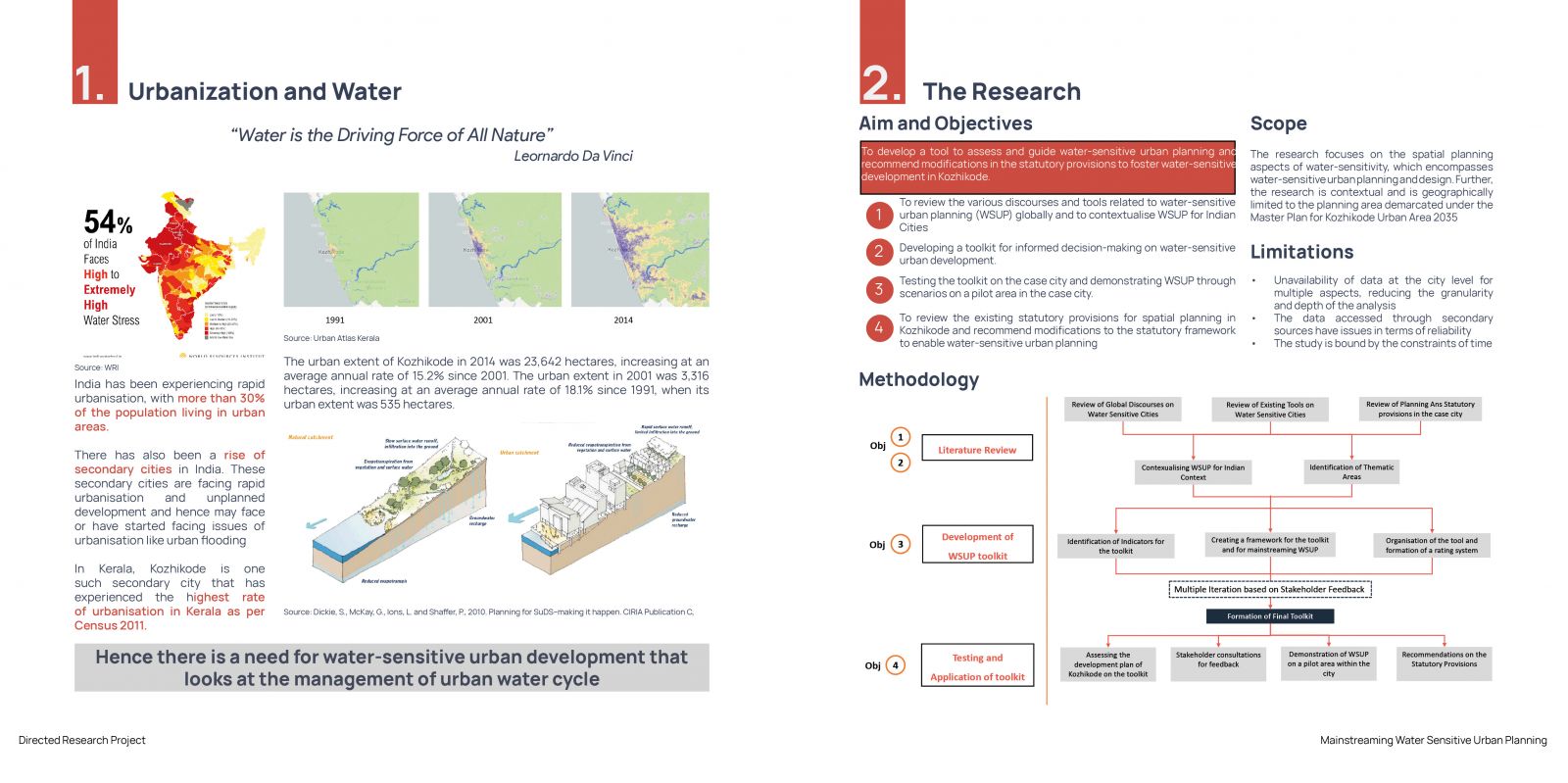
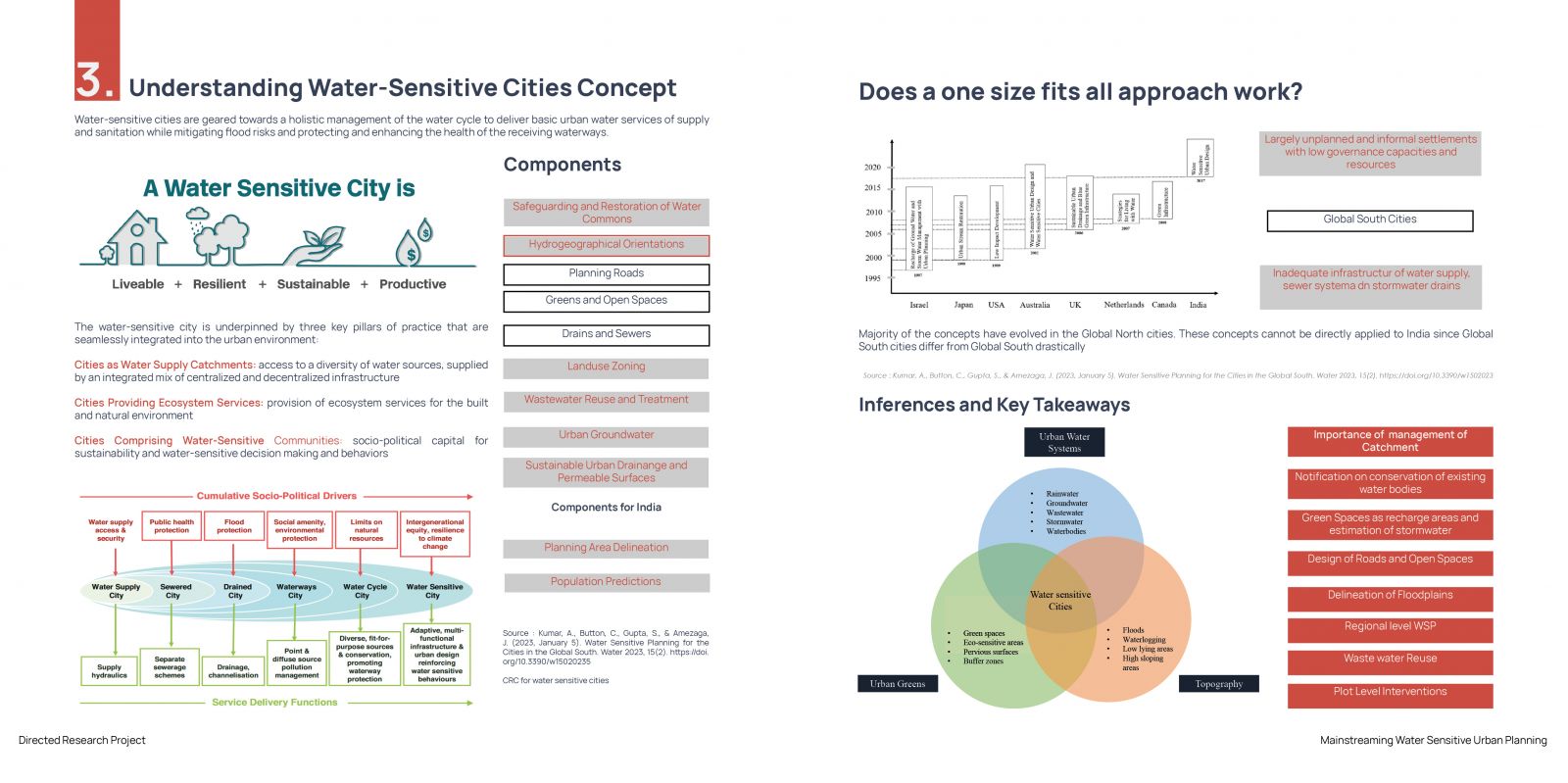
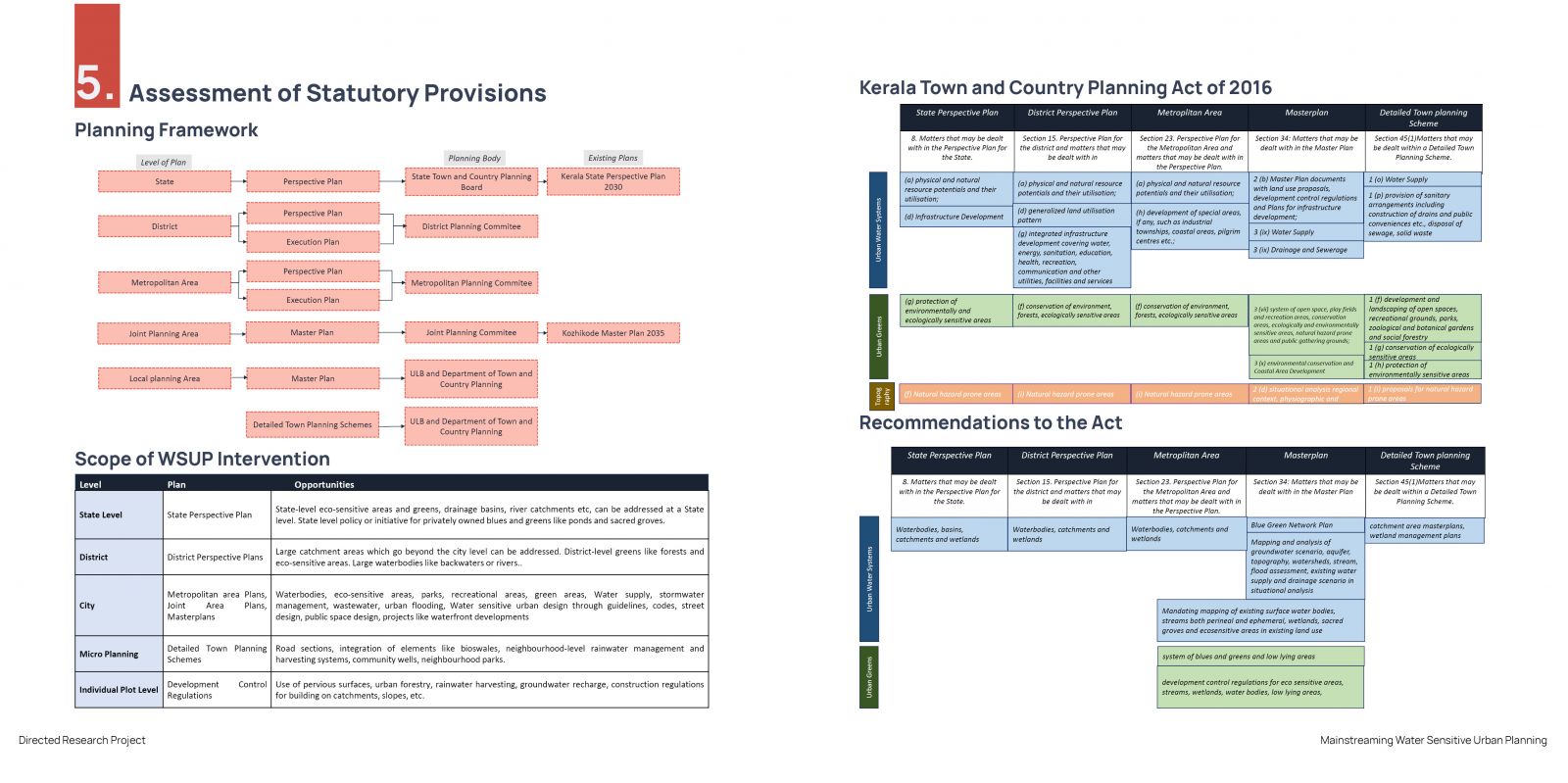
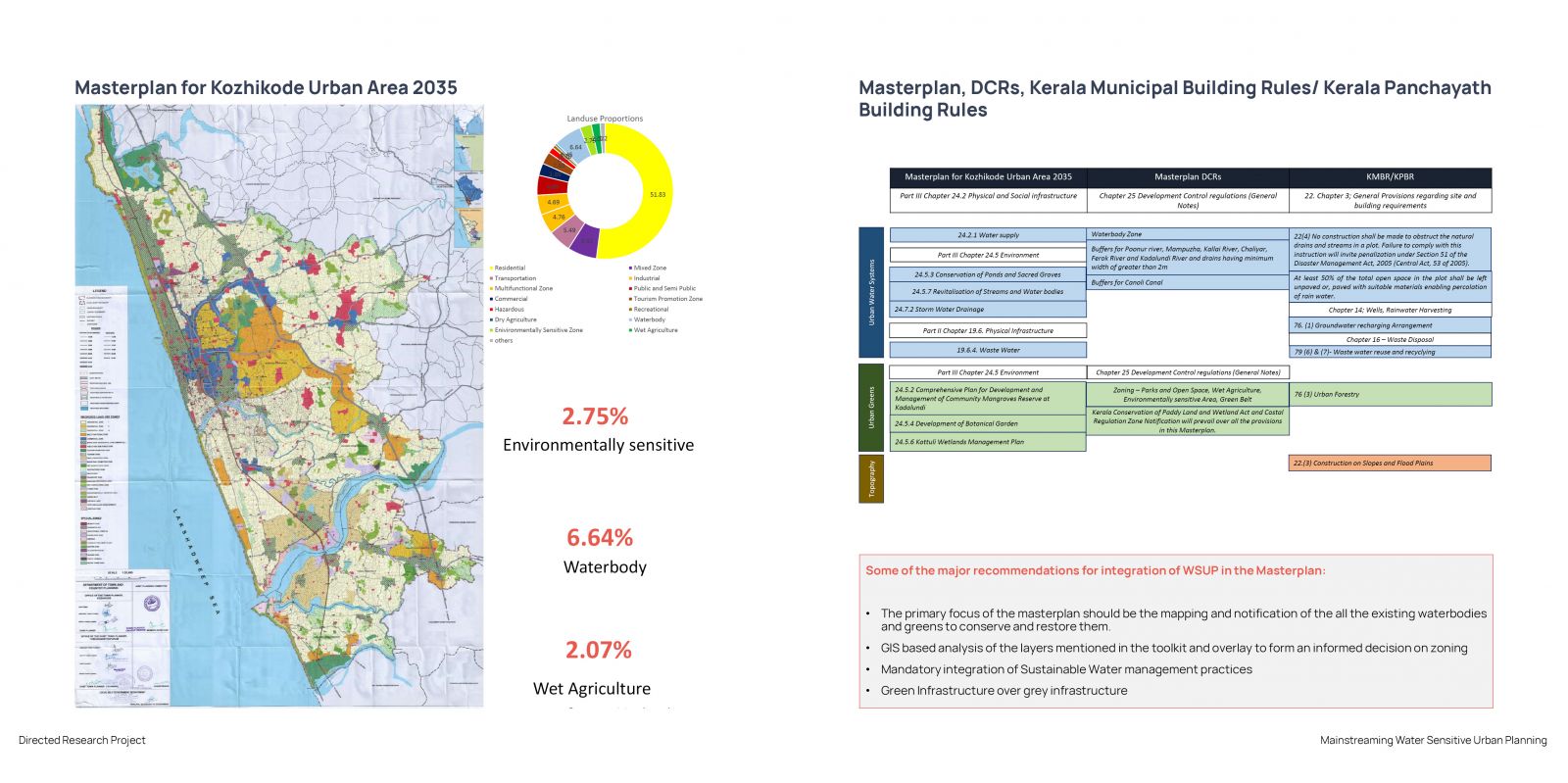
India is undergoing rapid urbanization, with over 30% of the population residing in urban areas. A significant portion of this urban population lives in emerging small cities, towns, and census towns, which are becoming new growth centers. While large cities are grappling with the impacts of climate change, such as urban flooding and water scarcity, these smaller urban centers are experiencing unplanned development, leading to potential water-related challenges in the future. Kozhikode, as a secondary city, is urbanizing rapidly and is likely to face such challenges. The increase in built-up areas and the use of impervious surfaces disrupt the natural water flow, leading to issues like urban flooding and water shortages. Hence, there is a critical need for cities to adopt water-sensitive approaches. Water-sensitive cities prioritize water bodies, address water challenges, and ensure the natural water cycle is preserved. One of the key challenges in achieving water sensitivity is the lack of frameworks and tools to guide decision-making in urban planning. This research aims to develop a visualization tool focusing on water-sensitive urban planning, specifically tailored to Kozhikode, and to propose adjustments to statutory provisions to facilitate the development of context-specific water-sensitive strategies.