Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
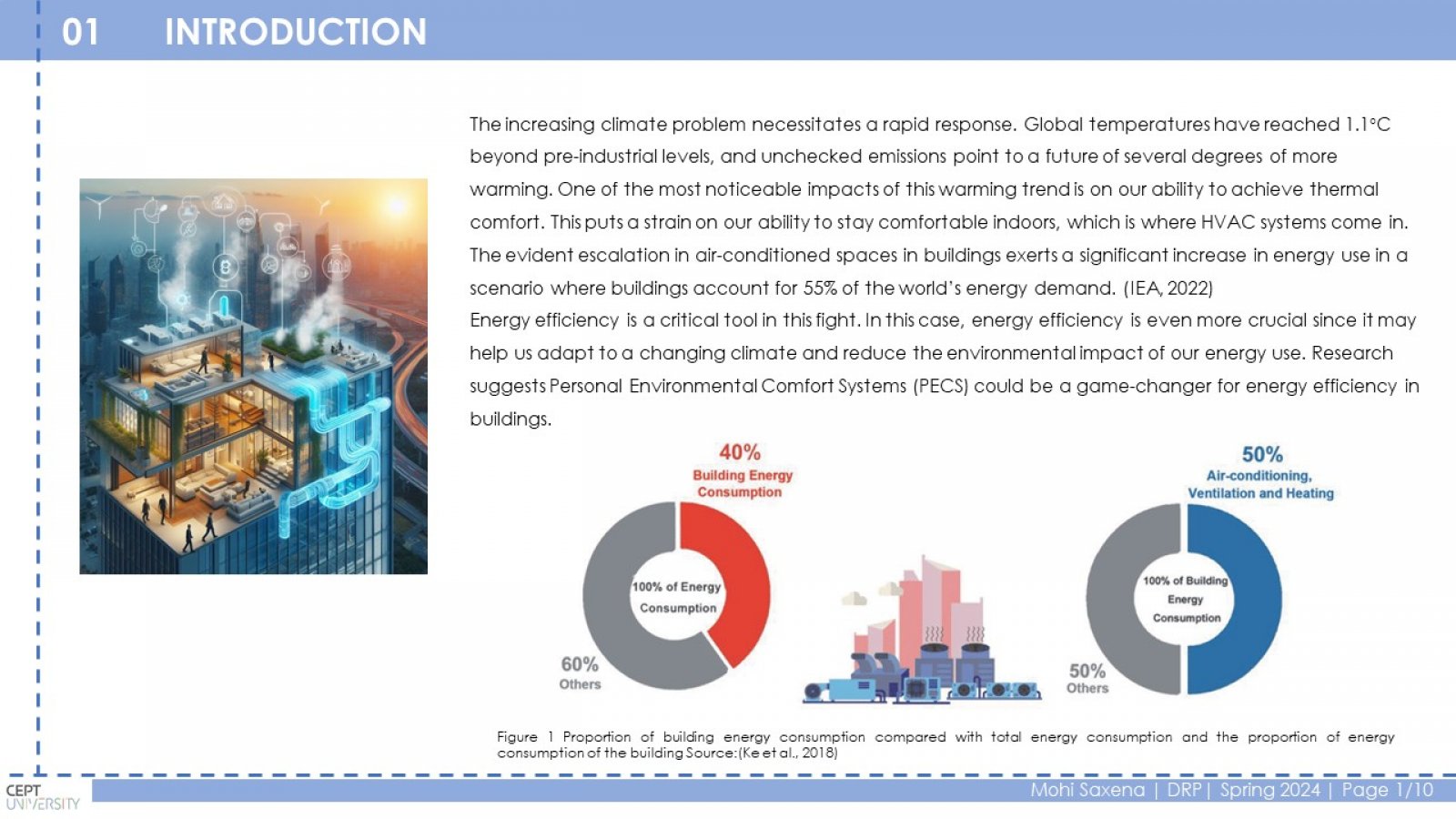
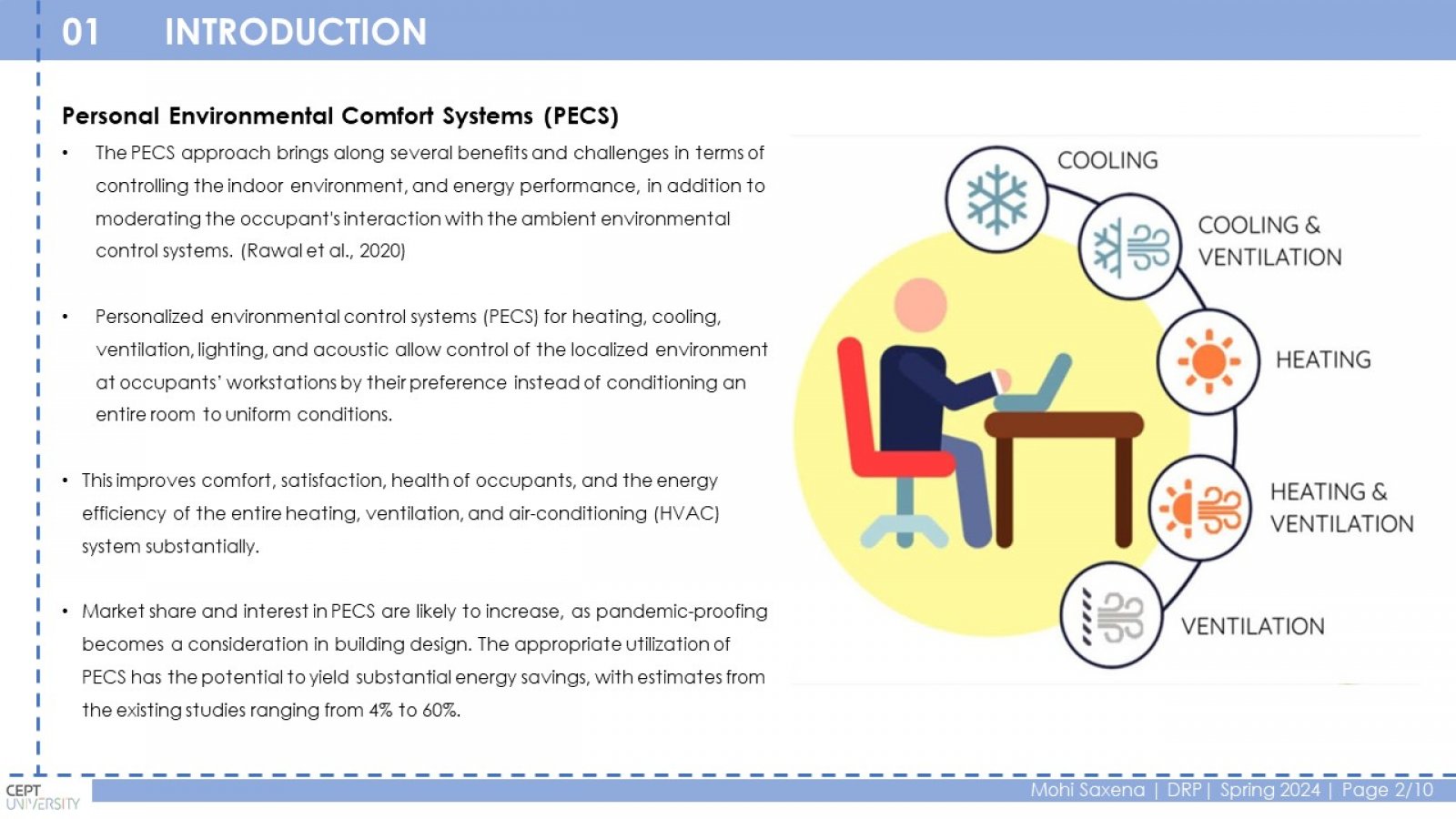
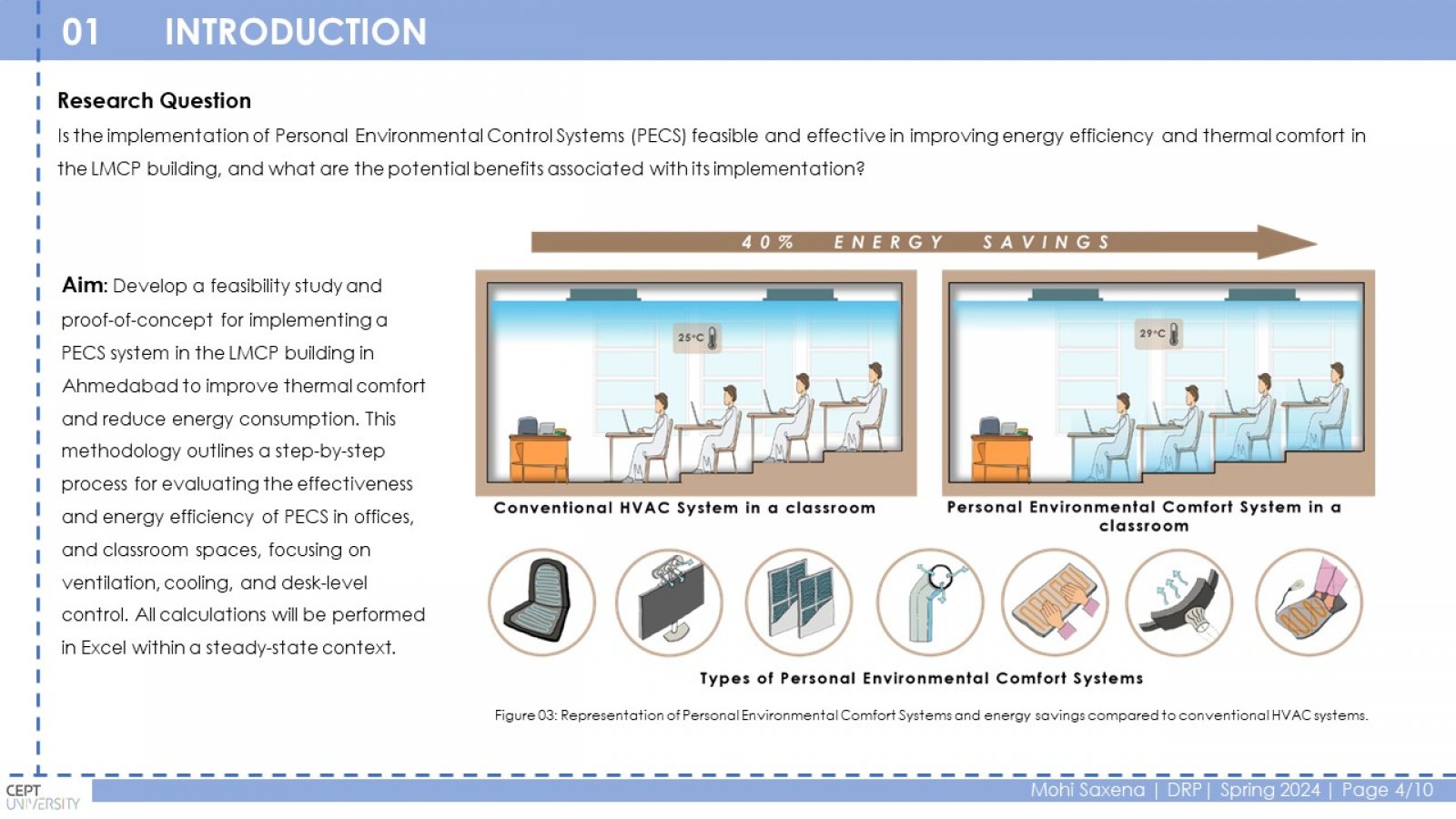
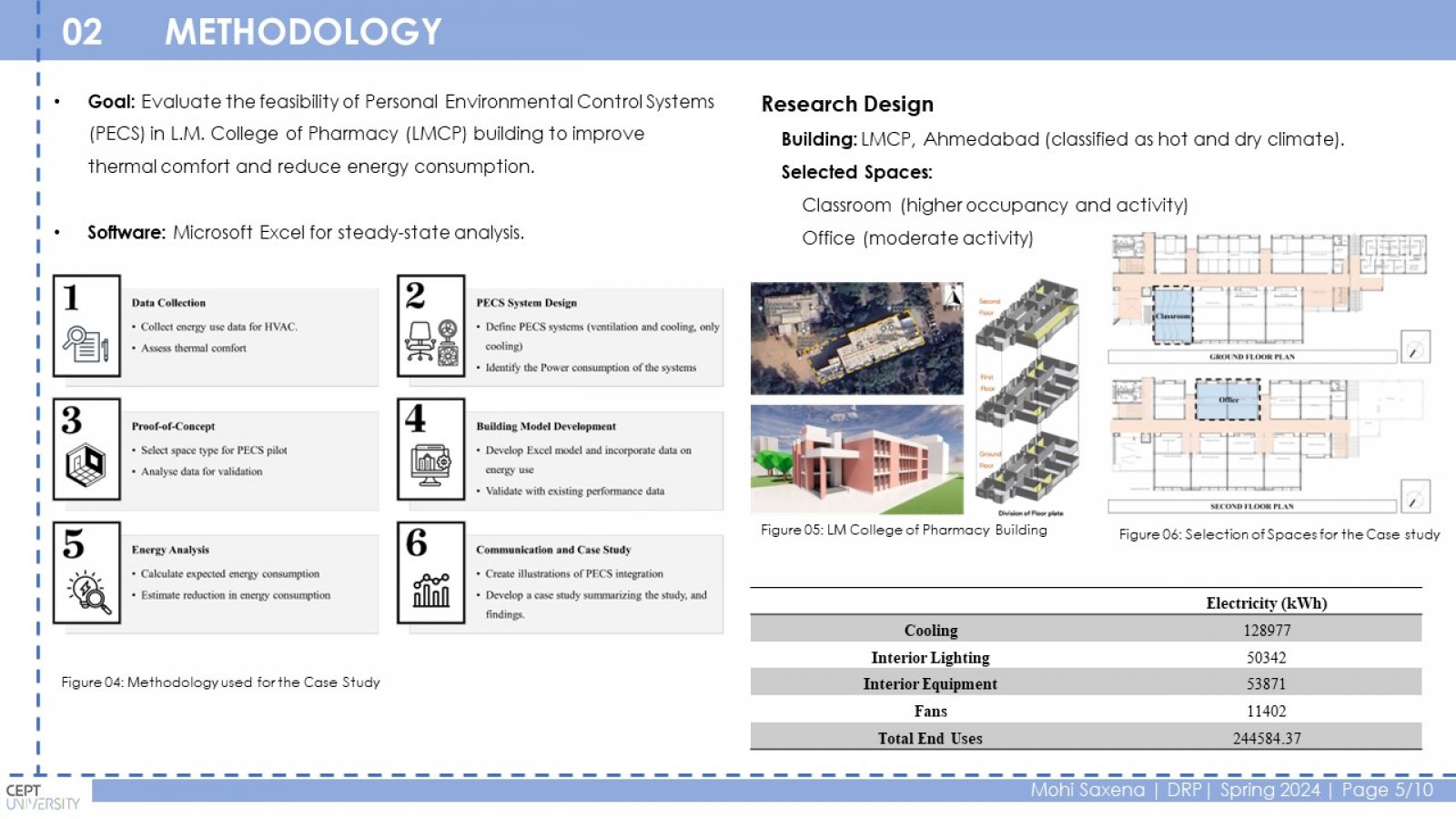
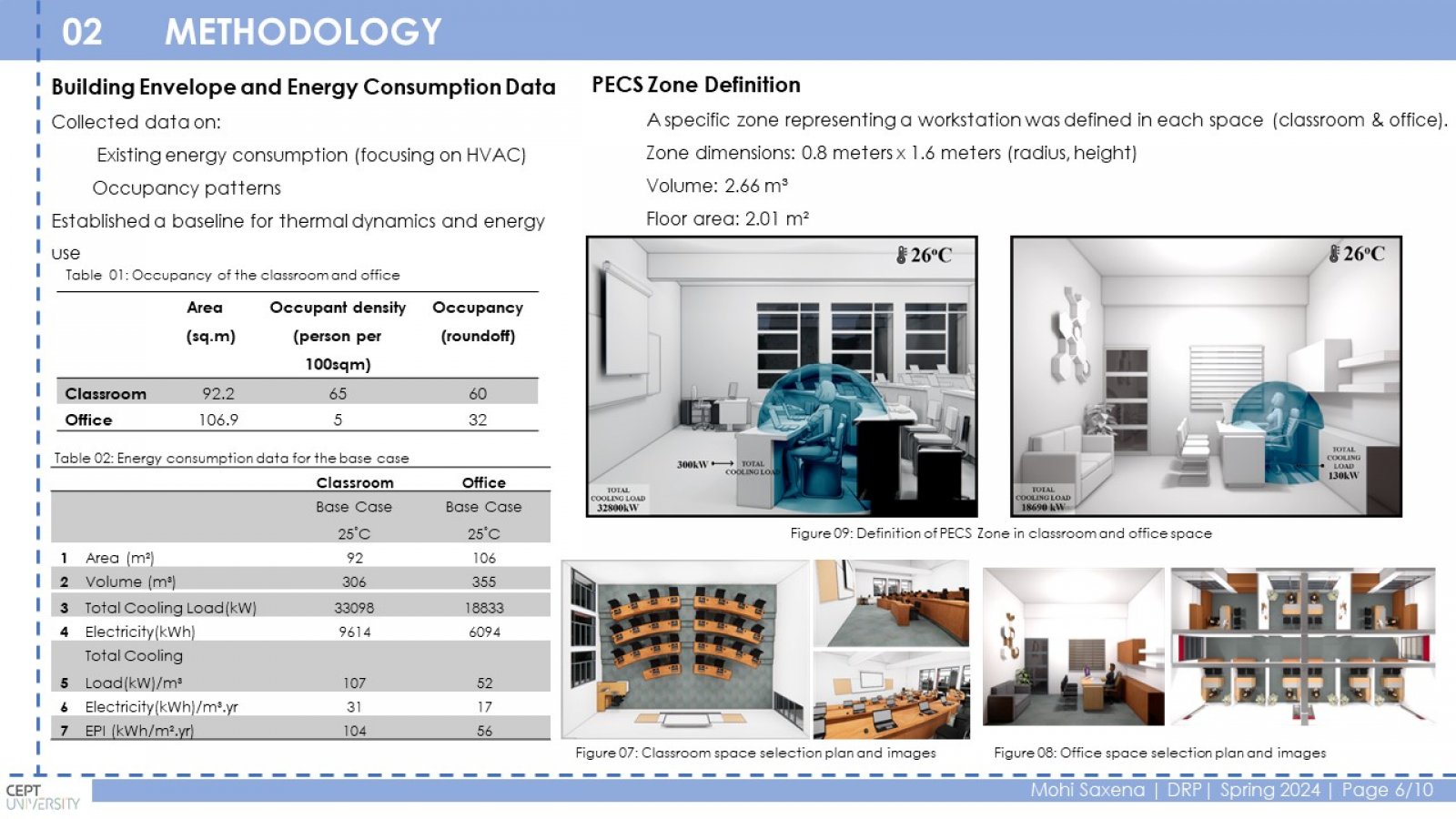
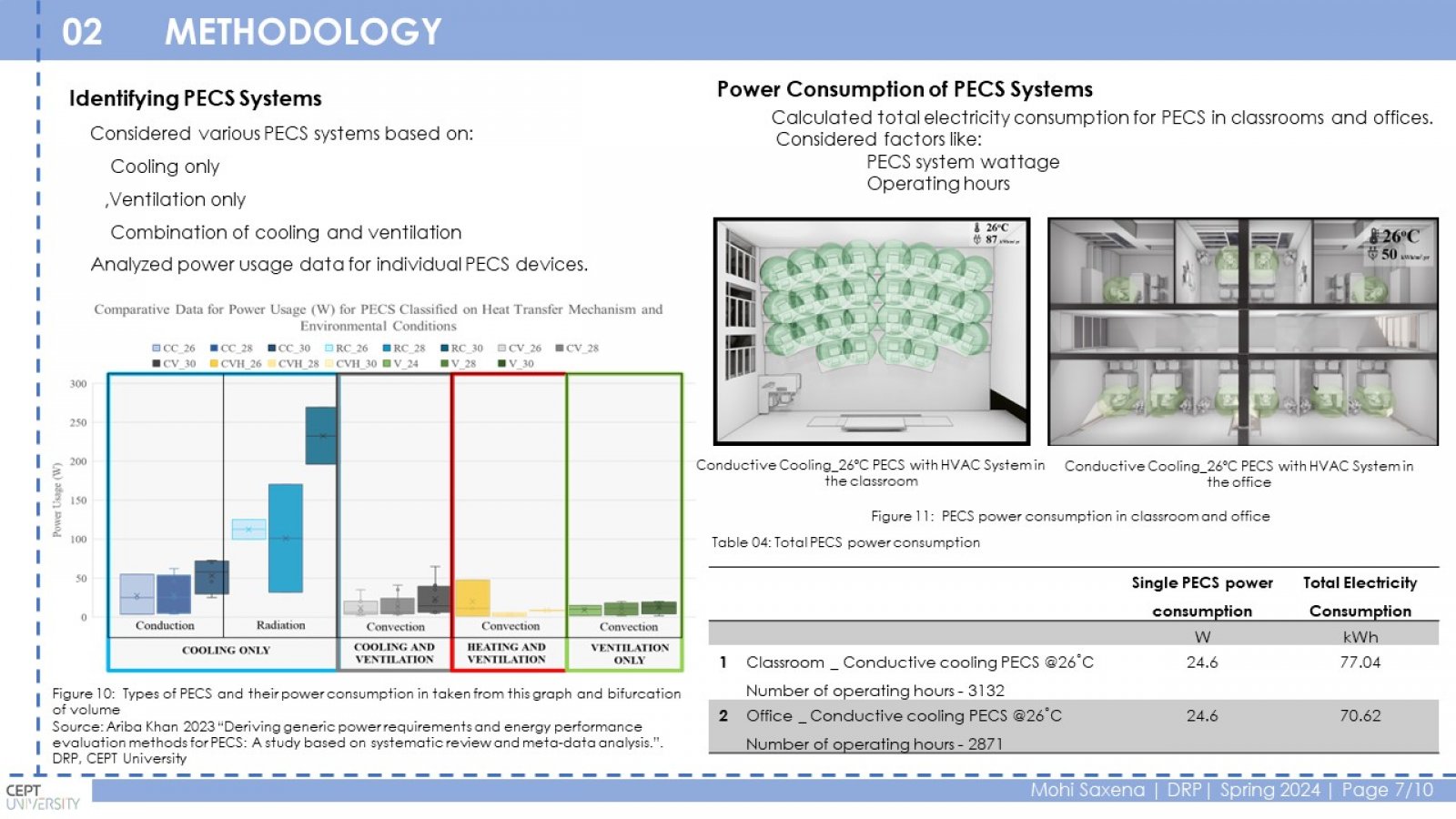
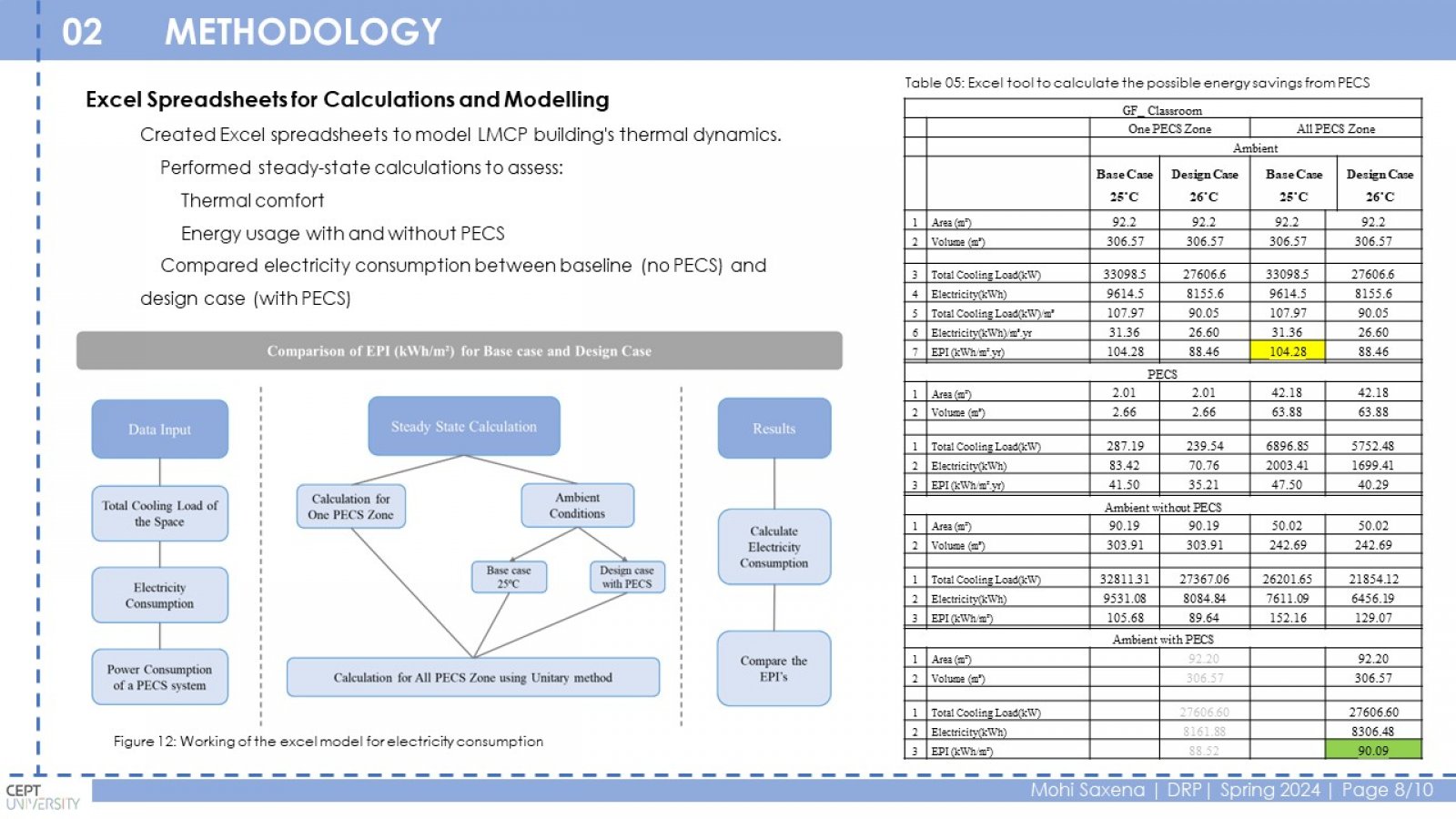
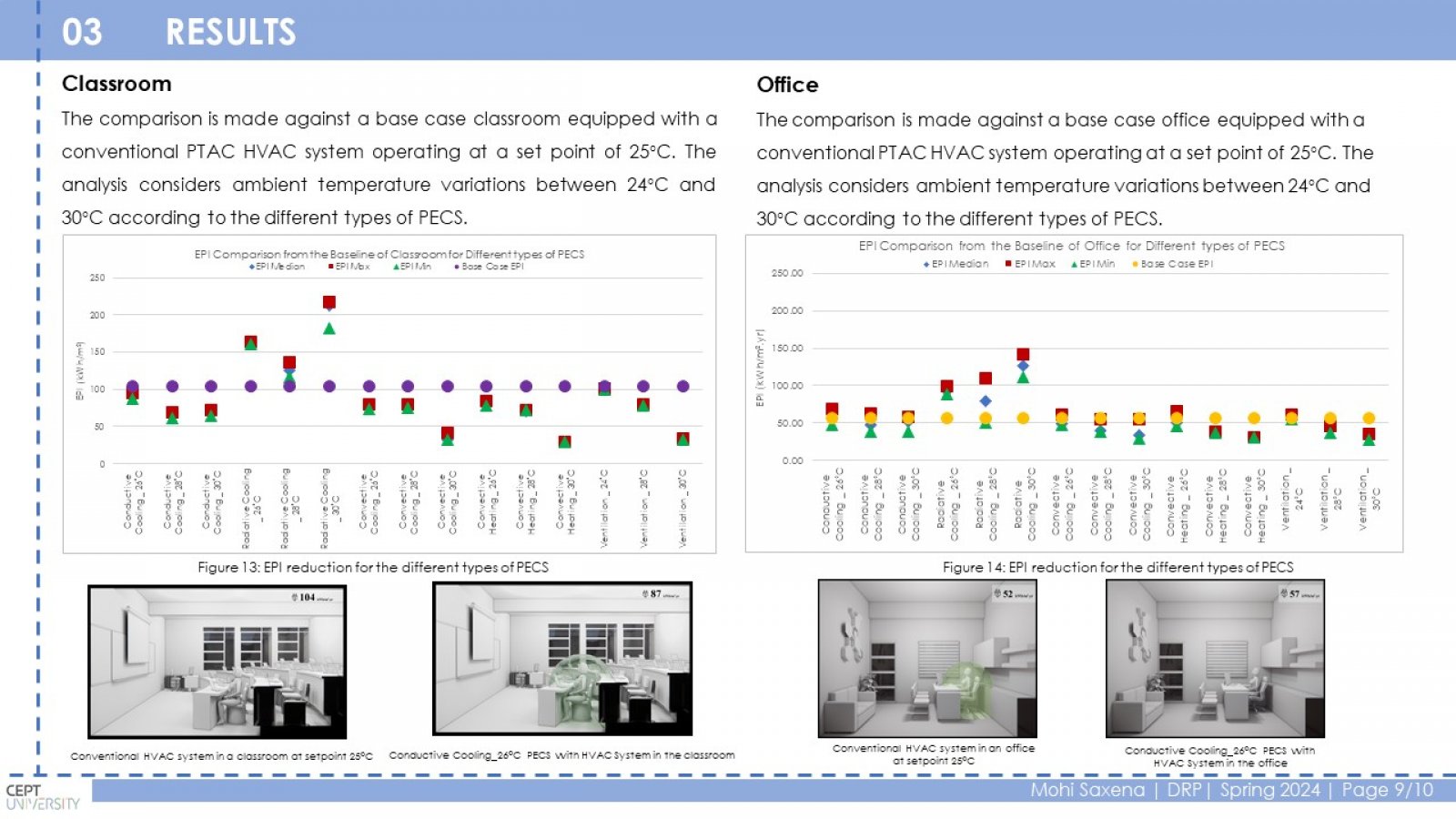
Conventional HVAC systems use a lot of energy to maintain a comfortable temperature throughout a building. This is inefficient because some occupants may prefer a warmer or cooler environment. PECS can improve comfort and potentially save energy by targeting only the occupied zones. This study investigates the relationship between PECS, thermal comfort, and energy efficiency in educational buildings. The research focuses on a case study of the LM College of Pharmacy (LMCP) building in Ahmedabad, India. Classrooms and offices were chosen as representative spaces. Different PECS options were analyzed using a spreadsheet tool to estimate energy consumption with and without PECS. The study found that PECS can significantly reduce energy consumption in classrooms (2% to 72%) and offices (1% to 50%) depending on the PECS type and ambient temperature. Conduction cooling, convective cooling, and convective heating PECS were the most effective in classrooms, achieving a range of 10% to 69% reduction in the Energy Performance Index (EPI). Ventilation PECS showed the most significant impact in offices, with a 4% to 52% EPI reduction. PECS can improve thermal comfort by providing personalized control and reducing energy consumption in educational buildings.