Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
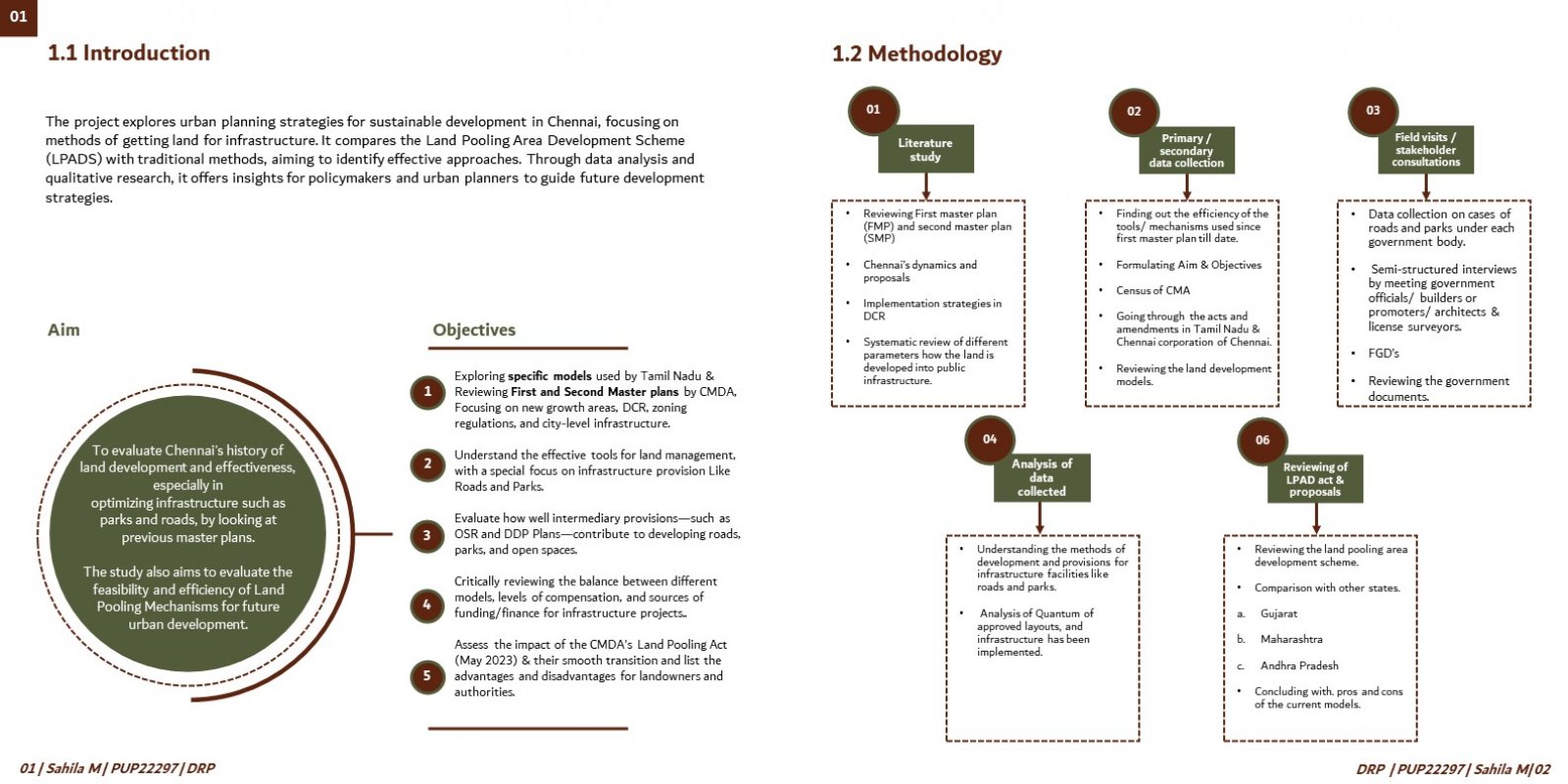
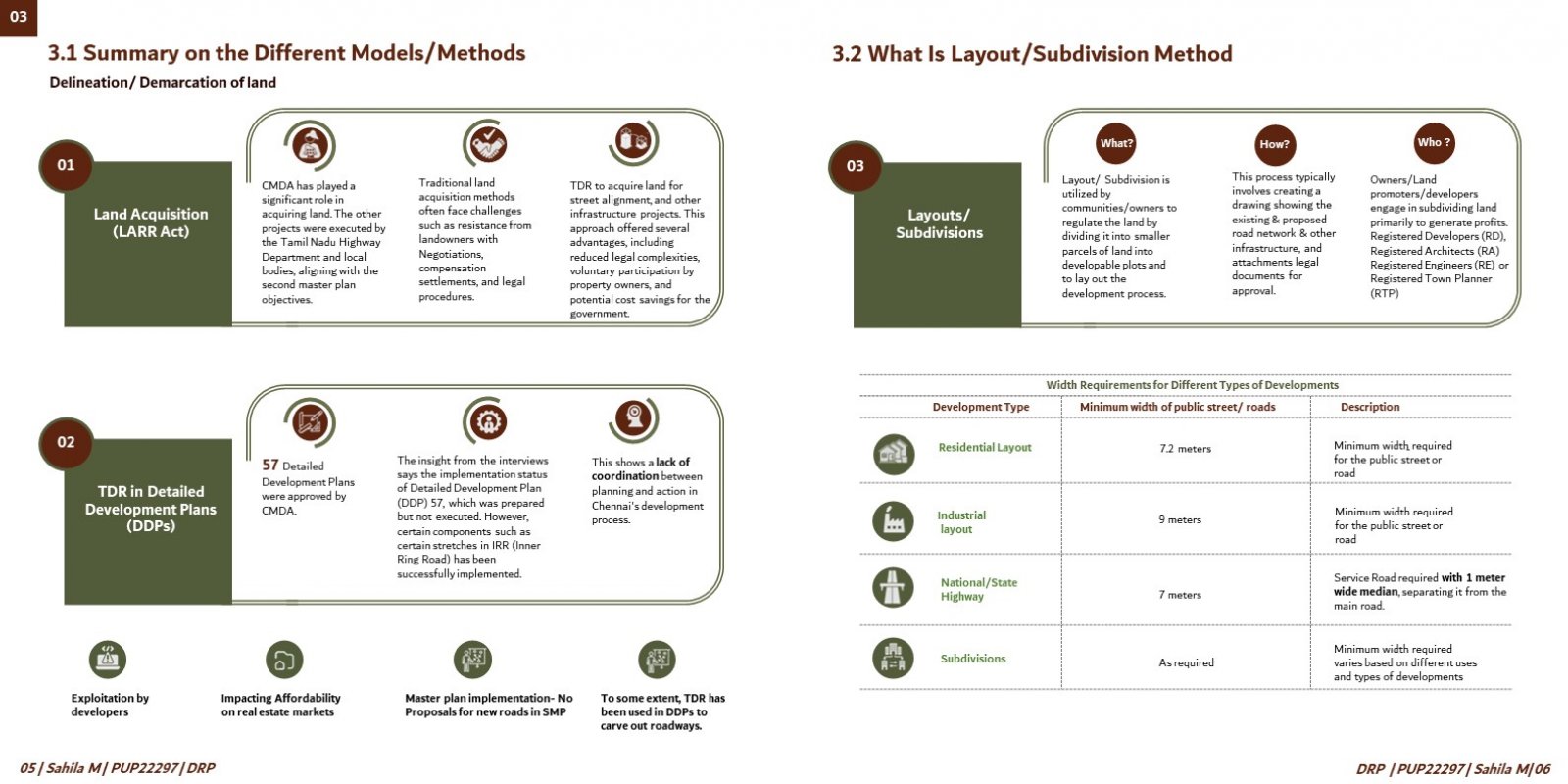
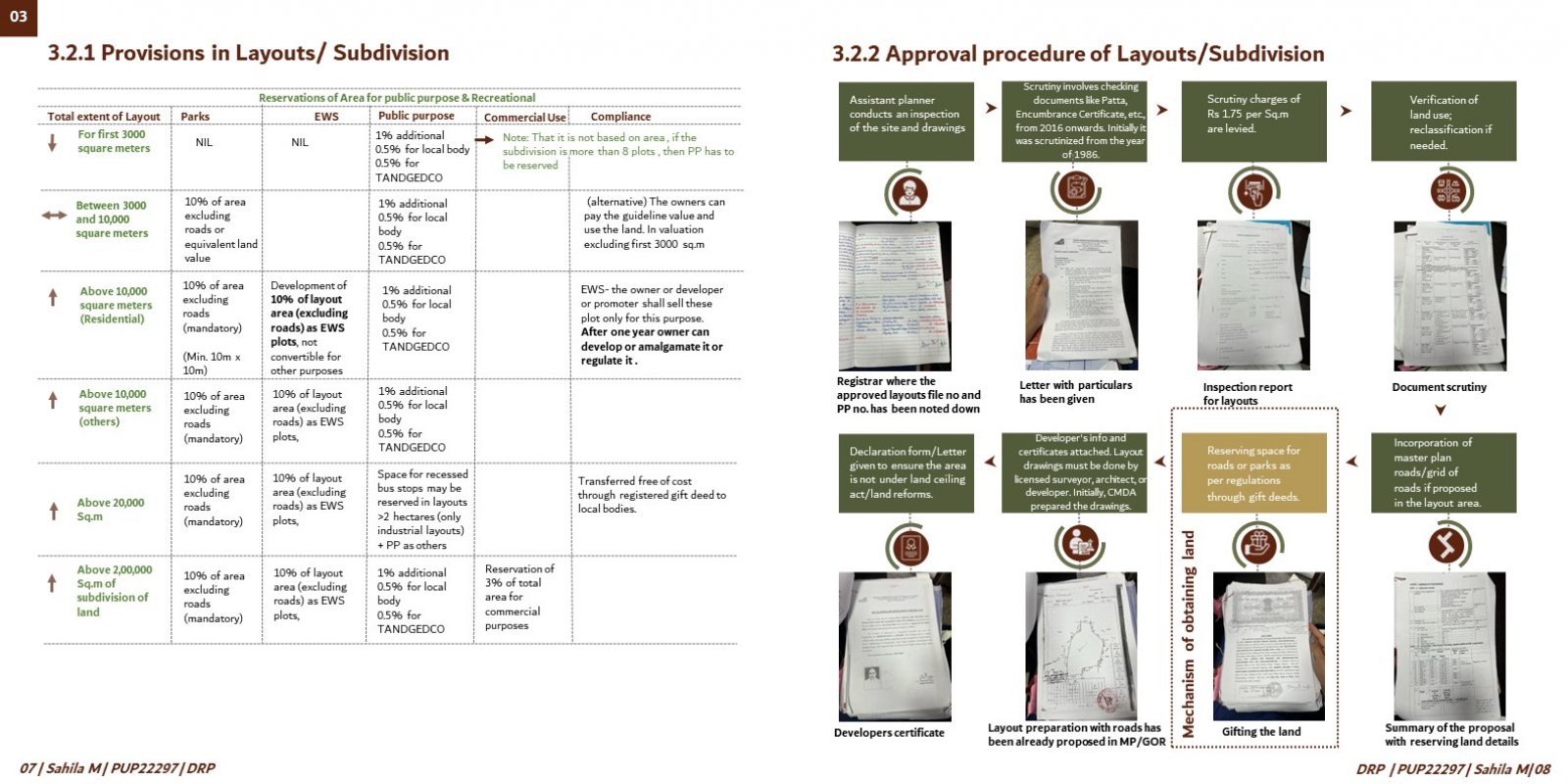
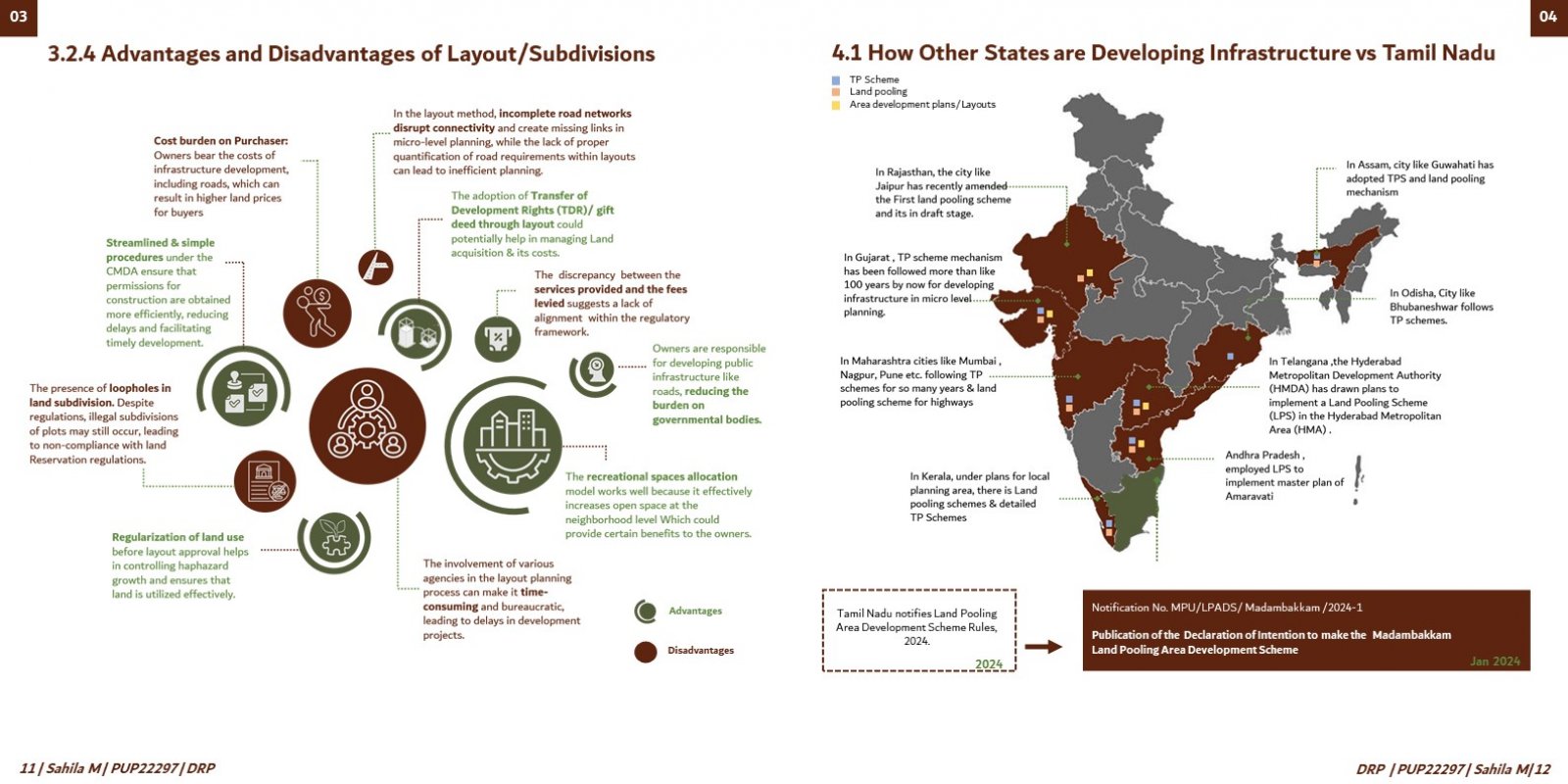
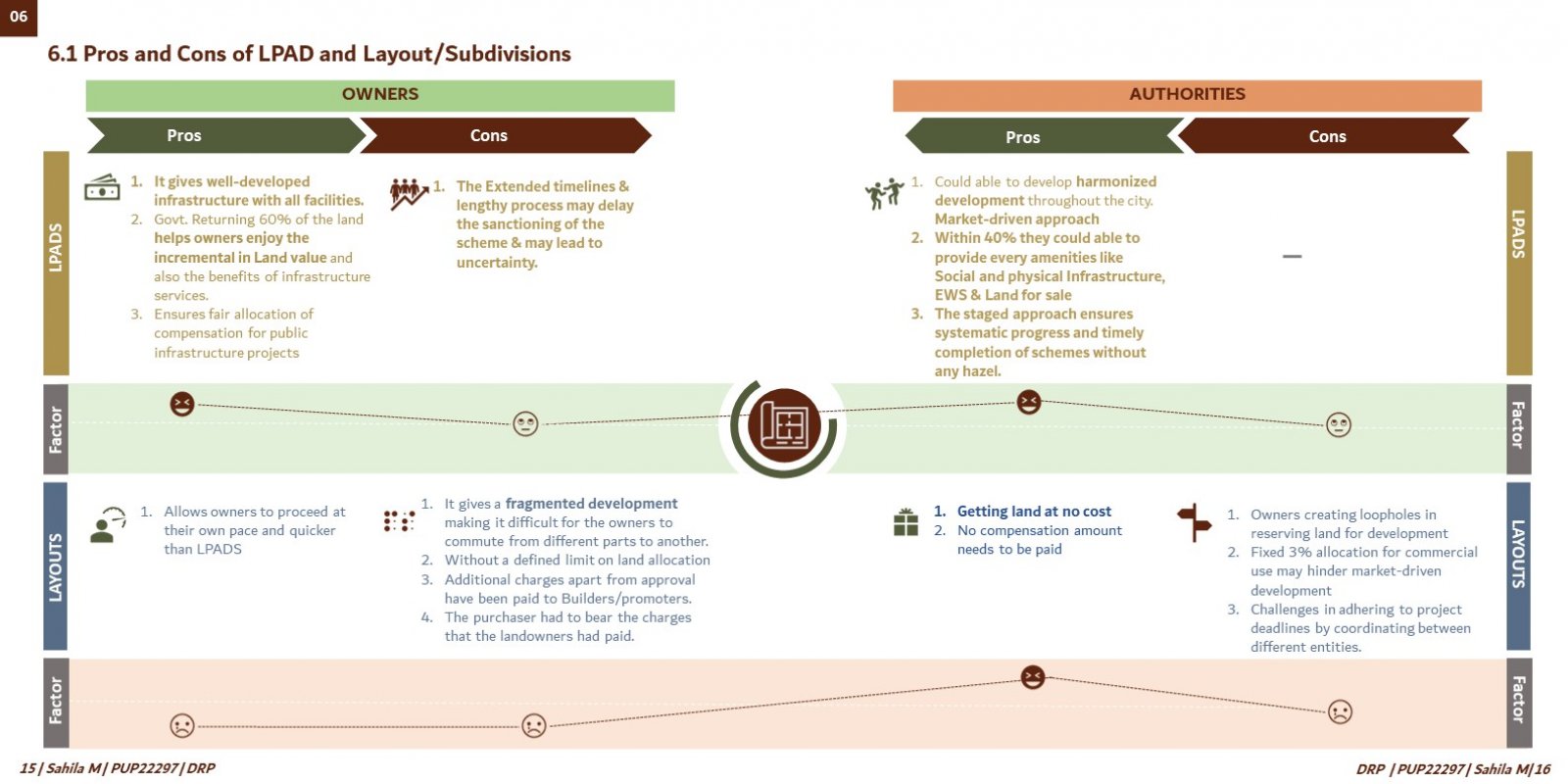
This comprehensive research critically assesses urban planning strategies in Chennai, particularly focusing on land development models for infrastructure development & comparison with mechanisms such as the Land Pooling Area Development Scheme (LPADS). The project aims to address the complex challenges associated with urban growth, land acquisition, and sustainable development in Chennai, Tamil Nadu. By examining the nuances of obtaining land for infrastructure development and analyzing the implementation processes of traditional methods, the research seeks to shed light on the impact of different approaches on urban environments and community well-being. The study is motivated by the urgent need to tackle obstacles in urban infrastructure development and explore innovative strategies for efficient land allocation and utilization in Chennai. The project is structured to undertake a thorough examination of the intricacies involved in urban planning, with a specific focus on the city's development landscape. It begins by conducting a detailed literature review to gain insights into past and current urban development models, including the evaluation of the first and second master plans created by the Chennai Metropolitan Development Authority (CMDA). Through this review, the project aims to understand the historical context and evolution of urban planning strategies in Chennai, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Subsequently, the research methodology encompasses primary and secondary data collection methods to gather comprehensive insights into the effectiveness of different land development models, especially LPADS, in addressing Chennai's urban challenges. Primary data collection involves conducting field visits, consultations, semi-structured interviews, and focus group discussions with relevant stakeholders, including government officials, builders, promoters, architects, licensed surveyors, and community representatives. These interactions aim to capture firsthand perspectives on infrastructure planning and development, funding mechanisms, and challenges faced in land acquisition and implementation processes. Moreover, secondary data sources such as census data, government documents, acts, amendments, and reports are extensively reviewed to complement the primary data and provide a holistic understanding of Chennai's urban planning landscape. This multi-faceted approach ensures the triangulation of data from various sources, enhancing the reliability and validity of the research findings. The project also incorporates an in-depth analysis of the Land Pooling Area Development (LPAD) scheme and its implications on urban development in Chennai. By comparing LPADS with traditional layout methods, the research aims to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with each approach. Through this comparative analysis, the project seeks to offer empirical evidence and practical insights into the effectiveness of different land development models in urban planning, thereby contributing to the body of knowledge in the field. Furthermore, the research explores specific funding models used by the Tamil Nadu government for infrastructure projects and evaluates their impact on urban development. It examines the balance between different funding sources, compensation structures, and financial mechanisms to ensure sustainable infrastructure development in Chennai. The findings of this research are expected to have significant implications for policymakers, urban planners, developers, and other stakeholders involved in urban development decision-making processes in Chennai. By providing empirical evidence, practical insights, and recommendations, the project aims to inform and guide future urban development strategies, fostering equitable growth, efficient land management, and sustainable urban environments in Chennai.