Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
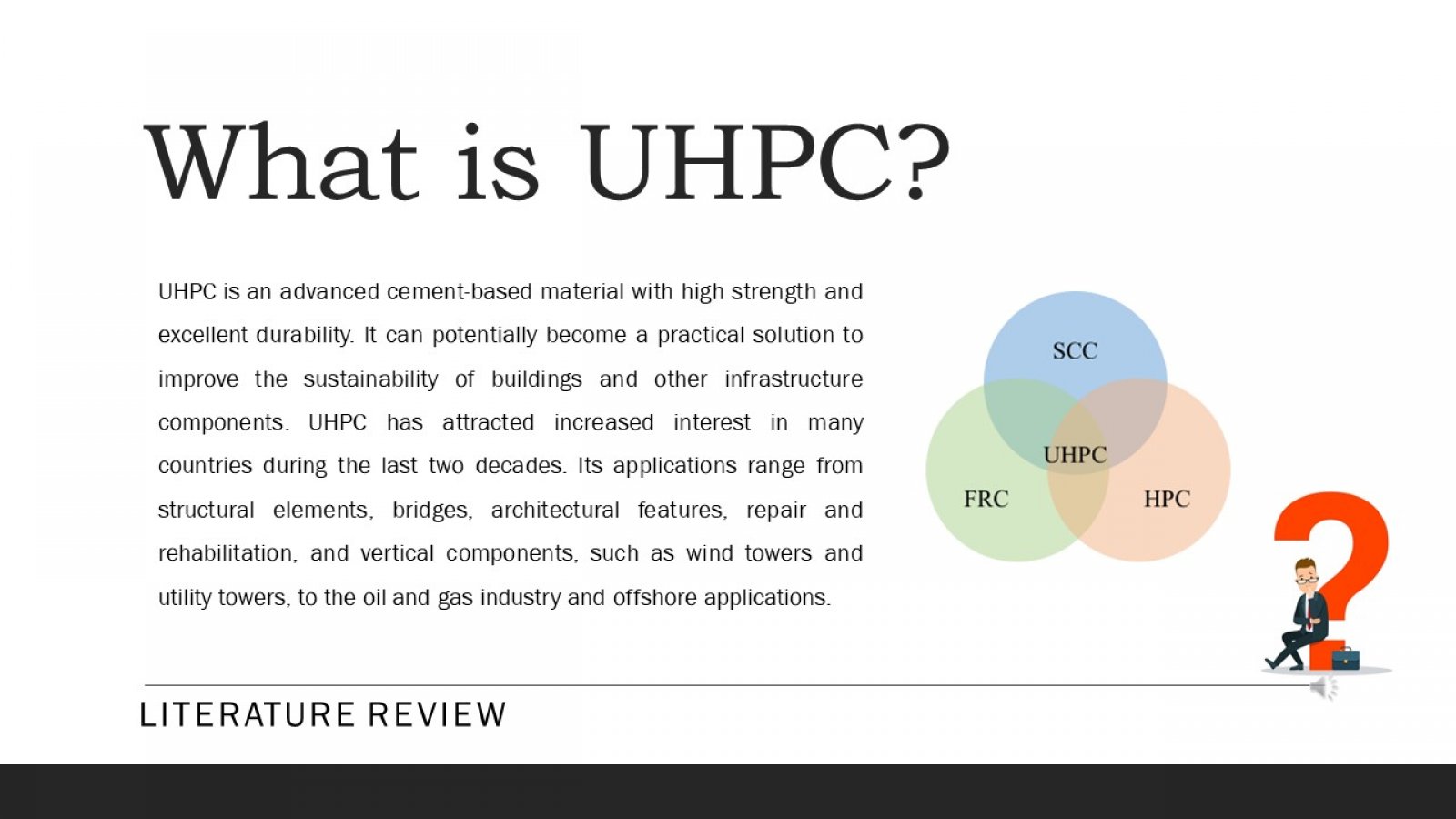
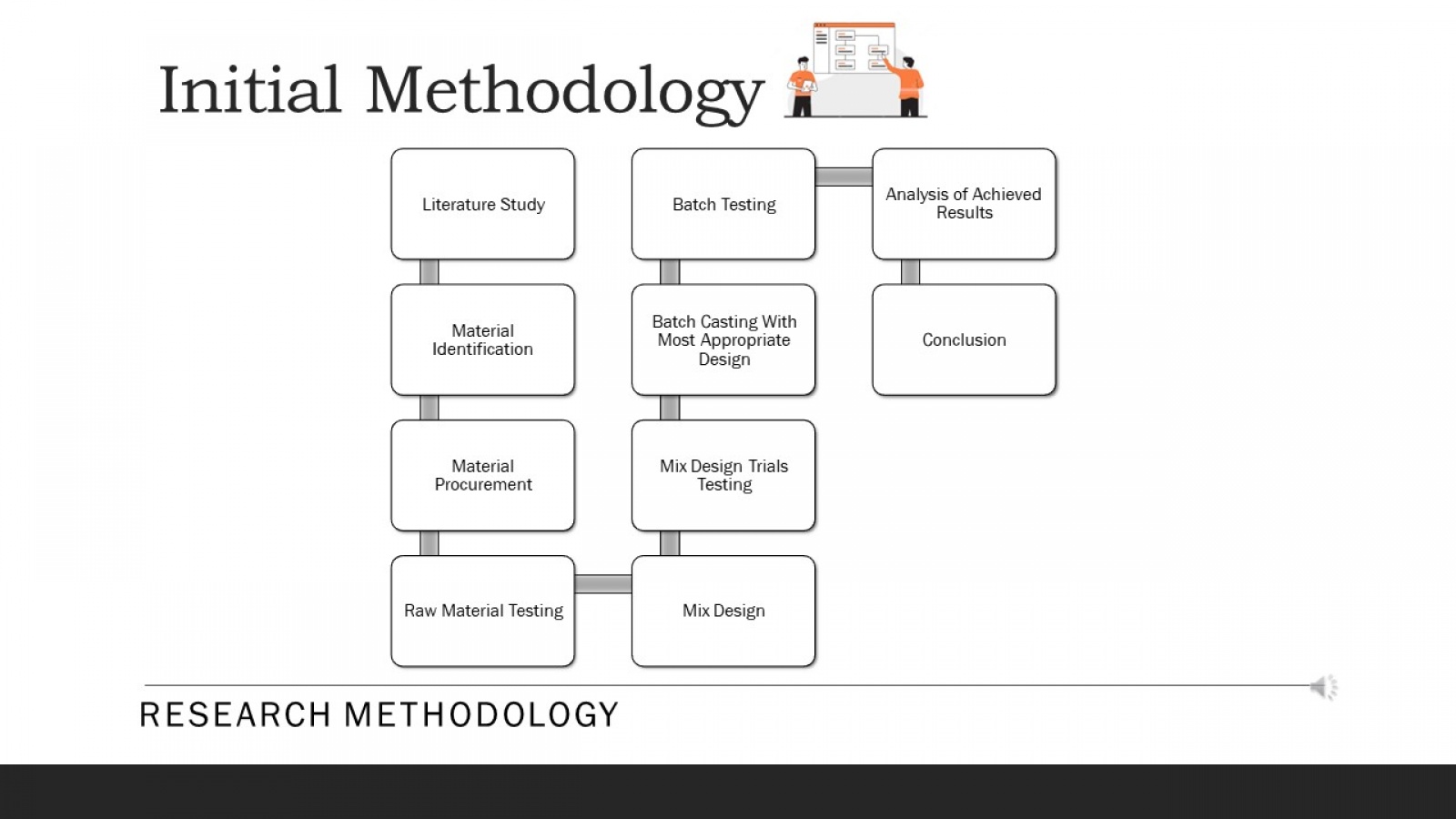
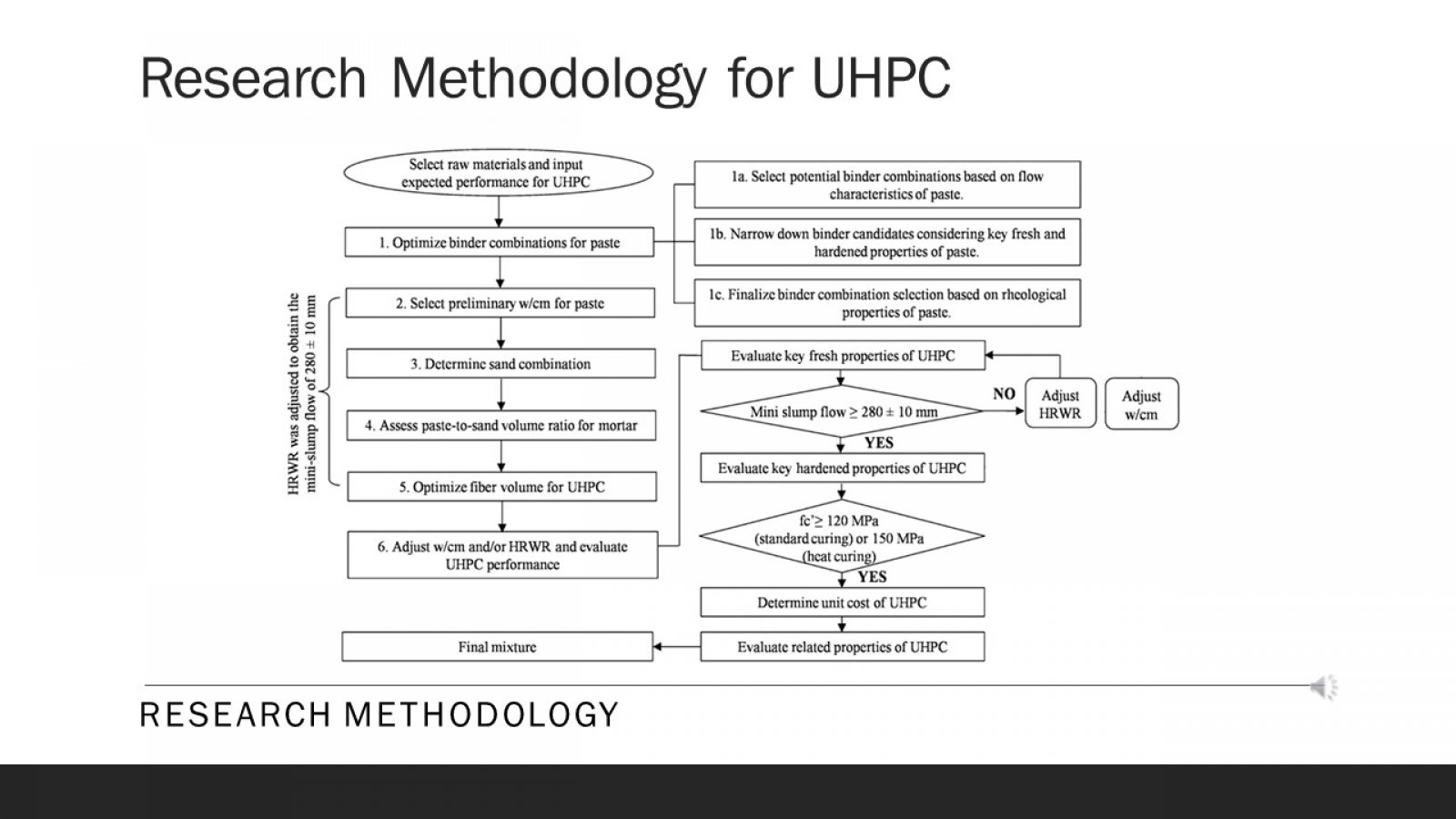
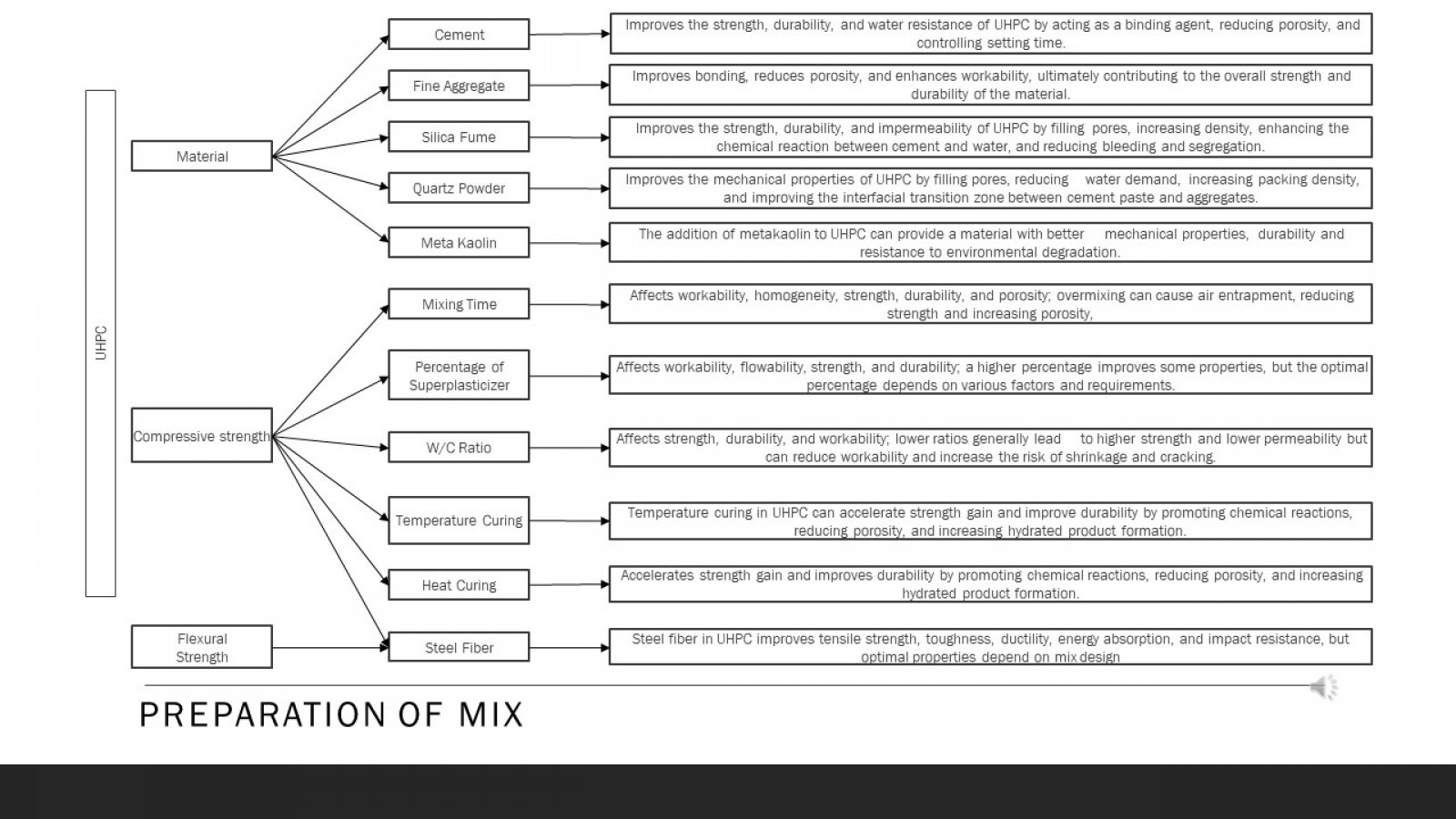
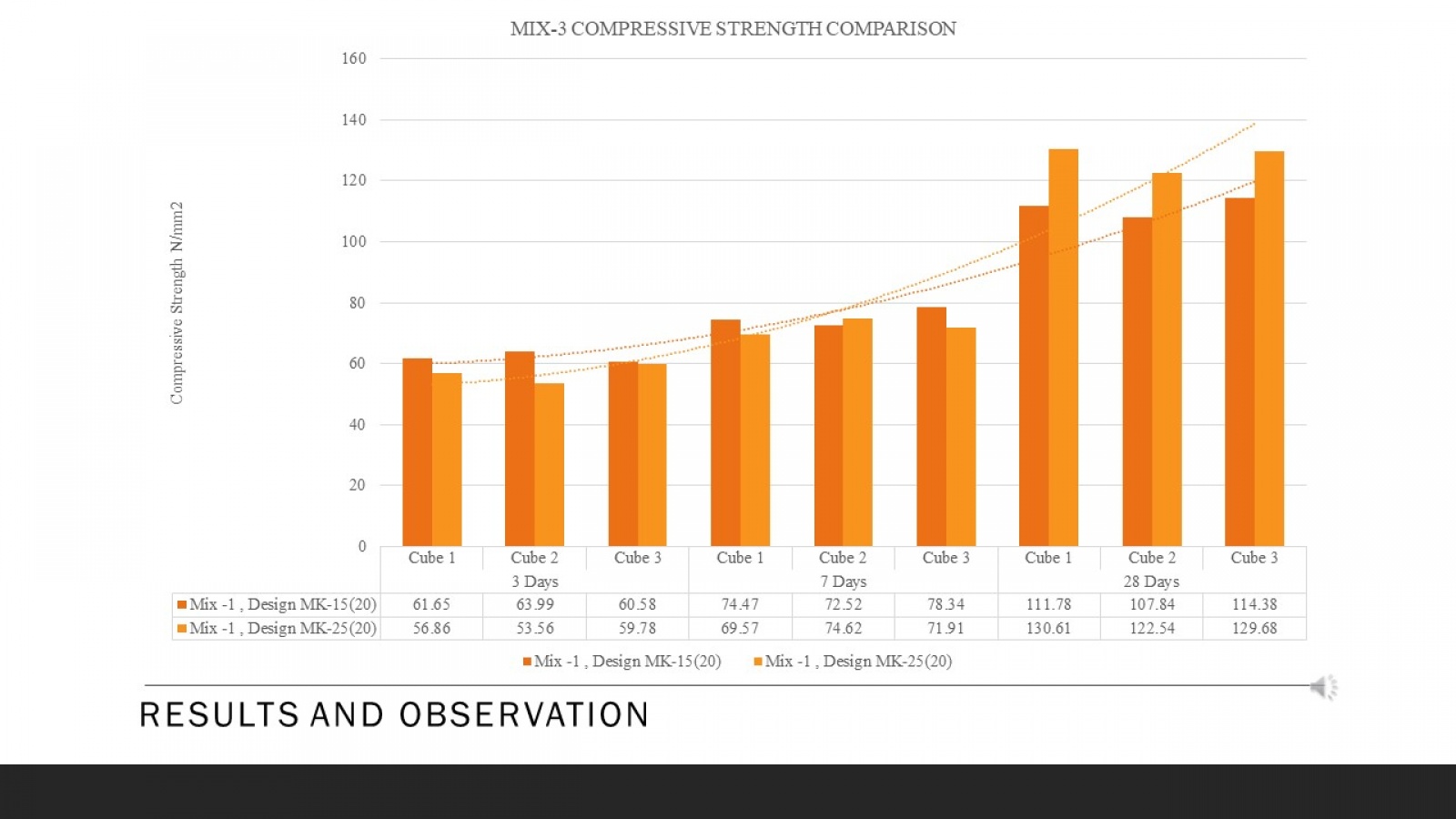
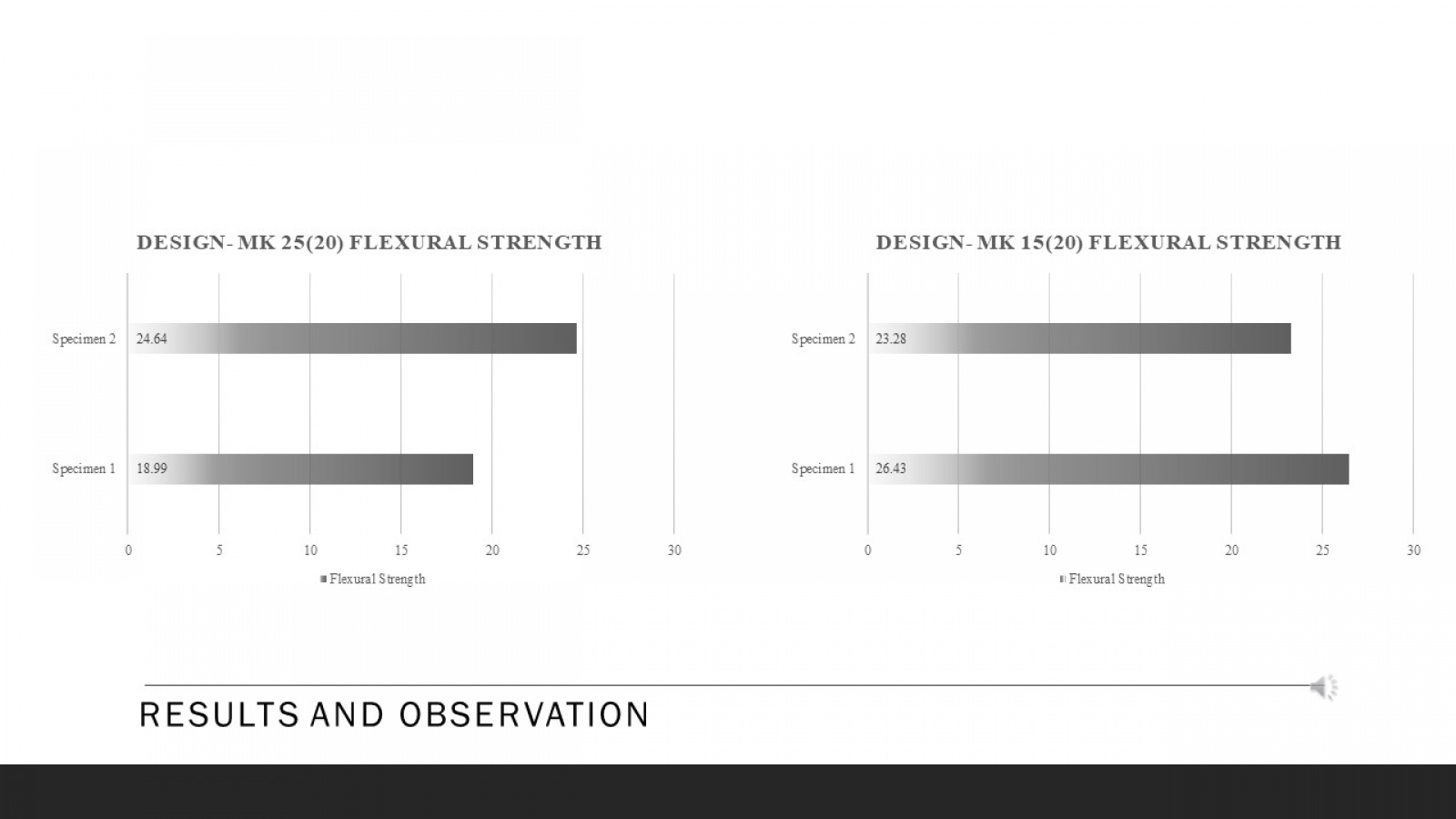
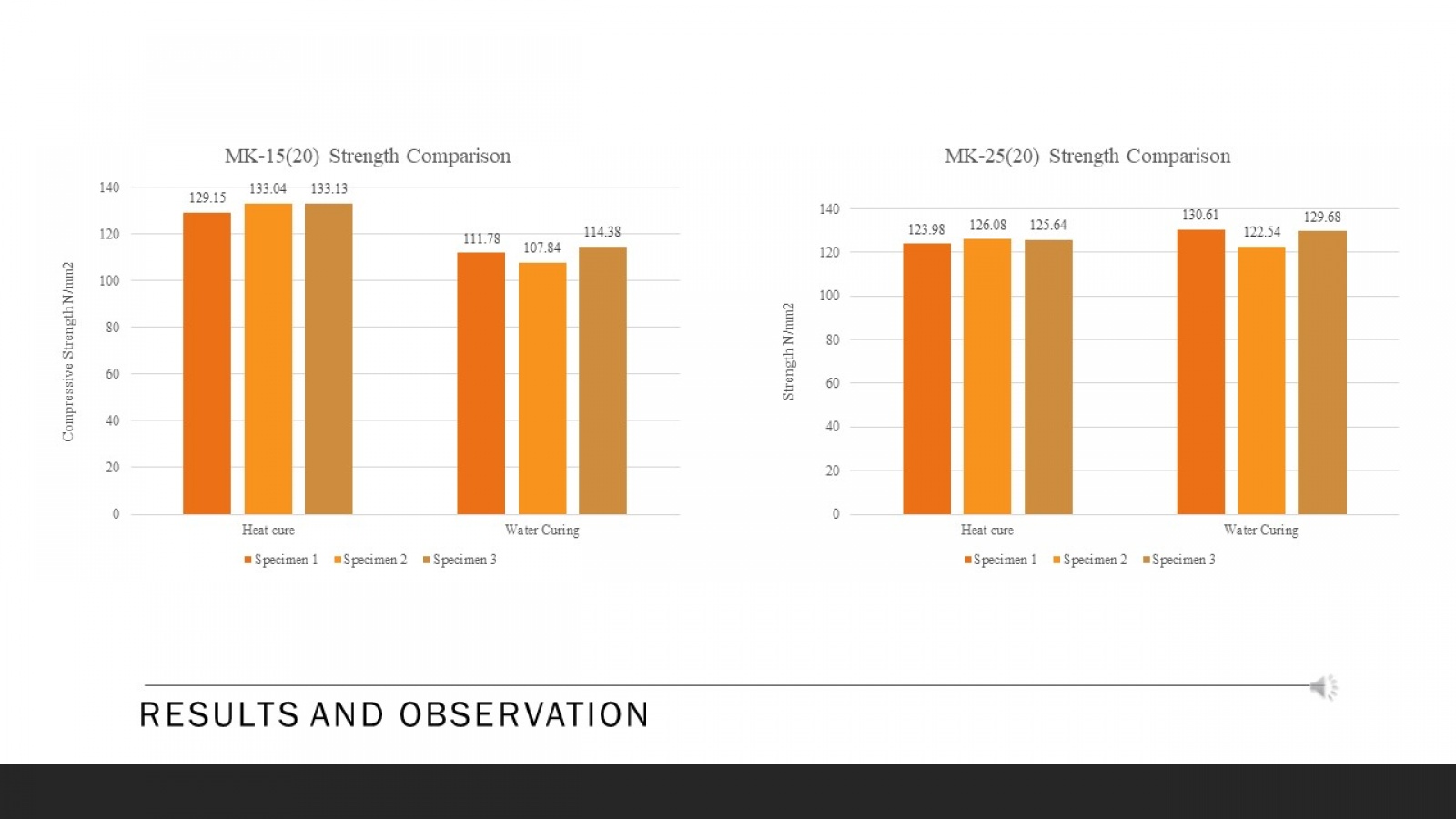
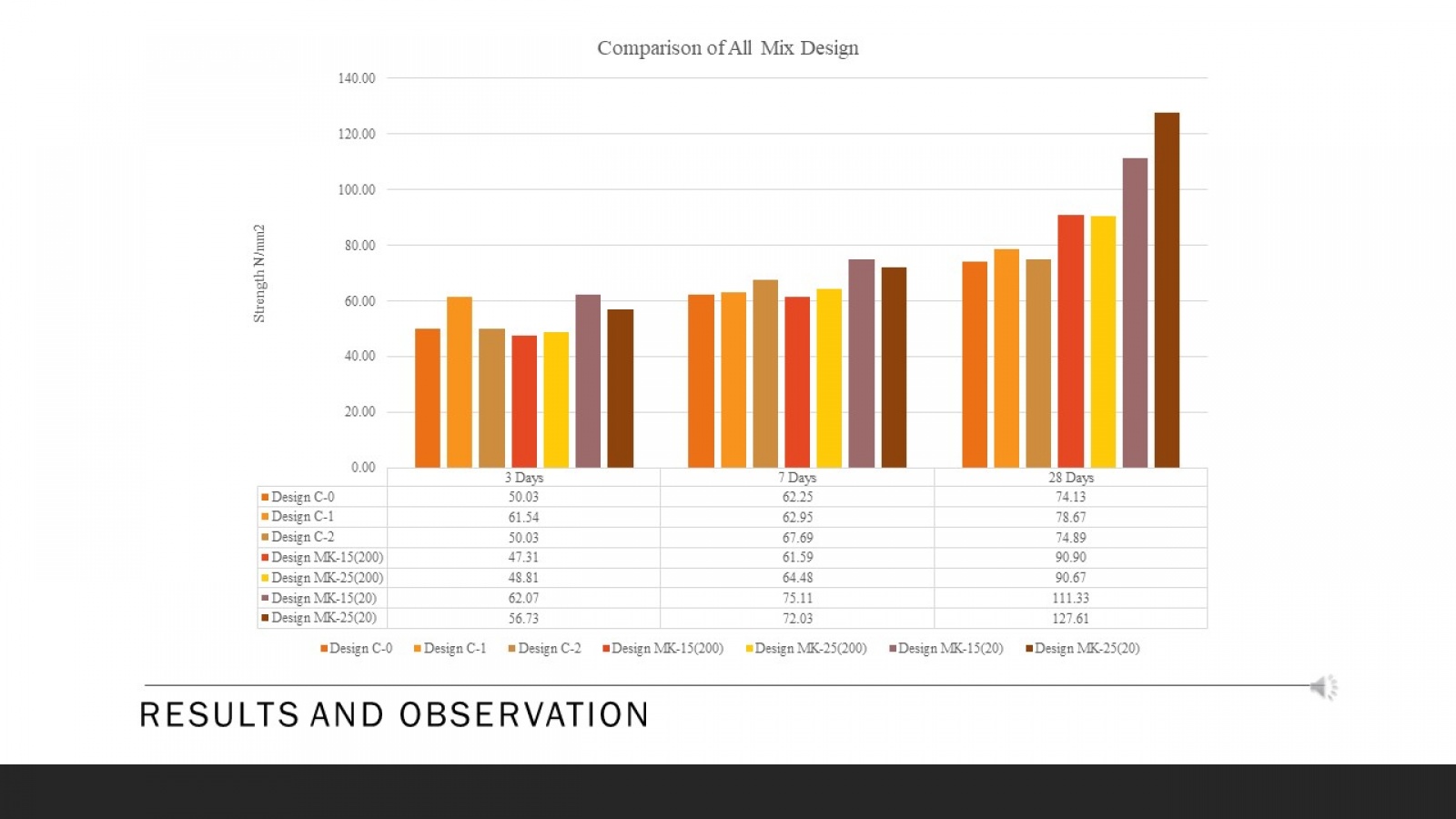
Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) is a material that has received increasing attention in civil engineering due to its exceptional mechanical properties. The paper begins by discussing the fundamental properties and characteristics of UHPC, including its high compressive and flexural strength. This study evaluates the compressive strength parameters of UHPC made with different materials and other curing methods. Moreover, the core aim is to achieve a compressive strength of 110 MPa or more. The paper then examines the essential components of UHPC mix design, such as cementitious materials, silica fume, superplasticizers, fibers, and their optimal proportions to achieve the desired properties. To achieve this goal, a series of tests were conducted using different materials such as silica fume and sand, meta kaolin, quartz powder and cement, and curing methods such as heat and water to determine the optimal combination to achieve high compressive and flexural strength. The test results showed that using specific materials and curing methods stated above, it can be concluded that the compressive and flexural strength will significantly improve UHPC. The paper discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each casting technique and provides practical recommendations for their application. Using steel fibers and a clear hardening way gave the highest compressive strength of 110 MPa. Apart from that, UHPC can be a very effective material for various civil engineering applications due to its exceptional mechanical properties, high strength and resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. The result shows that different types and proportions affect the strength parameter. This research contributes to ongoing efforts to develop durable and sustainable building materials for the future.
View Additional Work