Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
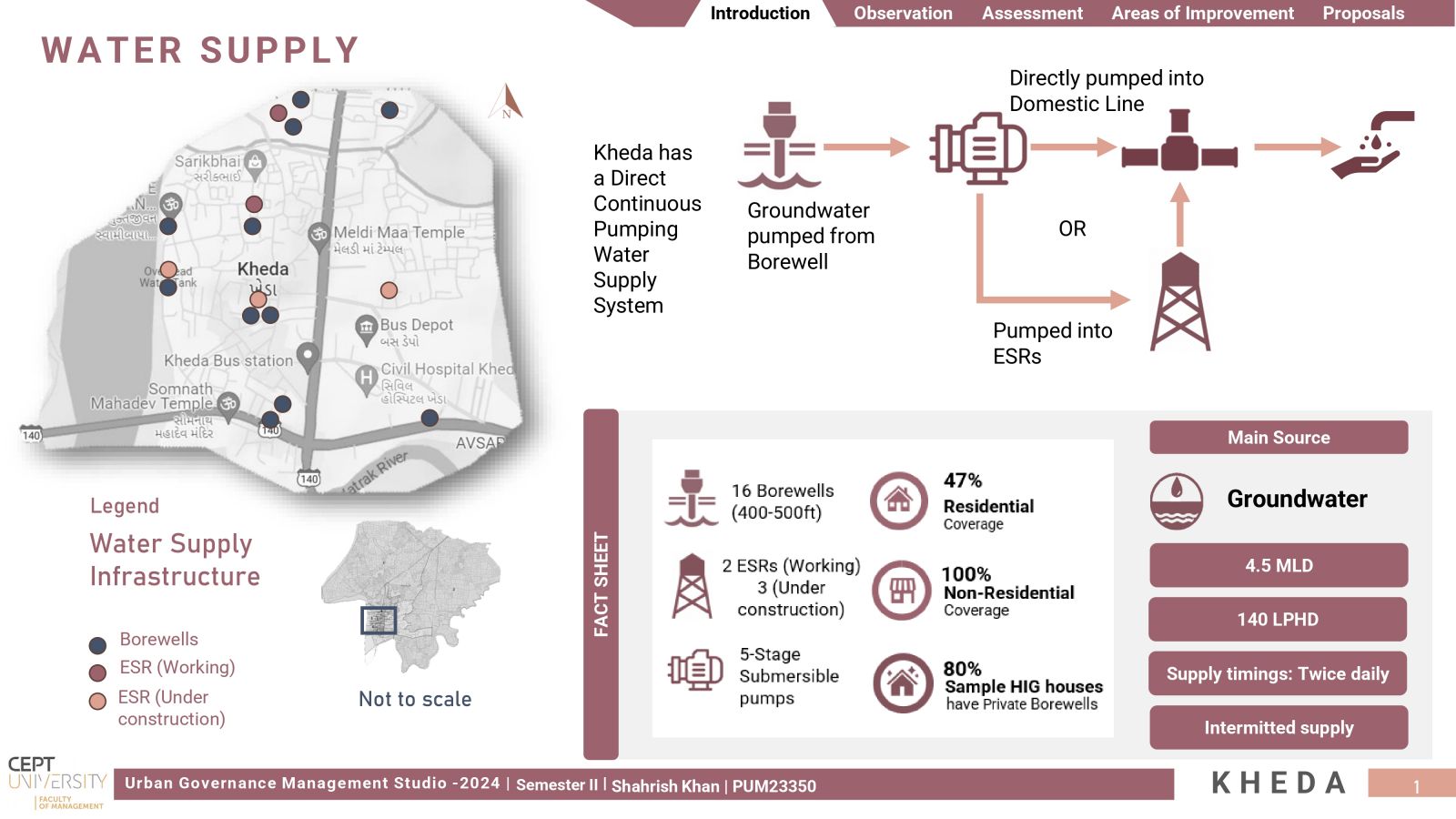
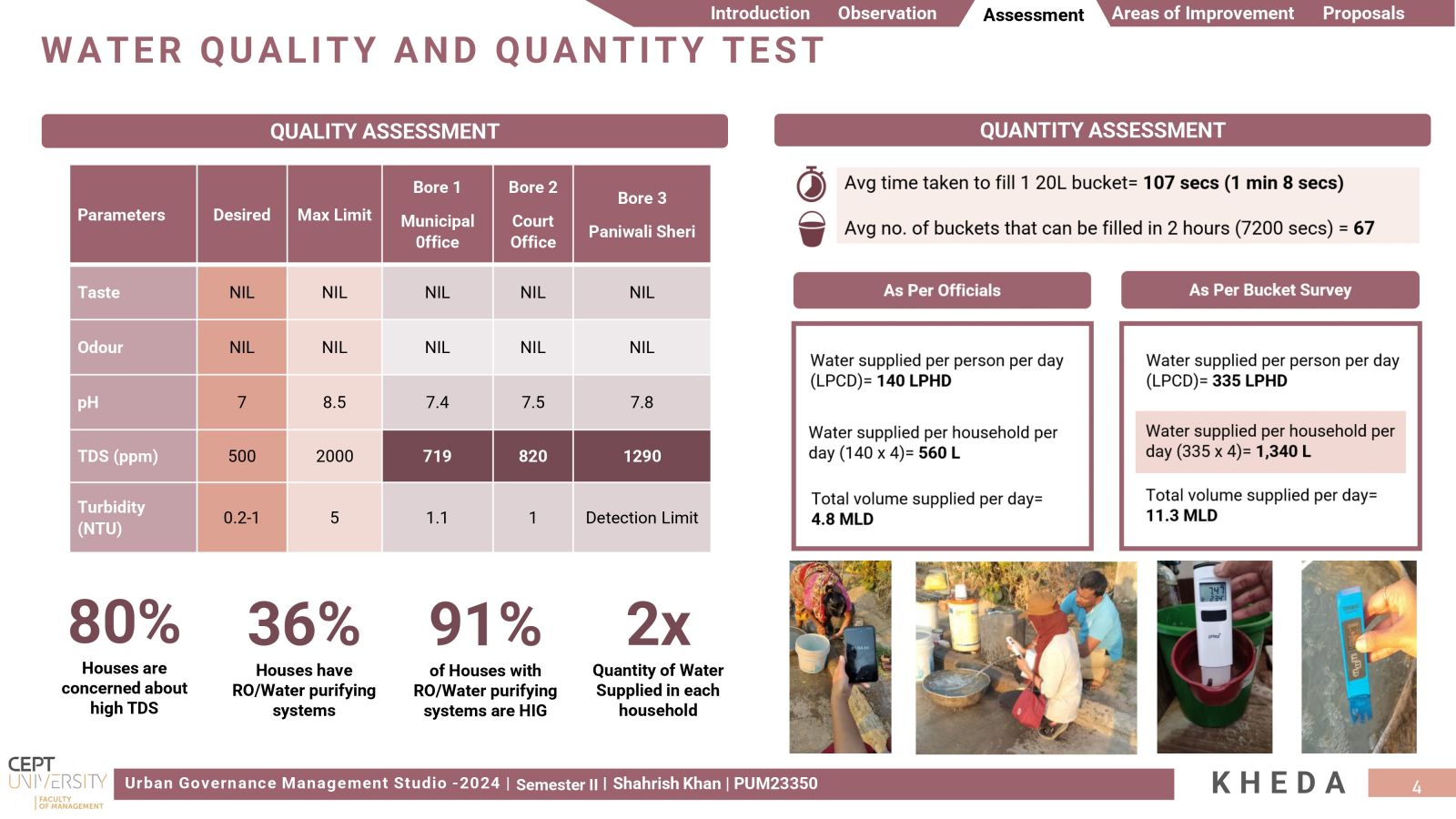
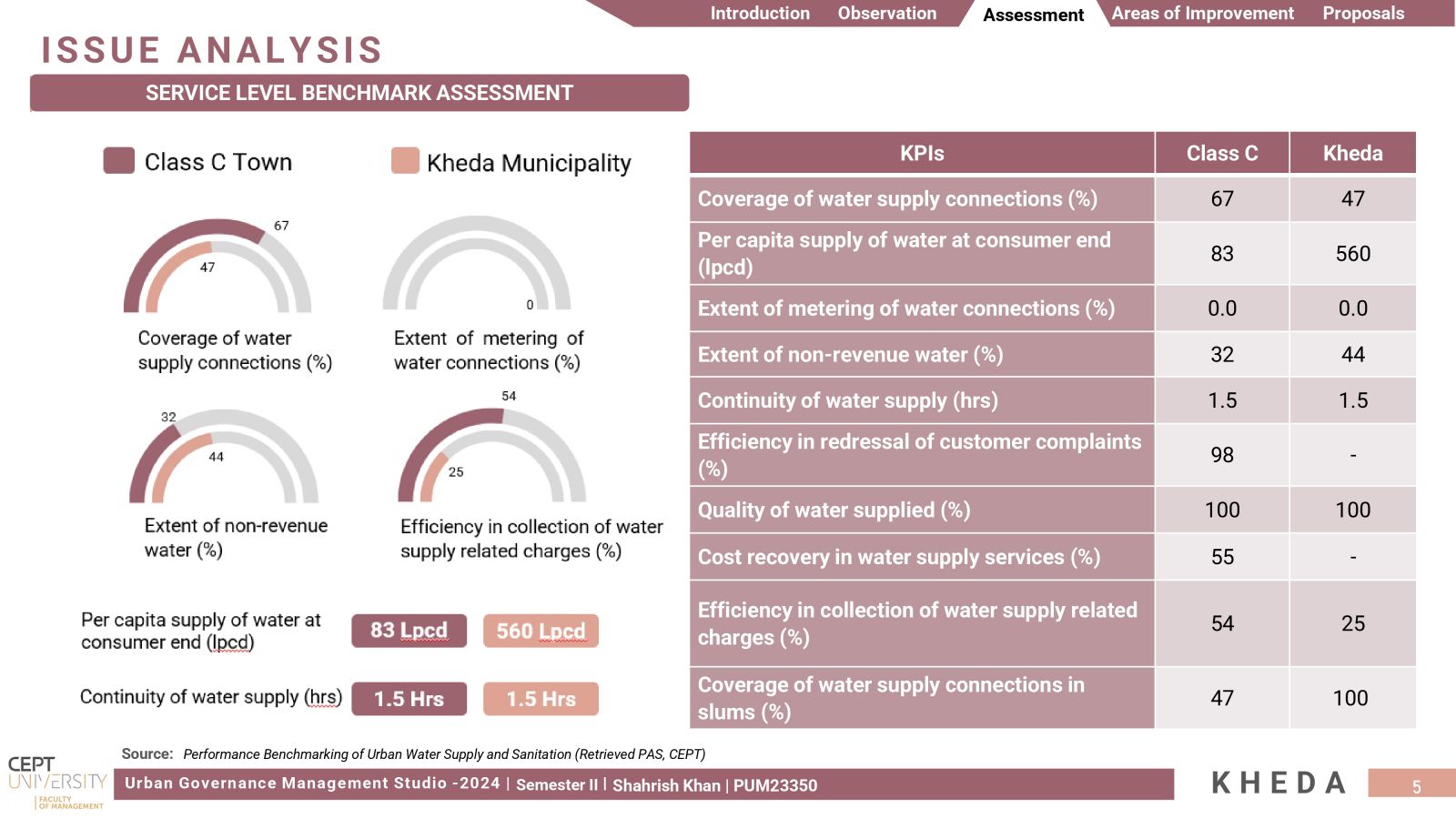
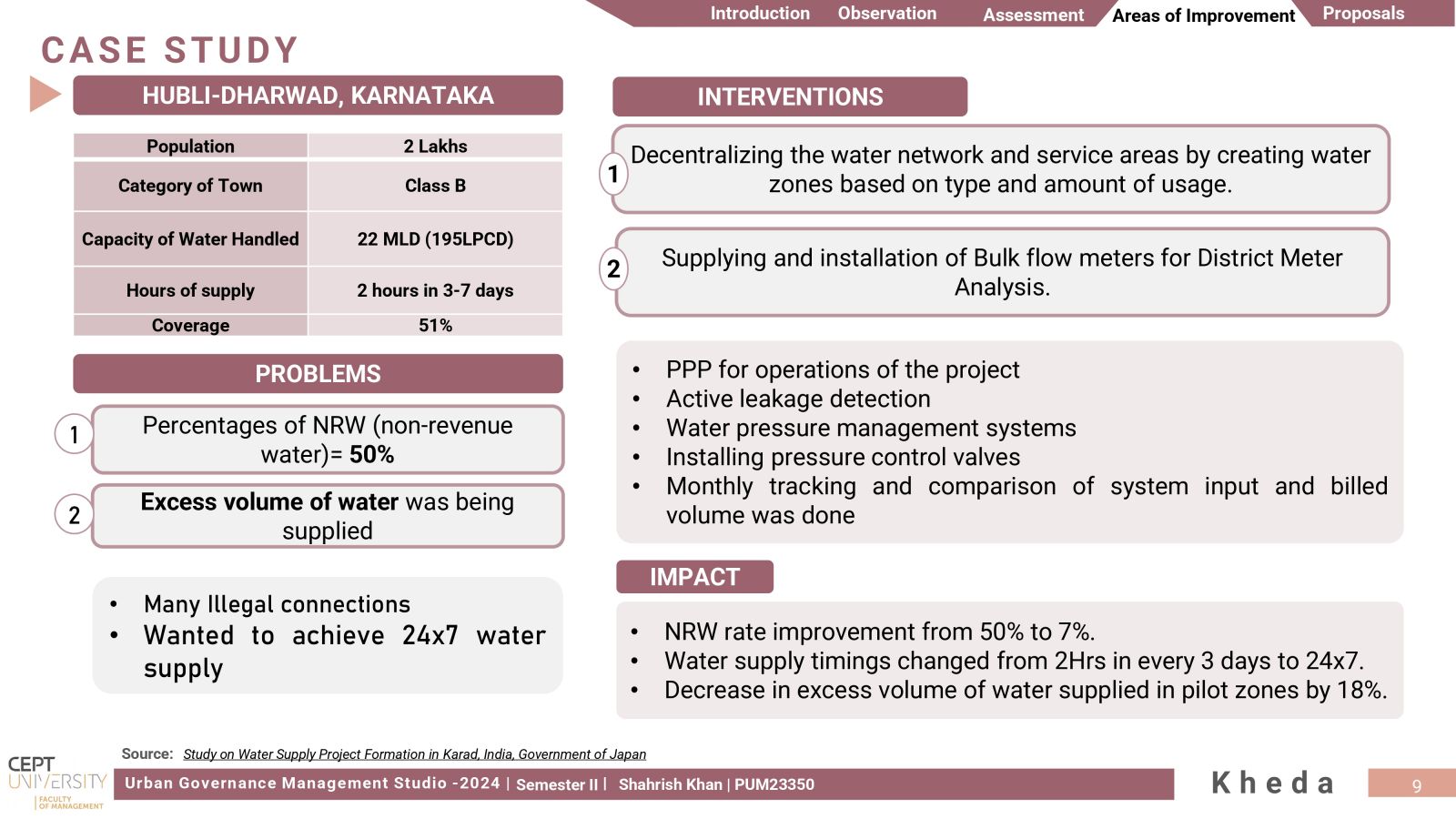
The aim was to investigate Kheda's management of its water resources within a water-stressed region, focusing on evaluating Water Security. It was unexpected to find that despite its small size as a 'Class C' city, Kheda encountered notable issues related to excessive water wastage. Addressing substantial levels of Non-Revenue Water and infrastructure leakages, proposals were made for water metering and implementing active leakage control measures, offering Kheda the opportunity to optimize its water supply.