Your browser is out-of-date!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
For a richer surfing experience on our website, please update your browser. Update my browser now!
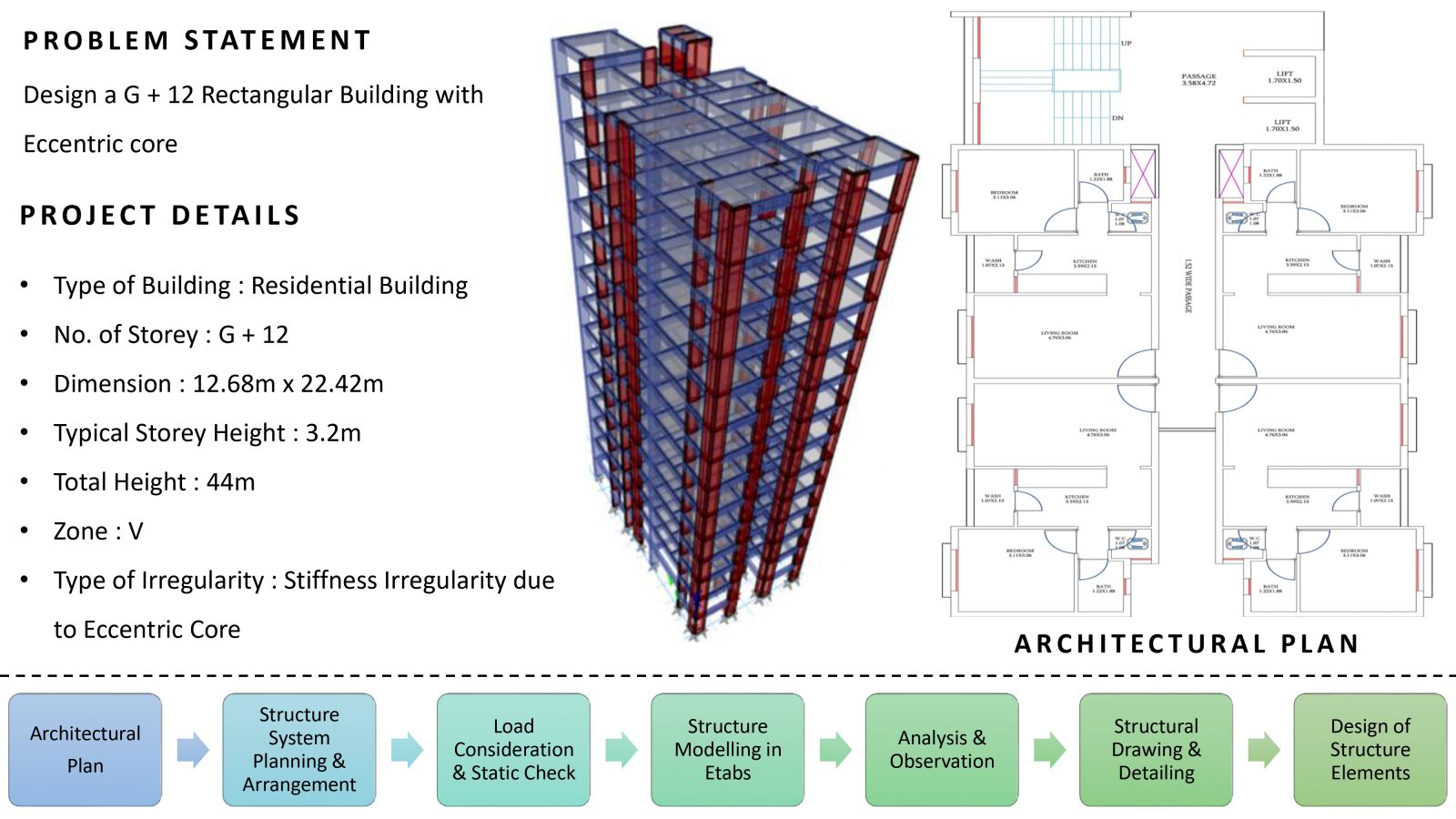
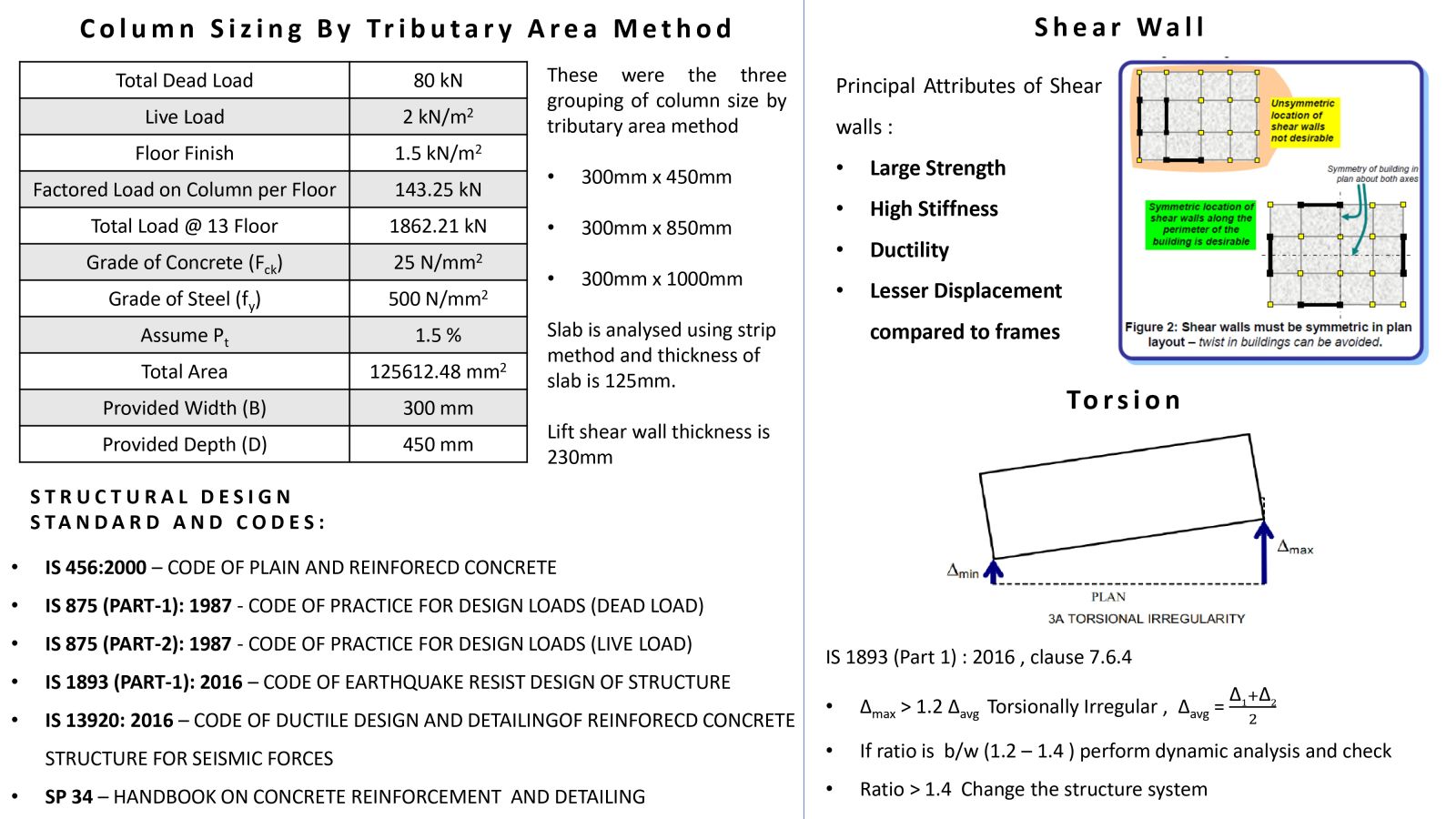
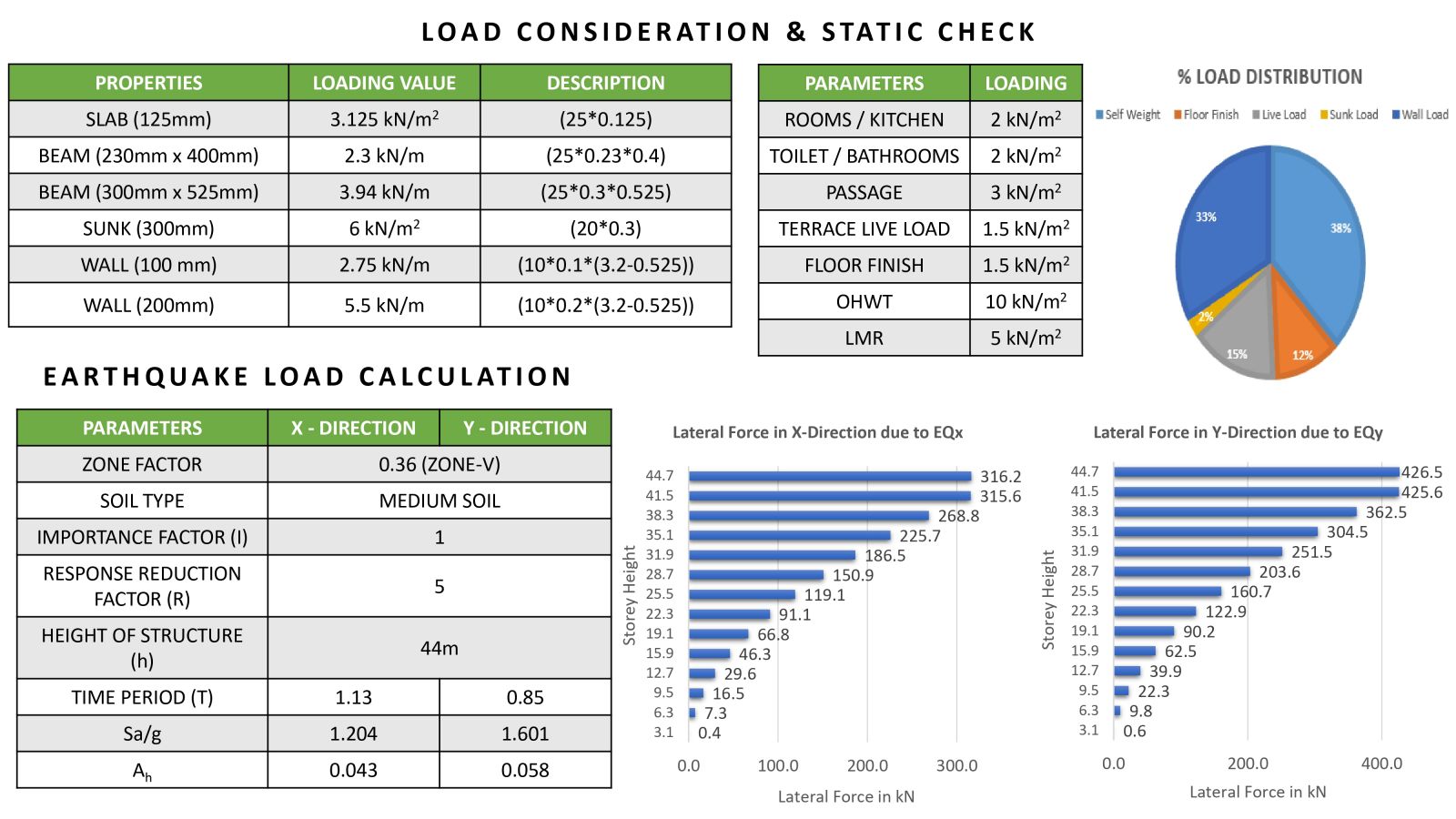
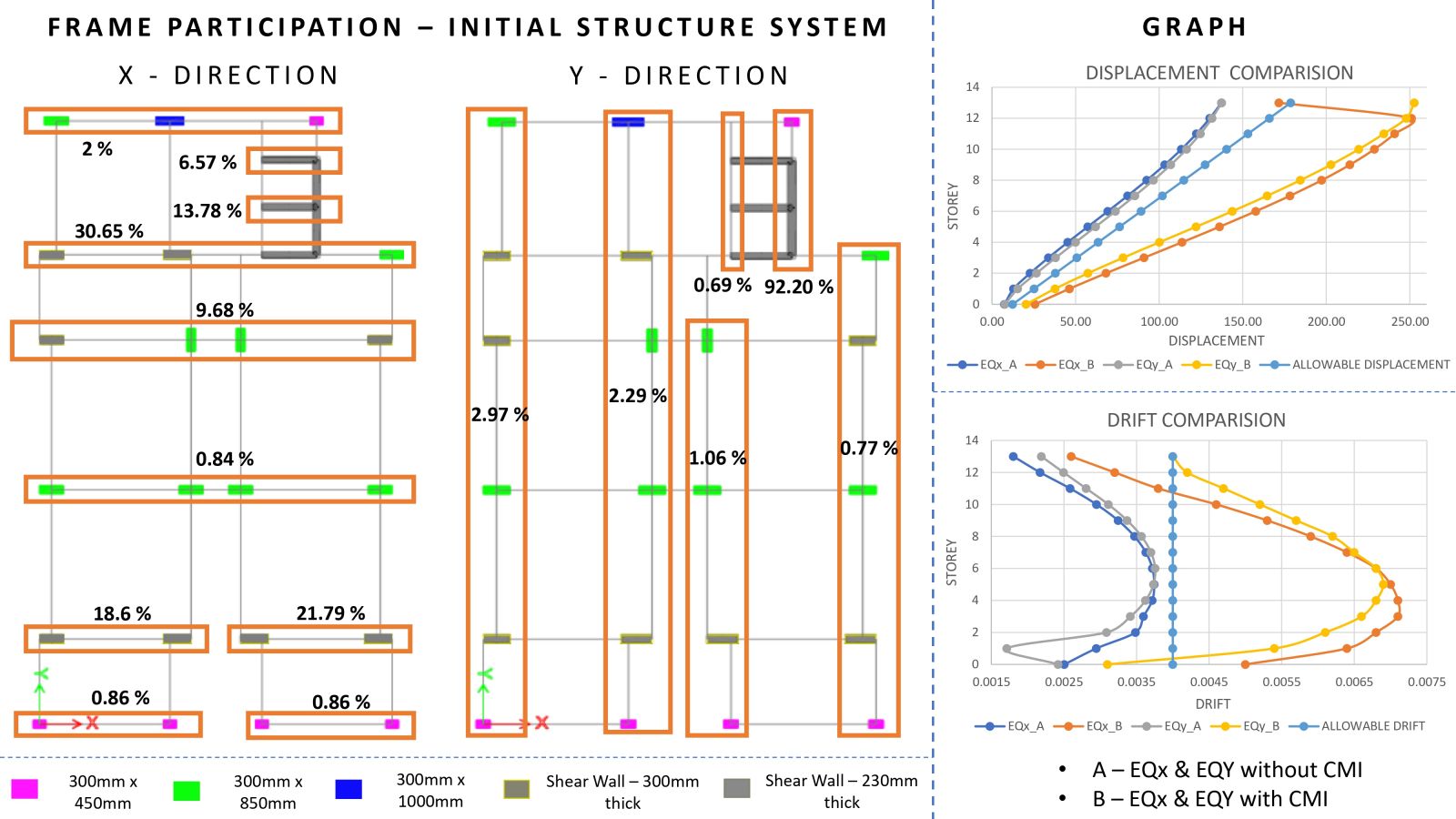
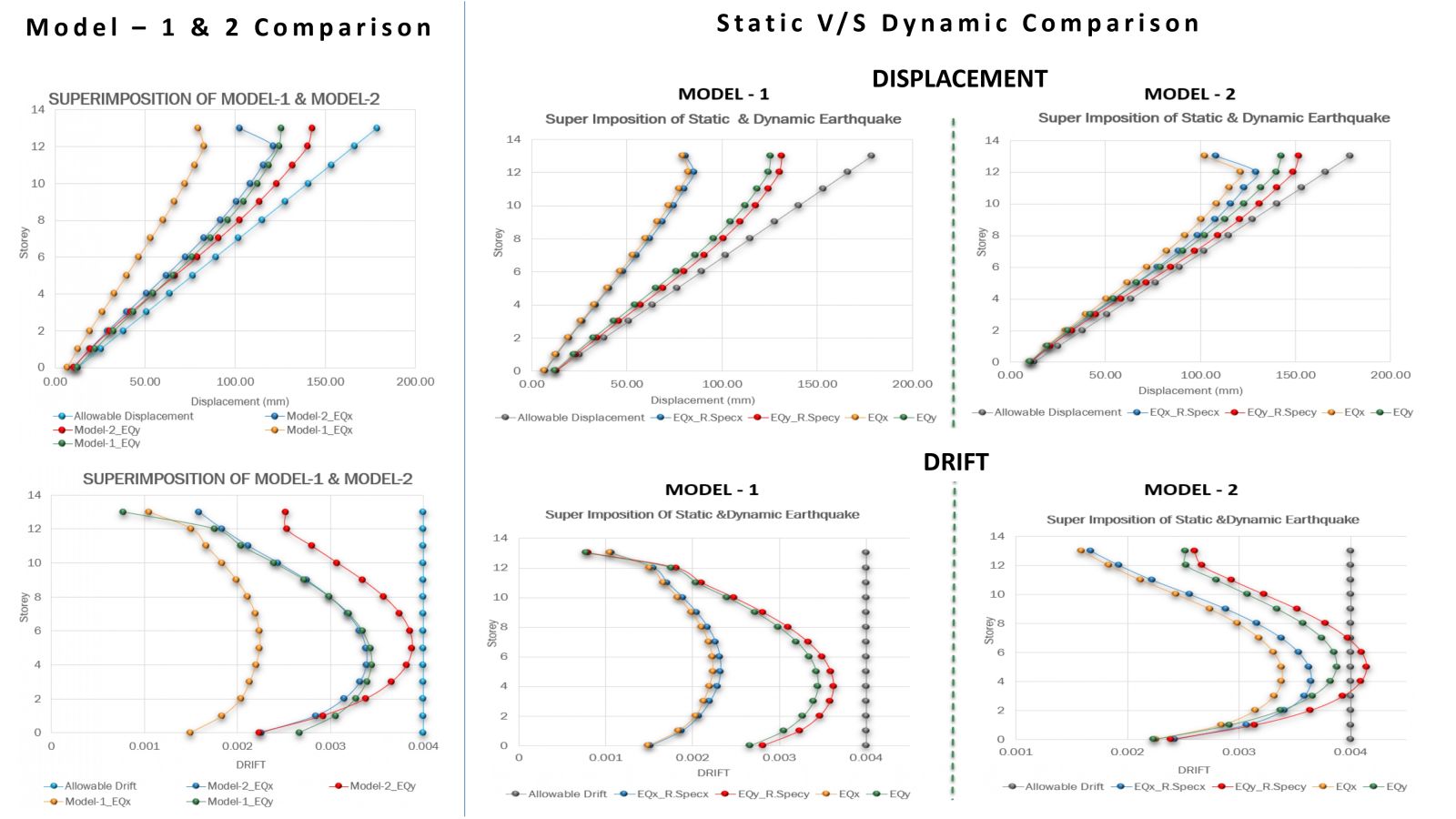
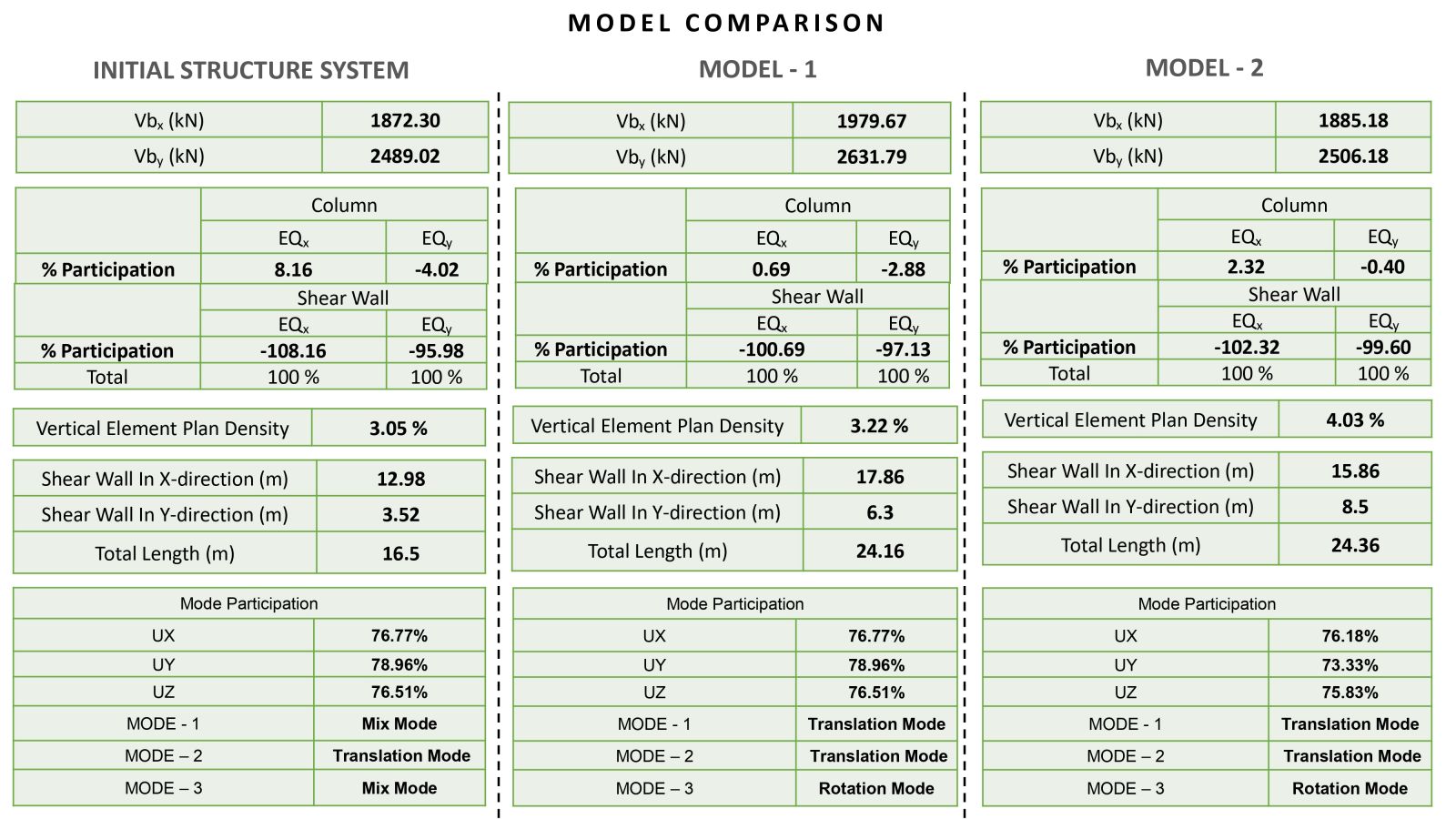
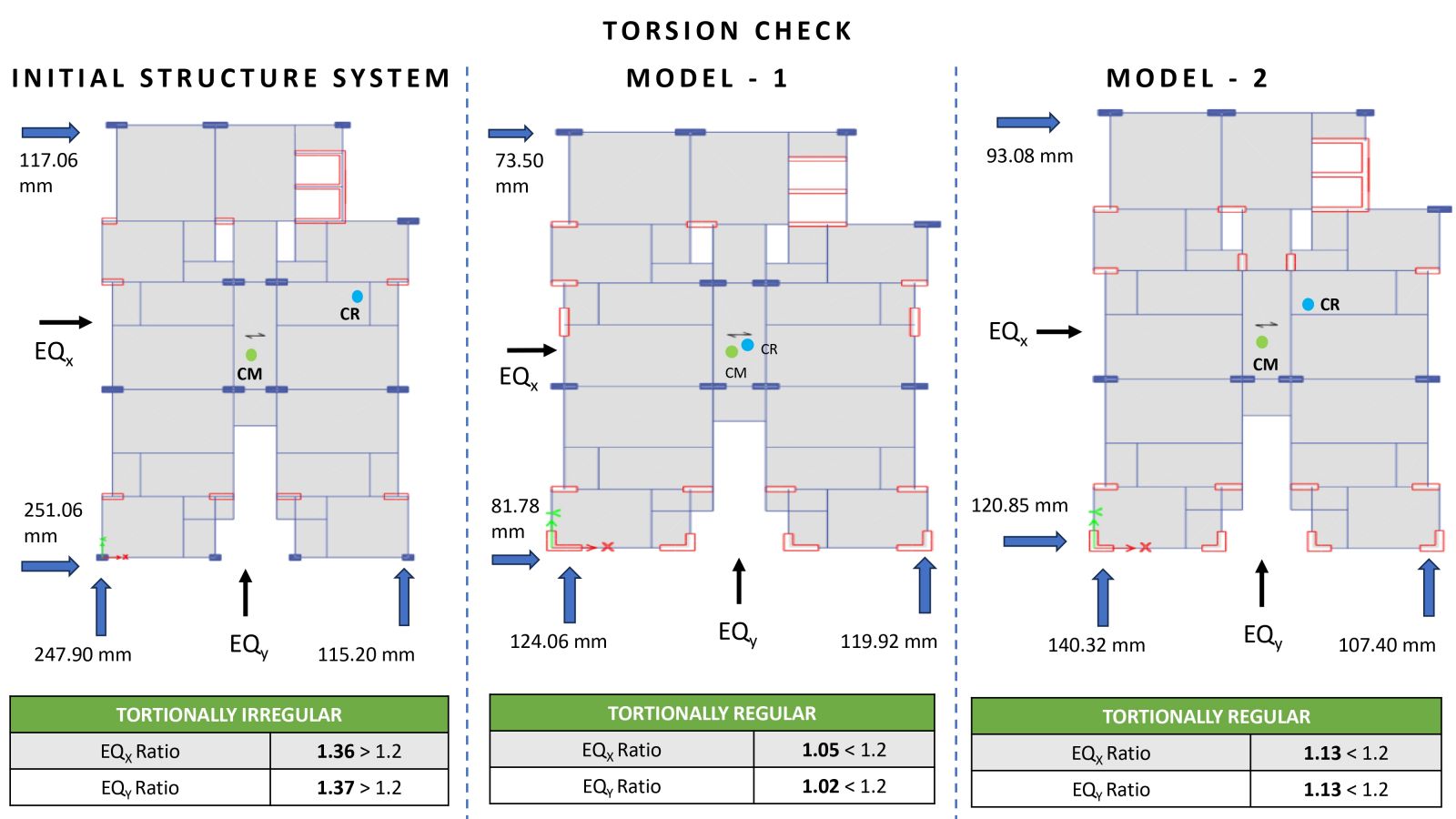
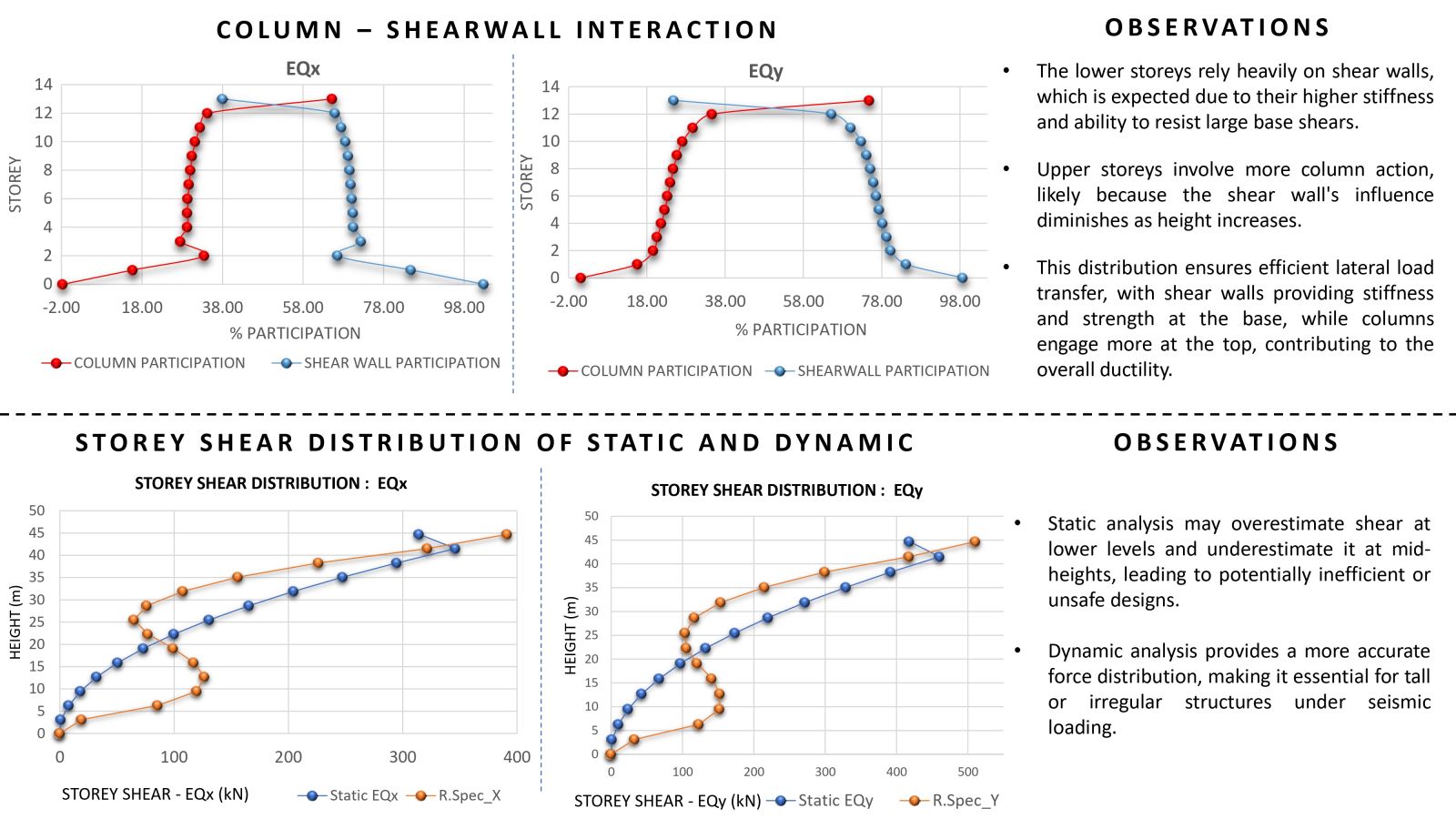
The main objective of this project is to study and understand the structural behavior of buildings exhibiting torsional irregularity, in accordance with IS 1893:2016 Table 5 and Clause 7.6.4. Torsional irregularity can arise due to irregularities in mass, stiffness, or plan configuration. This project specifically focuses on stiffness-induced torsional irregularity. A key challenge addressed is the control of torsion caused by an eccentrically placed lift core, which results in an offset between the center of mass and the center of stiffness, thereby generating torsional effects. To mitigate this, the project explores the efficient and optimized placement of shear walls. Two configurations were studied: one incorporating C-shaped shear walls and another with only horizontal shear walls at the lift core, where vertical walls are designed as RCC infill walls. In both models, torsion was effectively controlled and satisfied the code requirements. A comparative analysis of both models was carried out, and ductile detailing was performed as per IS 13920:2016.
View Additional Work